One-Step Automatic Radiosynthesis and Evaluation of [18F]TM-30089 as GPR44 Radiotracer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Efficient Identification of Promising 18F-Labeled GPR44 Radioligands (Non-Radioactivity Synthesis Section)
2.2. Establishment of Murine Models for the Evaluation of GPR44 Radioligands
2.2.1. NOD/SCID Mouse Model with a 1.1 B4 Tumor Cell Line
2.2.2. NOD/SCID Mouse Model Transplanted with Human Islets
2.3. Radiosynthesis of [18F]TM-30089
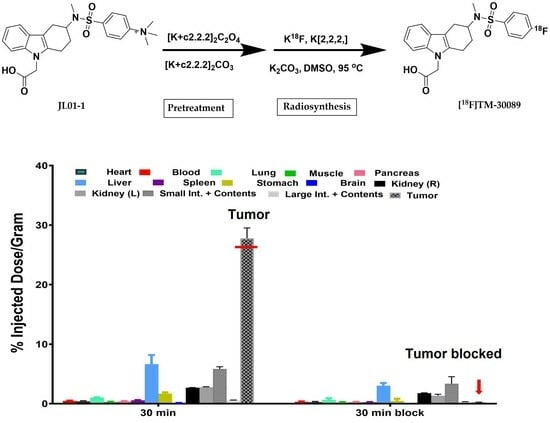
2.4. Biodistribution
2.5. Feasibility and Acceptability of Screening Strategy
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cells and Animals
3.1.1. Xenograft Tumor Model
3.1.2. Islet Transplantation
3.2. Western Blot Analysis
3.3. Histology Study
3.4. General Procedure for the Pretreatment of Precursor JL01-1
3.4.1. Preparation of [K+c2.2.2]2CO3
3.4.2. Preparation of [K+c2.2.2]2C2O4
3.4.3. Pretreatment of Precursor 4-(N-(9-(Carboxymethyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazol-3-yl)-N-methylsulfamoyl)-N,N,N-trimethylbenzenaminium
3.5. Radiosynthesis of [18F]TM-30089
3.5.1. Automatic Synthesis of [18F]TM-30089
3.5.2. Quality Control (QC)
3.6. Biodistributions
3.6.1. Biodistribution of [18F]TM30089 in NOD/SCID Control Mice
3.6.2. Biodistribution of [18F]TM30089 in NOD/SCID Mice with 1.1 B4 Cells
3.6.3. Biodistribution of [18F]TM-30089 in NOD/SCID Mice with Transplanted Human Islets in a Renal Capsule
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ann, V.; Hertzel, T.D.O.C.; Bernlohr, D.A. Chapter 6-Lipid receptors and signaling in adipose tissue. In Lipid Signaling and Metabolism; Ntambi, J.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 2020, pp. 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Monneret, G.; Gravel, S.; Diamond, M.; Rokach, J.; Powell, W.S. Prostaglandin D2 is a potent chemoattractant for human eosinophils that acts via a novel DP receptor. Blood 2001, 98, 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, A.; Sawzdargo, M.; Nguyen, T.; Cheng, R.; Heng, H.H.; Nowak, T.; Im, D.S.; Lynch, K.R.; George, S.R.; O’Dowd, B.F. Discovery of three novel orphan G-protein-coupled receptors. Genomics 1999, 56, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yao, D.; Deepak, R.; Liu, H.; Xiao, Q.; Fan, H.; Gong, W.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, C. Structures of the Human PGD(2) Receptor CRTH2 Reveal Novel Mechanisms for Ligand Recognition. Mol. Cell 2018, 72, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, N.; Cauchon, E.; Chateauneuf, A.; Cruz, R.P.; Nicholson, D.W.; Metters, K.M.; O’Neill, G.P.; Gervais, F.G. Molecular pharmacology of the human prostaglandin D2 receptor, CRTH2. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 137, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimarco, A.; Forese, M.G.; Alfieri, V.; Lucente, A.; Brambilla, P.; Dina, G.; Pieragostino, D.; Sacchetta, P.; Urade, Y.; Boizet-Bonhoure, B.; et al. Prostaglandin D2 synthase/GPR44: A signaling axis in PNS myelination. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 1682–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Yan, X.X.; Nagata, N.; Aritake, K.; Katsumata, Y.; Matsuhashi, T.; Nakamura, M.; Hirai, H.; Urade, Y.; Asano, K.; et al. PGD(2)-CRTH2 Pathway Promotes Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1797–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radnai, B.; Sturm, E.M.; Stancic, A.; Jandl, K.; Labocha, S.; Ferreiros, N.; Grill, M.; Hasenoehrl, C.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Marsche, G.; et al. Eosinophils Contribute to Intestinal Inflammation via Chemoattractant Receptor-homologous Molecule Expressed on Th2 Cells, CRTH2, in Experimental Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2016, 10, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojno, E.D.; Monticelli, L.A.; Tran, S.V.; Alenghat, T.; Osborne, L.C.; Thome, J.J.; Willis, C.; Budelsky, A.; Farber, D.L.; Artis, D. The prostaglandin D(2) receptor CRTH2 regulates accumulation of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the inflamed lung. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarashina, H.; Tsubosaka, Y.; Omori, K.; Aritake, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Hori, M.; Hirai, H.; Nakamura, M.; Narumiya, S.; Urade, Y.; et al. Opposing immunomodulatory roles of prostaglandin D2 during the progression of skin inflammation. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Haroun, S.; Parent, J.L.; de Brum-Fernandes, A.J. Prostaglandin D-2 induces apoptosis of human osteoclasts through ERK1/2 and Akt signaling pathways. Bone 2014, 60, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandl, K.; Heinemann, A. The therapeutic potential of CRTH2/DP2 beyond allergy and asthma. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017, 133, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, J.; Thadhani, E.; Samson, L.; Engelward, B. Inflammation-induced DNA damage, mutations and cancer. DNA Repair 2019, 83, 102673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Hong, Y.; Liu, T.; Ding, Z. Nomogram Personalizes and Visualizes the Overall Survival of Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Based on the Immune Genome. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 4029062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.B.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zhu, M.X.; Wang, L. Prognostic Signatures Based on Thirteen Immune-Related Genes in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 591739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Qiu, S.J.; Zhou, J.; Shi, Y.H.; Zhang, B.H.; Fan, J. Tumor stroma reaction-related gene signature predicts clinical outcome in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bie, Q.; Zhang, P.; Su, Z.; Zheng, D.; Ying, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, S.; Xu, H. Polarization of ILC2s in peripheral blood might contribute to immunosuppressive microenvironment in patients with gastric cancer. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 923135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabanelli, S.; Chevalier, M.F.; Martinez-Usatorre, A.; Gomez-Cadena, A.; Salome, B.; Lecciso, M.; Salvestrini, V.; Verdeil, G.; Racle, J.; Papayannidis, C.; et al. Tumour-derived PGD2 and NKp30-B7H6 engagement drives an immunosuppressive ILC2-MDSC axis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzurana, L.; Czarnewski, P.; Jonsson, V.; Wigge, L.; Ringner, M.; Williams, T.C.; Ravindran, A.; Bjorklund, A.K.; Safholm, J.; Nilsson, G.; et al. Tissue-specific transcriptional imprinting and heterogeneity in human innate lymphoid cells revealed by full-length single-cell RNA-sequencing. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lullo, G.; Marcatti, M.; Heltai, S.; Brunetto, E.; Tresoldi, C.; Bondanza, A.; Bonini, C.; Ponzoni, M.; Tonon, G.; Ciceri, F.; et al. Th22 cells increase in poor prognosis multiple myeloma and promote tumor cell growth and survival. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1005460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadpour, S.; Tyrberg, B.; Schive, S.W.; Huldt, C.W.; Gennemark, P.; Ryberg, E.; Ryden-Bergsten, T.; Smith, D.M.; Korsgren, O.; Skrtic, S.; et al. Inhibition of the prostaglandin D(2)-GPR44/DP2 axis improves human islet survival and function. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrtic, S.; Tyrberg, B.; Broberg, M.; Ericsson, H.; Schnecke, V.; Kjaer, M.; Hompesch, M.; Andersson, E.M.; Ryberg, E.; Aivazidis, A.; et al. Exploring the insulin secretory properties of the PGD2-GPR44/DP2 axis in vitro and in a randomized phase-1 trial of type 2 diabetes patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, O. GPR44 as a Target for Imaging Pancreatic Beta-Cell Mass. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2019, 19, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindskog, C.; Korsgren, O.; Ponten, F.; Eriksson, J.W.; Johansson, L.; Danielsson, A. Novel pancreatic beta cell-specific proteins: Antibody-based proteomics for identification of new biomarker candidates. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellstrom-Lindahl, E.; Danielsson, A.; Ponten, F.; Czernichow, P.; Korsgren, O.; Johansson, L.; Eriksson, O. GPR44 is a pancreatic protein restricted to the human beta cell. Acta Diabetol. 2016, 53, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehllehner, G.; Karp, J.S. Positron emission tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, R117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, J.; Roy, T.; Sawadjoon, S.; Bachmann, K.; Skold, C.; Larhed, M.; Weis, J.; Selvaraju, R.K.; Korsgren, O.; Eriksson, O.; et al. Synthesis and preclinical evaluation of the CRTH2 antagonist [(11)C]MK-7246 as a novel PET tracer and potential surrogate marker for pancreatic beta-cell mass. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2019, 71, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, O.; Johnstrom, P.; Cselenyi, Z.; Jahan, M.; Selvaraju, R.K.; Jensen-Waern, M.; Takano, A.; Sorhede Winzell, M.; Halldin, C.; Skrtic, S.; et al. In Vivo Visualization of beta-Cells by Targeting of GPR44. Diabetes 2018, 67, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.; Amin, M.A.; Zhang, B.; Lechi, F.; Korsgren, O.; Eriksson, J.; Odell, L.R.; Eriksson, O. [(18)F]MK-7246 for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of the Beta-Cell Surface Marker GPR44. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.A.; Huang, K.X.; Tu, J.; Kandeel, F.; Li, J.F. Ramatroban-Based Analogues Containing Fluorine Group as Potential F-18-Labeled Positron Emission Tomography (PET) G-Protein Coupled Receptor 44 (GPR44) Tracers. Molecules 2021, 26, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.H.; Huang, K.X.; Huang, L.A.; Ji, M.; Zhao, H.; Li, K.; Gao, A.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, T.; et al. Indole-Based and Cyclopentenylindole-Based Analogues Containing Fluorine Group as Potential 18F-Labeled Positron Emission Tomography (PET) G-Protein Coupled Receptor 44 (GPR44) Tracers. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uller, L.; Mathiesen, J.M.; Alenmyr, L.; Korsgren, M.; Ulven, T.; Hogberg, T.; Andersson, G.; Persson, C.G.; Kostenis, E. Antagonism of the prostaglandin D2 receptor CRTH2 attenuates asthma pathology in mouse eosinophilic airway inflammation. Respir. Res. 2007, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizuka, T.; Matsui, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Ohta, A.; Shichijo, M. Ramatroban (BAY u 3405): A novel dual antagonist of TXA2 receptor and CRTh2, a newly identified prostaglandin D2 receptor. Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 2004, 22, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, H.; Rawson, J.; Medrano, L.; Cook, C.A.; Barriga, A.; Gonzalez, N.; Salgado, M.; Omori, K.; Kandeel, F.; Tai, Y.C.; et al. Optimizing Temperature and Oxygen Supports Long-term Culture of Human Islets. Transplantation 2019, 103, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omori, K.; Valiente, L.; Orr, C.; Rawson, J.; Ferreri, K.; Todorov, I.; Al-Abdullah, I.H.; Medicherla, S.; Potter, A.A.; Schreiner, G.F.; et al. Improvement of human islet cryopreservation by a p38 MAPK inhibitor. Am. J. Transpl. 2007, 7, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, J.; Tang, W.; Rawson, J.; Miao, L.; Gonzalez, N.; Yin, R.; Chen, J.; Ji, M.; Li, Z.; Gao, A.; et al. One-Step Automatic Radiosynthesis and Evaluation of [18F]TM-30089 as GPR44 Radiotracer. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101480
Peng J, Tang W, Rawson J, Miao L, Gonzalez N, Yin R, Chen J, Ji M, Li Z, Gao A, et al. One-Step Automatic Radiosynthesis and Evaluation of [18F]TM-30089 as GPR44 Radiotracer. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(10):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101480
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Jiangling, Wei Tang, Jeffrey Rawson, Lynn Miao, Nelson Gonzalez, Runkai Yin, Jiaqi Chen, Melinda Ji, Zhixuan Li, Anna Gao, and et al. 2023. "One-Step Automatic Radiosynthesis and Evaluation of [18F]TM-30089 as GPR44 Radiotracer" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 10: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101480
APA StylePeng, J., Tang, W., Rawson, J., Miao, L., Gonzalez, N., Yin, R., Chen, J., Ji, M., Li, Z., Gao, A., Wu, A. Z., Shively, J. E., Kandeel, F., & Li, J. (2023). One-Step Automatic Radiosynthesis and Evaluation of [18F]TM-30089 as GPR44 Radiotracer. Pharmaceuticals, 16(10), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101480