Reporter Dyes Demonstrate Functional Expression of Multidrug Resistance Proteins in the Marine Flatworm Macrostomum lignano: The Sponge-Derived Dye Ageladine A Is Not a Substrate of These Transporters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
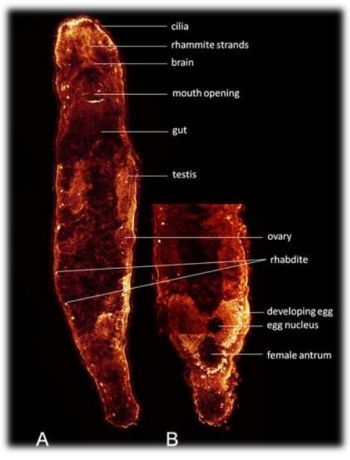
2. Results





3. Discussion
3.1. Multidrug Resistance Transporters

3.2. Reporter Dyes
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Animals and Cell Culture
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Fluorometric Measurements
4.4. Stability of Staining
4.5. Inhibition of Multidrug Resistance Transporters
4.6. Determination of Glutathione Content and Viability of Treated Astrocytes
4.7. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ladurner, P.; Scharer, L.; Salvenmoser, W.; Rieger, R.M. A new model organism among the lower Bilateria and the use of digital microscopy in taxonomy of meiobenthic Platyhelminthes: Macrostomum lignano, n. sp. (Rhabditophora, Macrostomorpha). J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2005, 43, 114–126. [Google Scholar]
- Rinehart, K.L. Secondary metabolites from marine organisms. Ciba Found. Symp. 1992, 171, 236–249. [Google Scholar]
- Demain, A.L.; Fang, A. The natural functions of secondary metabolites. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2000, 69, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Proksch, P. Defensive roles for secondary metabolites from marine sponges and sponge-feeding nudibranchs. Toxicon 1994, 36, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Nakao, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; Seiki, M.; Itoj, Y.; Yamashita, J.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Fusetani, N. Ageladine A: An antigiogenetic matrixmetalloproteinase inhibitor from the marine sponge Agelas nakamurai. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 1570–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Meketa, M.L.; Weinreb, S.M. Total synthesis of ageladine A, an angiogenesis inhibitor from the marine sponge Agelas nakamurai. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 1443–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shengule, S.R.; Karuso, P. Concise total synthesis of the marine natural product Ageladine A. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 4083–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meketa, M.L.; Weinreb, S.M. A convergent total synthesis of the marine sponge alkaloid Ageladine A via a strategic 6π-2-azatriene electrocyclization. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 9112–9119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meketa, M.L.; Weinreb, S.M.; Nakao, Y.; Fusetani, N. Application of a 6pi-1-azatriene electrocyclization strategy to the total synthesis of the marine sponge metabolite Ageladine A and biological evaluation of synthetic analogues. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 4892–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickmeyer, U.; Grube, A.; Klings, K.W.; Köck, M. Ageladine A, a pyrrole-imidazole alkaloid from marine sponges, is a pH sensitive membrane permeable dye. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bickmeyer, U.; Heine, M.; Podbielski, I.; Münd, D.; Köck, M.; Karuso, P. Tracking of fast moving neuronal vesicles with ageladine A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 402, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bickmeyer, U. The alkaloid ageladine A, originally isolated from marine sponges, used for pH-sensitive imaging of transparent marine animals. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivera-Ingraham, G.; Bickmeyer, U.; Abele, D. The physiological response of the marine platyhelminth Macrostomum lignano to different environmental oxygen concentrations. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shengule, S.R.; Loa-Kum-Cheung, W.L.; Parish, C.R.; Blairvacq, M.; Meijer, L.; Nakao, Y.; Karuso, P. A one-pot synthesis and biological activity of ageladine A and analogues. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 2492–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.F. ABC transporters: From microorganisms to man. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1992, 8, 67–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.L.; Ling, V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 455, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, S.P.C.; Deeley, R.G. Multidrug resistance mediated by the ATP-binding cassette transporter protein MRP. BioEssays 1998, 20, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavinas, H.; Krajcsi, P.; Cserepes, J.; Sarkadi, B. The role of ABC transporters in drug resistance, metabolism and toxicity. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2004, 1, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, M.; Rzhetsky, A.; Allikmets, R. The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, E.M.; Deeley, R.G.; Cole, S.P.C. Toxicological relevance of the multidrug resistance protein 1, MRP1 (ABCC1) and related transporters. Toxicology 2001, 167, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, P.; Elferink, R.O. Mammalian ABC transporters in health and disease. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 537–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirrlinger, J.; Schulz, J.B.; Dringen, R. Glutathione release from cultured brain cells: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1) mediates the release of GSH from astroglial cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 69, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruo, T.; Iida, H.; Naganuma, K.; Tsukagoshi, S.; Sakurai, Y. Promotion by verapamil of vincristine responsiveness in tumor cell lines inherently resistant to the drug. Cancer Res. 1983, 43, 808–813. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, R.; Mayer, L.D. Multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer—Mechanisms, reversal using modulators of MDR and the role of MDR modulators in influencing the pharmacokinetics of anticancer drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 11, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homolya, L.; Holló, Z.; Germann, U.A.; Pastan, I.; Gottesman, M.M.; Sarkadi, B. Fluorescent cellular indicators are extruded by the multidrug resistance protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 21493–21496. [Google Scholar]
- Brezden, C.; Hedley, D.W.; Rautha, M. Constitutive expression of P-Glycoprotein as a determinant of loading with fluorescent calcium probes. Cytometry 1994, 17, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, N.; Broxterman, H.J.; Währer, D.C.R.; Pinedo, H.M. ATP-dependent efflux of Calcein by the multidrug resistance protein (MRP): No inhibition by intracellular glutathione depletion. FEBS Lett. 1995, 368, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautier, D.; Canitrot, Y.; Deeley, R.G.F.; Cole, S.P.C. Multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug resistance protein (MRP) gene. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 52, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollapudi, S.; Kim, C.H.; Tran, B.N.; Sangha, S.; Gupta, S. Probenecid reverses multidrug resistance in multidrug resistance-associated protein-overexpressing HL60/AR and H69/AR cells but not in P-glycoprotein-overexpressing HL60/Tax and P388/ADR cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1997, 402, 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Gekeler, V.; Ise, W.; Sanders, K.H.; Ulrich, W.R.; Beck, J. The leukotriene LTD4 receptor antagonist MK571 specifically modulates MRP associated multidrug resistance. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 208, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, J.E.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, M.P.; Moores, K.E. Use of fluo-3 to measure cytosolic Ca2+ in platelets and neutrophils. Loading cells with the dye, calibration of traces, measurements in the presence of plasma, and buffering of cytosolic Ca2+. Biochem. J. 1990, 269, 513–519. [Google Scholar]
- Holló, Z.; Homolya, L.; Hegedüs, T.; Sarkadi, B. Transport properties of the multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) in human tumour cells. FEBS Lett. 1996, 383, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essodaïgui, M.; Broxterman, H.J.; Garnier-Suillerot, A. Kinetic analysis of calcein and calcein-acetoxymethylester efflux mediated by the multidrug resistance protein and p-glycoprotein. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüders, A.K.; Saborowski, R.; Bickmeyer, U. Inhibition of multidrug/xenobiotic resistance transporter by MK571 improves dye (Fura 2) accumulation in crustacean tissues from lobster, shrimp, and isopod. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 150, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, H.; Kusel, J.R.; Thornholl, J. Excretion of fluorescent substrates of mammalian multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) in the Schistosoma mansoni excretory system. Parasitology 2004, 128, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurelec, B. The multixenobiotic resistance mechanism in aquatic organisms. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1992, 22, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, A.; Lauritzen, B.; Jansen, D.; Böttcher, P.; Teguliwa, L.; Krüner, G.; Broeg, K. Detection of P-glycoprotein mediated MDR/MXR in Caranus maenas hepatopancreas by immuno-gold-silver labeling. Mar. Environ. Res. 1998, 46, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, S.M.; Woodin, B.R.; Stegeman, J.J. Expression of P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P450 1A in intertidal fish (Anoplarchus purpurescens) exposed to environmental contaminants. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 60, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdeking, A.; Köhler, A. Regulation of expression of multixenobiotic resistance (MXR) genes by environmental factors in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckenbach, T.; Altenburger, R.; Epel, D. Teasing apart activities of different types of ABC efflux pumps in bivalve gills using the concepts of independent action and concentration addition. Mar. Environ. Res. 2008, 66, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, C.; Wiltshire, K.H.; Bickmeyer, U. Inhibition of multidrug resistance transporters in the diatom Thalassiosira rotula facilitates dye staining. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kioka, N.; Tsubota, J.; Kakehi, Y.; Komano, T.; Gottesman, M.M.; Pastan, I.; Ueda, K. P-glycoprotein gene (MDR1) cDNA from human adrenal: Normal P-glycoprotein carries Gly185 with an altered pattern of multidrug resistance. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 162, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, S.P.C.; Bhardwaj, G.; Gerlach, J.H.; Mackie, J.E.; Grant, C.E.; Almquist, K.C.; Stewart, A.J.; Kurz, E.U.; Duncan, A.M.V.; Deeley, R.G. Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung-cancer cell-line. Science 1992, 258, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, J.A.; Raunio, H.; Gant, T.W.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Cloning and characterization of a member of the rat multidrug resistance (mdr) gene family. Gene 1991, 106, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, C.S.; Shen, D.D.; Ho, R.J. Cloning and characterization of the rat multidrug resistance-associated protein 1. AAPS PharmSci. 2002, 4, E15. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura, S.; Koto, H.; Ide, K.; Fujino, Y.; Setoguchi-Mukai, A.; Ohno, K.Y.; Tsujimoto, H. Induction of chemoresistance in a cultured canine cell line by retroviral transduction of the canine multidrug resistance 1 gene. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2007, 68, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Pratt, S.E.; Cao, J.; Dantzig, A.H.; Moore, R.E.; Slapak, C.A. Identification and characterization of the canine multidrug resistance-associated protein. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson, J.; Ayala, P.; Orozco, E.; Wirth, D. Emetine-resistant mutants of Entamoeba histolytica overexpress mRNAs for multidrug resistance. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1990, 15, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theologis, A.; Ecker, J.R.; Palm, C.J.; Federspiel, N.A.; Kaul, S.; White, O.; Alonso, J.; Altafi, H.; Araujo, R.; Bowman, C.L.; et al. Sequence and analysis of chromosome 1 of the plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 2000, 408, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.; Ladurner, P.; Rieger, R.; Pfister, D.; del Mar de Miguel-Bonet, M.; Jacobs, D.; Hartenstein, V. The Macrostomum lignano EST database as a molecular resource for studying platyhelminth development and phylogeny. Dev. Genes Evol. 2006, 216, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, S.E.; Hussain, A.; Davide, J.P.; Melera, P.W. Full length and alternatively spliced pgp1 transcripts in multidrug-resistant Chinese hamster lung cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 4545–4555. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi, B.; Homolya, L.; Szakács, G.; Váradi, A. Human multidrug resistance ABCB and ABCG transporters: Participation in a chemoimmunity defense system. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 1179–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelig, A. A general pattern for substrate recognition by P-glycoprotein. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 251, 252–261. [Google Scholar]
- Seelig, A.; Landwojtowicz, E. Structure-activity relationship of P-glycoprotein substrates and modifiers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 12, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litman, T.; Druley, W.D.; Stein, D.; Bate, S.E. From MDR to MXR: New understanding of multidrug resistance systems, their properties and clinical significance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 931–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, J.; Nies, A.T.; Cui, Y.; Leier, I.; Keppler, D. Conjugate export pumps of the multidrug resistance protein (MRP) family: Localization, substrate specificity, and MRP2-mediated drug resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1461, 377–394. [Google Scholar]
- Hamprecht, B.; Löffler, F. Primary glial cultures as a model for studying hormone action. Methods Enzymol. 1985, 109, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhold, C.R.W.; Reißmann, M. Personal communication, Institute for Chemistry, Carl von Ossietzky University Oldenburg: Carl von Ossietzky Straße 9-11, 26129 Oldenburg, Germany, 2013.
- Jedlitschky, G.; Leier, I.; Buchholz, U.; Barnouin, K.; Kurz, G.; Keppler, D. Transport of glutathione, glucuronate, and sulfate conjugate by the MRP gene-encoded conjugate export pump. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 988–994. [Google Scholar]
- Keppler, D. Multidrug resistance proteins (MRPs, ABCCs): Importance for pathophysiology and drug therapy. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 201, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, W.P.; Beatty, J.O.; Pitts, F.W.; Plippin, H.F. The influence of a new benzoic acid derivative on the metabolism of paraaminosalicylic acid (PAS) and penicillin. Ann. Intern. Med. 1950, 33, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.M. Studies on the effect of probenecid (“benemid”) in gout. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1954, 13, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phear, D.N. Verapamil in angina: A doubleblind Trial. Br. Med. J. 1968, 2, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkadi, B.; Müller, M. Search for specific inhibitors of multidrug resistance in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 1997, 8, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minier, C.; Moore, M.N. Rhodamine B accumulation and MXR protein expression in mussel blood cells: Effects of exposure to vincristine. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 142, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, T.W.; Clarke, D.M. Location of the Rhodamine-binding site in the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 44332–44338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaduto, R.C.; Grotyohann, L.W. Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential using fluorescent Rhodamine derivatives. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.S.; Oldham, M.L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J. Crystal structure of the multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein from Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2012, 490, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastan, I.; Gottesmann, M.M. Multidrug resistance! Annu. Rev. Med. 1991, 42, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, F. Enzymic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: Applications to mammalian blood and other tissues. Anal. Biochem. 1969, 27, 502–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dringen, R.; Hamprecht, B. Glutathione content as an indicator for the presence of metabolic pathways of amino acids in astroglial cultures. J. Neurochem. 1996, 67, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Tietje, K.; Rivera-Ingraham, G.; Petters, C.; Abele, D.; Dringen, R.; Bickmeyer, U. Reporter Dyes Demonstrate Functional Expression of Multidrug Resistance Proteins in the Marine Flatworm Macrostomum lignano: The Sponge-Derived Dye Ageladine A Is Not a Substrate of These Transporters. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3951-3969. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103951
Tietje K, Rivera-Ingraham G, Petters C, Abele D, Dringen R, Bickmeyer U. Reporter Dyes Demonstrate Functional Expression of Multidrug Resistance Proteins in the Marine Flatworm Macrostomum lignano: The Sponge-Derived Dye Ageladine A Is Not a Substrate of These Transporters. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(10):3951-3969. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103951
Chicago/Turabian StyleTietje, Kristin, Georgina Rivera-Ingraham, Charlotte Petters, Doris Abele, Ralf Dringen, and Ulf Bickmeyer. 2013. "Reporter Dyes Demonstrate Functional Expression of Multidrug Resistance Proteins in the Marine Flatworm Macrostomum lignano: The Sponge-Derived Dye Ageladine A Is Not a Substrate of These Transporters" Marine Drugs 11, no. 10: 3951-3969. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103951
APA StyleTietje, K., Rivera-Ingraham, G., Petters, C., Abele, D., Dringen, R., & Bickmeyer, U. (2013). Reporter Dyes Demonstrate Functional Expression of Multidrug Resistance Proteins in the Marine Flatworm Macrostomum lignano: The Sponge-Derived Dye Ageladine A Is Not a Substrate of These Transporters. Marine Drugs, 11(10), 3951-3969. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103951