Investigating Potential Cancer Therapeutics: Insight into Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) Inhibitions
Abstract
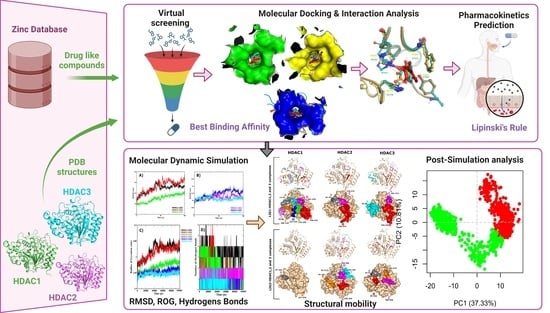
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Database Screening and Virtual Screening
2.2. Molecular Docking Interactions
2.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.4. Root Mean Square Deviation Assessment
2.5. Protein Compactness Analysis
2.6. Hydrogen Bonds Analysis
2.7. Solvent Accessible Surface Area (SASA)
2.8. Protein Residues Fluctuation Analysis
2.9. Post-Simulation Trajectories Analysis
2.10. Free Energy Landscape of the Ligand-Bound Complexes
2.11. Dynamic Cross-Correlation Matrix (DCCM)
2.12. Structural Deviations in HDACs
2.13. Drug Likeness and BOILED-Egg Model
2.14. Prediction of Biological Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Selection and Refinement of HDACs
3.2. Ligand Database Preparation
3.3. Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking
3.4. Ligand Receptor Interaction Analysis
3.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.6. MD Trajectory Analysis
3.7. Prediction of Pharmacokinetics, Drug Likeness, and Physiochemical Properties
3.8. Biological Activity Predictions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dawood, M.; Elbadawi, M.; Böckers, M.; Bringmann, G.; Efferth, T. Molecular docking-based virtual drug screening revealing an oxofluorenyl benzamide and a bromonaphthalene sulfonamido hydroxybenzoic acid as HDAC6 inhibitors with cytotoxicity against leukemia cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uba, A.I.; Hryb, M.; Singh, M.; Bui-Linh, C.; Tran, A.; Atienza, J.; Misbah, S.; Mou, X.; Wu, C. Discovery of novel inhibitors of histone deacetylase 6: Structure-based virtual screening, molecular dynamics simulation, enzyme inhibition and cell viability assays. Life Sci. 2024, 338, 122395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Barriopedro, I.; Raurell-Vila, H.; Vaquero, A. The role of hats and hdacs in cell physiology and disease. Gene Regul. Epigenetics Horm. Signal. 2017, 17, 101–136. [Google Scholar]
- Carta, F. Histone deacetylases and other epigenetic targets. In Metalloenzymes; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 265–281. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.T.; Li, H.Q.; Liu, F. Selective histone deacetylase small molecule inhibitors: Recent progress and perspectives. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2017, 27, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olawale, F.; Iwaloye, O.; Folorunso, I.M.; Shityakov, S. In silico High-Throughput Screening of ZINC Database of Natural Compounds to Identify Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. J. Comput. Biophys. Chem. 2023, 22, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cui, H.; Lu, Z.; Wang, H. Structure of histone deacetylase complex Rpd3S bound to nucleosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2023, 30, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaiah, M.J.; Tangutur, A.D.; Manyam, R.R. Epigenetic modulation and understanding of HDAC inhibitors in cancer therapy. Life Sci. 2021, 277, 119504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhan, A.; Deb, P.; Mandal, S.S. Epigenetic code: Histone modification, gene regulation, and chromatin dynamics. In Gene Regulation, Epigenetics and Hormone Signaling; Wiley: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ferioli, M.; Zauli, G.; Maiorano, P.; Milani, D.; Mirandola, P.; Neri, L.M. Role of physical exercise in the regulation of epigenetic mechanisms in inflammation, cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and aging process. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14852–14864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Feng, X.; He, T.; Wu, Y.; He, T.; Yue, Z.; Zhou, W. Discussion on structure classification and regulation function of histone deacetylase and their inhibitor. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2024, 103, e14366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verza, F.A.; Das, U.; Fachin, A.L.; Dimmock, J.R.; Marins, M. Roles of histone deacetylases and inhibitors in anticancer therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.S.; Maloney, M.E.; Lucas, R.; Fulton, D.J.; Patel, V.; Bagi, Z.; Kovacs-Kasa, A.; Kovacs, L.; Su, Y.; Verin, A.D. Zinc-Dependent Histone Deacetylases in Lung Endothelial Pathobiology. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neely, A.E.; Blumensaadt, L.A.; Ho, P.J.; Lloyd, S.M.; Kweon, J.; Ren, Z.; Bao, X. NUP98 and RAE1 sustain progenitor function through HDAC-dependent chromatin targeting to escape from nucleolar localization. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damaskos, C.; Psilopatis, I.; Garmpi, A.; Dimitroulis, D.; Nikolettos, K.; Vrettou, K.; Sarantis, P.; Koustas, E.; Kouraklis, G.; Antoniou, E.A.; et al. Evaluation of the Histone Deacetylase 2 (HDAC-2) Expression in Human Breast Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanka, G.; Begum, D.; Banerjee, S.; Adhikari, N.; Yogeeswari, P.; Ghosh, B. Pharmacophore-based virtual screening, 3D QSAR, Docking, ADMET, and MD simulation studies: An in silico perspective for the identification of new potential HDAC3 inhibitors. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 166, 107481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psilopatis, I.; Garmpis, N.; Garmpi, A.; Vrettou, K.; Sarantis, P.; Koustas, E.; Antoniou, E.A.; Dimitroulis, D.; Kouraklis, G.; Karamouzis, M.V.; et al. The Emerging Role of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Cervical Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Atty, M.M.; Farag, N.A.; Kassab, S.E.; Serya, R.A.; Abouzid, K.A. Design, synthesis, 3D pharmacophore, QSAR, and docking studies of carboxylic acid derivatives as Histone Deacetylase inhibitors and cytotoxic agents. Bioorganic Chem. 2014, 57, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanaei, M.; Kavoosi, F. Histone deacetylases and histone deacetylase inhibitors: Molecular mechanisms of action in various cancers. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2019, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhao, N.; Ge, D.; Chen, Y. Next-generation of selective histone deacetylase inhibitors. Rsc Adv. 2019, 9, 19571–19583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagni, C.; Citarella, A.; Oussama, M.; Rescifina, A.; Maugeri, A.; Navarra, M.; Scala, A.; Piperno, A.; Micale, N. Hydroxamic acid-based Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors bearing a pyrazole scaffold and a cinnamoyl linker. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaoye, O.O.; Watson, P.R.; Nawar, N.; Geletu, M.; Sedighi, A.; Bukhari, S.; Raouf, Y.S.; Manaswiyoungkul, P.; Erdogan, F.; Abdeldayem, A.; et al. Unique Molecular Interaction with the Histone Deacetylase 6 Catalytic Tunnel: Crystallographic and Biological Characterization of a Model Chemotype. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 2691–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Lu, K.; Xie, W.; Zhou, Z.; Tu, J. TO901317 inhibits the development of hepatocellular carcinoma by LXRα/Glut1 decreasing glycometabolism. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 316, G598–G607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liao, Y.; Long, D.; Yu, T.; Shen, F.; Lin, X. The Cdc2/Cdk1 inhibitor, purvalanol A, enhances the cytotoxic effects of taxol through Op18/stathmin in non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, C.; Coop, A.; E. Polli, J.; D. MacKerell, A. Recent advances in ligand-based drug design: Relevance and utility of the conformationally sampled pharmacophore approach. Curr. Comput.-Aided Drug Des. 2011, 7, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparoy, P.; Kumar Reddy, K.; Reddanna, P. Structure and ligand based drug design strategies in the development of novel 5-LOX inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 3763–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shi, D.; Zhou, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Yao, X. Molecular dynamics simulations and novel drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseem, H.; Mushtaq, N.; Saeed, A.; Shafi, N.; Inam, M. Piperidine Derivatives: Synthesis, Pharmacological Evaluation and Insilico Approach of Novel Potential Analgesics in 4-amino Methyl Piperidine Series. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirous, H.; Campiani, G.; Calderone, V.; Brogi, S. Discovery of novel hit compounds as potential HDAC1 inhibitors: The case of ligand-and structure-based virtual screening. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 137, 104808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, C.; Deng, T.; Tao, R.; Li, W. Novel urushiol derivatives as HDAC8 inhibitors: Rational design, virtual screening, molecular docking and molecular dynamics studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 36, 1966–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Xie, T.; Chen, D. Tumor cell membrane-coated continuous electrochemical sensor for GLUT1 inhibitor screening. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 13, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wei, H.; Hong, K.H.; Wu, X.; Zong, X.; Cao, M.; Wang, P.; Li, L.; Sun, C.; Chen, B.; et al. Discovery, bioactivity and docking simulation of Vorinostat analogues containing 1, 2, 4-oxadiazole moiety as potent histone deacetylase inhibitors and antitumor agents. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3457–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.; Li, X. Design, synthesis and preliminary biological evaluation of indoline-2, 3-dione derivatives as novel HDAC inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 4728–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er-rajy, M.; El Fadili, M.; Imtara, H.; Saeed, A.; Ur Rehman, A.; Zarougui, S.; Abdullah, S.A.; Alahdab, A.; Parvez, M.K.; Elhallaoui, M. 3D-QSAR studies, molecular docking, molecular dynamic simulation, and ADMET proprieties of novel pteridinone derivatives as PLK1 inhibitors for the treatment of prostate cancer. Life 2023, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, V.B.; Mhaldar, P.M.; Patil, M.V.; Mirzaei, M.; Pore, D.M. [Cell@ Al2O3 (HEPiPY)] DCA: A Cellulose Supported Ionic Liquid Catalyst for Synthesis of 11 b, 12-dihydro-6H, 13Hbenzo [5, 6][1, 3] oxazino [3, 4-a] quinazoline-6, 13-dione along with in silico assessments. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202303989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynak, B.T.; Krieger, J.M.; Dudas, B.; Dahmani, Z.L.; Costa, M.G.; Balog, E.; Scott, A.L.; Doruker, P.; Perahia, D.; Bahar, I. Sampling of protein conformational space using hybrid simulations: A critical assessment of recent methods. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 832847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, O.; Deora, G.S.; Tanwar, L.; Kumar, G.; Janardhan, S.; Alam, M.; Shaquiquzzaman; Akhter, M. Novel hydrazine derivatives as selective DPP-IV inhibitors: Findings from virtual screening and validation through molecular dynamics simulations. J. Mol. Model. 2014, 20, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, K.B.; Ballav, S.; Yadav, R.S.; Swamy, K.V.; Basu, S. Probing intermolecular interactions and binding stability of kaempferol, quercetin and resveratrol derivatives with PPAR-γ: Docking, molecular dynamics and MM/GBSA approach to reveal potent PPAR-γ agonist against cancer. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, G.; Nigam, V.K.; Pandey, D.M. The molecular docking and molecular dynamics study of flavonol synthase and flavonoid 3′-monooxygenase enzymes involved for the enrichment of kaempferol. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 2478–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K. Drug delivery systems, CNS protection, and the blood brain barrier. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 869269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrouji, M.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Alsayari, A.; Sharaf, S.E.; Shafi, S.; Anwar, S.; Shahwan, M.; Atiya, A.; Shamsi, A. Targeting Sirtuin 1 for therapeutic potential: Drug repurposing approach integrating docking and molecular dynamics simulations. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0293185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M. Blood–brain barrier endogenous transporters as therapeutic targets: A new model for small molecule CNS drug discovery. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eser Ocak, P.; Ocak, U.; Sherchan, P.; Zhang, J.H.; Tang, J. Insights into major facilitator superfamily domain-containing protein-2a (Mfsd2a) in physiology and pathophysiology. What do we know so far? J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauna, Z.E.; Ambudkar, S.V. About a switch: How P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) harnesses the energy of ATP binding and hydrolysis to do mechanical work. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lu, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Shi, J.; Yan, T.; Xie, C.; Li, Q.; Hu, M.; Liu, Z. Oral absorption basics: Pathways and physicochemical and biological factors affecting absorption. In Developing Solid Oral Dosage Forms; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 297–329. [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren, E.; Abrahamsson, B.; Augustijns, P.; Becker, D.; Bolger, M.B.; Brewster, M.; Brouwers, J.; Flanagan, T.; Harwood, M.; Heinen, C.; et al. In vivo methods for drug absorption–comparative physiologies, model selection, correlations with in vitro methods (IVIVC), and applications for formulation/API/excipient characterization including food effects. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 57, 99–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, M.P.; Rigalli, J.P.; Ceré, L.I.; Semeniuk, M.; Catania, V.A.; Ruiz, M.L. ABC transporters: Regulation and association with multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma and colorectal carcinoma. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 1224–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Berman, H.M.; Kleywegt, G.J.; Markley, J.L.; Nakamura, H.; Velankar, S. Protein Data Bank (PDB): The single global macromolecular structure archive. Protein Crystallogr. 2017, 1607, 627–641. [Google Scholar]
- Beshore, D.C.; Adam, G.C.; Barnard, R.J.; Burlein, C.; Gallicchio, S.N.; Holloway, M.K.; Krosky, D.; Lemaire, W.; Myers, R.W.; Patel, S.; et al. Redefining the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Pharmacophore: High Potency with No Zinc Cofactor Interaction. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. ZINC—A free database of commercially available compounds for virtual screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.A.; Nassar, I.F.; Shaban, A.K.; El-Kady, D.S.; Awad, H.M.; El Sayed, W.A. Synthesis, docking studies into CDK-2 and anticancer activity of new derivatives based pyrimidine scaffold and their derived glycosides. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1093–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathout, R.M.; Metwally, A.A. Towards better modelling of drug-loading in solid lipid nanoparticles: Molecular dynamics, docking experiments and Gaussian Processes machine learning. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, S.; Cozza, G.; Moro, S. Medicinal chemistry and the molecular operating environment (MOE): Application of QSAR and molecular docking to drug discovery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1555–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B.; Saeed, A.; Castrosanto, M.A.; Amir Zia, M.; Farooq, U.; Abbas, Z.; Khan, S. Identification of natural marine compounds as potential inhibitors of CDK2 using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 8506–8516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir ul Qamar, M.; Maryam, A.; Muneer, I.; Xing, F.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Khan, F.A.; Anwar, F.; Geesi, M.H.; Khalid, R.R.; Rauf, S.A.; et al. Computational screening of medicinal plant phytochemicals to discover potent pan-serotype inhibitors against dengue virus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Chan, H.S.; Filipek, S.; Vogel, H. PyMOL and Inkscape bridge the data and the data visualization. Structure 2016, 24, 2041–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.A.; Raza, H.; Siddiqui, S.Z.; Shah, S.A.A.; Hassan, M.; Seo, S.Y. Synthesis of novel N-(1, 3-thiazol-2-yl) benzamide clubbed oxadiazole scaffolds: Urease inhibition, Lipinski rule and molecular docking analyses. Bioorganic Chem. 2019, 83, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somavarapu, A.K.; Kepp, K.P. The dependence of amyloid-β dynamics on protein force fields and water models. ChemPhysChem 2015, 16, 3278–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, K.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, G.; Kumari, S.; Biswas, S.; Padmanabhan, P. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Bacillus clausii and computational profiling of nitrate reductase enzyme involved in production. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjærven, L.; Jariwala, S.; Yao, X.Q.; Grant, B.J. Online interactive analysis of protein structure ensembles with Bio3D-web. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3510–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glykos, N.M. Software news and updates carma: A molecular dynamics analysis program. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1765–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsattar, A.S.; Mansour, Y.; Aboul-ela, F. The Perturbed Free-Energy Landscape: Linking Ligand Binding to Biomolecular Folding. ChemBioChem 2021, 22, 1499–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çankaya, N.; Azarkan, S.Y.; Tanış, E. The molecular interaction of human anti-apoptotic proteins and in silico ADMET, drug-likeness and toxicity computation of N-cyclohexylmethacrylamide. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 45, 1963–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filimonov, D.A.; Lagunin, A.A.; Gloriozova, T.A.; Rudik, A.V.; Druzhilovskii, D.S.; Pogodin, P.V.; Poroikov, V.V. Prediction of the biological activity spectra of organic compounds using the PASS online web resource. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2014, 50, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagunin, A.; Stepanchikova, A.; Filimonov, D.; Poroikov, V. PASS: Prediction of activity spectra for biologically active substances. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 747–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Compounds | S-Score (kcal/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HDAC1 | HDAC2 | HDAC3 | |
| ZINC98207834-LIG1 | −19.1103 | −27.0314 | −27.4039 |
| ZINC77024375-LIG2 | −21.8915 | −23.2849 | −27.9976 |
| ZINC67801495-LIG3 | −17.5725 | −20.1273 | −16.1137 |
| ZINC85664535-LIG4 | −17.1144 | −18.8858 | −15.1259 |
| ZINC71792267-LIG5 | −14.8882 | −17.8317 | −16.4172 |
| ZINC71784493-LIG6 | −14.6239 | −17.4523 | −16.7444 |
| ZINC71792707-LIG7 | −16.7516 | −17.9025 | −197871 |
| ZINC79387365-LIG8 | −15.3222 | −16.7737 | −15.7455 |
| Complexes | Hydrogen Bond | π-Stacking Interactions | Hydrophobic Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIG1-HDAC1 | H178 | F205 | D99, L139, H140, H141, G149, F150, C151, G300, G301, Y303 |
| LIG2-HDAC1 | H178 | F150, F205 | M30, D99, H141, G149, L271, G301, Y303 |
| LIG3-HDAC1 | H141, H178, Y303 | F150 | H140, G149, F205, L271, G301, |
| LIG1-HDAC2 | H141, H142, H179 | - | G150, F251, Y205, F206, L272, Y304, G302 |
| LIG2-HDAC2 | H179 | F151 and F206 | M31, D100, L140, H141, H142, G150, C152, G301, G302, Y304, |
| LIG3-HDAC2 | H141, H142, H179, Y304 | F151 | D100, G150, F206, L272, G302 |
| LIG1-HDAC3 | H135, H172, Y298 | - | M24, H134, G143, F144, F200, L266, G295, G296 |
| LIG2-HDAC3 | H172 | F144 and F200 | M24, D93, H134, H135, G143, C145, L266, G296, Y298 |
| LIG3-HDAC3 | H135, H172 | F144 | D93, H134, G143, C145, F200, L266, G296, Y298 |
| Compounds | Lipinski | Ghose | Veber | Egan | Muegge | Bioavailability Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LIG1 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 |
| LIG2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.55 |
| LIG3 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.85 |
| Compounds | GI Absorption | BBB Permeation | P-Glycoprotein Substrate | CYP1A2 Inhibitor | CYP2C19 Inhibitor | CYP2C9 Inhibitor | CYP2D6 Inhibitor | CYP3A4 Inhibitor | LD 50 mg/kg | Carcinogenicity, Mutagenicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LIG1 | high | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | 3500 | probably safe |
| LIG2 | high | no | no | yes | yes | yes | no | yes | 800 | probably safe |
| LIG3 | high | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | 2300 | probably safe |
| Compounds | Pa | Pi | PBA |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIG1 | 0.925 | 0.001 | Mycothiol-S-conjugate amidase inhibitor |
| 0.837 | 0.004 | Peptide agonist | |
| 0.762 | 0.010 | NADPH-cytochrome-c2 reductase inhibitor | |
| LIG2 | 0.603 | 0.029 | Neurotransmitter uptake inhibitor |
| 0.508 | 0.068 | Complement factor D inhibitor | |
| 0.495 | 0.055 | Chloride peroxidase inhibitor | |
| LIG3 | 0.914 | 0.004 | Feruloyl esterase inhibitor |
| 0.904 | 0.004 | Prolyl aminopeptidase inhibitor | |
| 0.868 | 0.015 | Aspulvinone dimethylallyl transferase inhibitor |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, B.; Saeed, A.; Al-Amery, A.; Celik, I.; Ahmed, I.; Yaseen, M.; Khan, I.A.; Al-Fahad, D.; Bhat, M.A. Investigating Potential Cancer Therapeutics: Insight into Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) Inhibitions. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040444
Ahmad B, Saeed A, Al-Amery A, Celik I, Ahmed I, Yaseen M, Khan IA, Al-Fahad D, Bhat MA. Investigating Potential Cancer Therapeutics: Insight into Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) Inhibitions. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(4):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040444
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Basharat, Aamir Saeed, Ahmed Al-Amery, Ismail Celik, Iraj Ahmed, Muhammad Yaseen, Imran Ahmad Khan, Dhurgham Al-Fahad, and Mashooq Ahmad Bhat. 2024. "Investigating Potential Cancer Therapeutics: Insight into Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) Inhibitions" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 4: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040444
APA StyleAhmad, B., Saeed, A., Al-Amery, A., Celik, I., Ahmed, I., Yaseen, M., Khan, I. A., Al-Fahad, D., & Bhat, M. A. (2024). Investigating Potential Cancer Therapeutics: Insight into Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) Inhibitions. Pharmaceuticals, 17(4), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040444