Epidural Oxycodone for Acute Pain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Historical Aspects of the Pharmacology of Epidural Opioids
3. Oxycodone
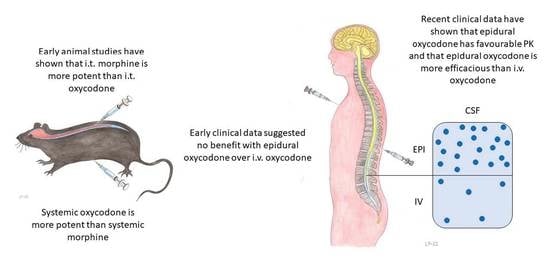
3.1. General
3.2. Experimental Animal Studies
3.3. Clinical Studies
3.4. Population Pharmacokinetics
4. Glymphatic Pathway and Epidural Analgesia
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gerbershagen, H.J.; Aduckathil, S.; van Wijck, A.J.; Peelen, L.M.; Kalkman, C.J.; Meissner, W. Pain Intensity on the First Day after Surgery: A Prospective Cohort Study Comparing 179 Surgical Procedures. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bell, A.F.; Rubin, L.H.; Davis, J.M.; Golding, J.; Adejumo, O.A.; Carter, C.S. The Birth Experience and Subsequent Maternal Caregiving Attitudes and Behavior: A Birth Cohort Study. Arch. Womens Ment. Health 2019, 22, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prabhakar, A.; Mancuso, K.F.; Owen, C.P.; Lissauer, J.; Merritt, C.K.; Urman, R.D.; Kaye, A.D. Perioperative Analgesia Outcomes and Strategies. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2014, 28, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schug, S.; Palmer, G.; Scott, D.; Alcock, M.; Halliwell, R.; Mott, J.; APM:SE Working Group of the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists and Faculty of Pain Medicine. Acute Pain Management: Scientific Evidence, 5th ed.; ANZCA & FPM: Melbourne, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anim-Somuah, M.; Smyth, R.M.; Cyna, A.M.; Cuthbert, A. Epidural Versus Non-Epidural or no Analgesia for Pain Management in Labour. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 5, CD000331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, P.; Murphy, C.; Halpern, S.; Carvalho, B. The Effect of Low Concentrations Versus High Concentrations of Local Anesthetics for Labour Analgesia on Obstetric and Anesthetic Outcomes: A Meta-Analysis. Can. J. Anaesth. 2013, 60, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Block, B.M.; Liu, S.S.; Rowlingson, A.J.; Cowan, A.R.; Cowan, J.A., Jr.; Wu, C.L. Efficacy of Postoperative Epidural Analgesia: A Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2003, 290, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, J.N.; Dolin, S.J. Respiratory and Haemodynamic Effects of Acute Postoperative Pain Management: Evidence from Published Data. Br. J. Anaesth. 2004, 93, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolin, S.J.; Cashman, J.N.; Bland, J.M. Effectiveness of Acute Postoperative Pain Management: I. Evidence from Published Data. Br. J. Anaesth. 2002, 89, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolin, S.J.; Cashman, J.N. Tolerability of Acute Postoperative Pain Management: Nausea, Vomiting, Sedation, Pruritus, and Urinary Retention. Evidence from Published Data. Br. J. Anaesth. 2005, 95, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guay, J.; Nishimori, M.; Kopp, S.L. Epidural Local Anesthetics Versus Opioid-Based Analgesic Regimens for Postoperative Gastrointestinal Paralysis, Vomiting, and Pain after Abdominal Surgery: A Cochrane Review. Anesth. Analg. 2016, 123, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.W.; Li, H.J.; Li, H.J.; Zhao, B.J.; Guo, X.Y.; Feng, Y.; Zuo, M.Z.; Yu, Y.P.; Kong, H.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Delirium in Older Patients after Combined Epidural-General Anesthesia or General Anesthesia for Major Surgery: A Randomized Trial. Anesthesiology 2021, 135, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigg, J.R.; Jamrozik, K.; Myles, P.S.; Silbert, B.S.; Peyton, P.J.; Parsons, R.W.; Collins, K.S.; MASTER Anaethesia Trial Study Group. Epidural Anaesthesia and Analgesia and Outcome of Major Surgery: A Randomised Trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomäki, T.E.; Leppäluoto, J.; Laitinen, J.O.; Vuolteenaho, O.; Nuutinen, L.S. Epidural Versus Intravenous Fentanyl for Reducing Hormonal, Metabolic, and Physiologic Responses after Thoracotomy. Anesthesiology 1993, 79, 672–679. [Google Scholar]
- Niemi, G.; Breivik, H. Adrenaline Markedly Improves Thoracic Epidural Analgesia Produced by a Low-Dose Infusion of Bupivacaine, Fentanyl and Adrenaline after Major Surgery. A Randomised, Double-Blind, Cross-Over Study with and without Adrenaline. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1998, 42, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufentanil. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/sufentanil (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Duramorph. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/018565s022lbl_duramorph.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Salomäki, T.E.; Kokki, H.; Turunen, M.; Havukainen, U.; Nuutinen, L.S. Introducing Epidural Fentanyl for on-Ward Pain Relief after Major Surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1996, 40, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, M.; Kokki, H.; Hautajärvi, H.; Tuovinen, K.; Kokki, M. Oxycodone for Pain Management in the Latent Phase of Labour—A Pragmatic Trial. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2020, 64, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, M.; Piirainen, P.; Kokki, H.; Lammi, P.; Kokki, M. Updated Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Oxycodone. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olkkola, K.T.; Kontinen, V.K.; Saari, T.I.; Kalso, E.A. Does the Pharmacology of Oxycodone Justify its Increasing use as an Analgesic? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäcklund, M.; Lindgren, L.; Kajimoto, Y.; Rosenberg, P.H. Comparison of Epidural Morphine and Oxycodone for Pain after Abdominal Surgery. J. Clin. Anesth. 1997, 9, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokki, M.; Välitalo, P.; Kuusisto, M.; Ranta, V.P.; Raatikainen, K.; Hautajärvi, H.; Kokki, H. Central Nervous System Penetration of Oxycodone after Intravenous and Epidural Administration. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 112, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olczak, B.; Kowalski, G.; Leppert, W.; Bienert, A.; Tezyk, A.; Adamski, M.; Rzymski, S.; Wieczorowska-Tobis, K. Analgesic Efficacy and Safety of Epidural Oxycodone in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Pilot Study. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 2303–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piirainen, P.; Kokki, H.; Hautajärvi, H.; Ranta, V.P.; Kokki, M. The Analgesic Efficacy and Pharmacokinetics of Epidural Oxycodone after Gynaecological Laparotomy: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy Comparison with Intravenous Administration. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piirainen, P.; Kokki, H.; Anderson, B.; Hannam, J.; Hautajärvi, H.; Ranta, V.P.; Kokki, M. Analgesic Efficacy and Pharmacokinetics of Epidural Oxycodone in Pain Management after Gynaecological Laparoscopy-A Randomised, Double Blind, Active Control, Double-Dummy Clinical Comparison with Intravenous Administration. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 1798–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sng, B.L.; Kwok, S.C.; Mathur, D.; Ithnin, F.; Newton-Dunn, C.; Assam, P.N.; Sultana, R.; Sia, A.T. Comparison of Epidural Oxycodone and Epidural Morphine for Post-Caesarean Section Analgesia: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Indian J. Anaesth. 2016, 60, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Wang, Y.L.; Teng, W.B.; He, R.; Li, Y.H.; Huang, S.Q. The Median Effective Concentration (EC(50)) of Epidural Ropivacaine with Different Doses of Oxycodone during Limb Surgery in Elderly Patients. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 808850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagidate, F.; Dohi, S. Epidural Oxycodone or Morphine Following Gynaecological Surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2004, 93, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, H.Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Zhang, W.; Cai, S. Effects of Adding Oxycodone to Ropivacaine on Labor Analgesia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. J. Pain 2020, 36, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, M.; Kokki, H.; Hautajärvi, H.; Huhta, H.; Ranta, V.P.; Räsänen, J.; Voipio, H.M.; Kokki, M. Oxycodone Pharmacokinetics and Fetal Exposure after Intravenous or Epidural Administration to the Ewe. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2018, 97, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, M.; Kokki, H.; Hautajärvi, H.; Lantto, J.; Räsänen, J.; Voipio, H.M.; Kokki, M. Oxycodone Concentrations in the Central Nervous System and Cerebrospinal Fluid after Epidural Administration to the Pregnant Ewe. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamminsalo, M.; Piirainen, P.; Kokki, H.; Knibbe, C.A.J.; Ranta, V.P.; Välitalo, P.; Kokki, M. Population Pharmacokinetics of Oxycodone in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid after Epidural and Intravenous Administration. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, J.D.; Hannam, J.A.; Anderson, B.J.; Kokki, H.; Kokki, M. Oxycodone Target Concentration Dosing for Acute Pain in Children. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2021, 31, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, J.D.; Sundermann, M.; Hannam, J.A.; Kokki, H.; Kokki, M.; Anderson, B.J. Population Pharmacokinetics of Oxycodone: Premature Neonates to Adults. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2021, 31, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, H.L.; Emson, P.C.; Leigh, B.K.; Gilbert, R.F.; Iversen, L.L. Multiple Opiate Receptor Sites on Primary Afferent Fibres. Nature 1980, 284, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaksh, T.L.; Rudy, T.A. Analgesia Mediated by a Direct Spinal Action of Narcotics. Science 1976, 192, 1357–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, M.; Magora, F.; Olshwang, D.; Davidson, J.T. Epidural Morphine in Treatment of Pain. Lancet 1979, 1, 527–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, M.J.; Mather, L.E. Intrathecal and Epidural Administration of Opioids. Anesthesiology 1984, 61, 276–310. [Google Scholar]
- Geller, E.; Chrubasik, J.; Graf, R.; Chrubasik, S.; Schulte-Monting, J. A Randomized Double-Blind Comparison of Epidural Sufentanil Versus Intravenous Sufentanil or Epidural Fentanyl Analgesia after Major Abdominal Surgery. Anesth. Analg. 1993, 76, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomäki, T.E.; Laitinen, J.O.; Nuutinen, L.S. A Randomized Double-Blind Comparison of Epidural Versus Intravenous Fentanyl Infusion for Analgesia after Thoracotomy. Anesthesiology 1991, 75, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinard, J.P.; Mavrocordatos, P.; Chiolero, R.; Carpenter, R.L. A Randomized Comparison of Intravenous Versus Lumbar and Thoracic Epidural Fentanyl for Analgesia after Thoracotomy. Anesthesiology 1992, 77, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, J.D.; Hullander, R.M.; Bready, R.J.; Leivers, D. A Comparison of Patient Controlled Epidural Analgesia with Sufentanil by the Lumbar Versus Thoracic Route after Thoracotomy. Anesth. Analg. 1994, 78, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grass, J.A. Fentanyl: Clinical use as Postoperative Analgesic–Epidural/Intrathecal Route. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 1992, 7, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grass, J.A. Sufentanil: Clinical use as Postoperative Analgesic–Epidural/Intrathecal Route. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 1992, 7, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernards, C.M.; Shen, D.D.; Sterling, E.S.; Adkins, J.E.; Risler, L.; Phillips, B.; Ummenhofer, W. Epidural, Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Plasma Pharmacokinetics of Epidural Opioids (Part 1): Differences among Opioids. Anesthesiology 2003, 99, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ummenhofer, W.C.; Arends, R.H.; Shen, D.D.; Bernards, C.M. Comparative Spinal Distribution and Clearance Kinetics of Intrathecally Administered Morphine, Fentanyl, Alfentanil, and Sufentanil. Anesthesiology 2000, 92, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansdottir, V.; Hedner, T.; Woestenborghs, R.; Nordberg, G. The CSF and Plasma Pharmacokinetics of Sufentanil after Intrathecal Administration. Anesthesiology 1991, 74, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, G.; Hedner, T.; Mellstrand, T.; Borg, L. Pharmacokinetics of Epidural Morphine in Man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1984, 26, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourlay, G.K.; Cherry, D.A.; Plummer, J.L.; Armstrong, P.J.; Cousins, M.J. The Influence of Drug Polarity on the Absorption of Opioid Drugs into CSF and Subsequent Cephalad Migration Following Lumbar Epidural Administration: Application to Morphine and Pethidine. Pain 1987, 31, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourlay, G.K.; Murphy, T.M.; Plummer, J.L.; Kowalski, S.R.; Cherry, D.A.; Cousins, M.J. Pharmacokinetics of Fentanyl in Lumbar and Cervical CSF Following Lumbar Epidural and Intravenous Administration. Pain 1989, 38, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, J.D.; Owen, J.; Lamoreaux, W.; Viscomi, C.; McJames, S.; Cluff, M. The Effect of Distance from Injection Site to the Brainstem using Spinal Sufentanil. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2001, 26, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, R.; Malinovsky, J.M.; Le Corre, P.; Dollo, G.; Chevanne, F.; Le Verge, R. Cerebrospinal Fluid Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics of Bupivacaine and Lidocaine after Intrathecal and Epidural Administrations in Rabbits Using Microdialysis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Clement, R.; Malinovsky, J.M.; Hildgen, P.; Dollo, G.; Estebe, J.P.; Chevanne, F.; Le Verge, R.; Le Corre, P. Spinal Disposition and Meningeal Permeability of Local Anesthetics. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, F.X.; Estebe, J.P.; Ratajczak, M.; Wodey, E.; Chevanne, F.; Dollo, G.; Bec, D.; Malinovsky, J.M.; Ecoffey, C.; Le Corre, P. Epidural, Intrathecal Pharmacokinetics, and Intrathecal Bioavailability of Ropivacaine. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 105, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, H.B.; Christensen, B.; Findlay, J.W.; Jansen, J.A. Pharmacokinetics of Intravenous, Intrathecal and Epidural Morphine and Fentanyl in the Goat. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1986, 30, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, T.I.; Taverne, R.H.; Drost, R.H.; Roelofs, J.M.; Winckers, E.K.; Van Rossum, J.M. Epidural Morphine Anesthesia for Abdominal Aortic Surgery–Pharmacokinetics. Reg. Anesth. 1989, 14, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström, S.; Hartvig, P.; Persson, M.P.; Tamsen, A. Pharmacokinetics of Epidural Morphine and Meperidine in Humans. Anesthesiology 1987, 67, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansdottir, V.; Woestenborghs, R.; Nordberg, G. The Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Pharmacokinetics of Sufentanil after Thoracic or Lumbar Epidural Administration. Anesth. Analg. 1995, 80, 724–729. [Google Scholar]
- Hansdottir, V.; Bake, B.; Nordberg, G. The Analgesic Efficacy and Adverse Effects of Continuous Epidural Sufentanil and Bupivacaine Infusion after Thoracotomy. Anesth. Analg. 1996, 83, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.I.; Eisenach, J.C. Pharmacokinetics and Dynamics of Intravenous, Intrathecal, and Epidural Clonidine in Sheep. Anesthesiology 1989, 71, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenach, J.C.; Shafer, S.L.; Bucklin, B.A.; Jackson, C.; Kallio, A. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Intraspinal Dexmedetomidine in Sheep. Anesthesiology 1994, 80, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, H.; Sandvik, L.; Qvigstad, E.; Bjerkelund, C.E.; Raeder, J. A Comparison of Intravenous Oxycodone and Intravenous Morphine in Patient-Controlled Postoperative Analgesia after Laparoscopic Hysterectomy. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 109, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalso, E.; Vainio, A. Hallucinations during Morphine but Not during Oxycodone Treatment. Lancet 1988, 332, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalso, E.; Pöyhiä, R.; Onnela, P.; Linko, K.; Tigerstedt, I.; Tammisto, T. Intravenous Morphine and Oxycodone for Pain after Abdominal Surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1991, 35, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalso, E. Oxycodone. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2005, 29, S47–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinges, H.C.; Otto, S.; Stay, D.K.; Baumlein, S.; Waldmann, S.; Kranke, P.; Wulf, H.F.; Eberhart, L.H. Side Effect Rates of Opioids in Equianalgesic Doses via Intravenous Patient-Controlled Analgesia: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, J.L.; Cmielewski, P.L.; Reynolds, G.D.; Gourlay, G.K.; Cherry, D.A. Influence of Polarity on Dose-Response Relationships of Intrathecal Opioids in Rats. Pain 1990, 40, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöyhiä, R.; Kalso, E.A. Antinociceptive Effects and Central Nervous System Depression Caused by Oxycodone and Morphine in Rats. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1992, 70, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, M.; Nakamura, A.; Ozaki, M.; Imai, S.; Miyoshi, K.; Suzuki, M.; Suzuki, T. Comparative Pharmacological Profiles of Morphine and Oxycodone under a Neuropathic Pain-Like State in Mice: Evidence for Less Sensitivity to Morphine. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 1097–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boström, E.; Simonsson, U.S.; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M. In Vivo Blood-Brain Barrier Transport of Oxycodone in the Rat: Indications for Active Influx and Implications for Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boström, E.; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M.; Simonsson, U.S. Blood-Brain Barrier Transport Helps to Explain Discrepancies in in Vivo Potency between Oxycodone and Morphine. Anesthesiology 2008, 108, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.R.; Irvine, R.J.; Somogyi, A.A.; Bochner, F. Mu Receptor Binding of some Commonly used Opioids and their Metabolites. Life Sci. 1991, 48, 2165–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalovic, B.; Kharasch, E.; Hoffer, C.; Risler, L.; Liu-Chen, L.Y.; Shen, D.D. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Oral Oxycodone in Healthy Human Subjects: Role of Circulating Active Metabolites. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 79, 461–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, J.; Rivero, G.; Baptist, M.; Llorente, J.; Al-Sabah, S.; Krasel, C.; Dewey, W.L.; Bailey, C.P.; Rosethorne, E.M.; Charlton, S.J.; et al. Mu-Opioid Receptors: Correlation of Agonist Efficacy for Signalling with Ability to Activate Internalization. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 78, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peckham, E.M.; Traynor, J.R. Comparison of the Antinociceptive Response to Morphine and Morphine-Like Compounds in Male and Female Sprague-Dawley Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, C.M.; Wojno, H.; Greiner, E.; May, E.L.; Rice, K.C.; Selley, D.E. Activation of G-Proteins by Morphine and Codeine Congeners: Insights to the Relevance of O- and N-Demethylated Metabolites at Mu- and Delta-Opioid Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemberg, K.K.; Kontinen, V.K.; Siiskonen, A.O.; Viljakka, K.M.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J.T.; Korpi, E.R.; Kalso, E.A. Antinociception by Spinal and Systemic Oxycodone: Why does the Route make a Difference? In Vitro and in Vivo Studies in Rats. Anesthesiology 2006, 105, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, D.D.; Artru, A.A.; Adkison, K.K. Principles and Applicability of CSF Sampling for the Assessment of CNS Drug Delivery and Pharmacodynamics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1825–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapila, A.; Glass, P.S.; Jacobs, J.R.; Muir, K.T.; Hermann, D.J.; Shiraishi, M.; Howell, S.; Smith, R.L. Measured Context-Sensitive Half-Times of Remifentanil and Alfentanil. Anesthesiology 1995, 83, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Välitalo, P.; Ranta, V.P.; Hooker, A.C.; Kokki, M.; Kokki, H. Population Pharmacometrics in Support of Analgesics Studies. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2014, 58, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.M.; Lee, Y.H.; An, S.M.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, E.K.; Noh, G.J. Population Pharmacokinetics and Analgesic Potency of Oxycodone. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saari, T.I.; Ihmsen, H.; Neuvonen, P.J.; Olkkola, K.T.; Schwilden, H. Oxycodone Clearance is Markedly Reduced with Advancing Age: A Population Pharmacokinetic Study. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 108, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jessen, N.A.; Munk, A.S.; Lundgaard, I.; Nedergaard, M. The Glymphatic System: A Beginner’s Guide. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 2583–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, M.K.; Mestre, H.; Nedergaard, M. The Glymphatic Pathway in Neurological Disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benveniste, H.; Heerdt, P.M.; Fontes, M.; Rothman, D.L.; Volkow, N.D. Glymphatic System Function in Relation to Anesthesia and Sleep States. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 128, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.F.; Liu, D.X.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, F.Y.; Dai, G.Y.; Zeng, J.S.; Pei, Z.; Xu, G.Q.; Lan, Y. Voluntary Exercise Promotes Glymphatic Clearance of Amyloid Beta and Reduces the Activation of Astrocytes and Microglia in Aged Mice. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Holstein-Rathlou, S.; Petersen, N.C.; Nedergaard, M. Voluntary Running Enhances Glymphatic Influx in Awake Behaving, Young Mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 662, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benveniste, H.; Lee, H.; Ding, F.; Sun, Q.; Al-Bizri, E.; Makaryus, R.; Probst, S.; Nedergaard, M.; Stein, E.A.; Lu, H. Anesthesia with Dexmedetomidine and Low-Dose Isoflurane Increases Solute Transport via the Glymphatic Pathway in Rat Brain when Compared with High-Dose Isoflurane. Anesthesiology 2017, 127, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Vinitsky, H.S.; Sun, Q.; Staeger, F.F.; Sigurdsson, B.; Mortensen, K.N.; Lilius, T.O.; Nedergaard, M. Increased Glymphatic Influx is Correlated with High EEG Delta Power and Low Heart Rate in Mice under Anesthesia. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, F.; Zhang, C.; Xue, R.; Shan, L.; Gong, S.; Wang, G.; Tao, J.; Xu, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L. The Pathway of Subarachnoid CSF Moving into the Spinal Parenchyma and the Role of Astrocytic Aquaporin-4 in this Process. Life Sci. 2017, 182, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilius, T.O.; Blomqvist, K.; Hauglund, N.L.; Liu, G.; Staeger, F.F.; Baerentzen, S.; Du, T.; Ahlstrom, F.; Backman, J.T.; Kalso, E.A.; et al. Dexmedetomidine Enhances Glymphatic Brain Delivery of Intrathecally Administered Drugs. J. Control. Release 2019, 304, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, K.J.; Skogster, M.O.B.; Kurkela, M.J.; Rosenholm, M.P.; Ahlström, F.H.G.; Airavaara, M.T.; Backman, J.T.; Rauhala, P.V.; Kalso, E.A.; Lilius, T.O. Systemic Hypertonic Saline Enhances Glymphatic Spinal Cord Delivery of Lumbar Intrathecal Morphine. J. Control. Release 2022, 344, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, F.W.; Abrishami, A.; Brull, R. The Facilitatory Effects of Intravenous Dexmedetomidine on the Duration of Spinal Anesthesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Anesth. Analg. 2013, 117, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskuner, I.; Tekin, M.; Kati, I.; Yagmur, C.; Elcicek, K. Effects of Dexmedetomidine on the Duration of Anaesthesia and Wakefulness in Bupivacaine Epidural Block. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2007, 24, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zuylen, M.L.; Ten Hoope, W.; Bos, E.; Hermanides, J.; Stevens, M.F.; Hollmann, M.W. Safety of Epidural Drugs: A Narrative Review. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2019, 18, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, L.L.; Grell, A.M.; Garle, M.; Rane, A.; Schildt, B. Kinetics of Morphine in Cerebrospinal Fluid after Epidural Administration. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1984, 28, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, G.; Hedner, T.; Mellstrand, T.; Dahlstrom, B. Pharmacokinetic Aspects of Epidural Morphine Analgesia. Anesthesiology 1983, 58, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, G.; Hansdottir, V.; Kvist, L.; Mellstrand, T.; Hedner, T. Pharmacokinetics of Different Epidural Sites of Morphine Administration. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1987, 33, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöyhiä, R.; Seppälä, T. Liposolubility and Protein Binding of Oxycodone in Vitro. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1994, 74, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokki, M.; Franco, M.G.; Raatikainen, K.; Välitalo, P.; Sankilampi, U.; Heinonen, S.; Neuvonen, P.J.; Kokki, H. Intravenous Oxycodone for Pain Relief in the First Stage of Labour--Maternal Pharmacokinetics and Neonatal Exposure. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 111, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernards, C.M. Sophistry in Medicine: Lessons from the Epidural Space. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2005, 30, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenach, J.C.; Hood, D.D.; Tuttle, R.; Shafer, S.; Smith, T.; Tong, C. Computer-Controlled Epidural Infusion to Targeted Cerebrospinal Fluid Concentrations in Humans. Clonidine. Anesthesiology 1995, 83, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juul, R.V.; Nyberg, J.; Lund, T.M.; Rasmussen, S.; Kreilgaard, M.; Christrup, L.L.; Simonsson, U.S. A Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Model of Morphine Exposure and Subsequent Morphine Consumption in Postoperative Pain. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambic, C.R.; Avram, M.J.; Gupta, D.K.; Wong, C.A. Effect of Ritonavir-Induced Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibition on Plasma Fentanyl Concentrations during Patient-Controlled Epidural Labor Analgesia: A Pharmacokinetic Simulation. Int. J. Obstet. Anesth. 2014, 23, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, N.; Orlov, D.; Alie, T.; Chong, M.; Cheng, J.; Thabane, L.; Paul, J. What Epidural Opioid Results in the Best Analgesia Outcomes and Fewest Side Effects after Surgery?: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Anesth. Analg. 2014, 119, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokki, M.; Pesonen, M.; Vehviläinen, P.; Litmala, O.; Pasanen, M.; Kokki, H. Cytotoxicity of Oxycodone and Morphine in Human Neuroblastoma and Mouse Motoneuronal Cells: A Comparative Approach. Drugs R D 2016, 16, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coombs, D.W.; Colburn, R.W.; DeLeo, J.A.; Hoopes, P.J.; Twitchell, B.B. Comparative Spinal Neuropathology of Hydromorphone and Morphine after 9- and 30-Day Epidural Administration in Sheep. Anesth. Analg. 1994, 78, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaney, M.A. Side Effects of Intrathecal and Epidural Opioids. Can. J. Anaesth. 1995, 42, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Drug | Species | Fcsf (%) | tmax-csf (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lidocaine | Rabbit | 18 | 7.0 | [53] |
| Bupivacaine | Rabbit | 13 | 6.8 | [54] |
| Rabbit | 5.5 | 5.6 | [53] | |
| Ropivacaine | Rabbit | 11 | 6.8 | [54] |
| Sheep | 11 | 12 | [55] | |
| Morphine | Goat | 2.3–11 * | 13 | [56] |
| Man | 3.2 1.9 3.6 | 56 135 80 | [49,57,58] | |
| Sufentanil | Man -bolus -infusion | 2.7 0.4–0.7 | 46–126 ** | [59,60] |
| Fentanyl | Goat | 0.8–3.3 * | 13 | [56] |
| Clonidine | Sheep | 14 | 32 | [61] |
| Dexmedetomidine | Sheep | 22 | 12 | [62] |
| Study | Epidural Group 1 | Epidural Group 2 | Control Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bäcklund et al., 1997 | Epid. oxycodone 0.15 mg kg−1 + infusion 0.03 mg kg−1 h−1 | Epid. morphine 0.015 mg kg−1 + infusion 0.003 mg kg−1 h−1 | i.v. oxycodone 0.15 mg kg−1 + infusion 0.03 mg kg−1 h−1 |
| Yanagidate and Dohi 2004 | Epid. oxycodone 2 mg with 25 mg bupivacaine + oxycodone infusion 6 mg d−1 | Epid. oxycodone 4 mg with 25 mg bupivacaine 10 mL + oxycodone infusion 12 mg d−1 | Epid. morphine 2 mg with 25 mg bupivacaine 10 mL + morphine infusion 6 mg d−1 |
| Piirainen et al., 2018 | Epid. oxycodone 0.1 mg kg−1 | i.v. oxycodone 0.1 mg kg−1 | |
| Piirainen et al., 2019 | Epid. oxycodone 0.1 mg kg−1 | i.v. oxycodone 0.1 mg kg−1 | |
| Xie et al., 2022 | Epid. oxycodone 2.5 mg with ropivacaine in 15 mL | Epidural oxycodone 5 mg with ropivacaine in 15 mL | Epidural ropivacaine 15 mL |
| Variable | Morphine | Sufentanil | Oxycodone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Administration Site | Administration Site | Administration Site | |||
| L2–3 | Th7–8 | L2–3 or L3–4 | Th5–6 or Th6–7 | Th12–L1 or L1–2 | |
| Plasma | mean (SD) | mean (SD) | median (range) | ||
| Cmax (ng·mL−1) | 16.3 (2.5) | 0.40 (0.14) | 0.26 (0.15) | 29 (14–77) | |
| tmax (h) | 0.15 (0.08) | 0.12 (0.12) | 0.27 (0.20) | 2.1 (0.6–4.2) | |
| AUC (ng·h·mL−1) | 1.2 (0.4) | 1.5 (0.3) | 201 (140–500) | ||
| t½ (h) | 4.1 (1.2) | 6.3 (2.9) | 3.8 (3.1–5.1) | ||
| CSF lumbar | L3–4 | L3–4 or L4–5 | L3–4 | ||
| Cmax-CSF (ng·mL−1) | 390 (139) | 206 (120) | 17.8 (29.6) | 2.2 (4.9) | 10,000 (982–10,000) * |
| Cmax-CSF dose−1 (ng·mL−1) | 2.0 × 10−4 (7.0 × 10−5) | 1.0 × 10−4 (6 × 10−5) | 2.4 × 10−4 (4.0 × 10−4) | 2.9 × 10−5 (6.5 × 10−5) | 1.6 × 10−3 (1.5 × 10−4–1.6 × 10−3) |
| tmax-CSF (h) | 2.4 (2.9) | 3.6 (2.3) | 0.8 (0.5) | 2.1 (1.4) | 0.6 (0.2–4.0) |
| AUCCSF (ng·h·mL−1) | 2700 (925) | 1370 (465) | 22.9 (25.8) | 4.9 (7.9) | 23,000 (8300–42,000) |
| AUCCSF dose−1 (ng·h·mL−1) | 1.4 × 10–3 (4.6 × 10−4) | 6.9 × 10–4 (2.3 × 10−4) | 3.1 × 10–4 (3.4 × 10−4) | 6.5 × 10–5 (1.1 × 10−4) | 3.6 × 10−3 (1.3 × 10−3–6.6 × 10−3) |
| t½-CSF (h) | 2.8 (0.9) | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piirainen, P.; Kokki, H.; Kokki, M. Epidural Oxycodone for Acute Pain. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050643
Piirainen P, Kokki H, Kokki M. Epidural Oxycodone for Acute Pain. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(5):643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050643
Chicago/Turabian StylePiirainen, Panu, Hannu Kokki, and Merja Kokki. 2022. "Epidural Oxycodone for Acute Pain" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 5: 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050643
APA StylePiirainen, P., Kokki, H., & Kokki, M. (2022). Epidural Oxycodone for Acute Pain. Pharmaceuticals, 15(5), 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050643