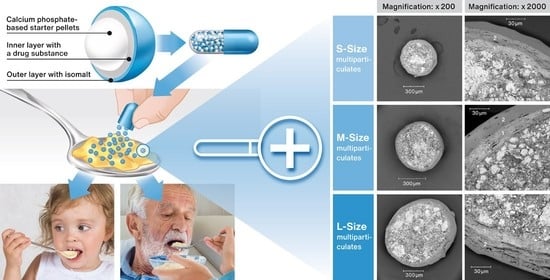
The Use of Calcium Phosphate-Based Starter Pellets for the Preparation of Sprinkle IR MUPS Formulation of Rosuvastatin Calcium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of RSC Multiparticulates
2.2. Effectiveness of Taste Masking
2.3. Dissolution Test
2.4. Release of RSC on Various Vehicles
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation and Characterization of RSC Multiparticulates
4.2. Analysis of Taste Masking Efficiency with an E-Tongue
4.3. Dissolution Tests
4.4. Release of RSC on Various Vehicles
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farpour, S.; Farpour, H.R.; Smithard, D.G. Oropharyngeal dysphagia and its related health problems in Iranian elderly people: A scope of work for the future. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 21, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, N. The prevalence of dysphagia among adults in the United States. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 151, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnaby-Mann, G.; Crary, M. Pill Swallowing by adults with dysphagia. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 131, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlowska, H.; Szymanska, M.; Sznitowska, M. Comparison of different liquid and semisolid vehicles selected for oral administration of pellets and minitablets with diazepam: In Vitro investigation. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020, 21, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloyd, J.C.; Kriel, R.L.; Jones-Saete, C.M.; Ong, B.Y.; Jancik, J.T.; Remmel, R.P. Comparison of sprinkle versus syrup formulations of valproate for bioavailability, tolerance, and preference. J. Pediatr. 1992, 120, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, M.G.; Kim, K.T.; Cho, C.W.; Kim, D.D.; Lee, J.Y. Sprinkle formulations—A review of commercially available products. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 15, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drugs Administration Guidance for Industry. Size of Beads in Drug Products Labeled for Sprinkle. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/size-beads-drug-products-labeled-sprinkle-rev1 (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- US Food and Drugs Administration Guidance for Industry. Use of Liquids and/or Soft Foods as Vehicles for Drug Administration: General Considerations for Selection and In Vitro Methods for Product Quality Assessments. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/use-liquids-andor-soft-foods-vehicles-drug-administration-general-considerations-selection-and-vitro (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Zakowiecki, D.; Frankiewicz, M.; Hess, T.; Cal, K.; Gajda, M.; Dabrowska, J.; Kubiak, B.; Paszkowska, J.; Wiater, M.; Hoc, D.; et al. Development of a biphasic-release Multiple-Unit Pellet System with diclofenac sodium using novel calcium phosphate-based starter pellets. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, E.S.K.; Chan, L.W.; Heng, P.W.S. Coating of multiparticulates for sustained release. Am. J. Drug Deliv. 2005, 3, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, N.; Avari, J. Formulation and evaluation of taste mask pellets of granisetron hydrochloride as orodispersible tablet. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 51, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kállai-Szabó, N.; Lengyel, M.; Farkas, D.; Barna, Á.T.; Fleck, C.; Basa, B.; Antal, I. Review on Starter Pellets: Inert and Functional Cores. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, E.; Benaiges, D.; Pedro-Botet, J. Hydrophilic or lipophilic statins? Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 687585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AstraZeneca. Crestor (Rosuvastatin Calcium) Tablets Rev 01/05. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2005/21366slr005lbl.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Piecha, M.; Sarakha, M.; Trebse, P.; Kocar, D. Stability studies of cholesterol lowering statin drugs in aqueous samples using HPLC and LC–MS. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgic, M. Stable Rosuvastatin Formulations. WO/2011/139256, 10 November 2011. Available online: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2011139256 (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Virágh, M.; Monostori, I. Pharmaceutical Compositions Containing Rosuvastatin Calcium. WO/2008/035128, 27 March 2008. Available online: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2008035128 (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Ocepek, U.; Vrecer, F.; Toporisic, R.; Bukovec, P.; Jursic, U. Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising a Statin. WO/2009/156173, 30 December 2009. Available online: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2009156173 (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Creekmore, J.R.; Wiggins, N.A. Pharmaceutical Compositions Comprising a HMG Reductase Inhibitor. WO/2001/054668, 2 August 2001. Available online: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2001054668 (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Creekmore, J.R.; Wiggins, N.A. Pharmaceutical Compositions. U.S. Patent US6548513B1, 15 April 2003. Available online: https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/aa/8a/7c/504152a8ca6c13/US6548513.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Zakowiecki, D.; Hess, T.; Cal, K.; Mikolaszek, B.; Garbacz, G.; Haznar-Garbacz, D. Directly compressible formulation of immediate release rosuvastatin calcium tablets stabilized with tribasic calcium phosphate. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2022, 27, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakowiecki, D.; Lachmann, M.; Schaum, V.; Hess, T. Novel starter pellets based on dibasic calcium phosphate anhydrous: Properties and application. Express Pharm. 2019, 15, 34–36. Available online: https://www.expresspharma.in/novel-starter-pellets-based-on-dibasic-calcium-phosphate-anhydrous-properties-and-application/ (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Zakowiecki, D.; Szczepanska, M.; Hess, T.; Cal, K.; Mikolaszek, B.; Paszkowska, J.; Wiater, M.; Hoc, D.; Garbacz, G. Preparation of delayed-release multiparticulate formulations of diclofenac sodium and evaluation of their dissolution characteristics using biorelevant dissolution methods. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 101986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual Cruz, M.; Chimenos Küstner, E.; García Vicente, J.A.; Mezquiriz Ferrero, X.; Borrell Thio, E.; López López, J. Adverse side effects of statins in the oral cavity. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2008, 13, E98–E101. Available online: http://www.medicinaoral.com/pubmed/medoralv13_i2_pE98.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Tahamtan, S.; Shirban, F.; Bagherniya, M.; Johnston, T.P.; Sahebkar, A. The effects of statins on dental and oral health: A review of preclinical and clinical studies. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jańczyk, M.; Kutyła, A.; Sollohub, K.; Wosicka, H.; Cal, K.; Ciosek, P. Electronic tongue for the detection of taste-masking microencapsulation of active pharmaceutical substances. Bioelectrochemistry 2010, 80, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesoły, M.; Cal, K.; Ciosek, P.; Wróblewski, W. Influence of dissolution-modifying excipients in various pharmaceutical formulations on electronic tongue results. Talanta 2017, 162, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun Pharma. Dysphagia and Rosuvastatin Capsules for Sprinkling; Pulse: London, UK, 2022; Available online: https://www.pulsetoday.co.uk/sponsored/sponsored-by-sun-pharma/dysphagia-rosuvastatin/ (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Radhakrishnan, C.; Sefidani Forough, A.; Cichero, J.A.Y.; Smyth, H.E.; Raidhan, A.; Nissen, L.M.; Steadman, K.J. A Difficult pill to swallow: An investigation of the factors associated with medication swallowing difficulties. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2021, 15, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiele, J.T.; Quinzler, R.; Klimm, H.D.; Pruszydlo, M.G.; Haefeli, W.E. Difficulties swallowing solid oral dosage forms in a general practice population: Prevalence, causes, and relationship to dosage forms. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 69, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun Pharma Launches Ezallor Sprinkle (Rosuvastatin) in the U.S. for People Who Have Difficulty Swallowing. Available online: https://sunpharma.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Press-Release-launch-of-Ezallor-Sprinkle-Rosuvastatin-in-the-US.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Ernst, D. FDA Approves Sprinkle Formulation of Rosuvastatin. Available online: https://www.empr.com/home/news/fda-approves-sprinkle-formulation-of-rosuvastatin/ (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Handattu, M.S.; Thirumaleshwar, S.; Prakash, G.M.; Somareddy, H.K.; Veerabhadrappa, G.H. A Comprehensive Review on Pellets as a Dosage Form, in Pharmaceuticals. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, S.; Chandewar, A.V.; Jaiswal, S.B. A flexible technology for modified-release drugs: Multiple-unit pellet system (MUPS). J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.G.; Patel, S.A.; Joshi, A. Multiple unit pellet system (MUPS technology) for development of modified release fast disintegrating tablets: A review. J. Pharm. Sci. Innov. 2017, 6, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Hong, X.; Han, X.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Liu, N.; Gao, X.; et al. Taste masking study based on an electronic tongue: The formulation design of 3D printed levetiracetam instant-dissolving tablets. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Douroumis, D. An in-vitro-in-vivo taste assessment of bitter drug: Comparative electronic tongues study. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podrazka, M.; Bączynska, E.; Kundys, M.; Jelen, P.S.; Witkowska Nery, E. Electronic tongue - a tool for all tastes? Biosensors 2017, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Ahmed, S.; Yuen, K.H.; Sarfraz, M.K.; Akhtar, M. Influence of drug solubility, binders and pellet size in formulating sustained release pellets. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2010, 29, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar]
- Soltani, F.; Kamali, H.; Akhgari, A.; Garekani, H.A.; Nokhodchi, A.; Sadeghi, F. Different trends for preparation of budesonide pellets with enhanced dissolution rate. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JRS Pharma GmbH & Co. Technical information: Performance of MCC spheres and sugar spheres in a multi-particulate omeprazole formulation. Available online: https://www.jrspharma.com/pharma-wAssets/docs/technical-information/ti_mcc-spheres-vs-sugar-spheres_gb_1609.pdf (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Tsukasa, S.; Katsuki, N.; Koki, H.; Yoshinori, N. Rosuvastatin-Containing Intraoral Quick Disintegrating Tablets. Japanese Patent JP6108635B2, 5 April 2017. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/JP6108635B2/en (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Yates, L.B. Adverse oral effects of statins. In Proceedings of UCLA Healthcare; UCLA Department of Medicine: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2020; Volume 24, Available online: https://proceedings.med.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Yates-A200610LY-BLM-formatted.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Wasilewska, K.; Szekalska, M.; Ciosek-Skibinska, P.; Lenik, J.; Basa, A.; Jacyna, J.; Markuszewski, M.; Winnicka, K. Ethylcellulose in organic solution or aqueous dispersion form in designing taste-masked microparticles by the spray drying technique with a model bitter drug: Rupatadine fumarate. Polymers 2019, 11, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łabańska, M.; Ciosek-Skibińska, P.; Wróblewski, W. Critical Evaluation of laboratory potentiometric electronic tongues for pharmaceutical analysis—An overview. Sensors 2019, 19, 5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshora, D.H.; Haq, N.; Alanazi, F.K.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Shakeel, F. Solubility of rosuvastatin calcium in different neat solvents at different temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 94, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, S.; Hasan, S.M.F.; Hassan, M.M.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Neau, S.H. Directly compressed rosuvastatin calcium tablets that offer hydrotropic and micellar solubilization for improved dissolution rate and extent of drug release. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, P.R.; Shaikh, K.S.; Chaudhari, P.D. Application of liquisolid technology for enhancing solubility and dissolution of rosuvastatin. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 4, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Pellet Size: Coating Step | Inlet Airflow Rate (m3/min) | Inlet Air Temperature (°C) | Product Temperature(°C) | Coating Mixture Flow Rate (g/min) | Nozzle Airflow (dm3/min) | Spraying Pressure (bar) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size S:step 1 | 0.19 ± 0.1 | 65 ± 2 | 43.5 ± 2 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 8.3 ± 0.1 | 1.07 ± 0.2 |
| Size S:step 2 | 0.22 ± 0.1 | 65 ± 2 | 46.0 ± 2 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 8.7 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.2 |
| Size M:step 1 | 0.17 ± 0.1 | 60 ± 2 | 42.5 ± 2 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 10.1 ± 0.1 | 1.07 ± 0.2 |
| Size M:step 2 | 0.19 ± 0.1 | 65 ± 2 | 40.0 ± 2 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 10.1 ± 0.1 | 1.07 ± 0.2 |
| Size L:step 1 | 0.17 ± 0.1 | 60 ± 2 | 42.5 ± 2 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 10.1 ± 0.1 | 1.07 ± 0.2 |
| Size L:step 2 | 0.19 ± 0.1 | 65 ± 2 | 40.0 ± 2 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 10.1 ± 0.1 | 1.07 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cal, K.; Mikolaszek, B.; Hess, T.; Papaioannou, M.; Lenik, J.; Ciosek-Skibińska, P.; Wall, H.; Paszkowska, J.; Romanova, S.; Garbacz, G.; et al. The Use of Calcium Phosphate-Based Starter Pellets for the Preparation of Sprinkle IR MUPS Formulation of Rosuvastatin Calcium. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020242
Cal K, Mikolaszek B, Hess T, Papaioannou M, Lenik J, Ciosek-Skibińska P, Wall H, Paszkowska J, Romanova S, Garbacz G, et al. The Use of Calcium Phosphate-Based Starter Pellets for the Preparation of Sprinkle IR MUPS Formulation of Rosuvastatin Calcium. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(2):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020242
Chicago/Turabian StyleCal, Krzysztof, Barbara Mikolaszek, Tobias Hess, Markos Papaioannou, Joanna Lenik, Patrycja Ciosek-Skibińska, Helene Wall, Jadwiga Paszkowska, Svitlana Romanova, Grzegorz Garbacz, and et al. 2023. "The Use of Calcium Phosphate-Based Starter Pellets for the Preparation of Sprinkle IR MUPS Formulation of Rosuvastatin Calcium" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 2: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020242
APA StyleCal, K., Mikolaszek, B., Hess, T., Papaioannou, M., Lenik, J., Ciosek-Skibińska, P., Wall, H., Paszkowska, J., Romanova, S., Garbacz, G., & Zakowiecki, D. (2023). The Use of Calcium Phosphate-Based Starter Pellets for the Preparation of Sprinkle IR MUPS Formulation of Rosuvastatin Calcium. Pharmaceuticals, 16(2), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020242