Oxidative Stress-Induced Silver Nano-Carriers for Chemotherapy
Abstract
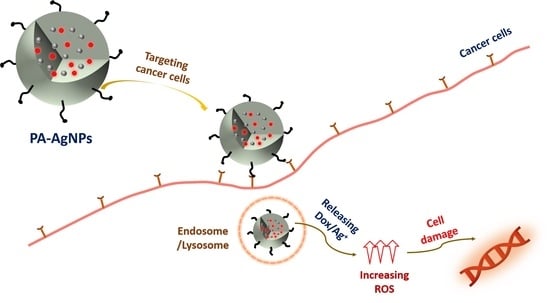
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Structure of PA
2.2. Characterization of PA-AgNPs
2.3. Cellular Uptake Ability
2.4. In Vitro Drug Release
2.5. Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
2.7. Cell Apoptosis Assay
2.8. In Vivo Therapy Studies
2.9. Biosafety In Vivo Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
3.3. PA Synthesis
3.4. Encapsulation of AgNPs with PA
3.5. Physicochemical and Structural Characterizations
3.6. In Vitro Drug Release
3.7. Cell Viability
3.8. Cellular Uptake
3.9. Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
3.10. Cell Apoptosis Assay
3.11. In Vivo Experiments
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.P.; Wang, T.T.; Wang, D.G.; Dong, A.J.; Li, Y.P.; Yu, H.J. Smart nanoparticles improve therapy for drug-resistant tumors by overcoming pathophysiological barriers. Acta Pharm. Sinica 2017, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schirrmacher, V. From chemotherapy to biological therapy: A review of novel concepts to reduce the side effects of systemic cancer treatment. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- Damia, D.; Garattini, S. The pharmacological point of view of resistance to therapy in tumors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, B.; Donato, M.D.; Pezone, A.; Zazzo, E.D.; Giovannelli, P.; Galasso, G.; Castoria, G. ROS in cancer therapy: The bright side of the moon. A Migliaccio ExP. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukai, M.U.; Nakamura, Y. Reactive oxygen species and angiogenesis: NADPH oxidases as target for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2008, 266, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umapathi, A.; Kumawat, M.; Daima, H.K. Engineered nanomaterials for biomedical applications and their toxicity: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 445–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.B.; Li, F.; Choi, J.; Mano, J.F. Nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, 2000574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Jose, S.; Sumod, U.S.; Sabitha, M. Nanotechnology in cosmet-ics: Opportunities and challenges. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E.; Chen, Z.; Shin, D.M. Nanoparticle therapeutics: An emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; FaroKHzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, T.; Bravo, F.M.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, I.X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Li, Q.; Chu, C.H. The antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and its application in dentistry. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomathi, A.C.; Rajarathinam, S.R.X.; Sadiq, A.M.; Rajeshkumar, S. Anticancer activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized using aqueous fruit shell extract of Tamarindus indica on MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttacavoli, M.; Albanese, N.N.; Cara, G.D.; Alduina, R.; Faleri, C.; Gallo, M.; Pizzolanti, G.; Gallo, G.; Feo, S.; Baldi, F.; et al. Anticancer activity of biogenerated silver nanoparticles: An integrated proteomic investigation. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 9685–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webb, B.A.; Chimenti, M.; Jacobson, M.P.; Barber, D.L. Dysregulated pH: A perfect storm for cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Vakili, M.R.; Abyaneh, H.S.; Molavi, O.; Lai, R.; Lavasanifar, A. Mitochondrial delivery of doxorubicin via triphenylphosphine modification for overcoming drug resistance in MDA-MB-435/DOX cells. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2014, 11, 2640–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorini, S.; Angelis, A.D.; Berrino, L.; Malara, N.; Rosano, G.; Ferraro, E. Chemotherapeutic drugs and mitochondrial dysfunction: Focus on doxorubicin, trastuzumab, and sunitinib. Oxidative Med. and Cel. Long. 2018, 7582730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.; Nguyen, M.P.; Choi, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, D. Bioadhesive nanoaggregates based on polyaspartamide-g-C18/DOPA for wound healing. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2402–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Zhuo, R. An enzyme-mediated in situ hydrogel based on polyaspartamide derivatives for localized drug delivery and 3D scaffolds. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 101334–101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, P.; Antoni, G.; Benvenuti, F.; Cocola, F.; Gazzei, G. Synthesis of alpha beta-poly((2-hydroxyethyl)-DL-aspartamide), a new plasma expander. J. Med. Chem. 1973, 16, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.P.; Nguyen, M.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, D. Encapsulation of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with polyaspartamide biopolymer for hyperthermia therapy. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 122, 109396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Jeong, J.; Kim, D. Intracellular uptake and pH-dependent release of doxorubicin from the self-assembled micelles based on amphiphilic polyaspartamide graft copolymers. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Chu, L.Y. Biotin-conjugated block copolymeric nanoparticles as tumor-targeted drug delivery systems. Macromol. Res. 2007, 15, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, C.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, C.Y.; Xia, W.; Zhang, Z. Combination delivery of adjudin and doxorubicin via integrating drug conjugation and nanocarrier approaches for the treatment of drug-resistant cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, V.T.T.; Lim, C.W.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, C.H.; Kim, D. Self-assembled nanoaggregates based on polyaspartamide graft copolymers for pH-controlled release of Doxorubicin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2978–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Bharti, A.; Meena, V.K. Green synthesis of multi-shaped silver nanoparticles: Optical, morphological and antibacterial properties. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 3638–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Du, J.; Singh, P.; Yi, T.H. Ecofriendly synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by Euphrasia officinalis leaf extractand its biomedical applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotech 2015, 401, 1362417. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.P.; Thuy, V.T.T.; Kim, D. Integration of iron oxide nanoparticles and polyaspartamide biopolymer for MRI image contrast enhancement and an efficient drug-delivery system in cancer therapy. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 335712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Cai, B.; He, N.; Wang, Z. Fenton reaction-based nanomedicine in cancer chemodynamic and synergistic therapy. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 21, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czupiel, P.; Delplace, V.; Shoichet, M. Nanoparticle delivery of a pH-sensitive produg of doxorubicin and a mitochondria targeting VES-H8R8 synergistically kill multi-drug resistant breast cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 8726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, D. Release behavior of amoxicillin from glycol chitosan superporous hydrogels. J. Biomater. Sci Polym. Ed. 2009, 20, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, D.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Young, F. Real time monitoring and quantification of reactive oxygen species in breast cancer cell line MCF-7 by 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCFDA) assay. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2018, 94, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Ye, J.; Soong, R.; Wu, B.; Yu, L.; Simpson, A.J.; Chan, A.W.H. Relationship between chemical composition and oxidative potential of secondary organic aerosol from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 3987–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Logue, S.E.; Elgendy, M.; Martin, S.J. Expression, purification and use of recombinant annexin V for the detection of apoptotic cells. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, A.M.; Nelson, K.L.; Konowalchuk, J.D.; Barreda, D.R. Modified annexin V/Propidium iodide apoptosis assay for accurate assessment of cell death. J. Visualized Exp. 2011, 50, e2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, B.; Luo, C.; Zhang, X.; Guo, M.; Sun, M.; Yu, H.; Chen, Q.; Yang, W.; Wang, M.; Zuo, S.; et al. Probing the impact of sulfur/selenium/carbon linkages on prodrug nanoassemblies for cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, G.; Chang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, B.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Zhang, H. Electron compensation effect suppressed silver ion release and contributed safety of Au@Ag core-shell nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 4478–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavrakidis, I.; Jóźwiak, K.; Hauptmann, M. Statistical analysis of longitudinal data on tumour growth in mice experiments. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Synthesis Process | Material | Function | Status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Chemical Formula/Dilution | |||
| PSI | N,N’-dimethylformamide | DMF, 99.8% | Solvent | Solution |
| L-Aspartic acid | 98% | Substrate | Powder | |
| Phosphoric acid | 85% | Catalyst | Solution | |
| Mesitylene | 98% | Solvent | Solution | |
| Sulfolane | 99% | Solvent | Solution | |
| PA | Octadecylamine | C18, 99% | Substrate | Powder |
| O-(2-aminoethyl)polyethylene glycol | PEG, Mp 5000 | Substrate | Powder | |
| Biotin | ≥99% | Substrate | Powder | |
| Hydrazine hydrate | 50–60% | Substrate | Solution | |
| Doxorubicin hydrochloride | 98–102% | Substrate | Powder | |
| N,N’-dicyclohexincarbodiimide | 99% | Catalyst | Powder | |
| 4-(Dimethylamino)pyridine | ≥99% | Catalyst | Powder | |
| Triethylamine | ≥99.5% | Catalyst | Solution | |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide | DMSO, ≥99% | Solvent | Solution | |
| AgNPs and Encapsulation | Toluene | ≥99.8% | Solvent | Solution |
| Distilled Water | DIW | Solvent | Solution | |
| Oleyamine | 99% | Surfactant | Solution | |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 99% | Solvent | Solution | |
| Silver acetate | 99% | Substrate | Powder | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, M.P.; Pham, D.P.; Kim, D. Oxidative Stress-Induced Silver Nano-Carriers for Chemotherapy. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121449
Nguyen MP, Pham DP, Kim D. Oxidative Stress-Induced Silver Nano-Carriers for Chemotherapy. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(12):1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121449
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Minh Phuong, Duy Phong Pham, and Dukjoon Kim. 2022. "Oxidative Stress-Induced Silver Nano-Carriers for Chemotherapy" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 12: 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121449
APA StyleNguyen, M. P., Pham, D. P., & Kim, D. (2022). Oxidative Stress-Induced Silver Nano-Carriers for Chemotherapy. Pharmaceuticals, 15(12), 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121449