Illicit Drugs in Surface Waters: How to Get Fish off the Addictive Hook
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Occurrence of Illicit Drugs in the Aquatic Environment
| Substance | Country | Place | Concentration Range ng/L | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent | Effluent | ||||
| Medical-based illicit drugs | |||||
| Methadone | France | Corbeil | 26.0 | 22.0 | [34] |
| Germany | ND | 130.0 | 120.0 | [35] | |
| Netherlands | Various cities | <45.0 | 8.7–47.0 | [36] | |
| Italy | Nosedo | 11.6 ± 1.7 | 9.1 ± 0.5 | [37] | |
| Slovakia | Petrzalka | 25 ± 3 | 18 ± 3.0 | [38] | |
| SPAIN | Catalonia | 3.4–1531.0 | 3.4–732 | [39] | |
| Switzerland | Zurich | 42.0–202.0 | 44.0–128.0 | [40] | |
| Logano | 49.7 ± 9.6 | 36.2 ± 2.8 | [37] | ||
| United Kingdom | Various locations | 171.1 | 68.8 | [41] | |
| England | 2.6–171.1 | 1.4–91.0 | [42] | ||
| Morphine | Costa Rica | El Roble | 67.0–77.0 | 15.0–61.0 | [43] |
| Germany | ND | 820.0 | 110.0 | [44] | |
| 440.0 | 29.0 | [35] | |||
| Martinique | Fort de France | 154.0 ± 27.0 | 58.7 ± 7.0 | [45] | |
| Spain | Catalonia | 25.5–278.0 | 12.0–81.1 | [39] | |
| Iberian Pensinsula | 54.2–166.0 | 5.4–80.5 | [46] | ||
| Southeast region | 90.0–275.0 | 60.0–155.0 | [47] | ||
| Switzerland | Logano | 204.4 ± 49.9 | 55.4 ± 11.1 | [37] | |
| Taiwan | Taipei | 38.0 | 29.0 | [48] | |
| USA | Various cities | 4523.0–1060.0 | <50.0 | [49] | |
| Codeine | Costa Rica | Liberia | 143.0–325.0 | 11.0–29.0 | [43] |
| Cyprus | ND | 2316.0–6460.0 | <LOD–3783.0 | [50] | |
| Germany | ND | 540.0 | 260.0 | [44] | |
| Italy | Verone | 275.0–335.0 | 110.0–126.0 | [51] | |
| Netherlands | Various cities | 240.0–536.0 | 173.0–245.0 | [36] | |
| Slovakia | Petrzalka | 123.0 ± 11.0 | 24.0 ± 2.0 | [38] | |
| Spain | Southeast region | 234.0–1556.0 | 289.0–786.0 | [47] | |
| United Kingdom | Various locations | 2703.5 | 1206.2 | [42] | |
| Tramadol | Germany | ND | 470.0 | 370.0 | [35] |
| Slovakia | Petrzalka | 860.0 ± 120.0 | 710 ± 50 | [38] | |
| United Kingdom | ND | 1320.7 ± 59.3 | 506.0 ± 46.6 | [52] | |
| Illicit drugs | |||||
| Cocaine | Australia | South-east Queensland | 20–200a | ND | [53] |
| China | Beijing | 32–562 | ND | [54] | |
| Belgium | Flanders region | 22–687 | ND | [55] | |
| Canada | Eastern Canada (3 cities) | 209–823 | <LOQ–530 | [56] | |
| Croatia | Velika Gorica, Varazdin and Karlovac | 0.7–53 | ND | [57] | |
| France | Paris | 21–1532 | ND | [58] | |
| Ireland | Dublin’s surroundings | 489 | 47–138 | [59] | |
| Netherlands | Utrecht, Eindhoven, Apeldoorn and Amsterdam | 87–957 | <6–159 | [36] | |
| Amphetamine | China | Beijing | 2–101 | 0.9–2.8 | [60] |
| Belgium | Brussels and Flanders region | 76a | ND | [61] | |
| Canada | Eastern Canada (3 cities) | <LOQ–25 | <LOD–14 | [56] | |
| France | Various cities | 125–194 | ND | [58] | |
| Netherlands | Utrecht, Eindhoven, Apeldoorn and Amsterdam | 81–682 | <4–6.9 | [36] | |
| Methamphetamine | China | Beijing | 21.2–304 | 0.4–12.2 | [60] |
| Belgium | Brussels and Flanders region | 2 | ND | [61] | |
| FRANCE | Various cities | 51 | 24 | [58] | |
| China | Hong Kong | 97.8 | ND | [53] | |
| USA | Nebraska | ND | 350.1 ± 78.3 | [62] | |
| Netherlands | Utrecht, Eindhoven, Apeldoorn and Amsterdam | <15–17 | <5 | [36] | |
| Canada | Eastern Canada (3 cities) | <LOQ–65 | 17–95 | [56] | |
| Heroin | Belgium | Brussels and Flanders region | 415 | ND | [61] |
| FRANCE | Various cities | 25–194 | 31 | [58] | |
3. Bioaccumulation of Illicit Drugs and Their Toxicity
3.1. Bioaccumulation of Illicit Drugs in Fish
3.2. Behavior Disorders in Fish as the Frontline Response to Illicit Drugs
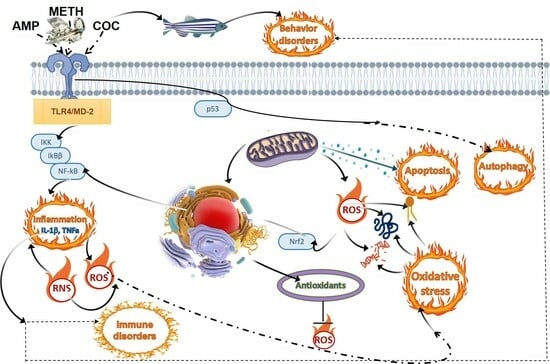
3.3. Illicit Drugs-Induced Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Changes in Fish
3.3.1. Metabolic Alterations in Fish Exposed to Illicit Drugs
3.3.2. Oxidative Stress as the Marker of Illicit Drugs in Fish
3.4. Endocrine-, Immune-Modulatory, and Inflammatory Effects of Illicit Drugs in Fish
3.5. Geno- and Cytotoxic Effects of Illicit Drugs in Fish
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- NCDAS: Substance Abuse and Addiction Statistics. 2023. Available online: http://drugabusestatistics.org (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- At a Glance—Estimates of Drug Use in the European Union (Updated June 2022). Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/media-library/glance-%E2%80%94-estimates-drug-use-european-union-updated-june-2022_en (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- World Drug Report 2023—Statistical Annex. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/wdr2023_annex.html (accessed on 25 February 2024).
- Drug Overdose Deaths. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/deaths/index.html (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Conway, F.N.; Samora, J.; Brinkley, K.; Jeong, H.; Clinton, N.; Claborn, K.R. Impact of COVID-19 among People Who Use Drugs: A Qualitative Study with Harm Reduction Workers and People Who Use Drugs. Harm Reduct. J. 2022, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Been, F.; Emke, E.; Matias, J.; Baz-Lomba, J.A.; Boogaerts, T.; Castiglioni, S.; Campos-Mañas, M.; Celma, A.; Covaci, A.; de Voogt, P.; et al. Changes in Drug Use in European Cities during Early COVID-19 Lockdowns—A Snapshot from Wastewater Analysis. Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, K.; Liu, G.; Mallia, E.; Ow, N.; Glowacki, K.; Hastings, K.G.; Mathias, S.; Sutherland, J.M.; Barbic, S. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Alcohol or Drug Use Symptoms and Service Need among Youth: A Cross-Sectional Sample from British Columbia, Canada. Subst. Abuse Treat. Prev. Policy 2022, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, D.G.J. Pollution from Drug Manufacturing: Review and Perspectives. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Kolpin, D.W.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Lai, R.W.S.; Galbán-Malagón, C.; Adell, A.D.; Mondon, J.; Metian, M.; Marchant, R.A.; et al. Pharmaceutical Pollution of the World’s Rivers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113947119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzymski, P.; Gwenzi, W.; Poniedziałek, B.; Mangul, S.; Fal, A. Climate Warming, Environmental Degradation and Pollution as Drivers of Antibiotic Resistance. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacorte, S.; Gómez-Canela, C.; Calas-Blanchard, C. Pharmaceutical Residues in Senior Residences Wastewaters: High Loads, Emerging Risks. Molecules 2021, 26, 5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, D.; Spasiano, D.; Vaccaro, M.; Cochran, K.H.; Richardson, S.D.; Andreozzi, R.; Li Puma, G.; Reis, N.M.; Marotta, R. Investigation on the Removal of the Major Cocaine Metabolite (benzoylecgonine) in Water Matrices by UV254/H2O2 Process by Using a Flow Microcapillary Film Array Photoreactor as an Efficient Experimental Tool. Water Res. 2016, 89, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Guo, C.; Sun, Z.; Xu, J. Occurrence, Bioaccumulation and Toxicological Effect of Drugs of Abuse in Aquatic Ecosystem: A Review. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimaszyk, P.; Rzymski, P. Water and Aquatic Fauna on Drugs: What Are the Impacts of Pharmaceutical Pollution? In Water Management and the Environment: Case Studies; Zelenakova, M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 255–278. ISBN 9783319790145. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, H.; Yin, X.; Chen, L.; Wu, D.; Xu, J. Occurrence and Removal of Illicit Drugs in Different Wastewater Treatment Plants with Different Treatment Techniques. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, H.G., Jr.; Wood, R.I.; Rogol, A.; Nyberg, F.; Bowers, L.; Bhasin, S. Adverse Health Consequences of Performance-Enhancing Drugs: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 341–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosi-Marshall, E.J.; Snow, D.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.L.; Paspalof, A.; Tank, J.L. A Review of Ecological Effects and Environmental Fate of Illicit Drugs in Aquatic Ecosystems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guo, C.; Lv, J.; Hua, Z.; Hou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, W.; Xu, J. Drugs of Abuse and Their Metabolites in the Urban Rivers of Beijing, China: Occurrence, Distribution, and Potential Environmental Risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, M.K.; Maranho, L.A.; Pereira, C.D.S. Review on the Occurrence and Biological Effects of Illicit Drugs in Aquatic Ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 30998–31034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, E.; Volschenk, M.; Brocker, L.; Wolfaardt, G.M. A Two-Year Study of Emerging Micro-Pollutants and Drugs of Abuse in Two Western Cape Wastewater Treatment Works (South Africa). Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecotoxicity, Occurrence, and Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Illicit Drugs from Aquatic Systems. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 12530–12546. [CrossRef]
- Ripanda, A.S.; Rwiza, M.J.; Nyanza, E.C.; Machunda, R.L.; Vuai, S.H. Contribution of Illicit Drug Use to Pharmaceutical Load in the Environment: A Focus on Sub-Saharan Africa. J. Environ. Public Health 2022, 2022, 9056476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, R.Y.; Manikandan, S.; Subbaiya, R.; Biruntha, M.; Balachandar, R.; Karmegam, N. Origin, Transport and Ecological Risk Assessment of Illicit Drugs in the Environment—A Review. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ter Laak, T.L.; Emke, E. Environmental Impact of Synthetic Drug Production: Analysis of Groundwater Samples for Contaminants Derived from Illicit Synthetic Drug Production Waste. Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/drugs-library/environmental-impact-synthetic-drug-production-analysis-groundwater-samples-contaminants-derived-illicit-synthetic-drug-production-waste_en (accessed on 18 April 2024).
- Moslah, B.; Hapeshi, E.; Jrad, A.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Hedhili, A. Pharmaceuticals and Illicit Drugs in Wastewater Samples in North-Eastern Tunisia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 18226–18241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.Y.; Lai, F.Y.; Kim, H.-Y.; Thai, P.K.; Mueller, J.F.; Oh, J.-E. The First Application of Wastewater-Based Drug Epidemiology in Five South Korean Cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daglioglu, N.; Guzel, E.Y.; Kilercioglu, S. Assessment of Illicit Drugs in Wastewater and Estimation of Drugs of Abuse in Adana Province, Turkey. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 294, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, J.; Kannan, A.M.; Castrignanò, E.; Jagadeesan, K.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Wastewater-Based Epidemiology Combined with Local Prescription Analysis as a Tool for Temporalmonitoring of Drugs Trends—A UK Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wastewater Samples from over 100 European Cities Reveal Latest Drug-Taking Trends. Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/news/2023/2/wastewater-samples-over-100-european-cities-reveal-latest-drug-taking-trends_en (accessed on 25 February 2024).
- González-Mariño, I.; Baz-Lomba, J.A.; Alygizakis, N.A.; Andrés-Costa, M.J.; Bade, R.; Bannwarth, A.; Barron, L.P.; Been, F.; Benaglia, L.; Berset, J.-D.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Assessment of Illicit Drug Use at Large Scale: Evidence from 7 Years of International Wastewater Monitoring. Addiction 2020, 115, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, L.d.A.A.; Radis-Baptista, G. Pharmaceutical Pollution and Disposal of Expired, Unused, and Unwanted Medicines in the Brazilian Context. J. Xenobiot. 2021, 11, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, K.; Ritter, A.; Valentine, K.; Rhodes, T. “A More Accurate Understanding of Drug Use”: A Critical Analysis of Wastewater Analysis Technology for Drug Policy. Int. J. Drug Policy 2019, 63, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisielius, V.; Kharel, S.; Skaarup, J.; Lauritzen, B.S.; Lukas, M.; Bogusz, A.; Szumska, M.; Bester, K. Process Design for Removal of Pharmaceuticals in Wastewater Treatment Plants Based on Predicted No Effect Concentration (PNEC). Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, C.; Roosen, M.; Levi, Y.; Karolak, S. Validation of an Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method to Quantify Illicit Drug and Pharmaceutical Residues in Wastewater Using Accuracy Profile Approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1500, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, A.; Fink, G.; Joss, A.; Siegrist, H.; Ternes, T.A. Fate of Beta Blockers and Psycho-Active Drugs in Conventional Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1060–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijlsma, L.; Emke, E.; Hernández, F.; de Voogt, P. Investigation of Drugs of Abuse and Relevant Metabolites in Dutch Sewage Water by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiglioni, S.; Zuccato, E.; Crisci, E.; Chiabrando, C.; Fanelli, R.; Bagnati, R. Identification and Measurement of Illicit Drugs and Their Metabolites in Urban Wastewater by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 8421–8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackuľak, T.; Birošová, L.; Grabic, R.; Škubák, J.; Bodík, I. National Monitoring of Nicotine Use in Czech and Slovak Republic Based on Wastewater Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 14000–14006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boleda, M.A.R.; Galceran, M.A.T.; Ventura, F. Monitoring of Opiates, Cannabinoids and Their Metabolites in Wastewater, Surface Water and Finished Water in Catalonia, Spain. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berset, J.-D.; Brenneisen, R.; Mathieu, C. Analysis of Llicit and Illicit Drugs in Waste, Surface and Lake Water Samples Using Large Volume Direct Injection High Performance Liquid Chromatography--Electrospray Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). Chemosphere 2010, 81, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Multi-Residue Analysis of Drugs of Abuse in Wastewater and Surface Water by Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Positive Electrospray Ionisation Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 1620–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Spatial and Temporal Occurrence of Pharmaceuticals and Illicit Drugs in the Aqueous Environment and during Wastewater Treatment: New Developments. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 454–455, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Causanilles, A.; Ruepert, C.; Ibáñez, M.; Emke, E.; Hernández, F.; de Voogt, P. Occurrence and Fate of Illicit Drugs and Pharmaceuticals in Wastewater from Two Wastewater Treatment Plants in Costa Rica. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, D.; Löffler, D.; Fink, G.; Ternes, T.A. Simultaneous Determination of Psychoactive Drugs and Their Metabolites in Aqueous Matrices by Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7321–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devault, D.A.; Néfau, T.; Levi, Y.; Karolak, S. The Removal of Illicit Drugs and Morphine in Two Waste Water Treatment Plants (WWTPs) under Tropical Conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 25645–25655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postigo, C.; López de Alda, M.J.; Barceló, D. Drugs of Abuse and Their Metabolites in the Ebro River Basin: Occurrence in Sewage and Surface Water, Sewage Treatment Plants Removal Efficiency, and Collective Drug Usage Estimation. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Bueno, M.J.; Uclés, S.; Hernando, M.D.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Development of a Solvent-Free Method for the Simultaneous Identification/quantification of Drugs of Abuse and Their Metabolites in Environmental Water by LC-MS/MS. Talanta 2011, 85, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lee, W.-N. Prevalence and Sunlight Photolysis of Controlled and Chemotherapeutic Drugs in Aqueous Environments. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerrity, D.; Trenholm, R.A.; Snyder, S.A. Temporal Variability of Pharmaceuticals and Illicit Drugs in Wastewater and the Effects of a Major Sporting Event. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5399–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapeshi, E.; Gros, M.; Lopez-Serna, R.; Boleda, M.-R.; Ventura, F.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Licit and Illicit Drugs in Urban Wastewater in Cyprus. Clean 2015, 43, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repice, C.; Dal Grande, M.; Maggi, R.; Pedrazzani, R. Licit and Illicit Drugs in a Wastewater Treatment Plant in Verona, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, S.E.; Davies, P.; Lubben, A.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Determination of Chiral Pharmaceuticals and Illicit Drugs in Wastewater and Sludge Using Microwave Assisted Extraction, Solid-Phase Extraction and Chiral Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 882, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, F.Y.; Bruno, R.; Hall, W.; Gartner, C.; Ort, C.; Kirkbride, P.; Prichard, J.; Thai, P.K.; Carter, S.; Mueller, J.F. Profiles of Illicit Drug Use during Annual Key Holiday and Control Periods in Australia: Wastewater Analysis in an Urban, a Semi-Rural and a Vacation Area. Addiction 2013, 108, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Nuijs, A.L.N.; Pecceu, B.; Theunis, L.; Dubois, N.; Charlier, C.; Jorens, P.G.; Bervoets, L.; Blust, R.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Occurrence of Cocaine and Benzoylecgonine in Waste- and Surface Water from Belgium and Removal during Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghe, A.; van Nuijs, A.; Pecceu, B.; Bervoets, L.; Jorens, P.G.; Blust, R.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Analysis of Cocaine and Its Principal Metabolites in Waste and Surface Water Using Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Ion Trap Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalfe, C.; Tindale, K.; Li, H.; Rodayan, A.; Yargeau, V. Illicit Drugs in Canadian Municipal Wastewater and Estimates of Community Drug Use. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3179–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senta, I.; Krizman, I.; Ahel, M.; Terzic, S. Integrated Procedure for Multiresidue Analysis of Dissolved and Particulate Drugs in Municipal Wastewater by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3255–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nefau, T.; Karolak, S.; Castillo, L.; Boireau, V.; Levi, Y. Presence of Illicit Drugs and Metabolites in Influents and Effluents of 25 Sewage Water Treatment Plants and Map of Drug Consumption in France. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bones, J.; Thomas, K.V.; Paull, B. Using Environmental Analytical Data to Estimate Levels of Community Consumption of Illicit Drugs and Abused Pharmaceuticals. J. Environ. Monit. 2007, 9, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, W.; Peng, Q.; Jiang, M.; Luo, C.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fang, M.; Mo, Z. Effect of Rhynchophylline on Conditioned Place Preference on Expression of NR2B in Methamphetamine-Dependent Mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 452, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Nuijs, A.L.N.; Mougel, J.-F.; Tarcomnicu, I.; Bervoets, L.; Blust, R.; Jorens, P.G.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Sewage Epidemiology—A Real-Time Approach to Estimate the Consumption of Illicit Drugs in Brussels, Belgium. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelt-Hunt, S.L.; Snow, D.D.; Damon, T.; Shockley, J.; Hoagland, K. The Occurrence of Illicit and Therapeutic Pharmaceuticals in Wastewater Effluent and Surface Waters in Nebraska. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brieudes, V.; Lardy-Fontan, S.; Vaslin-Reimann, S.; Budzinski, H.; Lalere, B. Development of a Multi-Residue Method for Scrutinizing Psychotropic Compounds in Natural Waters. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1047, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 3166-1; Codes of Country Names and Their Administrative Units—Part 1: Country Codes, PN-EN ISO 3166-1:2021-03. Available online: https://www.iso.org/iso-3166-country-codes.html (accessed on 18 April 2024).
- Muñiz-Bustamante, L.; Caballero-Casero, N.; Rubio, S. Drugs of Abuse in Tap Water from Eight European Countries: Determination by Use of Supramolecular Solvents and Tentative Evaluation of Risks to Human Health. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paciuszkiewicz, K.; Ryan, M.; Wright, I.A.; Reynolds, J.K. Variations in Illicit Compound Discharged from Treated Wastewater. Water 2019, 11, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-J.; Lee, C.-L.; Fang, M.-D.; Tu, B.-W.; Liang, Y.-J. Impacts of Emerging Contaminants on Surrounding Aquatic Environment from a Youth Festival. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.Y.-C.; Wang, X.-H.; Lin, C.-F. Impact of Wastewaters and Hospital Effluents on the Occurrence of Controlled Substances in Surface Waters. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Occurrence, Distribution and Risk Assessment of Abused Drugs and Their Metabolites in a Typical Urban River in North China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2019, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, G.; Randak, T.; Golovko, O.; Kodes, V.; Grabicova, K.; Grabic, R. A Passive Sampling Method for Detecting Analgesics, Psycholeptics, Antidepressants and Illicit Drugs in Aquatic Environments in the Czech Republic. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-G.; Zheng, Q.-D.; Wang, X.-P.; Du, J.; Tian, C.-G.; Wang, Z.; Ge, L.-K. Illicit Drugs and Their Metabolites in 36 Rivers That Drain into the Bohai Sea and North Yellow Sea, North China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 16495–16503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebele, A.J.; Oluseyi, T.; Drage, D.S.; Harrad, S.; Abou-Elwafa Abdallah, M. Occurrence, Seasonal Variation and Human Exposure to Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Surface Water, Groundwater and Drinking Water in Lagos State, Nigeria. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Bagnati, R.; Chiabrando, C.; Grassi, P.; Fanelli, R. Illicit Drugs, a Novel Group of Environmental Contaminants. Water Res. 2008, 42, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunbanwo, O.M.; Kay, P.; Boxall, A.B.; Wilkinson, J.; Sinclair, C.J.; Shabi, R.A.; Fasasi, A.E.; Lewis, G.A.; Amoda, O.A.; Brown, L.E. High Concentrations of Pharmaceuticals in a Nigerian River Catchment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatib, I.; Rychter, P.; Falfushynska, H. Pesticide Pollution: Detrimental Outcomes and Possible Mechanisms of Fish Exposure to Common Organophosphates and Triazines. J. Xenobiot. 2022, 12, 236–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, B.; Moffat, C.F. Occurrence and Fate of Chiral and Achiral Drugs in Estuarine Water—A Case Study of the Clyde Estuary, Scotland. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, K.; Moffat, C.F.; Petrie, B. Multi-Residue Enantioselective Determination of Emerging Drug Contaminants in Seawater by Solid Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borova, V.L.; Maragou, N.C.; Gago-Ferrero, P.; Pistos, C.; Thomaidis, N.S. Highly Sensitive Determination of 68 Psychoactive Pharmaceuticals, Illicit Drugs, and Related Human Metabolites in Wastewater by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 4273–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klosterhaus, S.L.; Grace, R.; Hamilton, M.C.; Yee, D. Method Validation and Reconnaissance of Pharmaceuticals, Personal Care Products, and Alkylphenols in Surface Waters, Sediments, and Mussels in an Urban Estuary. Environ. Int. 2013, 54, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.D.S.; Maranho, L.A.; Cortez, F.S.; Pusceddu, F.H.; Santos, A.R.; Ribeiro, D.A.; Cesar, A.; Guimarães, L.L. Occurrence of Pharmaceuticals and Cocaine in a Brazilian Coastal Zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548–549, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-García, E.; Mastroianni, N.; Ponsà-Borau, N.; Barceló, D.; Postigo, C.; López de Alda, M. Drugs of Abuse and Their Metabolites in River Sediments: Analysis, Occurrence in Four Spanish River Basins and Environmental Risk Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Yang, F. Species-Specific Bioaccumulation and Risk Prioritization of Psychoactive Substances in Cultured Fish. Chemosphere 2023, 325, 138440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. Impact of Ketamine on the Behavior and Immune System of Adult Medaka (Oryzias latipes) at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations and Eco-Risk Assessment in Surface Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 121577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Guo, C.; Deng, Y.; Jin, X.; Teng, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, F. Tissue-Specific Accumulation, Elimination, and Toxicokinetics of Illicit Drugs in Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaldo, A.; Gay, F.; Maddaloni, M.; Valiante, S.; De Falco, M.; Lenzi, M.; Laforgia, V. Presence of Cocaine in the Tissues of the European Eel, Anguilla Anguilla, Exposed to Environmental Cocaine Concentrations. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2012, 223, 2137–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondarza, P.M.; Haddad, S.P.; Avigliano, E.; Miglioranza, K.S.B.; Brooks, B.W. Pharmaceuticals, Illicit Drugs and Their Metabolites in Fish from Argentina: Implications for Protected Areas Influenced by Urbanization. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirla, K.T.; Groh, K.J.; Steuer, A.E.; Poetzsch, M.; Banote, R.K.; Stadnicka-Michalak, J.; Eggen, R.I.L.; Schirmer, K.; Kraemer, T. From the Cover: Zebrafish Larvae Are Insensitive to Stimulation by Cocaine: Importance of Exposure Route and Toxicokinetics. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 154, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabicova, K.; Grabic, R.; Fedorova, G.; Fick, J.; Cerveny, D.; Kolarova, J.; Turek, J.; Zlabek, V.; Randak, T. Bioaccumulation of Psychoactive Pharmaceuticals in Fish in an Effluent Dominated Stream. Water Res. 2017, 124, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Han, S.; Xu, Z.; Du, P.; Li, X. Assessment on the Adverse Effects on Different Kinds of Fish Induced by Methamphetamine during the Natural Attenuation Process Based on Adverse Outcome Pathway. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Su, H.; Li, H.-X.; Liu, J.-J.; Lin, L.; Xu, X.-R.; Zuo, L.-Z.; Zhao, J.-L. Uptake, Elimination, and Biotransformation Potential of a Progestagen (Cyproterone Acetate) in Tilapia Exposed at an Environmental Concentration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6804–6813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, M.K.; Rosati, L.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Maranho, L.A.; Laforgia, V.; Capaldo, A. Aquatic Pollution and Risks to Biodiversity: The Example of Cocaine Effects on the Ovaries of Anguilla Anguilla. Animals 2022, 12, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, F.; Ferrandino, I.; Monaco, A.; Cerulo, M.; Capasso, G.; Capaldo, A. Histological and Hormonal Changes in the European Eel (Anguilla anguilla) after Exposure to Environmental Cocaine Concentration. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaldo, A.; Gay, F.; Lepretti, M.; Paolella, G.; Martucciello, S.; Lionetti, L.; Caputo, I.; Laforgia, V. Effects of Environmental Cocaine Concentrations on the Skeletal Muscle of the European Eel (Anguilla anguilla). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaldo, A.; Gay, F.; Laforgia, V. Changes in the Gills of the European Eel (Anguilla anguilla) after Chronic Exposure to Environmental Cocaine Concentration. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, P.K.; Misra, A.L.; Mulé, S.J. Physiological Disposition and Biotransformation of (3H) Cocaine in Acutely and Chronically Treated Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1976, 196, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kirla, K.T.; Niklaus, S.; Kraemer, T.; Groh, K.; Schirmer, K.; Neuhauss, S. Cocaine Accumulation in Zebrafish Eyes Leads to Augmented Amplitudes in the Electroretinogram. Matters 2017, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Ma, R.; Barrett, H.; Wang, B.; Han, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, P.; Wang, W.; Peng, G.; Yu, G. How Microplastics Affect Chiral Illicit Drug Methamphetamine in Aquatic Food Chain? From Green Alga (Chlorella pyrenoidosa) to Freshwater Snail (Cipangopaludian cathayensis). Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, H.; Wang, F.; Barrett, H.; Wang, B.; Han, J.; Wu, J.; Huang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yu, G. Synthetical Effect of Microplastics and Chiral Drug Amphetamine on a Primary Food Source Algae Chlorella Pyrenoids. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 169, 113415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolter, C.; Arlinghaus, R. Navigation Impacts on Freshwater Fish Assemblages: The Ecological Relevance of Swimming Performance. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2003, 13, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, T.; Fick, J.; Jonsson, M.; Klaminder, J. Dilute Concentrations of a Psychiatric Drug Alter Behavior of Fish from Natural Populations. Science 2013, 339, 814–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho Santos, M.E.; Horký, P.; Grabicová, K.; Steinbach, C.; Hubená, P.; Šálková, E.; Slavík, O.; Grabic, R.; Randák, T. From Metabolism to Behaviour—Multilevel Effects of Environmental Methamphetamine Concentrations on Fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.-H.; Hwang, C.-C.; Chen, T.-H.; Chen, P.-J. Developmental Exposures to Waterborne Abused Drugs Alter Physiological Function and Larval Locomotion in Early Life Stages of Medaka Fish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 165, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horký, P.; Grabic, R.; Grabicová, K.; Brooks, B.W.; Douda, K.; Slavík, O.; Hubená, P.; Sancho Santos, E.M.; Randák, T. Methamphetamine Pollution Elicits Addiction in Wild Fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, jeb242145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riehl, R.; Kyzar, E.; Allain, A.; Green, J.; Hook, M.; Monnig, L.; Rhymes, K.; Roth, A.; Pham, M.; Razavi, R.; et al. Behavioral and Physiological Effects of Acute Ketamine Exposure in Adult Zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2011, 33, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelotti, P.; Quadros, V.A.; Pereira, M.E.; Rosemberg, D.B. Ketamine Modulates Aggressive Behavior in Adult Zebrafish. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 684, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, V.M.; Bortolotto, J.W.; Kist, L.W.; Azevedo, M.B.d.; Fritsch, R.S.; Oliveira, R.d.L.; Pereira, T.C.B.; Bonan, C.D.; Vianna, M.R.; Bogo, M.R. Endosulfan Exposure Inhibits Brain AChE Activity and Impairs Swimming Performance in Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Patiño, M.A.; Yu, L.; Cabral, H.; Zhdanova, I.V. Anxiogenic Effects of Cocaine Withdrawal in Zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 93, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.-X.; Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M.; Leon, J.; Czarnocki, Z. Melatonin as an Antioxidant: Biochemical Mechanisms and Pathophysiological Implications in Humans. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2003, 50, 1129–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumnongprakhon, P.; Govitrapong, P.; Tocharus, C.; Pinkaew, D.; Tocharus, J. Melatonin Protects Methamphetamine-Induced Neuroinflammation Through NF-κB and Nrf2 Pathways in Glioma Cell Line. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panmak, P.; Nopparat, C.; Permpoonpattana, K.; Namyen, J.; Govitrapong, P. Melatonin Protects against Methamphetamine-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathological Changes in Rat Hippocampus. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 148, 105121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namyen, J.; Permpoonputtana, K.; Nopparat, C.; Tocharus, J.; Tocharus, C.; Govitrapong, P. Protective Effects of Melatonin on Methamphetamine-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Rat Model. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 37, 640–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Deng, Y.; Guo, C.; Ding, C.; Xu, J.; Wu, F. Behavioral Changes and Metabolic Responses of Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Exposed to Methamphetamine. ACS EST Water 2023, 3, 2551–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morash, A.J.; Bureau, D.P.; McClelland, G.B. Effects of Dietary Fatty Acid Composition on the Regulation of Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase (CPT) I in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 152, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.; Di Monte, D.A.; Luo, J.J.; DeLanney, L.E.; Irwin, I.; Langston, J.W. Rapid ATP Loss Caused by Methamphetamine in the Mouse Striatum: Relationship between Energy Impairment and Dopaminergic Neurotoxicity. J. Neurochem. 1994, 62, 2484–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Gu, H.; Lin, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhu, R.; Kong, J.; Luo, L.; Long, H.; Liu, B.; Chen, B.; et al. Remodeling of Brain Lipidome in Methamphetamine-Sensitized Mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 279, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. The Exploration of Joint Toxicity and Associated Mechanisms of Primary Microplastics and Methamphetamine in Zebrafish Larvae. Toxics 2024, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jang, W.-J.; Yu, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.-K.; Jeong, C.-H.; Lee, S. Revealing Metabolic Perturbation Following Heavy Methamphetamine Abuse by Human Hair Metabolomics and Network Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Peng, Q.; Fang, M.; Liu, W.; Kang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Yung, K.K.L.; Mo, Z. Inhibiting Effects of Rhynchophylline on Zebrafish Methamphetamine Dependence Are Associated with Amelioration of Neurotransmitters Content and down-Regulation of TH and NR2B Expression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 68, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wisner, A.S.; Schiefer, I.T.; Williams, F.E.; Hall, F.S. Methamphetamine-Induced Lethal Toxicity in Zebrafish Larvae. Psychopharmacology 2022, 239, 3833–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Nguyen, A.H.; Jilani, D.; Trigo Torres, R.S.; Schmiess-Heine, L.; Le, T.; Xia, X.; Cao, H. Consecutive Treatments of Methamphetamine Promote the Development of Cardiac Pathological Symptoms in Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaldo, A.; Gay, F.; Caputo, I.; Lionetti, L.; Paolella, G.; Di Gregorio, I.; Martucciello, S.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Rosati, L.; Laforgia, V. Effects of Environmental Cocaine Concentrations on COX and Caspase-3 Activity, GRP-78, ALT, CRP and Blood Glucose Levels in the Liver and Kidney of the European Eel (Anguilla anguilla). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shu, G.; Bai, Y.; Chao, J.; Chen, X.; Yao, H. Effect of Methamphetamine on the Fasting Blood Glucose in Methamphetamine Abusers. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 1585–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argente Villaplana, C.R.; Civera Andrés, M.; Real Collado, J.T.; Martínez-Hervás, S.; Ascaso Gimilio, J.F.; Carmena Rodríguez, R. Hyperglycemia Secondary to Consumption of Cocaine and Atypical Antipsychotic Drugs. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2008, 55, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.-D.; Shi, W.-J.; Li, S.-Y.; Zhang, J.-G.; Lu, Z.-J.; Long, X.-B.; Liu, X.; Huang, C.-S.; Ying, G.-G. Ephedrine and Cocaine Cause Developmental Neurotoxicity and Abnormal Behavior in Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 265, 106765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolini, M.; Bini, L.; Magni, S.; Rizzo, A.; Ghilardi, A.; Landi, C.; Armini, A.; Del Giacco, L.; Binelli, A. Exposure to Cocaine and Its Main Metabolites Altered the Protein Profile of Zebrafish Embryos. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toborek, M.; Seelbach, M.J.; Rashid, C.S.; András, I.E.; Chen, L.; Park, M.; Esser, K.A. Voluntary Exercise Protects against Methamphetamine-Induced Oxidative Stress in Brain Microvasculature and Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Mol. Neurodegener. 2013, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berríos-Cárcamo, P.; Quezada, M.; Quintanilla, M.E.; Morales, P.; Ezquer, M.; Herrera-Marschitz, M.; Israel, Y.; Ezquer, F. Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation as a Pivot in Drug Abuse. A Focus on the Therapeutic Potential of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Agents and Biomolecules. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.M.; Liu, J.-H.; Shu, L.-H.; Chen, C.H. Anti-Oxidative Responses of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Gill, Liver and Brain Tissues upon Acute Cold Shock. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 187, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, J. Methamphetamine Shows Different Joint Toxicity for Different Types of Microplastics on Zebrafish Larvae by Mediating Oxidative Stress. Toxics 2023, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, E.-J.; Tran, H.-Q.; Nguyen, P.-T.; Jeong, J.H.; Nah, S.-Y.; Jang, C.-G.; Nabeshima, T.; Kim, H.-C. Role of Mitochondria in Methamphetamine-Induced Dopaminergic Neurotoxicity: Involvement in Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Pro-Apoptosis—A Review. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatib, I.; Horyn, O.; Bodnar, O.; Lushchak, O.; Rychter, P.; Falfushynska, H. Molecular and Biochemical Evidence of the Toxic Effects of Terbuthylazine and Malathion in Zebrafish. Animals 2023, 13, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falfushynska, H.; Poznanskyi, D.; Kasianchuk, N.; Horyn, O.; Bodnar, O. Multimarker Responses of Zebrafish to the Effect of Ibuprofen and Gemfibrozil in Environmentally Relevant Concentrations. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 109, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falfushynska, H.; Khatib, I.; Kasianchuk, N.; Lushchak, O.; Horyn, O.; Sokolova, I.M. Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Common Pesticides (Roundup and Chlorpyrifos) and Their Mixtures in a Zebrafish Model (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falfushynska, H.; Horyn, O.; Osypenko, I.; Rzymski, P.; Wejnerowski, Ł.; Dziuba, M.K.; Sokolova, I.M. Multibiomarker-Based Assessment of Toxicity of Central European Strains of Filamentous Cyanobacteria Aphanizomenon gracile and Raphidiopsis raciborskii to Zebrafish Danio rerio. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falfushynska, H.; Kasianchuk, N.; Siemens, E.; Henao, E.; Rzymski, P. A Review of Common Cyanotoxins and Their Effects on Fish. Toxics 2023, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedrossiantz, J.; Bellot, M.; Dominguez-García, P.; Faria, M.; Prats, E.; Gómez-Canela, C.; López-Arnau, R.; Escubedo, E.; Raldúa, D. A Zebrafish Model of Neurotoxicity by Binge-Like Methamphetamine Exposure. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 770319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mao, K.; Du, W.; Cai, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. Diluted Concentrations of Methamphetamine in Surface Water Induce Behavior Disorder, Transgenerational Toxicity, and Ecosystem-Level Consequences of Fish. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolini, M.; Ghilardi, A.; Della Torre, C.; Magni, S.; Prosperi, L.; Calvagno, M.; Del Giacco, L.; Binelli, A. Environmental Concentrations of Cocaine and Its Main Metabolites Modulated Antioxidant Response and Caused Cyto-Genotoxic Effects in Zebrafish Embryo Cells. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 226, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, L.; Caputo, I.; Lionetti, L.; Fontes, M.K.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Capaldo, A. Side Effects of Human Drug Use: An Overview of the Consequences of Eels’ Exposure to Cocaine. Fish 2023, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. The Stress Response in Fish. Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 591–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Alarcón, N.; Osorio-Méndez, J.J.; Ayala-Fajardo, A.; Garzón-Méndez, W.F.; Garavito-Aguilar, Z.V. Zebrafish and Artemia Salina in Vivo Evaluation of the Recreational 25C-NBOMe Drug Demonstrates Its High Toxicity. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, X.; Qu, L.; Zhou, W.; Sun, X.; Hou, J.; Xu, H.; Cheng, M. Gut Microbiota Taxon-Dependent Transformation of Microglial M1/M2 Phenotypes Underlying Mechanisms of Spatial Learning and Memory Impairment after Chronic Methamphetamine Exposure. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0030223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awkerman, J.A.; Lavelle, C.M.; Henderson, W.M.; Hemmer, B.L.; Lilavois, C.R.; Harris, P.; Zielinski, N.; Hoglund, M.D.; Glinski, D.A.; MacMillan, D.; et al. Cross-Taxa Distinctions in Mechanisms of Developmental Effects for Aquatic Species Exposed to Trifluralin. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 1797–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Miller, G.M. Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 as a Monoaminergic Modulator in Brain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, A.; Hirano, K.; Shimizu, M.; Fukada, H.; Fujita, T.; Ito, F.; Takada, H.; Nakamura, M.; Iguchi, T. Carp (Cyprinus Carpio) Vitellogenin: Characterization of Yolk Proteins, Development of Immunoassays and Use as Biomarker of Exposure to Environmental Estrogens. Environ. Sci. 2007, 14, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, T.; Ohkubo, N.; Andoh, T.; Sullivan, C.V.; Hara, A. Two Forms of Vitellogenin, Yielding Two Distinct Lipovitellins, Play Different Roles during Oocyte Maturation and Early Development of Barfin Flounder, Verasper Moseri, a Marine Teleost That Spawns Pelagic Eggs. Dev. Biol. 1999, 213, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, S. Phosvitin Plays a Critical Role in the Immunity of Zebrafish Embryos via Acting as a Pattern Recognition Receptor and an Antimicrobial Effector. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 22653–22664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, J.G.; Dybing, E.; Greim, H.A.; Ladefoged, O.; Lambré, C.; Tarazona, J.V.; Brandt, I.; Vethaak, A.D. Health Effects of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals on Wildlife, with Special Reference to the European Situation. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2000, 30, 71–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arinç, E.; Bozcaarmutlu, A. Catalyzation of Cocaine N-demethylation by Cytochromes P4502B, P4503A, and P4502D in Fish Liver. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2003, 17, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrapalan, T.; Kwong, R.W.M. Functional Significance and Physiological Regulation of Essential Trace Metals in Fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, jeb238790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.R.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; Wightman, R.M.; Caron, M.G. Mechanisms of Amphetamine Action Revealed in Mice Lacking the Dopamine Transporter. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccone, G.; Capillo, G.; Fernandes, J.M.O.; Kiron, V.; Lauriano, E.R.; Alesci, A.; Lo Cascio, P.; Guerrera, M.C.; Kuciel, M.; Zuwala, K.; et al. Expression of the Antimicrobial Peptide Piscidin 1 and Neuropeptides in Fish Gill and Skin: A Potential Participation in Neuro-Immune Interaction. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzenback, B.A. Antimicrobial Peptides as Mediators of Innate Immunity in Teleosts. Biology 2015, 4, 607–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, L.R.; Mihu, M.R.; Gácser, A.; Santambrogio, L.; Nosanchuk, J.D. Methamphetamine Enhances Histoplasmosis by Immunosuppression of the Host. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, M.M.; Napier, T.C.; Graves, S.M.; Mahmood, F.; Raeisi, S.; Baum, L.L. Methamphetamine Decreases CD4 T Cell Frequency and Alters pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production in a Model of Drug Abuse. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 752, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potula, R.; Haldar, B.; Cenna, J.M.; Sriram, U.; Fan, S. Methamphetamine Alters T Cell Cycle Entry and Progression: Role in Immune Dysfunction. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitha, A.N.; Chow, D.; Vaval, V.; Guerrero, P.; Rivera-Rodriguez, D.E.; Martinez, L.R. Methamphetamine Compromises the Adaptive B Cell-Mediated Immunity to Antigenic Challenge in C57BL/6 Mice. Front. Toxicol. 2021, 3, 629451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, M.; Raza, A.; Fraser, S.; Nurgali, K.; Apostolopoulos, V. Methamphetamine and Its Immune-Modulating Effects. Maturitas 2019, 121, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftis, J.M.; Janowsky, A. Neuroimmune Basis of Methamphetamine Toxicity. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2014, 118, 165–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vilca, S.J.; Margetts, A.V.; Fleites, I.; Wahlestedt, C.; Tuesta, L.M. Microglia Contribute to Methamphetamine Reinforcement and Reflect Persistent Transcriptional and Morphological Adaptations to the Drug. bioRxiv 2024, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.R. Structure of Fish Toll-like Receptors (TLR) and NOD-like Receptors (NLR). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 1602–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulkes, M.J.; Henry, K.M.; Rougeot, J.; Hooper-Greenhill, E.; Loynes, C.A.; Jeffrey, P.; Fleming, A.; Savage, C.O.; Meijer, A.H.; Jones, S.; et al. Expression and Regulation of Drug Transporters in Vertebrate Neutrophils. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stosik, M.; Tokarz-Deptuła, B.; Deptuła, W. Haematopoiesis in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 902941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belo, M.A.A.; Oliveira, M.F.; Oliveira, S.L.; Aracati, M.F.; Rodrigues, L.F.; Costa, C.C.; Conde, G.; Gomes, J.M.M.; Prata, M.N.L.; Barra, A.; et al. Zebrafish as a Model to Study Inflammation: A Tool for Drug Discovery. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kong, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, L.; Nie, G.; Li, X. Toll-like Receptor Recognition of Bacteria in Fish: Ligand Specificity and Signal Pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loes, A.N.; Hinman, M.N.; Farnsworth, D.R.; Miller, A.C.; Guillemin, K.; Harms, M.J. Identification and Characterization of Zebrafish Tlr4 Coreceptor Md-2. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersche, K.D.; Döffinger, R. Inflammation and Infection in Human Cocaine Addiction. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2017, 13, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, M.; Alenina, N.; Bader, M.; Przegaliński, E. Behavioral Evidence for the Significance of Serotoninergic (5-HT) Receptors in Cocaine Addiction. Addict. Biol. 2010, 15, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mersereau, E.J.; Poitra, S.L.; Espinoza, A.; Crossley, D.A., 2nd; Darland, T. The Effects of Cocaine on Heart Rate and Electrocardiogram in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 172–173, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kacprzak, V.; Patel, N.A.; Riley, E.; Yu, L.; Yeh, J.-R.J.; Zhdanova, I.V. Dopaminergic Control of Anxiety in Young and Aged Zebrafish. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2017, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, E.; Maymi, V.; Pawlyszyn, S.; Yu, L.; Zhdanova, I.V. Prenatal Cocaine Exposure Disrupts the Dopaminergic System and Its Postnatal Responses to Cocaine. Genes Brain Behav. 2018, 17, e12436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, F.; Torraca, V.; Meijer, A.H. Chemokine Receptors and Phagocyte Biology in Zebrafish. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periyasamy, P.; Liao, K.; Kook, Y.H.; Niu, F.; Callen, S.E.; Guo, M.-L.; Buch, S. Cocaine-Mediated Downregulation of miR-124 Activates Microglia by Targeting KLF4 and TLR4 Signaling. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 3196–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.-H.; Wang, L.-Q.; He, J.-Y.; Zhu, X.-L.; Huang, W.; Wang, S.-W.; Qin, Q.-W.; Sun, H.-Y. MicroRNA-124 Promotes Singapore Grouper Iridovirus Replication and Negatively Regulates Innate Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 767813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mersereau, E.J.; Boyle, C.A.; Poitra, S.; Espinoza, A.; Seiler, J.; Longie, R.; Delvo, L.; Szarkowski, M.; Maliske, J.; Chalmers, S.; et al. Longitudinal Effects of Embryonic Exposure to Cocaine on Morphology, Cardiovascular Physiology, and Behavior in Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butelman, E.R.; Yuferov, V.; Kreek, M.J. κ-Opioid Receptor/dynorphin System: Genetic and Pharmacotherapeutic Implications for Addiction. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Santiago, A.E.; Gómez-Cabrera, A.S.; Baptista-Rosas, R.C.; Zúñiga-González, G.M.; Gómez-Meda, B.C.; Navarro, A.A.S.; Sánchez-Parada, M.G. Cytogenotoxicity Effects in Addicts with Multidrug Consumption. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2024, 65, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limanaqi, F.; Gambardella, S.; Biagioni, F.; Busceti, C.L.; Fornai, F. Epigenetic Effects Induced by Methamphetamine and Methamphetamine-Dependent Oxidative Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4982453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.W.; Jeng, W.; Wells, P.G. Methamphetamine-Initiated Neurodevelopmental Deficits Are Enhanced in Oxoguanine Glycosylase 1 (ogg1) Knock-out Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 78, 379. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, S.; Ji, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Gu, A. 8-Oxoguanine DNA Glycosylase 1 (ogg1) Maintains the Function of Cardiac Progenitor Cells during Heart Formation in Zebrafish. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 2954–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redman, P.T.; He, K.; Hartnett, K.A.; Jefferson, B.S.; Hu, L.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Levitan, E.S.; Aizenman, E. Apoptotic Surge of Potassium Currents Is Mediated by p38 Phosphorylation of Kv2.1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3568–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoguchi, H.; Yamada, K.; Mizuno, M.; Mizuno, T.; Nitta, A.; Noda, Y.; Nabeshima, T. Regulations of Methamphetamine Reward by Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2/ets-like Gene-1 Signaling Pathway via the Activation of Dopamine Receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zang, S.; Chen, X.; Jiang, L.; Gu, A.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Xiao, H. Involvement of the Delayed Rectifier Outward Potassium Channel Kv2.1 in Methamphetamine-Induced Neuronal Apoptosis via the p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Barros, W.A.; Nunes, C.d.S.; Souza, J.A.d.C.R.; Nascimento, I.J.D.S.; Figueiredo, I.M.; de Aquino, T.M.; Vieira, L.; Farias, D.; Santos, J.C.C.; de Fátima, Â. The New Psychoactive Substances 25H-NBOMe and 25H-NBOH Induce Abnormal Development in the Zebrafish Embryo and Interact in the DNA Major Groove. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 2, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, O.; Ribeiro, C.; Félix, L.; Gaivão, I.; Carrola, J.S. Effects of Acute Metaphedrone Exposure on the Development, Behaviour, and DNA Integrity of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 49567–49576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikshenas Shahrestani, V.; Haddadi, M.; Samzadeh Kermani, A.R. Behavioral and Molecular Analysis of Antioxidative Potential of Rosmarinic Acid Against Methamphetamine-Induced Augmentation of Casp3a mRNA in the Zebrafish Brain. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, W.A.; Vijayan, M.M. Zygotic Venlafaxine Exposure Impacts Behavioral Programming by Disrupting Brain Serotonin in Zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14578–14588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| IDs | Enantiomer | Place | Location | Concentration [ng/L] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamine | S(+)-AMP | Scotland | Clyde Estuary (5 different locations) | ND | [76] |
| R(−)-AMP | <40 | ||||
| R/S(±)-AMP | <30 | [77] | |||
| Southern Aegean Sea | Santorini Island INF/EFF | <10.1/<LOD | [78] | ||
| USA | San Francisco Bay | <9.8 | [79] | ||
| Methamphetamine | S(+)-METH | Scotland | Clyde Estuary (5 different locations) | ND | [76] |
| R(−)-METH | ND | ||||
| Southern Aegean Sea | Santorini Island INF/EFF | <LOD | [78] | ||
| Cocaine | Brazil Sao Paulo | Santos Bay, surface | 12.6–400.5 | [80] | |
| Santos Bay, bottom | 29.8–537 | ||||
| Southern Aegean Sea | Santorini Island INF/EFF | 4.4–49.3/<11.5 | [78] | ||
| USA | San Francisco Bay | <2.5 | [79] | ||
| Benzoylecgonine | Brazil Sao Paulo | Santos Bay, surface | 10.9–19.5 | [80] | |
| Santos Bay, bottom | 4.6–20.8 | ||||
| Southern Aegean Sea | Santorini Island INF/EFF | 9.0–104.6/<77.3 | [78] | ||
| Morphine | 1.8–19.8/<2.7 | ||||
| Methadone | 0.9–5.6/<4.5 | ||||
| 9-tetrahydrocannabinol | 2.8–31.7/1.2–22.0 | ||||
| -lysergic acid diethylamide | <1.6 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Falfushynska, H.; Rychter, P.; Boshtova, A.; Faidiuk, Y.; Kasianchuk, N.; Rzymski, P. Illicit Drugs in Surface Waters: How to Get Fish off the Addictive Hook. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040537
Falfushynska H, Rychter P, Boshtova A, Faidiuk Y, Kasianchuk N, Rzymski P. Illicit Drugs in Surface Waters: How to Get Fish off the Addictive Hook. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(4):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040537
Chicago/Turabian StyleFalfushynska, Halina, Piotr Rychter, Anastasiia Boshtova, Yuliia Faidiuk, Nadiia Kasianchuk, and Piotr Rzymski. 2024. "Illicit Drugs in Surface Waters: How to Get Fish off the Addictive Hook" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 4: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040537
APA StyleFalfushynska, H., Rychter, P., Boshtova, A., Faidiuk, Y., Kasianchuk, N., & Rzymski, P. (2024). Illicit Drugs in Surface Waters: How to Get Fish off the Addictive Hook. Pharmaceuticals, 17(4), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040537