Implementation of an Enzyme Membrane Reactor to Intensify the α-O-Glycosylation of Resveratrol Using Cyclodextrins
Abstract
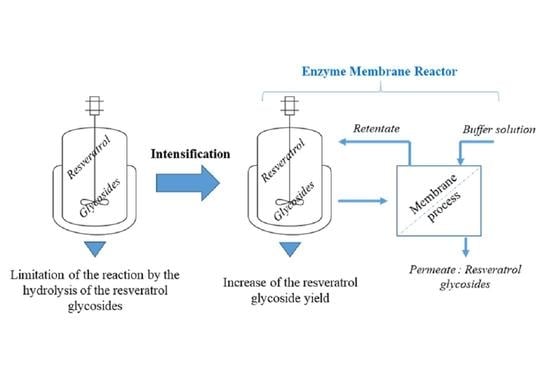
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Proof-of-Concept of the Selective Filtration
2.2. Choice of the Membranes According to the Screening on Model Solution
2.2.1. Results of the Membrane Screening
2.2.2. Determination of the Membrane Permeabilities
2.3. Implementation of the Enzyme Membrane Reactor for the Resveratrol Glycosylation
2.3.1. Membrane Separation in Dead-End Configuration
2.3.2. Membrane Separation in a Cross-Flow Configuration
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Chemical Products
4.2. Obtention of the Resveratrol α-glycosides from β-Cyclodextrin–Resveratrol Complex in Water
4.3. Membrane Screening on Model Solution
4.3.1. Composition of the Model Solution
4.3.2. Description of the Membrane Process Used to the Screening
4.3.3. Protocol for the Membrane Screening
4.4. Description of the Enzyme Membrane Reactor
4.5. HPLC Analysis
4.6. Simulation of the Complexation with β-Cyclodextrin
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baxter, R.A. Anti-aging properties of resveratrol: Review and report of a potent new antioxidant skin care formulation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2008, 7, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratz-Łyko, A.; Arct, J. Resveratrol as an active ingredient for cosmetic and dermatological applications: A review. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2019, 21, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oi, N.; Jeong, C.-H.; Nadas, J.; Cho, Y.-Y.; Pugliese, A.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Resveratrol, a Red Wine Polyphenol, Suppresses Pancreatic Cancer by Inhibiting Leukotriene A4 Hydrolase. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9755–9764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tellone, E.; Galtieri, A.; Russo, A.; Giardina, B.; Ficarra, S. Resveratrol: A Focus on Several Neurodegenerative Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Y.; Gao, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cui, B. Resveratrol ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in rats through negative regulation of the p38 MAPK/TGF-β1 pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 3223–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frazzi, R.; Guardi, M. Cellular and Molecular Targets of Resveratrol on Lymphoma and Leukemia Cells. Molecules 2017, 22, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitaglione, P.; Sforza, S.; Galaverna, G.; Ghidini, C.; Caporaso, N.; Vescovi, P.P.; Fogliano, V.; Marchelli, R. Bioavailability oftrans-resveratrol from red wine in humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, E.; Somoza, V. Metabolism and bioavailability oftrans-resveratrol. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuan, N.H.; Sohng, J.K. Recent biotechnological progress in enzymatic synthesis of glycosides. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 1329–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regev-Shoshani, G.; Shoseyov, O.; Bilkis, I.; Kerem, Z. Glycosylation of resveratrol protects it from enzymic oxidation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desmet, T.; Soetaert, W. Enzymatic glycosyl transfer: Mechanisms and applications. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2011, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marié, T.; Willig, G.; Teixeira, A.R.S.; Barboza, E.G.; Kotland, A.; Gratia, A.; Courot, E.; Hubert, J.; Renault, J.-H.; Allais, F. Enzymatic Synthesis of Resveratrol α-Glycosides from β-Cyclodextrin-Resveratrol Complex in Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5370–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rha, C.-S.; Choi, J.-M.; Jung, Y.-S.; Kim, E.-R.; Ko, M.J.; Seo, D.-H.; Kim, D.-O.; Park, C.-S. High-efficiency enzymatic production of α-isoquercitrin glucosides by amylosucrase from Deinococcus geothermalis. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2019, 120, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Adlercreutz, P. Regioselective glycosylation of hydroquinone to α-arbutin by cyclodextrin glucanotransferase from Thermoanaerobacter sp. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 79, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyawali, Y.; Vanbroekhoven, K.; Dejonghe, W. Process intensification: The future for enzymatic processes? Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 121, 196–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-Mouro, A.; Gullón, B.; Lu-Chau, T.A.; Eibes, G. Green and sustainable synthesis of oligorutin using an enzymatic membrane reactor: Process optimization. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 124, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.; Santos, J.; Crespo, J.G. Solvent resistant diananofiltration for production of steryl esters enriched extracts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 135, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.; Santos, J.; Crespo, J.G. Assessment of solvent resistant nanofiltration membranes for valorization of deodorizer distillates. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Shahid, S.; Shen, J.; Emanuelsson, E.A.C.; Patterson, D.A. A wide range and high resolution one-filtration molecular weight cut-off method for aqueous based nanofiltration and ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellouze, F.; Amar, N.B.; Mokhtar, M.N.; Zimmermann, W.; Deratani, A. Fractionation of homologous CD6 to CD60 cyclodextrin mixture by ultrafiltration and nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 374, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, O.; Vaillant, F.; Pérez, A.M.; Dornier, M. Potential of ultrafiltration for separation and purification of ellagitannins in blackberry (Rubus adenotrichus Schltdl.) juice. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 125, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupančič, Š.; Lavrič, Z.; Kristl, J. Stability and solubility of trans-resveratrol are strongly influenced by pH and temperature. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Cheng, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, G. Complexation of resveratrol with cyclodextrins: Solubility and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. A new model for calculating atomic charges in molecules. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 19, 3181–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—A rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 1980, 36, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Supplier | Microdyn Nadir | Hydranautics—Nitto | GE | GH | PT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane Cut-Off Threshold (kDa) | 0.4 | 0.72 | 0.9 | 1.4 | 5 |
| Piceid Retention Rates (%) | >90 | >90 | 71.4 (6 bar) | 89.1 (6 bar) | 56.4 (6 bar) |
| Lp (L × h−1 × m−2 × bar−1) | Before Filtration | After Filtration | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| GE | 7.34 | 5.65 | −23% |
| GH | 6.73 | 4.64 | −30% |
| Supplier | Type | Membrane | Material | Cut-Off Threshold (Da) | Maximum Temperature and Pressure | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Electrics | Ultrafiltration | GE | Proprietary thin film | 900 | 70 °C/40 b | 1–11 |
| GH | 1400 | 70 °C/27 b | ||||
| PT | Polyethersulfone /polysulfone | 5000 | 70 °C/10 b | |||
| Microdyn Nadir | Nanofiltration | NP030 | Polyethersulfone | 400 | 95 °C/40 b | 0–14 |
| Hydranautics–Nitto | Nanofiltration | HYDRACoRe 70 pHT | Sulfonated polyethersulfone | 720 | 60 °C/41 b | 2–11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ioannou, I.; Barboza, E.; Willig, G.; Marié, T.; Texeira, A.; Darme, P.; Renault, J.-H.; Allais, F. Implementation of an Enzyme Membrane Reactor to Intensify the α-O-Glycosylation of Resveratrol Using Cyclodextrins. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040319
Ioannou I, Barboza E, Willig G, Marié T, Texeira A, Darme P, Renault J-H, Allais F. Implementation of an Enzyme Membrane Reactor to Intensify the α-O-Glycosylation of Resveratrol Using Cyclodextrins. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(4):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040319
Chicago/Turabian StyleIoannou, Irina, Eduardo Barboza, Gaëlle Willig, Thomas Marié, Andreïa Texeira, Pierre Darme, Jean-Hugues Renault, and Florent Allais. 2021. "Implementation of an Enzyme Membrane Reactor to Intensify the α-O-Glycosylation of Resveratrol Using Cyclodextrins" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 4: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040319
APA StyleIoannou, I., Barboza, E., Willig, G., Marié, T., Texeira, A., Darme, P., Renault, J. -H., & Allais, F. (2021). Implementation of an Enzyme Membrane Reactor to Intensify the α-O-Glycosylation of Resveratrol Using Cyclodextrins. Pharmaceuticals, 14(4), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040319