Effect of Betanin, the Major Pigment of Red Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.), on the Activity of Recombinant Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
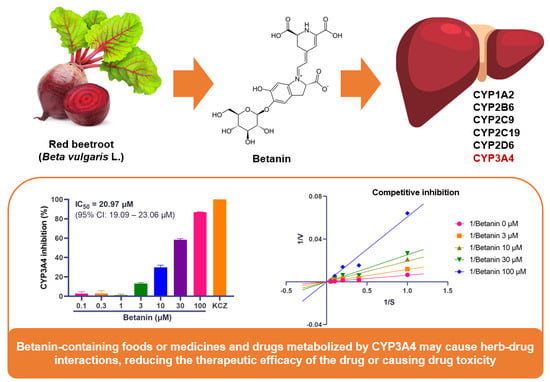
2.1. Inhibitory Effect of Betanin on CYP Activity Using Fluorescence-Based Assay
2.2. Inhibitory Mechanism of Betanin on CYP Enzyme Activity
2.3. Induction Effect of Betanin on CYP Activity Using Luminescence-Based Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Recombinant CYPs
4.2. Fluorescence-Based CYP Inhibition Assay
4.3. Determination of CYP Activity
4.4. HepG2 Cell Culture and Viability Assay
4.5. Luminescence-Based CYP Induction Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BOMCC | 7-benzyloxymethyloxy-3-cyanocoumarin |
| BPP | bupropion |
| CYPs | cytochrome P450 enzymes |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EOMCC | 7-ethoxymethoxy-3-cyanocoumarin |
| FRL | furafylline |
| FVX | fluvoxamine |
| HDIs | herb–drug interactions |
| KCZ | ketoconazole |
| Ki | inhibition constant |
| MEM | Minimum Essential Medium |
| OPZ | omeprazole |
| P-gp | P-glycoprotein |
| QND | quinidine |
| RFC | rifampicin |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
References
- Yuan, H.; Ma, Q.; Ye, L.; Piao, G. The Traditional Medicine and Modern Medicine from Natural Products. Molecules 2016, 21, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, E.; Samuel, S.M.; Abotaleb, M.; Cheema, S.; Mamtani, R.; Büsselberg, D. The “Yin and Yang” of Natural Compounds in Anticancer Therapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. Cancers 2018, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordell, G.A.; Colvard, M.D. Natural Products and Traditional Medicine: Turning on a Paradigm. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikram, M.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Kifayatullah, M.; Olukanni, A.; Zahoor, M.; Naeem, M.; Amin, M.; Shah, M.; Abdelaziz, A.S.; Ullah, R.; et al. Chemotherapeutic Potential of Carthamus Oxycantha Root Extract as Antidiarrheal and In Vitro Antibacterial Activities. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, M.; Ikram, M.; Nazir, N.; Naz, S.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Kamran, A.W.; Tomczyk, M.; Kabrah, A. A Comprehensive Review on the Medicinal Importance; Biological and Therapeutic Efficacy of Lagenaria Siceraria (Mol.) (Bottle Gourd) Standley Fruit. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 1788–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.-S.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Ikram, M.; Mulla, Z.S.; El-Hack, M.E.A.; Taha, A.E.; Algammal, A.M.; Elewa, Y.H.A. The Pharmacological Activity, Biochemical Properties, and Pharmacokinetics of the Major Natural Polyphenolic Flavonoid: Quercetin. Foods 2020, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.U.; Forman, J.D.; Sarkar, F.; Hillman, G.; Banerjee, M.; Doerge, D.; Heath, E.; Vaishampayan, U.; Cher, M.; Kucuk, O. Reduction of Adverse Events by Soy Isoflavones in Patients Undergoing External Beam Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 72, S318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.; Malik, A.; Qureshi, M.S.; Manan, A.; Pushparaj, P.N.; Asif, M.; Qazi, M.H.; Qazi, A.M.; Kamal, M.A.; Gan, S.H.; et al. Recent Updates in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders Using Natural Compounds. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. ECAM 2014, 2014, 979730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.S.; Sultan, M.T.; Butt, M.S.; Iqbal, J. Garlic: Nature’s Protection against Physiological Threats. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasole, R.; Martin, H.D.; Kimiywe, J. Traditional Medicine and Its Role in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus: “Patients’ and Herbalists’ Perspectives”. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. ECAM 2019, 2019, 2835691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramsoltani, R.; Rahimi, R.; Farzaei, M.H. Pharmacokinetic Interactions of Curcuminoids with Conventional Drugs: A Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 209, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Duan, L.X.; Wu, J.J.; Hu, M.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wang, C.Y. Potential of Herb-Drug / Herb Interactions between Substrates and Inhibitors of UGTs Derived from Herbal Medicines. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 150, 104510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.G.; Eom, S.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.H.; Huh, E.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, H.; Oh, M.S. A Comprehensive Review of Recent Studies on Herb-Drug Interaction: A Focus on Pharmacodynamic Interaction. J. Altern. Complement. Med. N. Y. 2016, 22, 262–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanapi, N.A.; Azizi, J.; Ismail, S.; Mansor, S.M. Evaluation of Selected Malaysian Medicinal Plants on Phase I Drug Metabolizing Enzymes, CYP2C9, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 Activities in Vitro. IJP—Int. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 6, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guengerich, F.P. Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. In Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry, 4th ed.; Ortiz de Montellano, P.R., Ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2015; pp. 523–785. ISBN 978-3-319-12108-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zanger, U.M.; Schwab, M. Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in Drug Metabolism: Regulation of Gene Expression, Enzyme Activities, and Impact of Genetic Variation. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 103–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usia, T.; Watabe, T.; Kadota, S.; Tezuka, Y. Potent CYP3A4 Inhibitory Constituents of Piper Cubeba. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, H.-H.S.; Hakim, I.A.; Vining, D.R.; Crowell, J.A.; Cordova, C.A.; Chew, W.M.; Xu, M.-J.; Hsu, C.-H.; Ranger-Moore, J.; Alberts, D.S. Effects of Repeated Green Tea Catechin Administration on Human Cytochrome P450 Activity. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 2473–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werba, J.P.; Giroli, M.; Cavalca, V.; Nava, M.C.; Tremoli, E.; Dal Bo, L. The Effect of Green Tea on Simvastatin Tolerability. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 149, 286–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.; Buddha, B.; Dey, S.; Pal, D.; Mitra, A.K. In Vitro Interaction of the HIV Protease Inhibitor Ritonavir with Herbal Constituents: Changes in P-Gp and CYP3A4 Activity. Am. J. Ther. 2004, 11, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.H.; Lee, M.; Chung, H.J.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, D.-H. Effects of Diosmin, a Flavonoid Glycoside in Citrus Fruits, on P-Glycoprotein-Mediated Drug Efflux in Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7620–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, M.; Gamian, A.; Sroka, Z. Antiradical Activity of Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.) Betalains. Molecules 2021, 26, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia Bangar, S.; Sharma, N.; Sanwal, N.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Sahu, J.K. Bioactive Potential of Beetroot (Beta vulgaris). Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmiran, P.; Houshialsadat, Z.; Gaeini, Z.; Bahadoran, Z.; Azizi, F. Functional Properties of Beetroot (Beta vulgaris) in Management of Cardio-Metabolic Diseases. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutor-Świeży, K.; Antonik, M.; Proszek, J.; Nemzer, B.; Pietrzkowski, Z.; Popenda, Ł.; Świergosz, T.; Wybraniec, S. Dehydrogenation of Betacyanins in Heated Betalain-Rich Extracts of Red Beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereddy, R.; Chan, A.; Fanning, K.; Nirmal, N.; Sultanbawa, Y. Betalain Rich Functional Extract with Reduced Salts and Nitrate Content from Red Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.) Using Membrane Separation Technology. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esatbeyoglu, T.; Wagner, A.E.; Schini-Kerth, V.B.; Rimbach, G. Betanin—A Food Colorant with Biological Activity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, C.; Tesoriere, L.; Allegra, M.; Livrea, M.A.; D’Alessio, P. Antioxidant Betalains from Cactus Pear (Opuntia Ficus-Indica) Inhibit Endothelial ICAM-1 Expression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1028, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaswant, M.; Brown, L.; McAinch, A.J.; Mathai, M.L. Beetroot and Sodium Nitrate Ameliorate Cardiometabolic Changes in Diet-Induced Obese Hypertensive Rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ma, D.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Tan, D. Natural Antioxidant Betanin Protects Rats from Paraquat-Induced Acute Lung Injury Interstitial Pneumonia. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 608174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesoriere, L.; Allegra, M.; Butera, D.; Livrea, M.A. Absorption, Excretion, and Distribution of Dietary Antioxidant Betalains in LDLs: Potential Health Effects of Betalains in Humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I. Plant Betalains: Safety, Antioxidant Activity, Clinical Efficacy, and Bioavailability. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, G.J.; Rao, G.S.; Ramachandran, C.; Iida, A.; Suzuki, N.; Tokuda, H. Synergistic Cytotoxicity of Red Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.) Extract with Doxorubicin in Human Pancreatic, Breast and Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2013, 10, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Mak, J.W.; Ong, C.E. Heterologous Expression of Human Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C19 in Escherichia Coli and Establishment of RP-HPLC Method to Serve as Activity Marker. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2013, 27, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubetskoy, O.V.; Gibson, J.R.; Marks, B.D. Highly Miniaturized Formats for in Vitro Drug Metabolism Assays Using Vivid Fluorescent Substrates and Recombinant Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. J. Biomol. Screen. 2005, 10, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelcheva, V.; Persson, I.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Genetic Polymorphism of Human Cytochrome P450 2E1. Methods Enzymol. 1996, 272, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, B.; Banks, P.; Cali, J.J.; Sobol, M.; Shultz, S. Automated Luminescence-Based Cytochrome P450 Profiling Using a Simple, Elegant Robotic Platform. JALA J. Assoc. Lab. Autom. 2011, 16, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, L.H.; Remley, M.J.; Raunig, D.; Vaz, A.D.N. In Vitro Drug Interactions of Cytochrome P450: An Evaluation of Fluorogenic to Conventional Substrates. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2003, 31, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, A.S.; Thomas, A.B.; Chitlange, S.S. Herb-Drug Interaction Studies of Herbs Used in Treatment of Cardiovascular Disorders-A Narrative Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Phytother. Res. PTR 2020, 34, 1008–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Park, E.K.; Kim, K.-T.; Bae, J.-S. Impacts of Drug Interactions on Pharmacokinetics and the Brain Transporters: A Recent Review of Natural Compound-Drug Interactions in Brain Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fragoso, L.; Martínez-Arismendi, J.L.; Orozco-Bustos, D.; Reyes-Esparza, J.; Torres, E.; Burchiel, S.W. Potential Risks Resulting from Fruit/Vegetable-Drug Interactions: Effects on Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes and Drug Transporters. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, R112–R124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomford, N.E.; Dzobo, K.; Chopera, D.; Wonkam, A.; Maroyi, A.; Blackhurst, D.; Dandara, C. In Vitro Reversible and Time-Dependent CYP450 Inhibition Profiles of Medicinal Herbal Plant Extracts Newbouldia Laevis and Cassia Abbreviata: Implications for Herb-Drug Interactions. Molecules 2016, 21, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, T.; Howatson, G.; West, D.J.; Stevenson, E.J. The Potential Benefits of Red Beetroot Supplementation in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2801–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gengatharan, A.; Dykes, G.A.; Choo, W.S. Betalains: Natural Plant Pigments with Potential Application in Functional Foods. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Paluszczak, J.; Szaefer, H.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Betanin, a Beetroot Component, Induces Nuclear Factor Erythroid-2-Related Factor 2-Mediated Expression of Detoxifying/Antioxidant Enzymes in Human Liver Cell Lines. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 2138–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, W.C.; Chenge, J.; Chen, T. Structural Perspectives of the CYP3A Family and Their Small Molecule Modulators in Drug Metabolism. Liver Res. 2019, 3, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, M. Molecular Modes of Action of Cytotoxic Alkaloids: From DNA Intercalation, Spindle Poisoning, Topoisomerase Inhibition to Apoptosis and Multiple Drug Resistance. Alkaloids Chem. Biol. 2007, 64, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Tan, D. Betanin Attenuates Paraquat-Induced Liver Toxicity through a Mitochondrial Pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2014, 70, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Gao, C.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Tan, D. Betanin Attenuates Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4)-Induced Liver Injury in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 40, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R. Modulation of Enzyme Activity. In xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference; Enna, S.J., Bylund, D.B., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 1–11. ISBN 978-0-08-055232-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, T.; Suzuki, I.; Chiba, T.; Tousen, Y. Safety Assessment of Herbal Supplement Components Targeting Hepatotoxicity and CYP3A4 Induction in Cell-Based Assay Using HepG2 Cells. J. Food Sci. 2022, 88, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Km, G.; Sm, H. Transporters in Drug Development and Clinical Pharmacology. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 94, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespi, C.L.; Chang, T.K.; Waxman, D.J. Determination of CYP2C9-Catalyzed Diclofenac 4′-Hydroxylation by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Methods Mol. Biol. 1998, 107, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| P450 Isoform | Substrate | Positive Inhibitor (µM) | Incubation Time (min) | Wavelengths (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excitation | Emission | ||||
| CYP1A2 | EOMCC | Furafylline, 5 | 15 | 408 | 455 |
| CYP2B6 | BOMCC | Bupropion, 50 | 30 | 409 | 460 |
| CYP2C9 | BOMCC | Omeprazole, 50 | 45 | 408 | 455 |
| CYP2C19 | EOMCC | Fluvoxamine, 100 | 30 | 408 | 455 |
| CYP2D6 | EOMCC | Quinidine, 50 | 15 | 405 | 450 |
| CYP3A4 | BOMCC | Ketoconazole, 1 | 10 | 409 | 460 |
| HepG2 Cell | Luminogenic Substrate | Substrate Concentration (µM) | Incubation Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CYP1A2 | Luciferin-1A2 | 6 | 120 |
| CYP2B6 | Luciferin-2B6 | 3 | 150 |
| CYP2C9 | Luciferin-H | 100 | 150 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, S.H.; Bae, S.; Lee, H.S.; Han, H.-K.; Choi, C.-I. Effect of Betanin, the Major Pigment of Red Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.), on the Activity of Recombinant Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091224
Lim SH, Bae S, Lee HS, Han H-K, Choi C-I. Effect of Betanin, the Major Pigment of Red Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.), on the Activity of Recombinant Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(9):1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091224
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Sung Ho, Seoungpyo Bae, Ho Seon Lee, Hyo-Kyung Han, and Chang-Ik Choi. 2023. "Effect of Betanin, the Major Pigment of Red Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.), on the Activity of Recombinant Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 9: 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091224
APA StyleLim, S. H., Bae, S., Lee, H. S., Han, H. -K., & Choi, C. -I. (2023). Effect of Betanin, the Major Pigment of Red Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.), on the Activity of Recombinant Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. Pharmaceuticals, 16(9), 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091224