Ketogal Safety Profile in Human Primary Colonic Epithelial Cells and in Mice
Abstract
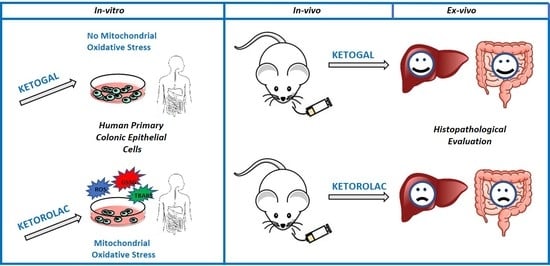
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Stability of Ketogal and Ketorolac in PBS and CoEpi Cell Medium
2.2. Human CoEpi Cell Viability
2.3. Quantitative Evaluation of Ketogal and Ketorolac in CoEpi Cells
2.4. Mitochondrial Depolarization and Oxidative Parameters
2.5. Intracellular Glutathione Measurement
2.6. Evaluation of Small Intestine and Liver Toxicity after Repeated Oral Administration of Ketorolac and Ketogal
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Materials
4.2. Stability of Ketogal and Ketorolac in Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) and Colonic Epithelial (CoEpi) Cell Medium
4.3. Cells
4.3.1. Viability Assay
4.3.2. Sample Preparation for the Quantitative Evaluation of Ketogal and Ketorolac in CoEpi Cells
4.3.3. RP-HPLC Analysis
4.3.4. Extraction of Mitochondria
4.3.5. Mitochondrial Depolarization
4.3.6. Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
4.3.7. Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS)
4.3.8. Intracellular Glutathione Measurement
4.4. Animals
Ethics Statement
4.5. Histological Evaluations
4.6. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, R. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug prescribing: Past, present, and future. Am. J. Med. 2001, 110, 4S–7S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, C.M.; Mody, S.K.; Patel, H.B.; Dudhatra, G.B.; Avinash, K.; Madhavi, A. Toxicopathological overview of analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs in animals. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason, I.; Hayllar, J.; Macpherson, A.J.; Russell, A.S. Side effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the small and large intestine in humans. Gastroenterology 1993, 104, 1832–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, B.J.R. Gastrointestinal effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 17, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittle, B.J.R. Mechanisms underlying intestinal injury induced by anti-inflammatory COX inhibitors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 500, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.L. Mechanisms, prevention and clinical implications of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug enteropathy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 1861–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudanno, O.M.; Cesolari, J.A.; Esnarriaga, J.; Flaherty, P.; Vada, J.; Guastalli, G.; San Miguel, P.; Bedini, O.A. In vivo selectivity of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and gastrointestinal ulcers in rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 45, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sostres, C.; Gargallo, C.J.; Lanas, A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and upper and lower gastrointestinal mucosal damage. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bjarnason, I.; Fehilly, B.; Smethurst, P.; Menzies, I.S.; Levi, A.J. Effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on permeability of the small intestine in humans. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 1992, 19, 83–84. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, V.M.; Coates, J.E.; Chooi, J.; Thomson, A.B.; Russell, A.S. Small bowel permeability-a variable effect of NSAIDS. Clin. Invest. Med. 1995, 18, 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Freedberg, D.E.; Yang, Y.X.; Abrams, J.A. Proton Pump Inhibitors and Myocardial Infarction. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 830–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, B.; Chen, Y.; Wilson, F.P.; Sang, Y.; Chanq, A.R.; Coresh, J.; Grams, M.E. Proton pump inhibitor use and the risk of chronic kidney disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, J.L.; Syer, S.; Denou, E.; De Palma, G.; Vong, L.; McKnight, W.; Jury, J.; Bolla, M.; Bercik, P.; Collins, S.M.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors exacerbate NSAID-induced small intestinal injury by inducing dysbiosis. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsanullah, R.S.; Page, M.C.; Tildesley, G.; Wood, J.R. Prevention of gastroduodenal damage induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Controlled trial of ranitidine. BMJ 1988, 297, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanas, A.; Ferrandez, A. NSAIDs and the colon. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 25, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, M.; Conforti, A.; Lenti, M.C.; Capuano, A.; Bortolami, O.; Motola, D.; Moretti, U.; Vannacci, A.; Rafaniello, C.; Vaccheri, A.; et al. Risk of acute and serious liver injury associated to nimesulide and other NSAIDs: Data from drug-induced liver injury case–control study in Italy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 82, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bessone, F. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: What is the actual risk of liver damage? World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 5651–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Tanaka, A.; Kato, S.; Amagase, K.; Satoh, H. Roles of COX inhibition in pathogenesis of NSAID-induced small intestinal damage. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Tanigawa, T.; Nadatani, Y.; Otani, K.; Machida, H.; Okazaki, H.; Yamagami, H.; Watanabe, K.; Tominaga, K.; Arakawa, T. Mitochondrial disorders in NSAIDs-induced small bowel injury. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2011, 48, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somasundaram, S.; Rafi, S.; Hayllar, J.; Sigthorsson, G.; Jacob, M.; Price, A.B.; Macpherson, A.; Mahmod, T.; Scott, D.; Wrigglesworth, J.M.; et al. Mitochondrial damage: A possible mechanism of the “topical” phase of NSAID induced injury to the rat intestine. Gut 1997, 41, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, S.; Hayllar, H.; Rafi, S.; Wrigglesworth, J.M.; Macpherson, A.J.S.; Bjarnason, I. The Biochemical Basis of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Induced Damage to the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Review and a Hypothesis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1995, 30, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masubuchi, Y.; Nakayama, S.; Horie, T. Role of mitochondrial permeability transition in diclofenac-induced hepatocyte injury in rats. Hepatology 2002, 35, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nasser, J.A. Salicylate-induced kidney mitochondrial permeability transition is prevented by cyclosporin A. Toxicol. Lett. 1999, 105, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, L.C.; Lemasters, J.J. Role of the mitochondrial permeability transition in salicylate toxicity to cultured rat hepatocytes: Implications for the pathogenesis of Reye’ syndrome. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1997, 147, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, N.; Kumar, J.; Erdahl, W.E.; Pfeiffer, D.R.; Gadd, M.E.; Graff, G.; Yanni, J.M. Differential effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on mitochondrial dysfunction during oxidative stress. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 490, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, M.; Bjarnason, I.; Simpson, R.J. In vitro evidence for mitochondrial effects of indomethacin. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1998, 26, S315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basivireddy, J.; Jacob, M.; Ramamoorthy, P.; Pulimood, A.B.; Balasubramanian, K.A. Indomethacin-induced free radical-mediated changes in the intestinal brush border membranes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalini, S.; Mathan, M.M.; Balasubramanian, K.A. Free radical-induced damage intestinal ischaemia reperfusion in normal and xanthine oxidase deficient rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1993, 124, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anup, R.; Aparna, V.; Pulimood, A.; Balasubramanian, K.A. Surgical stress and the small intestine: Role of oxygen free radicals. Surgery 1999, 125, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melisi, D.; Curcio, A.; Luongo, E.; Morelli, E.; Rimoli, M.G. D-galactose as a vector for prodrug design. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 2288–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, R.; De Caro, C.; Avallone, B.; Magliocca, S.; Nieddu, M.; Boatto, G.; Troiano, R.; Cuomo, R.; Cirillo, C.; Avagliano, C.; et al. Ketogal: A Derivative Ketorolac Molecule with Minor Ulcerogenic and Renal Toxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curcio, A.; Sasso, O.; Melisi, D.; Nieddu, M.; La Rana, G.; Russo, R.; Gavini, E.; Boatto, G.; Abignente, E.; Calignano, A.; et al. Galactosyl prodrug of ketorolac: Synthesis, stability, and pharmacological and pharmacokinetic evaluations. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 3794–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, A.P.; Gunasekara, D.B.; Speer, J.; Reed, M.I.; Peña, A.N.; Midkiff, B.R.; Magness, S.T.; Bultman, S.J.; Allbritton, N.L.; Redinbo, M.R. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Induced Leaky Gut Modeled Using Polarized Monolayers of Primary Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larregieu, C.A.; Benet, L.Z. Drug discovery and regulatory considerations for improving in silico and in vitro predictions that use Caco-2 as a surrogate for human intestinal permeability measurements. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omatsu, T.; Naito, Y.; Handa, O.; Hayashi, N.; Mizushima, K.; Qin, Y.; Hirata, I.; Adachi, S.; Okayama, T.; Kishimoto, E.; et al. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in indomethacin-induced apoptosis of small intestinal epithelial cells. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherratt, H.S. Mitochondria: Structure and function. Rev. Neurol. 1991, 147, 417–430. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.H. NSAID-induced hepatotoxicity. Clin. Liver Dis. 1998, 2, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amacher, D.E.; Chalasani, N. Drug-induced hepatic steatosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2014, 34, 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, V.; Sanyal, A.J. Drug-Induced Steatohepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2013, 17, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magliocca, S.; Sodano, F.; Nieddu, M.; Burrai, L.; Boatto, G.; Rimoli, M.G. New Galactosylated NSAIDS prodrugs in a green context: Synthesis and stability. IJPSR 2017, 8, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiyama, M.; Shiga, M.; Sasamoto, K.; Mizoguchi, M.; He, P.-G. A new sulfonated tetrazolium salt that produces a highly water-soluble formazan dye. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campia, I.; Lussiana, C.; Pescarmona, G.; Ghigo, D.; Bosia, A.; Riganti, C. Geranylgeraniol prevents the cytotoxic effects of mevastatin in THP-1 cells, without decreasing the beneficial effects on cholesterol synthesis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao-Peng, L.; Hu, J.; Wei, J.; Ye, S.; Bu, J.; Xu, W.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhu, L.; et al. Silencing of circFoxO3 Protects HT22 Cells from Glutamate-Induced Oxidative Injury via Regulating the Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 40, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Dawn-Linsley, M.; Ekinci, F.J.; Ortiz, D.; Rogers, E.; Shea, T.B. Monitoring thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARs) as an assay for oxidative damage in neuronal cultures and central nervous system. J. Neurosci. Methods 2005, 141, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzano, E.; Riganti, C.; Tomatis, M.; Turci, F.; Bosia, A.; Fubini, B.; Ghigo, D. Potential toxicity of nonregulated asbestiform minerals: Balangeroite from the western Alps. Part 3: Depletion of antioxidant defenses. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2005, 68, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliuca, C.; Cicatiello, A.G.; Colicchio, R.; Greco, A.; Cerciello, R.; Auletta, L.; Albanese, S.; Scaglione, E.; Pagliarulo, C.; Pastore, G.; et al. Novel Approach for Evaluation of Bacteroides fragilis Protective Role against Bartonella henselae Liver Damage in Immunocompromised Murine Model. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avallone, B.; Agnisola, C.; Cerciello, R.; Panzuto, R.; Simoniello, P.; Cretì, P.; Motta, C.M. Structural and functional changes in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) skeletal muscle after cadmium exposure. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2015, 31, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.O.; Haglund, U.; Bulkley, G.B.; Fält, K. The sequence of development of intestinal tissue injury after strangulation ischemia and reperfusion. Surgery 1990, 107, 574–580. [Google Scholar]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sodano, F.; Avallone, B.; Tizzano, M.; Fogliano, C.; Rolando, B.; Gazzano, E.; Riganti, C.; Magliocca, S.; Cuozzo, M.; Albrizio, S.; et al. Ketogal Safety Profile in Human Primary Colonic Epithelial Cells and in Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111149
Sodano F, Avallone B, Tizzano M, Fogliano C, Rolando B, Gazzano E, Riganti C, Magliocca S, Cuozzo M, Albrizio S, et al. Ketogal Safety Profile in Human Primary Colonic Epithelial Cells and in Mice. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(11):1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111149
Chicago/Turabian StyleSodano, Federica, Bice Avallone, Monica Tizzano, Chiara Fogliano, Barbara Rolando, Elena Gazzano, Chiara Riganti, Salvatore Magliocca, Mariarosaria Cuozzo, Stefania Albrizio, and et al. 2021. "Ketogal Safety Profile in Human Primary Colonic Epithelial Cells and in Mice" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 11: 1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111149
APA StyleSodano, F., Avallone, B., Tizzano, M., Fogliano, C., Rolando, B., Gazzano, E., Riganti, C., Magliocca, S., Cuozzo, M., Albrizio, S., Calignano, A., Cristiano, C., Russo, R., & Rimoli, M. G. (2021). Ketogal Safety Profile in Human Primary Colonic Epithelial Cells and in Mice. Pharmaceuticals, 14(11), 1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111149