Synthetic Strategies to Terpene Quinones/Hydroquinones
Abstract
:1. Introduction


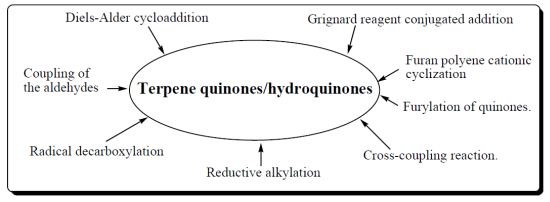
2. Synthetic Approches Terpenylquinone/Hydroquinone
- ➢ Diels-Alder cycloaddition reaction.
- ➢ Coupling of the aldehydes with lithiated hydroquinone ether.
- ➢ Radical decarboxylation and quinone addition reaction
- ➢ Grignard reagent conjugated addition to α,β-unsaturated carbonyl group.
- ➢ Reductive alkylation of enones.
- ➢ Cross-coupling reaction.
- ➢ Furylation of quinones.
- ➢ Furan polyene cationic cyclization.
3. Diels-Alder Cycloaddition Reaction






4. Coupling of the Aldehydes with Lithiated Hydroquinone Ethers










5. Radical Decarboxylation and Quinone Addition Reaction




6. Grignard Reagent Conjugated Addition to α,β-Unsaturated Carbonyl Group


7. Reductive Alkylation of Enones





8. Cross-Coupling Reaction


9. Furylation of Quinones

10. Furan Polyene Cationic Cyclization

11. Application of Cell Culture for the Production of Bioactive Compounds from Sponges
12. Summary
Acknowledgements
References
- Mishra, B.B.; Tiwari, V.K. Natural Product in Drug Discovery: Clinical Evaluations and Investigations. In Opportunity, Challenge, and Scope of Natural Products in Medicinal Chemistry; Tiwari, V.K., Mishra, B.B., Eds.; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2011; pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, B.B.; Tiwa, V.K. Natural products: An evolving role in future drug discovery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4769–4807. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, G.T. Natural products and Pharma 2011: Strategic changes spur new opportunities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products of therapeutic importance. Compr. Nat. Prod. II 2010, 2, 623–650. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.W.-H.; Vederas, J.C. Drug discovery and natural products: End of an era or an endless frontier? Science 2009, 325, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakuni, D.S.; Rawat, D.S. Bioactive Natural Products; Springer & Anamaya Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, A.L. Natural products as a screening resource. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2007, 11, 480–484. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 461–477. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M.; Snader, K.M. The influence of natural products upon drug discovery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2000, 17, 215–234. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M.; Snader, K.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, I.; Anderson, E.A. The renaissance of natural products as drug candidates. Science 2005, 310, 451–453. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Deng, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, L.; He, R.; Xu, Y. The screening toolbox of bioactive substances from natural products: A review. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar]
- Verpoorte, R. Exploration of nature’s chemodiversity: The role of secondary metabolites as leads in drug development. Drug Discov. Today 1988, 3, 232–238. [Google Scholar]
- Sticher, O. Natural product isolation. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 517–554. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, Z.E.; Brimble, M.A. Molecules derived from the extremes of life. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 44–71. [Google Scholar]
- Bemis, G.W.; Murcko, M.A. The properties of known drugs. 1. Molecular frameworks. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 2887–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A. The impact of natural products upon modern drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 306–317. [Google Scholar]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Natural products sources of drugs: Plants, microbes, marine organisms, and animals. Compr. Med. Chem. II 2007, 1, 355–403. [Google Scholar]
- Buss, A.D.; Butler, M.S. Natural Product Chemistry for Drug Discovery; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Grothaus, G.P.; Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Plant natural products in anticancer drug discovery. Curr. Org. Chem. 2010, 14, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, Y.-W.; Balunas, M.J.; Chai, H.B.; Kinghorn, A.D. Drug discovery from natural sources. AAPS J. 2006, 8, E239–E253. [Google Scholar]
- Koehn, F.E.; Carter, G.T. The envolving role of natural products in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 206–220. [Google Scholar]
- Balunas, M.J.; Kinghorn, A.D. Drug discovery from medicinal plants. Life Sci. 2005, 78, 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, W.P.; Chin, Y.-W.; Kinghorn, A.D. The role of pharmacognosy in modern medicine and pharmacy. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 247–264. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, M.S. The role of natural product chemistry in drug discovery. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 2141–2153. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, M.S. Natural products to drugs: Natural products derived compounds in clinical trials. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 162–195. [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant, D.S.; Farnsworth, N.R. The value of plants used in traditional medicine for drug discovery. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Kinghorn, A.D. The Discovery of Drugs from Higher Plants. In The Discovery of Natural Products with Therapeutic Potential; Gullo, V.P., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 81–108. [Google Scholar]
- Raviña, E. The Evolution of Drug Discovery. From Traditional Medicines to Modern Drugs; Wiley-WCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bailly, C. Ready for comeback of natural products in oncololoy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Cragg, G.M.; Grothaus, P.G.; Newman, D.J. Impact of natural products on developing new anti-cancer agents. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3012–3043. [Google Scholar]
- Gordaliza, M. Natural products as leads to anticancer drugs. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2007, 9, 767–776. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.-H. Discovery and development of natural product-derived chemotherapeutic agents based on a medicinal chemistry approach. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 500–516. [Google Scholar]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Industrial Applications Natural Products for Medicinal Purposes. Drugs from Nature: Present, Development and Future Prospects. In Natural Products in the New Millenium: Prospects and Industrial Applications; Rauter, A.P., Palma, F.B., Justino, J., Araújo, M.E., Dos Santos, S.P., Eds.; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 441–461. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, J.; Cragg, G. Natural products in medicinal chemistry. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.-Y.; Xiao, O.; Pan, J.-Y.; Wu, J. Natural products from semi-mangrove flora: Source, chemistry and bioactivities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 281–298. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M.; Kingston, D.G.I. Natural Products as Pharmaceuticals and Sources for Lead Structures. In The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry; Wermuth, C.G., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2003; pp. 159–186. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J. Natural products as leads to potential drugs: An old process or the new hope for drug discovery? J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 2589–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galm, U.; Shen, B. Natural products drug discovery: The times have never been better. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Rishton, G.M. Natural products as a robust source of new drugs and drug leads: Past successes and present day issues. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 43D–49D. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, K.S. New aspects of natural products in drug discovery. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, A.L. Natural product in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 894–901. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, M.S. Natural product to drug: Natural products derived compounds in clinical trials. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 475–516. [Google Scholar]
- Langer, T.; Laggner, C.; Rollinger, J.M.; Stuppner, H. Pharmacophore-based screening for the successful identification of bio-active natural products. Chimia 2007, 61, 350–354. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, G.; Mayhudin, N.A.; Mitova, M.I.; Sun, L.; van der Sar, S.; Blunt, J.W.; Cole, A.L.; Ellis, G.; Laatsch, H.; Munro, M.H. Evolving trends in the dereplication of natural product extracts: New methodology for rapid, small-scale investigation of natural product extracts. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.M.; Danishefsky, S.J. Small molecule natural products in the discovery of therapeutic agents: The synthesis connection. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 8329–8351. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.M.; Danishefsky, S.J. Applications of total synthesis toward the discovery of clinically useful anticancer agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1207–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.-H. Current developments in discovery and design of new drug candidates from plant natural. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 273–283. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.-P.; Yuan, J.; Sun, L.; She, Z.-G.; Wu, J.-H.; Lan, X.-J.; Zhu, X.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, S.-P. Statistical research on marine natural products based on data obtained between 1985 and 2008. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 514–525. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products: Metabolites of marine algae and herbivorous marine molluscs. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1984, 1, 251–280. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products: Metabolites of marine invertebrates. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1984, volume, 1551–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1986, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1987, 4, 539–576. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1988, 5, 613–663. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1990, 7, 269–309. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1991, 8, 97–147. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1992, 9, 323–364. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1993, 10, 497–539. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1994, 11, 355–394. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1995, 12, 223–269. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1996, 13, 75–125. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1997, 14, 259–302. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1998, 15, 113–158. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1999, 16, 155–198. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2000, 17, 7–5. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2001, 18, 1R–9R. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcotec, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2003, 20, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcotec, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcotec, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 15–61. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcotec, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 26–78. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Hu, W.P.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcotec, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 31–86. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Hu, W.P.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcotec, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Hu, W.P.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcotec, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 170–244. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcotec, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 165–237. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcotec, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 196–228. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, R.A. Marine natural product. Annu. Rep. Prog. Chem. Sect. B 2010, 106, 156–173. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, W.; Feeney, R.J. Contributions to the study of marine products XXXII. The nucleosides of sponges. I. J. Org. Chem. 1951, 16, 981–997. [Google Scholar]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug development from marine natural products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Highlights of marine natural products chemistry (1972–1999). Nat. Prod. Rep. 2000, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Proksch, P.; Ebel, R.; Edrada, R.A.; Schupp, P.; Lin, W.H.; Sudarsono; Wray, V.; Steube, K. Detection of pharmacologically active natural products using ecology. Selected examples from Indopacific marine invertebrates and sponge-derived fungi. Pure Appl. Chem. 2003, 75, 343–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, P.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R. Drugs from the seas-urrent status and microbiological implications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 125–214. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, R.K.; Xu, Z.R. Biomedical compounds from marine organisms. Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 123–146. [Google Scholar]
- Smit, A.J. Medicinal and pharmaceutical uses of seaweed natural products: A review. J. Appl. Phycol. 2004, 16, 245–322. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.T. Bioactive natural products from marine cyanobacteria for drug discovery. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 954–999. [Google Scholar]
- Gulder, T.A.M.; Moore, B.S. Chasing the treasures of the sea-bacterial marine natural products. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 252–320. [Google Scholar]
- Sabdono, A.; Radjasa, O.K. Microbial symbionts in marine sponges: Marine natural product factory. J. Coast. Dev. 2008, 11, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Piel, J. Metabolites from symbiotic bacteria. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 519–558. [Google Scholar]
- Skropeta, D. Deep-sea natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 1131–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg, C.; Zabriskie, T.M.; McPhail, K.L. Deep-sea hidrotermal: Potencial hot spot for natural products discovery. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 489–499. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G. Review of Dictionary of Marine Natural Products; Chapman & Hall/CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Haefner, B. Drugs from the deep: Marine natural products as drug candidates. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 536–544. [Google Scholar]
- El Sayed, K.A.; El Sayed, P.X.; Shen, X.; Perry, T.L.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Mark, T.C. Marine natural products as antituberculosis agents. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 949–953. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, T.-S.; Ngo, D.-H.; van Ta, Q.; Kim, S.-K. Marine organisms as a therapeutic source against herpes simplex virus infection. Eur. J. Phar. Sci. 2011, 44, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Abad, M.J.; Bermejo, P. Bioactive natural products from marine sources. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2001, 25, 683–755. [Google Scholar]
- Garson, M.J. Marine natural products as antifeedants. Compr. Nat. Prod. II 2010, 4, 503–537. [Google Scholar]
- Abad, M.J.; Bedoya, L.M.; Bermejo, P. Natural marine antiviral products. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2008, 35, 101–134. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, B.K. Marine natural products as a source of novel pharmacological agents. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1993, 4, 275–279. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, D.J. Natural products of marine algae: The interface of chemistry and biology. Mar. Chem. 1983, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, A.T.; Stach, J.E.M. Marine actinobacteria: New opportunities for natural product search and discovery. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 491–499. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, B.S. New dimensions in natural products research: Cultured marine microorganisms. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1995, 6, 284–291. [Google Scholar]
- Donia, M.; Hamann, M.T. Marine natural products and their potential applications as anti-infective agents. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 338–348. [Google Scholar]
- Glaser, K.B.; Mayer, A.M.S. A renaissance in marine pharmacology: From preclinical curiosity to clinical reality. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 440–448. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2005–6: Marine compounds with antihelmintic,antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 283–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.-X.; Jiang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Y. Marine natural products as sources of novel scaffolds: Achievement and concern. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 884–886. [Google Scholar]
- Albericio, F.; Álvarez, M.; Cuevas, C.; Francesch, A.; Pla, D.; Tulla-Puche, J. The Sea as a Source of New Drugs. In Molecular Imaging for Integrated Medical Therapy and Drug Development. Part IV; Tanaki, N., Kuge, Y., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, R.T.; Fenical, W. Pharmaceuticals from marine natural products: Surge or ebb? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausubel, J.H.; Crist, D.T.; Waggoner, P.E. Highlights of a Decade of Discovery. Census of Marine Life. 2010. Available online: http://www.coml.org/Highlights-2010 (accessed on 1 September 2011).
- Mayer, A.M.; Glaser, K.B.; Cuevas, C.; Jacobs, R.S.; Kem, W.; Little, R.D.; McIntosh, J.M.; Newman, D.J.; Potts, B.C.; Shuster, D.E. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: A current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- Fusetani, N. Biotechnological potentials of marine natural products. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 136, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, M.; Hendrik, L. Marine natural products: A new wave of drugs? Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusetani, N. Antifouling marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 400–410. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, A.L.; Moore, B.S. A sea of biosynthesis: Marine natural products meet the molecular age. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, P.; Putz, A.; Ortlepp, S.; Kjer, J.; Baye, M. Bioactive natural products from marine sponges and fungal endophytes. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 475–489. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikazu, S. Natural products from marine derived microorganisms. J. Synt. Org. Chem. Jpn. 2010, 68, 534–542. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, C.; Hsu, C.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Lin, C.-S. Anticancer drugs discovery and development from marine organisms. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 9, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Marine Microorganisms and Drug Discovery: Current Status and Future Potential. In Drugs from the Sea; Fusetani, N., Ed.; Karger: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 6–29. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartsmann, G.; Brondani, A.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Jimeno, J. Marine organisms and other novel natural sources of new cancer drugs. Lancet Oncol. 2001, 2, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, T.L.; Andrianasolo, T.L.; McPhail, K.; Flatt, P.; Gerwick, W.H. Marine natural products as anticancer drugs. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Nuijen, B.; Bouma, M.; Manada, C.; Jimeno, J.M.; Schellens, J.M.M.; Bult, A.; Beijnen, J.H. Pharmaceutical development of anticancer agents derived from marine sources. Anticancer Drugs 2000, 11, 793–811. [Google Scholar]
- Imhoff, J.F.; Labes, A.; Wiese, J. Bio-mining the microbial treasures of the ocean: New natural products. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 468–482. [Google Scholar]
- Hester, R.E.; Harrison, R.M.; Andersen, R.J.; Williams, D.E. Pharmaceuticals from the sea. Chem. Mar. Environ. 2000, 13, 55–80. [Google Scholar]
- Galeano, E.; Rojas, J.J.; Martínez, A. Pharmacological developments obtained from marine natural products and current pipeline perspective. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 287–300. [Google Scholar]
- Fattorusso, E.; Gerwick, W.H.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Handbook of Marine Natural Products; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Besse, J.-P.; Latour, J.-F.; Garric, J. Anticancer drugs in surface waters: What can we say about the occurrence and environmental significance of cytotoxic, cytostatic and endocrine therapy drugs? Environ. Int. 2012, 39, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjasa, O.K.; Vaske, Y.M.; Navarro, G.; Vervoort, H.C.; Tenney, K.; Linington, R.G.; Crews, P. Highlights of marine invertebrate-derived biosynthetic products: Their biomedical potential and possible production by microbial associants. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6658–6674. [Google Scholar]
- Miljanich, G.P. Ziconotide: Neural calcium channel blocker for treating severe chronic pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 3029–3040. [Google Scholar]
- Alicino, I.; Giglio, M.; Manca, F.; Bruno, F.; Puntillo, F. Intrathecal combination of ziconotide and morphine for refractory cancer pain: A rapidly acting and effective choice. Pain 2011, 152, 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas, C.; Francesch, A. Development of Yondelis® (trabectedin, ET-743). A semisynthetic process solves the supply problem. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfilippo, R.; Grosso, F.; Jones, R.L.; Banerjee, S.; Pilotti, S.; D’Incalci, M.; Dei Tos, A.P.; Raspagliesi, F.; Judson, I.; Casal, P.G. Trabectedin in advanced uterine leiomyosarcomas: A retrospective case series analysis from two reference centers. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 123, 553–556. [Google Scholar]
- Monneret, C. Impact actuel des produits naturels sur la découverte de nouveaux médicaments anticancéreux. Ann. Pharm. Fr. 2010, 68, 218–232. [Google Scholar]
- Burge, R.A. Advances in ovarian cancer disease control. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 124, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Meoni, G.; Cecere, F.L.; Chaib, I.; Giommoni, E.; di Costanzo, F. Prolonged response to trabectedin in a heavily pretreated patient with metastatic endometrial carcinoma: A case report and literature review. Gynecol. Oncol. Case Rep. 2011, 1, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Alday, P.H.; Correia, J.J. Macromolecular interaction of halichondrin B analogues eribulin (E7389) and E-076349 with tubulin by analitical ultacentrifugation. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 7927–7938. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.A.; Wilson, L.; Azarenko, O.; Zhu, X.; Lewis, B.M.; Littlefield, B.A.; Jordan, M.A. Eribulin binds at microtubule ends to a single site on tubulin to suppress dynamic instability. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, R.G. Eribulin in soft-tissue sarcomas. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 12, 988–989. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, R.G.; Yeung, B.K.S. Natural product drug discovery: The successful optimization of ISP-1 and halichondrin. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 523–528. [Google Scholar]
- Swami, U.; Chaudhary, I.; Ghalib, M.H.; Goel, S. Eribulin—Review of preclinical and clinical studies. Rev. Oncol. Hem. 2011, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Gordaliza, M. Terpeny-purines from the sea. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 833–847. [Google Scholar]
- Gordaliza, M. Cytotoxic terpene quinones from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2849–2870. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, B.M. Natural sesquiterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 1580–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, B.M. Natural sesquiterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 1180–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Marcos, I.S.; Conde, A.; Moro, R.F.; Basabe, P.; Díez, D.; Urones, J. Quinone/hydroquinone sesquiterpenes. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2010, 7, 230–254. [Google Scholar]
- Bozic, T.; Novakovic, I.; Gasic, M.J.; Juranic, Z.; Stanojkovic, T.; Tufegdzic, S.; Kljajic, Z.; Sladic, D. Synthesis and biological activity of derivatives of the marine quinone avarone. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 923–929. [Google Scholar]
- Benites, J.; Valderrama, J.A.; Rivera, F.; Rojo, L.; Campos, N.; Pedro, M.; Nascimento, M.S.J. Studies on quinones. Part 42: Synthesis of furylquinone and hydroquinones with antiproliferative activity against human tumor cell lines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 862–868, and all previous parts. [Google Scholar]
- Sladic, D.; Gasic, M.J. Reactivity and biological activity of marine sesquiterpene hydroquinones avarol and related compound from sponges of Order Dictyoceratida. Molecules 2006, 11, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Motti, C.A.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L.; Longeon, A.; Doyle, J.R.; Llewellyn, L.E.; Tapiolas, D.M.; Yin, P. Comparison of biological properties of several marine sponge-derived sesquiterpenoid quinOnes. Molecules 2007, 12, 1376–1388. [Google Scholar]
- De Rosa, S. Marine Natural Products: Analysis, Structure Elucidation, Bio-Activity and Potential Use as Drug. In Natural Products in the New Millenium: Prospects and Industrial Applications; Rauter, A.P., Palma, F.B., Justino, J., Araújo, M.E., Dos Santos, S.P., Eds.; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 441–461. [Google Scholar]
- Gordaliza, M.; Miguel del Corral, J.M.; Mahiques, M.M.; San Feliciano, A.; García-Grávalos, M.D. Terpenequinone with antitumor activity. PCT Int. Appl. WO 9604230 A1, 15 February 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Miguel del Corral, J.M.; Gordaliza, M.; Castro, M.A.; Mahiques, M.M.; Chamorro, P.; Molinari, A.; García-Grávalos, M.D.; Broughton, H.B.; San Feliciano, A. New selective cytotoxic diterpenylquinones and diterpeniylhydroquinones. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Amigo, M.; Terencio, M.; Paya, M.; Iodice, C.; de Rosa, S. Synthesis and evaluation of diverse thio avarol derivatives as potential UVB photoprotective candidates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 2561–2565. [Google Scholar]
- Schatton, W.; Schatton, M.; Pietschmamm, R. Method for the preparation of compositions with high avarol content from sponge and use for the prevention and treatment of psoriasis and tumors. Eur. Pat. Appl. EP 1391197 A1, 25 February 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Quideau, S.; Lebon, M.; Lamidey, A.-M. Enantiospecific synthesis of the antituberculosis marine sponge metabolite (+)-puupehenone. The arenol oxidative activation route. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 3975–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavatta, M.L.; Lopez-Gresa, M.P.; Gavagnin, M.; Melck, D.; Mauzo, E.; Guo, Y.-W.; van Soest, R.; Cimio, G. Studies on puupehenone-metabolites of Dysideas sp.: Structure and biological activity. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, H.; Kobayashi, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, I. Xestoquinone. A novel cardiotonic marine natural product isolated from the okinawan sea sponge Xestospongia sapra. Chem. Lett. 1985, 6, 713–716. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, P.; Kissau, L.; Mazitschek, R.; Huwe, A.; Furet, P.; Giannis, A.; Waldmann, H. Total synthesis and biological evaluation of the nakijiquinones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 11586–11593. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.-F.; Schetz, J.A.; Kelly, M.; Peng, J.-N.; Ang, K.K.H.; Flotow, H.; Leong, C.Y.; Ng, S.B.; Buss, A.D.; Wilkins, S.P.; et al. New antiinfective and human 5-HT2 receptor binding natural and semisynthetic compounds from the jamaican sponge Smenospongia aurea. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 476–480. [Google Scholar]
- Winder, P.L.; Baker, H.L.; Linley, P.; Guzmán, E.A.; Pomponi, S.A.; Diaz, M.C.; Reed, J.K.; Wright, A.E. Neopetrosiquinones A and B, sesquiterpene benzoquinones isolated from the deep-water sponge Neopetrosia cf. próxima. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6599–6603. [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer, R.H.; Müller, J.G.; Krauth-Siegel, R.L. Disulfide-reductase inhibitors as chemotherapeutic agents: The design of drugs for trypanosomiasis and malaria. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1995, 34, 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Monks, T.J.; Hanzlik, R.P.; Cohen, G.M.; Ross, D.; Graham, D.G. Quinone chemistry and toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1992, 112, 2–16. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, P.J. Molecular mechanisms of quinone cytotoxicity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1991, 80, 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Alegría, A.; Sánchez, S.; Sánchez-Muñoz, P.; Nieves, I.; Cruz, N.G.; Gordaliza, M.; Martín-Martín, M.L. Terpenylnaphthoquinones are reductively activated by NADH/NADH dehydrogenase. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2005, 87, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Alegría, A.; Cordones, E.; Marcano, Y.; Sanchez, S.; Gordaliza, M.; Martín-Martín, M.L. Reductive activation of terpenylnaphtoquinones. Toxicology 2002, 175, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, H.C.; Wenger, R.; Gerner, H.; Reuter, P.; Kuchino, Y.; Müller, W.E.G. Suppression of the modulatory effects of the antileukemic and anti-human immunodeficiency virus compound avarol on gene expression by tryptophan. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Sladić, D.; Gašić, M.J. Effects of iron(II) compounds on the amount of DNA damage in friend erythroleukemia cells induced by avarol. Role of hydroxyl radicals. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 1994, 59, 915–920. [Google Scholar]
- Novaković, I.; Vujčić, Z.; Božić, T.; Božić, N.; Milosavić, N.; Sladić, D. Chemical modification of β-lactoglobulin by quinones. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2003, 68, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Sladić, D.; Novaković, I.; Vujčić, Z.; Božić, T.; Božić, N.; Milić, D.; Šolaja, B.; Gašić, M.J. Protein covalent modification by biologically active quinones. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2004, 69, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunazuka, T. Total synthesis of natural products for finding pharmaceutical leads. Shinki Sozai Tansaku 2008, 146–153. [Google Scholar]
- Suyama, T.L.; Gerwick, W.H.; McPhail, K.L. Survey of marine marine product structure revisions: A synergy of spectroscopy and chemical synthesis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6675–6701. [Google Scholar]
- Baran, P.S.; Maimone, T.J.; Richter, J.M. Total synthesis of marine natural products without using protecting groups. Nature 2007, 446, 404–408. [Google Scholar]
- Hanessian, S. Structure-based synthesis: From natural products to drug prototypes. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, S. Natural product chemistry for drug discovery. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 697–701. [Google Scholar]
- Henkel, T.; Brunne, R.M.; Müller, H.; Reichel, F. Statistical investigation into the structural complementarity of natural products and synthetic compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 643–647. [Google Scholar]
- Feher, M.; Schmidt, J.M. Property distributions: Differences between drugs, natural products, and molecules from combinatorial chemistry. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 218–227. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, J.C.; Phillips, A.J. Marine natural products: Synthetic aspects. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 269–289. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, J.C.; Phillips, A.J. Marine natural products: Synthetic aspects. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 1186–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, J.C.; Phillips, A.J. Marine natural products: Synthetic aspects. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 245–265. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, J.C.; Phillips, A.J. Marine natural products: Synthetic aspects. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 95–117. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, J.C.; Nicholas, G.M.; Phillips, A.J. Marine natural products: Synthetic aspects. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 87–108. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas, G.M.; Phillips, A.J. Marine natural products: Synthetic aspects. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 79–99. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas, G.M.; Phillips, A.J. Marine natural products: Synthetic aspects. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 144–161. [Google Scholar]
- Capon, R.J. Marine natural products chemistry: Past, present, and future. Aust. J. Chem. 2010, 63, 851–854. [Google Scholar]
- ApSimon, J.; Thomson, R.H. The Total Synthesis of Naturally Occurring Quinones in Total Synthesis of Natural Products; ApSimon, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto, H.; Nakamura, E.; Kim, Y.P.; Okuyama, E.; Ishibashi, M.; Sassa, T. Immunomodulatoy constituents from an ascomycete, Eupenicillium crustaceum, and revised bsolute structure of macrophorin D. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1234–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhl, M.; Tanner, D. Recent applications of intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction to natural product synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2983–2992. [Google Scholar]
- Swersey, J.C.; Barrows, L.R.; Ireland, C.M. Mamanuthaquinone: An antimicrobial and cytotoxic metabolite of Fasciospongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 6687–6690. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, T.; Danishefsky, S.J.; de Gala, S. A concise total synthesis of (±)-mamanuthaquinone by using an exo-Diels-Alder reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1994, 33, 853–855. [Google Scholar]
- Gordaliza, M.; Miguel del Corral, J.M.; Castro, M.A.; Mahiques, M.M.; García-Grávalos, M.D.; San Feliciano, A. Synthesis and bioactivity of new antineoplastic terpenylquinones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1996, 6, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Hamann, M.T.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Biogenetically diverse, bioactive constituents of a sponge, order Verongida: Bromotyramines and sesquiterpene-shikimate derived metabolites. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 6565–6569. [Google Scholar]
- Kohmoto, S.; McConnell, O.J.; Wright, A.; Koehn, F.; Thompson, W.; Lui, M.; Snader, K.M. Puupehenone, a cytotoxic metabolite from a deep water marine sponge, Stronglyophora hartmani. J. Nat. Prod. 1987, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasu, S.S.; Yeung, B.K.S.; Hamann, T.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M.; Goins, K. Puupehenone-related metabolites from two Hawaiian sponges, Hyrtios sp. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 7290–7292. [Google Scholar]
- Pina, I.; Sanders, M.L.; Crews, P. Puupehenones congeners from an Indo-pacific Hyrtios sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, M.E.; Gonzales-Iriarte, M.; Barrero, A.F.; Salvador-Tormo, N.; Muñoz-Chapuli, R.; Medina, M.A.; Quesada, A.R. Study of puupehenone and related compounds as inhibitors of angiogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 110, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Manzaneda, E.; Chahboun, R.; Cabrera, E.; Alvarez, E.; Haidour, A.; Ramos, J.M.; Alvarez-Manzaneda, R.; Hmamouchi, M.; Bouanou, H. Diels-Alder cycloaddition approach to puupehenone-related metabolites: Synthesis of the potent angiogenesis inhibitor 8-epipuupedione. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 3332–3339. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Manzaneda, E.; Chahboun, R. Method for the preparation of mero sesquiterpenes from labdane diterpenes. WO 2009112622 A1, 17 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Barrero, A.F.; Alvarez-Manzaneda, E.J.; Herrador, M.; Chahboun, R.; Galera, P. Synthesis and antitumoral activities of marine ent-chromazonarol and related compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 2325–2328. [Google Scholar]
- Barrero, A.F.; Alvarez-Manzaneda, E.J.; Chahboun, R.; Cortes, M.; Armstrong, V. Synthesis and antitumoral activities of puupehedione and related compounds. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 15181–15208. [Google Scholar]
- Kamble, R.M.; Ramana, M.M.V. Microwave-assisted Diels-Alder reaction of 1,3,3-trimethyl-2-vinyl-1-cyclohexene with chromones-an expeditious approach to analogues of the puupehenone group of marine diterpenoids. Can. J. Chem. 2010, 88, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Kurata, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Suzuki, M. Cyclozonarone, a sesquiterpene-substituted benzoquinone derivative from the brown alga Dictyopteris undulata. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 749–752. [Google Scholar]
- Schroder, J.; Matthes, B.; Seifert, K. Total synthesis of the marine sesquiterpene quinone (−)-cyclozonarone. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 8151–8152. [Google Scholar]
- Cuellar, M.A.; Salas, C.; Cortés, M.J.; Morillo, A.; Maya, J.D.; Preite, M.D. Synthesis and in vitro trypanocide activity of several polycyclic drimane-quinone derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 2489–2497. [Google Scholar]
- Roll, D.M.; Scheuer, P.J.; Matsutsumoto, G.K.; Clardy, J. Halenaquinone, a pentacyclic polihetide from a marine sponge. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 6177–6178. [Google Scholar]
- Kienzler, M.A.; Suseno, S.; Trauner, D. Vinyl Quiñónez as Diles-Alder dienes: Concise sinthesis of (−)-halenaquinone. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8604–8605. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, H.S.; Souza, F.E.S.; Rodrigo, R.G.A. A Short synthesis of (±)-halenaquinone. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 3639–3641. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, J.; Magg, C.; Seiferd, K. Total synthesis of the marine sesquiterpene hydroquinone zonarol and isozonarol and the sequiterpene uinine zonarone e isozonarone. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 5469–5473. [Google Scholar]
- Laube, T.; Schröder, J.; Magg, C.; Strhle, R.; Seiferd, K. Total synthesis of yahazunol, zonarone and isozonarone. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 4299–4309. [Google Scholar]
- Fenical, W.; Sims, J.J.; Squatrito, D.; Wing, R.M.; Radlick, P. Marine natural products VII. Zonarol and isozonarol, fungitoxic hydroquinones from the brown seaweed Dictyopteris zonarioides. J. Org. Chem. 1973, 38, 2383–2386. [Google Scholar]
- Laube, T.; Bernet, A.; Dahne, H.; Jacobsen, I.D.; Seifert, K. Synthesis and pharmacological activities of some sequiterpene quinones and hydroquinones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Herlem, D.; Kerragoret, J.; Yu, D.; Khuong-Huu, F.; Kende, A.S. Studies toward the total synthesis of polyoxygenated labdanes: Preliminary approaches. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 607–618. [Google Scholar]
- Bernet, A.; Schroeder, J.; Seifert, K. Synthesis of the marine sesquiterpene quinones hyatellaquinone and spongiaquinone. Helv. Chim. Acta 2003, 86, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar]
- Capon, R.J.; Groves, D.R.; Urban, S.; Watson, R.G. Spongiaquinone Revisited: Structural and Stereochemical studies on marine sesquiterpene/quinones from a Southern Australian marine sponge, Spongia sp. Aust. J. Chem. 1993, 46, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Talpir, R.; Rudi, A.; Kashman, Y.; Loya, Y.; Hizi, A. Three new sesquiterpene hydroquinones from marine origin. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 4179–4184. [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas, R.; Murphy, P.T.; Warren, R.G.; Wells, R.J.; Blount, J.F. New quinones from a dictyoceratid sponge. Aust. J. Chem. 1978, 31, 2685–2697. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, B.; Djura, P.; McIntyre, E.; Faulker, J. Antimicrobial constituents of the sponge Siphonodictyon coralliphagum. Tetrahedron 1981, 37, 979–982. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, B.W.; Faulker, D.J.; Matsumoto, G.K.; Cun-Heng, H.; Cloardy, J. Metabolites of the burrowing sponge Siphonodictyon coralliphagu. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 4568–4573. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, M.; Suzuki, A.; Nakatani, M.; Fuchikami, T.; Inoue, M.; Katoh, T. A efficient synthesis of (+)-aureol via boron trifluoride etherate-promoted rearrangement of (+)-arenarol. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 6929–6932. [Google Scholar]
- Nakatami, N.; Nakamura, M.; Suzuki, A.; Fuchikami, T.; Inoue, M.; Katoh, T. Enantioselective total synthesis of (+)-aureol via a BF3·Et2O-promoted rearrangement/cyclization reaction of (+)-arenarol. Arkivoc 2003, 8, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Djura, P.; Stierle, D.B.; Sulliva, B.; Faulkner, D.J.; Arnold, E.; Clardy, J. Some metabolites of the marine sponges Smenospongia aurea and Smenospongia (.ident.Polyfibrospongia) echina. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Magno, S.; Pansini, M. Chemistry of verongida sponges. 10. Secondary metabolite composition of the caribbean sponge Verongula gigantean. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.E.; Cross, S.S.; Burres, N.S.; Koehn, F. Antiviral and antitumor terpene hydroquinones from marine sponge and methods of use. USA. PCT WO 9112250 A1, 22 August 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, T.; Nakatani, M.; Shikita, S.; Sampe, R.; Ishiwata, A.; Ohmori, O.; Nakamura, M.; Terashima, S. Studies toward the total synthesis of popolohuanone E: Enantioselective synthesis of 8-O-methylpopolohuanone E. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 2701–2704. [Google Scholar]
- Kawano, H.; Itoh, M.; Katoh, T.; Terashima, S. Studies toward the synthesis of popolohuanone E:Synthesis of natural (+)-arenarol related to the proposed biogenetic precursor of popolohuanone E. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 7769–7772. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.K.; Laya-Mimo, M. Synthesis of bioactive terpenes from Wieland-Miescher ketone and its methyl analog. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2000, 24, 175–213. [Google Scholar]
- Kondracki, M.L.; Guyot, M. Biologically active quinine and hydroquinones sesquiterpenoids from the sponge Smenospongia sp. Tetrahedron 1989, 45, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar]
- Takai, K.; Hotta, Y.; Oshima, K.; Nozaki, H. Wittig-type reaction of dimetallated carbodianion species as produced by zinc reduction of gem-polyhalogen compounds in the presence of Lewis acids. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1980, 53, 1698–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Moulines, J.; Lamidey, A.-M.; Desvergnes-Beuil, V. A practical synthesis of Ambrox® from sclareol using no metallic oxidant. Synth. Commun. 2001, 31, 749–758. [Google Scholar]
- Zhdankin, V.V.; Stang, P.J. Recent developments in the chemistry of polyvalent iodine compounds. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 2523–2584. [Google Scholar]
- Quideau, S.; Pouységu, L.; Oxoby, M.; Looney, M.A. 2-Alkoxyarenol-derived orthoquinols in carbon-oxygen, carbon-nitrogen and carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 319–329. [Google Scholar]
- Synder, S.A.; Teitler, D.S.; Brucks, A.P. Simple reagents for direct halonium-induced polyene cyclizations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14303–14314. [Google Scholar]
- Loya, S.; Bakhanaskvili, M.; Kashman, Y.; Hizi, A. Peyssonols A and B, two novel inhibitors of the reverse transcriptases of human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 316, 789–796. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, T.; Poupon, E.; Rueden, E.J.; Kim, S.H.; Theodorakis, E.A. Unified synthesis of quinone sesquiterpenes based on a radical decarboxylation and quinone addition reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12261–12267. [Google Scholar]
- Minale, L.; Riccio, R.; Sodano, G. Avarol, a novel sesquiterpenoid hydroquinone with a rearranged drimane skeleton from the sponge Dysidea avara. Tetrahedron Lett. 1974, 3401–3404. [Google Scholar]
- De Rosa, S.; Minale, L.; Riccio, R.; Sodano, G. The absolute configuration of avarol, a rearranged sesquiterpenoid hydroquinone from a marine sponge. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1976, 13, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, R.; de Giulio, A.; de Rosa, S.; Strazzullo, G.; Gašič, M.J.; Sladić, D.; Zlatović, M. Biological activities of avarol derivatives, 1. Amino derivatives. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Maidhof, A.; Zahn, R.K.; Schröder, H.C.M.; Gasic, M.J.; Heidemann, D.; Bernd, A.; Kurelec, B.; Eich, E.; Seibert, G. Potent antileukemic activity of the novel cytostatic agent avarone and its analogues in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1985, 45, 4822–4826. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Sobel, C.; Sachsse, W.; Diehl-Seifert, B.; Zahn, R.K.; Eich, E.; Kljajić, Z.; Schröder, H.C. Biphasic and differential effects of the cytostatic agents avarone and avarol on DNA metabolism of human and murine T and B lymphocytes. Eur. J. Cancer Clin. Onc. 1986, 22, 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Sobel, C.; Diehl-Seifert, B.; Maidhof, A.; Schöder, H.C. Influence of the antileukemic and anti-human immunodeficiency virus agent avarol on selected immune responses in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1987, 36, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Sarin, P.S.; Sun, D.; Thornton, A.; Müller, W.E.G. Inhibition of replication of the etiologic agent of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (human T-lymphotropic retrovirus/lymphadenopathy-associated virus) by avarol and avarone. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1987, 78, 663–666. [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara, H.; Uda, H. Optically pure (4aS)-(+)- or (4aR)-(−)-1,4a-dimethyl-4,4a,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalene-2,5(3H,6H)-dione and its use in the synthesis of an inhibitor of steroid biosynthesis. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 2308–2311. [Google Scholar]
- Dess, D.B.; Martin, J.C. A useful 12-I-5 triacetoxyperiodinane (the Dess-Martin periodinane) for the selective oxidation of primary or secondary alcohols and a variety of related 12-I-5 species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 7277–7287. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, T.; Poupon, E.; Rueden, E.J.; Theodorakis, E.A. Synthesis of (−)-Ilimaquinone via a radical decarboxylation and quinone addition reaction. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 819–822. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Namikoshi, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Yao, X.; Cai, G. Sesquiterpene quinones from a marine sponge Hippospongia sp. that inhibit maturation of starfish oocytes and induce cell cycle arrest with HepG2 cells. Pharm. Biol. 2006, 44, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondracki, M.L.; Guyot, M. Smenospongine: A cytotoxic and antimicrobial aminoquinone isolated from Smenospongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1987, 28, 5815–5818. [Google Scholar]
- Marcos, I.S.; Conde, A.; Moro, R.F.; Basabe, P.; Díez, D.; Urones, J. Synthesis of quinone/hydroquinone sesquiterpenes. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 8280–8290. [Google Scholar]
- Laube, T.; Beil, W.; Seifert, K. Total synthesis of two 12-nordrimanes and the pharmacological active sesquiteerpene hydroquinone yahazunol. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi, N.; Hata, T.; Soetjipto, H.; Kato, M.; Katsumura, S. Common synthetic strategy for optically active cyclic terpenoids having a 1,1,5-trimethyl-trans-decalin nucleus: Syntheses of (+)-acuminolide, (−)-spongianolide A, and (+)-scalarenedial. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 8425–8442. [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai, J.; Oguchi, T.; Watanabe, K.; Abe, H.; Kanno, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Katoh, T. Highly efficient total synthesis of the marine natural products (+)-avarone, (+)-avarol, (−)-neoavarone, (−)-neovarol and (+)-aureol. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 829–837. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, J.L.; Linn, J.A.; Selway, J.W.T. Synthesis and antirhinovirus activity of 6-(dimethylamino)-2-(trifluoromethyl)-9-(substituted benzyl)-9H-purines. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Stork, G.; rosen, P.; Goldman, N.; Coombs, R.V.; Tsuji, J. Alkylation and carbonation of ketones by trapping the enolates from the reduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1965, 87, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Bruner, S.D.; Radeke, H.S.; Tallarico, J.A.; Snapper, M.L. Total synthesis of (−)-ilimaquinone. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 1114–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Poigny, S.; Guyot, M.; Samadi, M. Efficient total synthesis of (−)-ilimaquinone. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 5890–5894. [Google Scholar]
- Stalh, P.; Waldmann, H. Asymmetric synthesis of the nakijiquinones-selective inhibitors of the her-2/Neu protooncogene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 3710–3713. [Google Scholar]
- Shigemori, H.; Madono, T.I.; Sasaki, T.; Mikami, Y.; Kobayashi, J. Nakijiquinones A and B, new antifungal sesquiterpenoid quinones with an amino acid residue from an Okinawan marine sponge. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 8347–8354. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J.; Madono, T.; Shigemori, H. Nakijiquinones C and D, new sesquiterpenoid quinones with a hydroxy amino acid residue from a marine sponge inhibiting c-erbB-2 kinase. Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 10867–10874. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Kubota, T.; Kobayashi, J. Nakijiquinones E and F, new dimeric sesquiterpenoid quinones from marine sponge. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2185–2188. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Kubota, T.; Ito, J.; Mikami, Y.; Fromont, J.; Kobayashi, J. Nakijiquinones G–I, new sesquiterpenoid quinones from marine sponge. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 7561–7564. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Ushio, M.; Kubota, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Fromont, J.; Kobayashi, J. Nakijiquinones J–R, Sesquiterpenoid quinones with an qmine residue from Okinawan marine sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 467–471. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, A.T.; Park, K.; Wiener, D.F. Application of the nickel-mediated neopentyl coupling in the total synthesis of the marine natural product arenarol. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 5102–5106. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, F.J.; Lakshmi, V.; Powell, D.R.; van der Helm, D. Arenarol and arenarona: Sesquiterpenoids with rearranged drimane skeletons from marine sponge Dysidea arenaria. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- Utkina, N.K.; Denisenko, V.A.; Krasokhin, V.B. Sesquiterpenoidd aminoquinones from marine sponge Dysidea sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 788–791. [Google Scholar]
- Valderrama, J.A.; Benites, J.; Cortés, M.; Pessoa-Mahana, H.; Prina, E.; Fournest, A. Studies on quinones. Part. 38: Synthesis and Leishmanicidal activity of sesquiterpene 1,4-quinones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 4713–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, J.A.; Benites, J.; Cortés, M.; Pessoa-Mahana, H.; Prina, E.; Fournest, A. Studies on quinones. Part. 35: Studies on quinones. Part 35: Access to antiprotozoal active euryfurylquinones and hydroquinones. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 881–886. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, G.; Likhite, N.S.; Kumar, C.S.A. A concise synthesis of the bioactive meroterpenoid natural product (±)-liphagal, a potent PI3K inhibitor. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 5260–5262. [Google Scholar]
- Marion, F.; Williams, D.E.; Patrick, D.O.; Hollander, I.; Mallon, R.; Kim, S.C.; Roll, D.M.; Feldberg, L.; Soest, R.V.; Andersen, R.J. Liphagal, a selective inhibitor of PI3 kinase α isolated from the sponge Aka coralliphaga: Structure elucidation and biomimetic synthesis. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom, T.J.; Anderson, A.C.; Wright, D.L. Inhibitors of phosphoinositide-3-kinase: A structure-based approach to understanding potency and selectivity. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 840–850. [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy, B.T.; Smith, D.L.; Ram, P.T.; Lu, Y.; Mills, G.B. Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 988–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, H.C.; Brümmer, F.; Fattorusso, E.; Aiello, A.; Menna, M.; de Rosa, S.; Batel, R.; Müller, W.E. Sustainable production of bioactive compounds from sponges: Primmorphs as bioreactors. Prog. Mol. Subcell Biol. 2003, 37, 163–197. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, W.E.; Böhm, M.; Batel, R.; de Rosa, S.; Tommonaro, G.; Müller, I.M.; Schröder, H.C. Application of cell culture for the production of bioactive compounds from sponges: Synthesis of avarol by primmorphs from Dysidea avara. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar]
- De Caralt, S.; Sánchez-Fontenla, J.; Uriz, M.J.; Wijffels, R.H. In situ aquaculture methods for Dysidea avara (demospongiae, porifera) in the northwestern mediterranean. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, W.E.; Grebenjuk, V.A.; Le Pennec, G.; Schröder, H.; Brümmer, F.; Hentschel, U.; Müller, I.M.; Breter, H. Sustainable production of bioactive compounds by sponges—Cell culture and gene cluster approach: A review. Mar. Biotechnol. 2004, 6, 105–117. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gordaliza, M. Synthetic Strategies to Terpene Quinones/Hydroquinones. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 358-402. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10020358
Gordaliza M. Synthetic Strategies to Terpene Quinones/Hydroquinones. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(2):358-402. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10020358
Chicago/Turabian StyleGordaliza, Marina. 2012. "Synthetic Strategies to Terpene Quinones/Hydroquinones" Marine Drugs 10, no. 2: 358-402. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10020358
APA StyleGordaliza, M. (2012). Synthetic Strategies to Terpene Quinones/Hydroquinones. Marine Drugs, 10(2), 358-402. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10020358