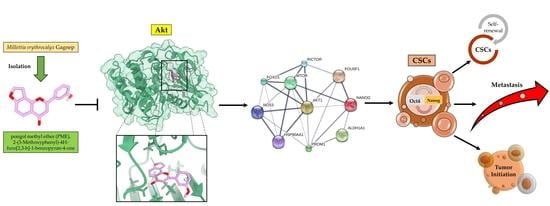
Pongol Methyl Ether Inhibits Akt and Suppresses Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes in Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cytotoxicity and Anti-Proliferative Effect of PME on H460 Lung Cancer Cells
2.2. PME Attenuates CSC Phenotypes during Anchorage-Independent Growth and Spheroid Formation
2.3. PME Reduces CSC Markers and Pluripotent Transcription Factors through the Reduction of the Akt Signalling Pathway
2.4. Molecular Docking Simulations Indicated the PME Interaction with the Akt-1 Protein
2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis of the CSC Marker Proteins in PME Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of Pongol Methyl Ether
4.2. Cell Lines and Cultures
4.3. Reagents and Antibodies
4.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Nuclear Staining Assay
4.6. Colony Formation Assay
4.7. Anchorage-Independent Growth Assay
4.8. Spheroid Formation Assay
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Immunofluorescence Assay
4.11. Protein and Ligands Preparation
4.12. Molecular Docking
4.13. Bioinformatics Analysis; PPI Networks Integration and KEGG Pathway Maps Analyses
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, J.C. Cancer stem cells: Role in tumor growth, recurrence, metastasis, and treatment resistance. Medicine 2016, 95, S20–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Yu, X.; Liu, S. Pluripotency transcription factors and cancer stem cells: Small genes make a big difference. Chin. J. Cancer 2013, 32, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanvorachote, P.; Luanpitpong, S. Iron induces cancer stem cells and aggressive phenotypes in human lung cancer cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 310, C728–C739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanvorachote, P.; Chamni, S.; Ninsontia, C.; Phiboonchaiyanan, P.P. Potential Anti-metastasis Natural Compounds for Lung Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 5707–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roudi, R.; Korourian, A.; Shariftabrizi, A.; Madjd, Z. Differential expression of cancer stem cell markers ALDH1 and CD133 in various lung cancer subtypes. Cancer Investig. 2015, 33, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiuthed, A.; Chantarawong, W.; Chanvorachote, P. Lung Cancer Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cell-targeting Natural Compounds. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3797–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Zhu, H.; Feng, J.; Ni, S.; Huang, J. High CD133 expression in the nucleus and cytoplasm predicts poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 986095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wan, L.; Geng, J.; Wu, C.L.; Bai, X. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 possesses stem-like properties and predicts lung cancer patient outcome. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiou, S.-H.; Wang, M.-L.; Chou, Y.-T.; Chen, C.-J.; Hong, C.-F.; Hsieh, W.-J.; Chang, H.-T.; Chen, Y.-S.; Lin, T.-W.; Hsu, H.-S. Coexpression of Oct4 and Nanog enhances malignancy in lung adenocarcinoma by inducing cancer stem cell–like properties and epithelial–mesenchymal transdifferentiation. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 10433–10444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortes-Dericks, L.; Galetta, D.; Spaggiari, L.; Schmid, R.A.; Karoubi, G. High expression of octamer-binding transcription factor 4A, prominin-1 and aldehyde dehydrogenase strongly indicates involvement in the initiation of lung adenocarcinoma resulting in shorter disease-free intervals. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2012, 41, e173–e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivas, S.; Gomez-Oro, C.; Anton, I.M.; Wandosell, F. Role of Akt Isoforms Controlling Cancer Stem Cell Survival, Phenotype and Self-Renewal. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Massion, P.P.; Taflan, P.M.; Shyr, Y.; Rahman, S.M.; Yildiz, P.; Shakthour, B.; Edgerton, M.E.; Ninan, M.; Andersen, J.J.; Gonzalez, A.L. Early involvement of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in lung cancer progression. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.W.; Zhou, Y.W.; Li, W.X.; Kang, B.; Zhang, X.Q.; Yang, Y.; ChENG, J.; Yin, S.Y.; Tong, Y.; He, J.Q. Akt-mediated phosphorylation of Oct4 is associated with the proliferation of stem-like cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, C.; Lu, J.; Yi, B.C.; Chang, K.K.; Simon, M.C.; Ryeom, S.; Yoon, S.S. PI3K/Akt pathway and Nanog maintain cancer stem cells in sarcomas. Oncogenesis 2021, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritularak, B.; Likhitwitayawuid, K.; Conrad, J.; Vogler, B.; Reeb, S.; Klaiber, I.; Kraus, W. New Flavones from Millettia e rythrocalyx. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 589–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhitwitayawuid, K.; Sritularak, B.; Benchanak, K.; Lipipun, V.; Mathew, J.; Schinazi, R.F. Phenolics with antiviral activity from Millettia erythrocalyx and Artocarpus lakoocha. Nat. Prod. Res. 2005, 19, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, B.F.; Predes, D.; Cerqueira, D.M.; Reis, A.H.; Amado, N.G.; Cayres, M.C.; Kuster, R.M.; Oliveira, F.L.; Mendes, F.A.; Abreu, J.G. Derricin and derricidin inhibit Wnt/β-catenin signaling and suppress colon cancer cell growth in vitro. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vetrivel, P.; Kim, S.M.; Ha, S.E.; Kim, H.H.; Bhosale, P.B.; Senthil, K.; Kim, G.S. Compound Prunetin Induces Cell Death in Gastric Cancer Cell with Potent Anti-Proliferative Properties: In Vitro Assay, Molecular Docking, Dynamics, and ADMET Studies. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunholz, D.; Saki, M.; Niehr, F.; Ozturk, M.; Borras Puertolas, B.; Konschak, R.; Budach, V.; Tinhofer, I. Spheroid Culture of Head and Neck Cancer Cells Reveals an Important Role of EGFR Signalling in Anchorage Independent Survival. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cleves, A.E.; Jain, A.N. Knowledge-guided docking: Accurate prospective prediction of bound configurations of novel ligands using Surflex-Dock. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2015, 29, 485–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sutherland, K.D.; Berns, A. Cell of origin of lung cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2010, 4, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo-Guzmán, M.E.; Bigoni-Ordóñez, G.D.; Hernández, M.I.; Ortiz-Sánchez, E. Cancer stem cell impact on clinical oncology. World J. Stem Cells 2018, 10, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinual, S.; Chanvorachote, P.; Pongrakhananon, V. Suppression of cancer stem-like phenotypes in NCI-H460 lung cancer cells by vanillin through an Akt-dependent pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhummaphan, N.; Chanvorachote, P. Gigantol Suppresses Cancer Stem Cell-Like Phenotypes in Lung Cancer Cells. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 836564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhummaphan, N.; Petpiroon, N.; Prakhongcheep, O.; Sritularak, B.; Chanvorachote, P. Lusianthridin targeting of lung cancer stem cells via Src-STAT3 suppression. Phytomedicine 2019, 62, 152932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Setrerrahmane, S.; Xu, H. Enrichment and characterization of cancer stem cells from a human non-small cell lung cancer cell line. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Gao, Q.; Suo, Z.; Munthe, E.; Solberg, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, M.; Westerdaal, N.A.; Kvalheim, G.; Gaudernack, G. Identification and characterization of cells with cancer stem cell properties in human primary lung cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Dan, S.; Su, T.; She, S.; Dong, W.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, J.; et al. Dual inhibiting OCT4 and AKT potently suppresses the propagation of human cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nandy, S.B.; Arumugam, A.; Subramani, R.; Pedroza, D.; Hernandez, K.; Saltzstein, E.; Lakshmanaswamy, R. MicroRNA-125a influences breast cancer stem cells by targeting leukemia inhibitory factor receptor which regulates the Hippo signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dvorak, P.; Dvorakova, D.; Hampl, A. Fibroblast growth factor signaling in embryonic and cancer stem cells. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 2869–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, Y.; Bai, X.; Huang, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Cui, D.; Yang, X. Basic fibroblast growth factor signalling regulates cancer stem cells in lung cancer A549 cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaguarnera, R.; Belfiore, A. The emerging role of insulin and insulin-like growth factor signaling in cancer stem cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, J.; Shen, J.; Liu, L.; Xia, F.; Xu, C.; Duan, G.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q. Nanog regulates self-renewal of cancer stem cells through the insulin-like growth factor pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, C.; Baranwal, S.; Patel, N.J.; Rodriguez-Agudo, D.; Pandak, W.M.; Majumdar, A.P.; Krystal, G.; Patel, B.B. Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor receptor/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin axis targets colorectal cancer stem cells by attenuating mevalonate-isoprenoid pathway in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15332–15347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Bittrich, S.; Chen, L.; Crichlow, G.V.; Christie, C.H.; Dalenberg, K.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, D437–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippa, B.; Pan, G.; Corbett, M.; Li, C.; Kauffman, G.S.; Pandit, J.; Robinson, S.; Wei, L.; Kozina, E.; Marr, E.S.; et al. Synthesis and structure based optimization of novel Akt inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 3359–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Word, J.M.; Lovell, S.C.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. Asparagine and glutamine: Using hydrogen atom contacts in the choice of side-chain amide orientation. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 285, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ravindranath, P.A.; Forli, S.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J.; Sanner, M.F. AutoDockFR: Advances in Protein-Ligand Docking with Explicitly Specified Binding Site Flexibility. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem in 2021: New data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J. Gaussian09. Available online: http://www.gaussian.com/ (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Pham, T.N.H.; Huy, N.T.; Bay, M.V.; Pham, M.Q.; Nam, P.C.; Vu, V.V.; Ngo, S.T. Autodock vina adopts more accurate binding poses but autodock4 forms better binding affinity. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 60, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forli, S.; Huey, R.; Pique, M.E.; Sanner, M.F.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Computational protein–ligand docking and virtual drug screening with the AutoDock suite. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









| No. | Compounds | Free Energy of Binding (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pongol methyl ether | −9.2 |
| 2 | (CQW) reference compound | −8.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silapech, A.; Racha, S.; Aksorn, N.; Lafauy, P.; Tungsukruthai, S.; Vinayanuwattikun, C.; Sritularak, B.; Chanvorachote, P. Pongol Methyl Ether Inhibits Akt and Suppresses Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes in Lung Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111085
Silapech A, Racha S, Aksorn N, Lafauy P, Tungsukruthai S, Vinayanuwattikun C, Sritularak B, Chanvorachote P. Pongol Methyl Ether Inhibits Akt and Suppresses Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes in Lung Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(11):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111085
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilapech, Arnon, Satapat Racha, Nithikoon Aksorn, Pennapa Lafauy, Sucharat Tungsukruthai, Chanida Vinayanuwattikun, Boonchoo Sritularak, and Pithi Chanvorachote. 2021. "Pongol Methyl Ether Inhibits Akt and Suppresses Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes in Lung Cancer Cells" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 11: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111085
APA StyleSilapech, A., Racha, S., Aksorn, N., Lafauy, P., Tungsukruthai, S., Vinayanuwattikun, C., Sritularak, B., & Chanvorachote, P. (2021). Pongol Methyl Ether Inhibits Akt and Suppresses Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes in Lung Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 14(11), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111085