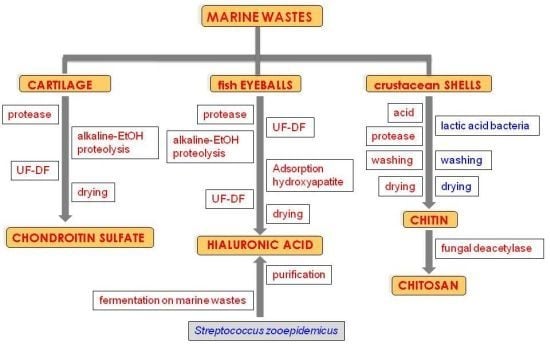
Chondroitin Sulfate, Hyaluronic Acid and Chitin/Chitosan Production Using Marine Waste Sources: Characteristics, Applications and Eco-Friendly Processes: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Glycosaminoglycans
2.1. Characteristics and Applications of CS
2.2. Characteristics and Applications of HA
3. CS Production Processes

Microbial Production of CS
4. HA Production Processes

Microbial Production of HA on Marine Food Wastes
| GAG | Type | Source | Process conditions | Yield ( Y)/Production (P) Purity (Pu) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | CS-C | shark cartilage | proteolysis, alcoholic precipitation, membrane purification | Y = 57% (w/v) | [21] |
| CS | CS-A, CS-C | ray and shark cartilage | proteolysis, cetylpyridinium HCl and NaCl precipitations, filtration and dialization | Y = 10%–11% (w/v) | [35] |
| CS | CS-A, CS-C | skate fin | proteolysis, cetylpyridinium HCl precipitation, electrophoresis and cromatographic purification | - | [62] |
| CS | CS-A, CS-C | skate cartilage | proteolysis, purification (UF-DF) | - | [63] |
| CS | CS-A, CS-C | ray cartilage | proteolysis, alkaline-hydroalcoholic precipitation, purification (UF-DF) | Y = 15% (w/w)/Pu > 99% | [66] |
| CS | CS-A, CS-C | shark fin | proteolysis, guanidine HCl extraction, electrophoresis and cromatographic purification | Y = 84% | [67] |
| CS | CS-A, CS-C, CS-O | zebrafish cartilage | proteolysis, electrophoresis and cromatographic purification | - | [68] |
| CS | CS-A, CS-C, CS-D, CS-O | dogfish cartilage | proteolysis, alcoholic precipitation, cromatographic purification | Y = 5% (w/w) | [69] |
| CS | CS-A, CS-C, CS-O, CS-E | salmon nasal cartilage | proteolysis, alkaline hydrolysis, alcoholic precipitation, cation exchange separation | Y = 24% (w/w)/Pu = 99% | [70] |
| CS | CS-A, CS-C, CS-O, CS-E | salmon nasal cartilage | proteolysis, alkaline hydrolysis, alcoholic precipitation, purification (UF) | - | [71] |
| CS | CS-O | E. coli O5:K4:H4 | batch operation | P = 0.2 g/L | [76] |
| CS | CS-O | E. coli O5:K4:H4 | fed-batch operation | P = 1.4 g/L | [77] |
| CS | CS-O | E. coli O5:K4:H4 | membrane bioreactor, fed-batch, purification (UF-DF) | Y = 80%/P = 3 g/L Pu = 90% | [78] |
| HA | - | shark HV | proteolysis, concentration (UF), selective precipitation, purification (UF-DF) | P = 0.3 g/L/Pu > 99.5% | [56] |
| HA | - | swordfish HV | proteolysis, concentration (UF), selective precipitation, purification (UF-DF) | P = 0.06 g/L/Pu > 99.5% | [56] |
| HA | - | S. zooepidemicus | medium: shark or ray peptones, fed-batch | P = 2.5 g/L | [101] |
| HA | - | S. zooepidemicus | medium: tuna peptones and MPW, batch | P = 2.5 g/L | [102] |
5. Chitin and Chitosan
Characteristics and Applications of CH and CHs
6. Traditional CH and CHs Production Processes

7. Alternative CH and CHs Production Processes

| Final Product | Source | Procedure | Process conditions | Yield (Y)/Efficiency (DM, DP, DD) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH | prawn shell | anaerobic fermentation | Sil-Al 4 × 4 TM inoculant, glucose, 30 °C, 7 days | DP = 91%/Y = 20% | [107] |
| CH | red crab shell | successive two-step fermentation | S. marcescens, L. paracasei, glucose, 30 °C, 7 days | DM = 94.3%/DP = 68.9%/Y = 38.7% | [111] |
| CH | shrimp waste | anaerobic fermentation | L. acidophilus SW01, glucose, 37 °C, 168 h | DM = 99.3%/DP = 96.5% | [133] |
| CH | demineralised prawn shell | solid-state fermentation | Stabisil inoculant, lactose, 25 °C | DP = 40% | [152] |
| CH | prawn shell | co-fermentation | L. lactis, T. turnirae, glucose, 7 days | DM = 70%/DP = 70%/Y = 95.5% | [153] |
| CH | red crab shell | co-fermentation | L. paracasei, S. marcescens, glucose, 30 °C, 7 days | DM = 97.2%/DP = 52.6% | [154] |
| CHs | M. rouxii | semi-continuous fermentation | nutrient broth, 28 °C, 24 h | DD = 86%–88%/Y = 4.4% | [69] |
| CHs | M. rouxii | fermentation | MSM, PDB, YPG | DD(MSM) = 87.2%/DD(PDB) = 89.8%/DD(YPG) = 82.8%/Y(MSM) = 7.7%/Y(PDB) = 6%/Y(YPG) = 6.3% | [159] |
8. Conclusions
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization, Estadísticas de Pesca: Captura y Desembarques; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2004.
- Gildberg, A. Recovery of proteinases and protein hydrolysates from fish viscera. Bioresour. Technol. 1992, 39, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.; Sotelo, C.G.; Chapela, M.J.; Pérez-Martín, R.I. Towards sustainable and efficient use of fishery resources: Present and future trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Community. On a European Community plan of action for the conservation and management of sharks. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/fisheries/marine_species/wild_species/sharks/index_en.htm (accessed on 10 November 2012).
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Kassaveti, A. Fish industry waste: Treatments, environmental impacts, current and potential uses. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 726–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senevirathne, M.; Kim, S.-K. Utilization of seafood processing by-products. Medicinal applications. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 65, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilakan, K.; Sultana, K.; Radhakrishna, K.; Bawa, A.S. Utilization of byproducts and waste materials from meat, poultry and fish processing industries: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsson, H.G.; Rasco, B. Fish protein hydrolysates: Production, biochemical and functional properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 43–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Turnay, J.; Fernández-Díaz, M.D.; Ulmo, N.; Lizarbe, M.A.; Montero, P. Structural and physical properties of gelatine extracted from different marine species: A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildberg, A. Enzymes and bioactive peptides from fish waste related to fish silage, fish feed and fish sauce preparation. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2004, 13, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percot, A.; Viton, C.; Domard, A. Optimization of chitin extraction from shrimp shells. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, J.A.; González, M.P.; Murado, M.A. A new marine medium. Use of different fish peatones and comparative study of selected species of marine bacteria. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2004, 35, 385–392. [Google Scholar]
- Aspmo, S.I.; Horn, S.J.; Eijsink, V.G.H. Hydrolysates from Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) viscera as components of microbial growth media. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 3714–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, J.A.; Docasal, S.F.; Mirón, J.; González, M.P.; Murado, M.A. Proteases production by two Vibrio species on residuals marine media. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 33, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vázquez, J.A.; Docasal, S.F.; Prieto, M.A.; González, M.P.; Murado, M.A. Growth and metabolic features of lactic acid bacteria in media with hydrolysed fish viscera. An approach to bio-silage of fishing by-products. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6246–6257. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Murado, M.A.; González, M.P.; Vázquez, J.A. Recovery of proteolytic and collagenolytic activities from viscera by-products of rayfish (Raja clavata). Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, B.; Alemám, A.; Montero, P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Antioxidant and functional properties of gelatine hydrolysates obtained from skin of sole and squid. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, J.A.; Nogueira, M.; Durán, A.; Prieto, M.A.; Rodríguez-Amado, I.; Rial, D.; González, M.P.; Murado, M.A. Preparation of marine silage of swordfish, ray and shark visceral waste by lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Eng. 2011, 103, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herpandi, N.H.; Adzitey, F. Fish bone and scale as a potential source of halal gelatine. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 6, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, H.B.; Bougatef, A.; Balti, R.; Triki-Ellouz, Y.; Souissi, N.; Nasri, M. Isolation and characterisation of trypsin from sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) viscera. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 2654–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-B.; Ji, C.-I.; Woo, J.-W.; Do, J.-R.; Cho, S.-M.; Lee, Y.-B.; Kang, S.-N.; Park, J.-H. Simplified purification of chondroitin sulphate from scapular cartilage of shortfin mako shark (Isurus oxyrinchus). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, P.; Hawboldt, K. A review of bio-oils from waste biomass: Focus on fish processing waste. Renew. Sustain. Ener. Rev. 2012, 16, 798–821. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, T.H.; Alves, A.; Ferreira, B.M.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reys, L.L.; Ferreira, R.J.F.; Sousa, R.A.; Silva, S.S.; Mano, J.F.; Reis, R.L. Materials of marine origin: A review on polymers and ceramics of biomedical interest. Int. Mat. Rev. 2012, 57, 276–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronca, F.; Palmieri, L.; Panicucci, P.; Ronca, G. Anti-inflammatory activity of chondroitin sulfate. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 1998, 6 (Suppl. A), 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, G.; Soltés, L.; Stern, R.; Gemeiner, P. Hyaluronic acid: A natural biopolymer with a broad range of biomedical and industrial applications. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.H.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Zhang, G.R.; Jin, H.M.; Nguyen, T.M.; Ouyang, H.W. Specific interactions between human fibroblasts and particular chondroitin sulphate molecules for wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1588–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.V.R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K. Chitin and chitosan: Functional biopolymers from marine crustaceans. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourya, V.K.; Inamdar, N.N. Chitosan-modifications and applications: Opportunities galore. React. Funct. Polym. 2008, 68, 1013–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seno, N.; Meyer, K. Comparative biochemistry of skin the mucopolysaccharides of shark skin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1963, 78, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.P.; Mourao, P.A. Occurrence of a unique fucosebranched chondroitin sulfate in the body wall of a sea cucumber. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 18176–18183. [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita-Toyoda, A.; Yamada, S.; Haslam, S.M.; Khoo, K.-H.; Sugiura, M.; Morris, H.R.; Dell, A.; Sugahara, K. Structural determination of five novel tetrasaccharides containing 3-O-sulfated d-glucuronic acid and two rare oligosaccharides containing a β-d-glucose branch isolated from squid cartilage chondroitin sulfate E. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 11063–11074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardingham, T. Solution Properties of Hyaluronan. In Chemistry and Biology of Hyaluronan; Garg, H.G., Hales, C.A., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Malavaki, C.; Mizumoto, S.; Karamanos, N.; Sugahara, K. Recent advance in the structural study of functional chondroitin sulfate and dermatan sulphate in health and disease. Connect. Tissue Res. 2008, 49, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnjanagoonchorn, W.; Wongekalak, L.; Engkagul, A. Determination of chondroitin sulfate from different sources of cartilage. Chem. Eng. Proc. 2007, 46, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauder, R.M. Chondroitin sulphate: A complex molecule with potential impacts on a wide range of biological systems. Complement. Ther. Med. 2009, 17, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiraldi, C.; Cimini, D.; de Rosa, M. Production of chondroitin sulphate and chondroitin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipitone, V.R. Chondroprotection with chondroitin sulphate. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1991, 17, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.H.; Liu, H.C.; Lin, C.C.; Chou, C.H.; Lin, F.H. Gelatin–chondroitin–hyaluronan tri-copolymer scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4853–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Liu, Y.; Shu, X.Z.; Prestwich, G.D. Injectable glycosaminoglycan hydrogels for controlled release of human basic fibroblast growth factor. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6054–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, D.S.; Tezcaner, A.; Korkusuz, P.; Korkusuz, F.; Hasirei, V. Collagen-chondroitin sulfate-based PLLA-SAIB-coated rhBMP-2 delivery system for bone repair. Biomaterials 2005, 6, 4023–4034. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, S.; Sugahara, K. Potential therapeutic application of chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulphate. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2008, 5, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalil, A.; Achur, R.N.; Valiyaveettil, M.; Ockenhouse, C.F.; Gowda, D.C. Structural requirements for the adherence of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes to chondroitin sulphate proteoglycans of human placenta. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 277, 8882–8889. [Google Scholar]
- Smetsers, T.F.; van de Westerlo, E.M.; ten Dam, G.B.; Overes, I.M.; Schalkwijik, J.; van Muijen, G.N.; van Kuppvelt, T.H. Human single-chain antibodies reactive with native chondroitin sulphate detect chondroitin sulphate alterations in melanoma and psoriasis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 701–716. [Google Scholar]
- Pothacharoen, P.; Siriaunkgul, S.; Ong-Chai, S.; Supabandhu, J.; Kumja, P.; Wanaphirak, C.; Sugahara, K.; Hardingham, T.; Kongtawelert, P. Raised serum chondroitin sulphate epitope level in ovarian epithelial cancer. J. Biochem. 2006, 140, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsig, L.; Wang, L.; Cavalcante, M.C.; Cardilo-Reis, L.; Ferreira, P.L.; Mourao, P.A.; Esko, J.D.; Pvao, M.S. Selectin blocking activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulphate glycosaminoglycan from sea cucumber. Effect on tumor metastasis and neutrophil recruitment. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14984–14991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamano, T.; Mitsuhashi, Y.; Acki, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Tsuji, S.; Ito, Y.; Oji, Y. High-performance liquid chromatography assay of chondroitin sulfate in food products. Analyst 1989, 114, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, A.; Volpi, N.; Palmieri, L.; Bahous, I.; Ronca, G. Biochemical and pharmacokinetic aspects of oral treatment with chondroitin sulphate. Arzneim. Forsch. 1995, 45, 918–925. [Google Scholar]
- Volpi, N. Quality of different chondroitin sulphate preparations in relation to their therapeutic activity. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, B.A.; Stucki, G.; Frey, D.; de Vathaire, F.; Vignon, E.; Bruehlmann, P.; Uebelhart, D. Chondroitins 4 and 6 sulfate in osteoarthritis of the knee: A randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, I.C.; Meekan, M.G.; Buckworth, R.C.; Bradshaw, C.J.A. Susceptibility of sharks, rays and chimaeras to global extinction. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2010, 56, 275–363. [Google Scholar]
- García, V.B.; Lucifora, L.O.; Myers, R.A. The importance of habitat and life history to extinction risk in sharks, skates, rays and chimaeras. Proc. R. Soc. B 2008, 275, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiedlin, A.; Bigelow, R.; Christopher, W.; Arbabi, S.; Yang, L.; Maier, R.V.; Wainwright, N.; Childs, A.; Miller, R.J. Evaluation of hyaluronan from different sources Streptococcus zooepidemicus, rooster comb, bovine vitreous, and human umbilical cord. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 2122–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, K.L.; Weiss, M.A.; Weiss, M.D. Hyaluronic acid fillers: A comprehensive review. Facial Plast. Surg. 2009, 25, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, B.F.; Blank, L.M.; Mclaughlin, R.; Nielsen, L.K. Microbial hyaluronic acid production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 66, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murado, M.A.; Montemayor, M.I.; Cabo, M.L.; Vázquez, J.A.; González, M.P. Optimization of extraction and purification process of hyaluronic acid from fish eyeball. Food Bioprod. Proc. 2012, 90, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, S.Y.; Kin, C.W. A novel approach to the production of hyaluronic acid by Streptococcus zooepidemicus. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 16, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar]
- Rangaswamy, V.; Jain, D. An efficient process for production and purification of hyaluronic acid from Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus. Biotechnol. Lett. 2008, 30, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodén, L.; Baker, J.R.; Cifonelli, J.A.; Mathews, M.B. Isolation and characterization of connective tissue polysaccharides. Methods Enzymol. 1972, 28, 73–140. [Google Scholar]
- Chascall, V.; Calabro, A.; Midura, R.J.; Yanagishita, M. Isolation and Characterization of Proteoglycans. In Methods in Enzymology; Lennarz, W.J., Hart, G.W., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994; Volume 230, pp. 390–417. [Google Scholar]
- Sumi, T.; Ohba, H.; Ikegami, T.; Shibata, M.; Sakaki, T.; Salay, I.; Park, S.S. Method for the Preparation of Chondroitin Sulfate Compounds. U.S. Patent 6,342,367, 29 January 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, B.; Ehrlich, J.; Stivala, S.S.; Singh, N.K. Comparative studies of mucopolysaccharides from marine animals. I. Raja eglanteria Bosc. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1980, 46, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lignot, B.; Lahogue, V.; Bourseau, P. Enzymatic extraction of chondroitin sulfate from skate cartilage and concentration-desalting by ultrafiltration. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 103, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollard, L.; Montillet, A.; Horriere, C.; Legrand, J.; Nguyen, T.H. Method for Obtaining Avian Biological Products. U.S. Patent 6,844,424, 18 January 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tadashi, E. Sodium Chondroitin Sulfate,Chondroitin-Sulfate-Containing Material and Processes for Producing the Same. U.S. Patent Appl. 20,060,014,256, 19 January 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Murado, M.A.; Fraguas, J.; Montemayor, M.I.; Vázquez, J.A.; González, M.P. Preparation of highly purified chondroitin sulphate from skate (Raja clavata) cartilage by-products. Process optimization including a new procedure of alkaline hydroalcoholic hydrolysis. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 49, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Michelacci, Y.M.; Horton, D.S.P.Q. Proteoglycans from the cartilage of young hammerhead shark Sphyrna lewini. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1989, 92B, 651–658. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.R.C.; Kozlowski, E.O.; Cerqueira, V.R.; Castelo-Branco, M.T.L.; Costa, M.L.; Pavão, M.S.G. Chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate are the major glycosaminoglycans present in the adult zebrafish Danio rerio (Chordata-Cyprinidae). Glycoconj. J. 2007, 24, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, V.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; de Castro, C. Structural analysis of chondroitin sulfate from Scyliorhinus canicula: A useful source of this polysaccharide. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, M.; Kono, H. Salmon-Origin Chondroitin Sulphate. U.S. Patent Appl. 20,030,162,744, 28 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nishigori, T.; Takeda, T.; Ohori, T. Method for Isolation and Purification of Chondroitin Sulfate. Jpn Patent 2000273102-A, 10 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.; Yoon, Y.K.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, H.S.; An, S.J.; Seo, J.H.; Cui, C.; Carbis, R. Optimization of Vi capsular polysaccharide production during growth of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi Ty2 in a bioreactor. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 135, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, D.; de Rosa, M.; Schiraldi, C. Production of glucuronic acid-based polysaccharides by microbial fermentation for biomedical applications. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 7, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimler, R.B. Presumptive identification of Pasteurella multocida serogroups A, D and F by capsule depolymerisation with mucopolysaccharides. Vet. Rec. 1994, 134, 191–192. [Google Scholar]
- Rimler, R.B.; Register, K.B.; Magyar, T.; Ackermann, M.R. Influence of chondroitinase on indirect hemagglutination titers and phagocytosis of Pasteurella multocida serogroups A, D and F. Vet. Microbiol. 1995, 47, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, D.; Restaino, O.F.; Catapano, A.; de Rosa, M.; Schiraldi, C. Production of capsular polysaccharide from Escherichia coli K4 for biotechnological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1779–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restaino, O.F.; Cimini, D.; de Rosa, M.; Catapano, A.; de Rosa, M.; Schiraldi, C. High cell density cultivation of Escherichia coli K4 in a microfiltration bioreactor: A step towards improvement of chondroitin precursor production. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiraldi, C.; Alfano, A.; Cimini, D.; de Rosa, M.; Panariello, A.; Restaino, O.F.; de Rosa, M. Application of a 22L scale membrane bioreactor and cross-flow ultrafiltration to obtain purified chondroitin. Biotechnol. Prog. 2012, 28, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiraldi, C.; Carcarino, L.I.; Alfano, A.; Restaino, O.F.; Panariello, A.; de Rosa, M. Purification of chondroitin precursor from Escherichia coli K4 fermentation broth using membrane processing. Biotechnol. J. 2011, 6, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedini, E.; de Castro, C.; de Rosa, M.; di Nola, A.; Iadonisi, A.; Restaino, O.F.; Schiraldi, C.; Parrilli, M. A microbiological-chemical strategy to produce chondroitin sulphate A,C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6160–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Nakano, K.; Sim, J.S. A simple rapid method to estimate hyaluronic acid concentrations in rooster comb and wattle using cellulose acetate electrophoresis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 2766–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullis-Hill, D. Preparation of Hyaluronic Acid from Synovial Fluid. U.S. Patent 4,879,375, 7 November 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Marcellin, E.; Chen, W.; Nielsen, L.K. Microbial Hyaluronic Acid Biosynthesis. In Microbial Production of Biopolymers and Polymer Precursors: Applications and Perspectives; Rehm, B.H.A., Ed.; Caister Academic Press: Norwich, UK, 2009; pp. 163–180. [Google Scholar]
- Imberty, A.; Lortat-Jacobb, H.; Pérez, S. Structural view of glycosaminoglycan–protein interactions. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, D.A. Studies on hyaluronic acid: I. The preparation and properties of rooster comb hyaluronic acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1968, 156, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazs, E.A. Ultrapure Hyaluronic Acid and the Use Thereof. U.S. Patent 4,141,973, 27 February 1979. [Google Scholar]
- O’Regan, M.; Martini, I.; Crescenzi, F.; de Luca, C.; Lansing, M. Molecular mechanisms and genetics of hyaluronan biosynthesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1994, 16, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulescu, G.; Lupescu, I.; Petrea, D.-M.; Scurei, H. Hyaluronic acid extraction from vitreous fluid. Biotechnol. Lett. 1997, 2, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.-Q.; Liu, J.-H.; Huo, X.; Shan, Y.-L.; Xu, Z.-X. The purification and identification of hyaluronic acid isolated from various tissues. Chin. Boichem. J. 1996, 12, 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno, H.; Iso, N.; Saito, T.; Ogawa, H.; Sawairi, H.; Saito, M. Characterization of hyaluronic acid of yellowfin tuna eyeball. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1991, 57, 517–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrodowski, C.S.; Hokka, C.O.; Santana, M.H.A. Production of hyaluronic acid by Streptococcus: The effects of the addition of lysozyme and aeration on the formation and the rheological properties of the product. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2005, 5, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Sun, J. Influence of hyaluronidase addition on the production of hyaluronic acid by batch culture of Streptococcus zooepidemicus. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, M.R.; Goh, L.T.; Oeggerli, A. Effect of pH, agitation and aeration on hyaluronic acid production by Streptococcus zooepidemicus. Biotechnol. Lett. 1994, 16, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, T.L. The role of dissolved oxygen and function of agitation in hyaluronic acid fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 32, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Sun, J. Comparative study on the influence of dissolved oxygen control approaches on the microbial hyaluronic acid production of Streptococcus zooepidemicus. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 32, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruta, O.; Yamamura, K.; Takebe, H.; Futamura, T.; Ilnuma, K.; Tanaka, H. Application of maxblend fermentor for microbial processes. J. Ferm. Bioeng. 1997, 83, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, M.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Enhanced hyaluronic acid production of Streptococcus zooepidemicus by an intermittent alkaline-stress strategy. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, L.M.; McLaughlin, R.L.; Nielsen, L.K. Stable production of hyaluronic acid in Streptococcus zooepidemicus chemostats operated at high dilution rate. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 90, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, X.; Yang, L.; Kong, Z. A serum-free medium for colony growth and hyaluronic acid production by Streptococcus zooepidemicus NJUST01. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Sun, J. Enhanced hyaluronic acid production by a two-stage culture strategy based on the modeling of batch and fed-batch cultivation of Streptococcus zooepidemicus. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8532–8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, J.A.; Montemayor, M.I.; Fraguas, J.; Murado, M.A. High production of hyaluronic and lactic acids by Streptococcus zooepidemicus in fed-batch culture using commercial and marine peptones from fishing by-products. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 44, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vázquez, J.A.; Montemayor, M.I.; Fraguas, J.; Murado, M.A. Hyaluronic acid production by Streptococcus zooepidemicus in marine by-products media from mussel processing wastewaters and tuna peptone viscera. Microb. Cell Fact. 2010, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Kawasaki, T. Microbial synthesis of hyaluronan and chitin: New approaches. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 99, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.L.; Khor, E.; Tan, T.K.; Lim, L.Y.; Tan, S.C. Concurrent production of chitin from shrimp shells and fungi. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 332, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, C.; Chagas, B.; Farinha, I.; Freitas, F.; Mafra, L.; Aguiar, F.; Oliveira, R.; Reis, M.A.M. Production of yeast chitin-glucan complex from biodiesel industry byproduct. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K.; Tomita, K.; Tada, T.; Ishii, S.; Nishimura, S.-I.; Shimoda, K. Squid chitin as a potential alternative chitin source: Deacetylation behavior and characteristic properties. J. Polym. Sci. A 1993, 31, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, M.; Green, A.; Healy, A. Bioprocessing of marine crustacean shell waste. Acta Biotechnol. 2003, 23, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, G.H.; Jung, W.J.; Kuk, J.H.; Oh, K.T.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, R.D. Screening of protease-producing Serratia marcescens FS-3 and its application to deproteinization of crab shell waste for chitin extraction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, L.; Ghorbel-Bellaaj, O.; Jellouli, K.; Younes, I.; Nasri, M. Extraction and characterization of chitin, chitosan, and protein hydrolysates prepared from shrimp waste by treatment with crude protease from Bacillus cereus SV1. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, J.; Jover, M.; Gutiérrez, J.F.; Corpas, R.; Cremades, O.; Fontiveros, E.; Iglesias, F.; Vega, J. Preparation of crayfish chitin by in situ lactic acid production. Process Biochem. 2001, 37, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.J.; Jo, G.H.; Kuk, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Oh, K.T.; Park, R.D. Production of chitin from red crab shell waste by successive fermentation with Lactobacillus paracasei KCTC-3074 and Serratia marcescens FS-3. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cira, L.A.; Huerta, S.; Hall, G.M.; Shirai, K. Pilot scale lactic acid fermentation of shrimp wastes for chitin recovery. Process Biochem. 2002, 37, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.S.; Stevens, W.F. Chitin production by Lactobacillus fermentation of shrimp biowaste in a drum reactor and its chemical conversion to chitosan. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A. Chitin; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minke, R.; Blackwell, J. The structure of β-chitin. J. Mol. Biol. 1978, 120, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synowiecki, J.; Al-Khateeb, N.A. Production, properties, and some new applications of chitin and its derivatives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 43, 145–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharanathan, R.N.; Kittur, F.S. Chitin—The undisputed biomolecule of great potential. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 43, 61–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.A.F. Chitin Chemistry; Macmillan Press Ltd.: London, UK, 1992; pp. 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford, F.A.; Austin, P.R. Marine Chitin Properties and Solvents. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Chitin/Chitosan; Muzzarelli, R.A.A., Pariser, E.R., Eds.; MIT Sea Grant Program: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1978; pp. 182–191. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, C.K.S.; Paul, W.; Sharma, C.P. Chitin and chitosan polymers: Chemistry, solubility and fiber formation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 641–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campaniello, D.; Bevilacqua, A.; Sinigaglia, M.; Corbo, M.R. Chitosan: Antimicrobial activity and potential applications for preserving minimally processed strawberries. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, W.; Kang, Y.; Wang, A. Chitin and chitosan as multipurpose natural polymers for groundwater arsenic removal and As2O3 delivery in tumor therapy. J. Macromol. Sci. Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 49, 971–979. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, R.; Stringari, G.B.; Franco, J.M.; Valencia, C.; Gallegos, C. Use of chitin, chitosan and acylated derivatives as thickener agents of vegetable oils for bio-lubricant applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aam, B.B.; Heggset, E.B.; Norberg, A.L.; Sørlie, M.; Vârum, K.M.; Eijsink, V.G.H. Production of chitooligosaccharides and their potential applications in medicine. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1482–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xia, W.; Liu, P.; Cheng, Q.; Tahirou, T.; Gu, W.; Li, B. Chitosan modification and pharmaceutical/biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1962–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Menon, D.; Manzoor, K.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H. Biomedical applications of chitin and chitosan based nanomaterials—A short review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.S.; Albertengo, L.A.; Agulló, E. Emulsification capacity of chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 48, 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo, P.; Martins, J.T.; Fuciños, C.; Pastrana, L.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A. Evaluation of a chitosan-based edible film as carrier of natamycin to improve the storability of Saloio cheese. J. Food Eng. 2010, 101, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anchisi, C.; Meloni, M.C.; Maccioni, A.M. Chitosan beads loaded with essential oils in cosmetic formulations. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2006, 57, 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi, F.; Synowiecki, J. Isolation and characterization of nutrients and value-added products from snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio) and shrimp (Pandalus borealis) processing discards. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolaimate, A.; Desbrières, J.; Rhazi, M.; Alagui, A. Contribution to the preparation of chitins and chitosans with controlled physico-chemical properties. Polymers 2003, 44, 7939–7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Li, L.; Zhuang, Z.; Wu, W.; Hong, S.; Zhou, J. Improved production of chitin from shrimp waste by fermentation with epiphytic lactic acid bacteria. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.L.B.; Tsai, G. Response surface optimization and kinetics of isolating chitin from pink shrimp (Solenocera melantho) shell waste. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 1900–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussignac, P. Unhaut polymere naturel peu connu dans l’industrie, Le chitosane. Chim. Ind. Genie Chim. 1968, 99, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Tolaimate, A.; Desbrières, J.; Rhazi, M.; Alagui, A.; Vincendon, M.; Vottero, P. On the influence of deacetylation process on the physicochemical characteristics of chitosan from squid chitin. Polymer 2000, 41, 2463–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Peña, A.U.; Espinoza-Pérez, J.D.; Sandoval-Fabian, G.C.; Balagurusamy, N.; Hernández-Rivera, A.; De-la-Garza-Rodríguez, I.M.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C. Screening of industrial enzymes for deproteinization of shrimp head for chitin recovery. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synowiecki, J.; Al-Khateeb, N.A.A.Q. The recovery of protein hydrolysate during enzymatic isolation of chitin from shrimp Crangon crangon processing discards. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Holanda, H.D.; Netto, F.M. Recovery of components from shrimp (Xiphopenaeus kroyeri) processing waste by enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, C298–C303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giyose, N.Y.; Mazomba, N.T.; Mabinya, L.V. Evaluation of proteases produced by Erwinia chrysanthemi for the deproteinization of crustacean waste in a chitin production process. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 707–711. [Google Scholar]
- Haddar, A.; Hmidet, N.; Ghorbel-Bellaaj, O.; Fakhfakh-Zouari, N.; Sellami-Kamoun, A.; Nasri, M. Alkaline proteases produced by Bacillus licheniformis RP1 grown on shrimp wastes: Application in chitin extraction, chicken feather-degradation and as a dehairing agent. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2011, 16, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sila, A.; Nasri, R.; Bougatef, A.; Nasri, M. Digestive alkaline proteases from the goby (Zosterisessor ophiocephalus): Characterization and potential application as detergent additive and in the deproteinization of shrimp wastes. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2012, 21, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachindra, N.M.; Bhaskar, N.; Siddegowda, G.S.; Sathisha, A.D.; Suresh, P.V. Recovery of carotenoids from ensilaged shrimp waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1642–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, K.; Daum, G.; Köster, M.; Kulicke, W.-M.; Meyer-Rammes, H.; Bisping, B.; Meinhardt, F. Genetic improvement of Bacillus licheniformis strains for efficient deproteinization of shrimp shells and production of high-molecular-mass chitin and chitosan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 8211–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, B. Microbiology of Fermented Foods, 2nd ed; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, M.S.; Muñoz, J.; Stevens, W.F. Critical factors in chitin production by fermentation of shrimp biowaste. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 54, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, K.; Guerrero, I.; Huerta, S.; Saucedo, G.; Castillo, A.; Gonzalez, R.O.; Hall, G.M. Effect of initial glucose concentration and inoculation level of lactic acid bacteria in shrimp waste ensilation. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2001, 28, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, N.; Suresh, P.V.; Sakhare, P.Z.; Sachindra, N.M. Shrimp biowaste fermentation with Pediococcus acidolactici CFR2182: Optimization of fermentation conditions by response surface methodology and effect of optimized conditions on deproteination/demineralization and carotenoid recovery. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbia, W.; Adour, L.; Amrane, A.; Lounici, H. Optimization of medium composition for enhanced chitin extraction from Parapenaeus longirostris by Lactobacillus helveticus using response surface methodology. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbel-Bellaaj, O.; Jellouli, K.; Younes, I.; Manni, L.; Ouled, S.M.; Nasri, M. A solvent-stable metalloprotease produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa A2 grown on shrimp shell waste and its application in chitin extraction. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 410–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sini, T.K.; Santhosh, S.; Mathew, P.T. Study on the production of chitin and chitosan from shrimp shell by using Bacillus subtilis fermentation. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2423–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, M.G.; Romo, C.R.; Bustos, R. Bioconversion of marine crustacean shell waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 1994, 11, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytekin, O.; Elibol, M. Cocultivation of Lactococcus lactis and Teredinobacter turnirae for biological chitin extraction from prawn waste. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 33, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.J.; Jo, G.H.; Kuk, J.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Park, R.D. Extraction of chitin from red crab shell waste by cofermentation with Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. tolerans KCTC-3074 and Serratia marcescens FS-3. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, N.; Garnica-González, M.; Ramírez-Hernández, J.Y.; Flores-Albino, B.; Gimeno, M.; Bárzana, E.; Shirai, K. Effect of temperature on chitin and astaxanthin recoveries from shrimp waste using lactic acid bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2849–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choorit, W.; Patthanamanee, W.; Manurakchinakorn, S. Use of response surface method for the determination of demineralization efficiency in fermented shrimp shells. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6168–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synowiecki, J.; Al-Khateeb, N.A.A.Q. Mycelia of Mucor rouxii as a source of chitin and chitosan. Food Chem. 1997, 60, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcidiacono, S.; Kaplan, D.L. Molecular weight distribution of chitosan isolated from Mucor rouxii under different culture and processing conditions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1992, 39, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Adhya, M.; Guha, A.K.; Chatterjee, B.P. Chitosan from Mucor rouxii: Production and physico-chemical characterization. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chatterjee, B.P.; Guha, A.K. Kinetics of Mucor rouxii fermentation in relation to chitosan production. Res. J. Microbiol. 2010, 5, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Martinou, A.; Bouriotis, V.; Stokke, B.T.; Vårum, K.M. Mode of action of chitin deacetylase from Mucor rouxii on partially N-acetylated chitosans. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 311, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trutnau, M.; Suckale, N.; Groeger, G.; Bley, T.; Ondruschka, J. Enhanced chitosan production and modeling hyphal growth of Mucor rouxii interpreting the dependence of chitosan yields on processing and cultivation time. Eng. Life Sci. 2009, 9, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejska, I.; Malesa-Ciecwierz, M.; Lerska, A.; Sikorski, Z. Properties of chitin deacetylase from crude extracts of Mucor rouxii mycelium. J. Food Biochem. 1999, 23, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Araki, Y.; Ito, E. A pathway of chitosan formation in Mucor rouxii: Enzymatic deacetylation of chitin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1974, 56, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeraj, N.; Kunic, B.; Lenasi, H.; Breskvar, K. Purification and molecular characterization of chitin deacetylase from Rhizopus nigricans. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, C.; Nuero, O.M.; Santamaria, F.; Reyes, F. Purification of a heat-stable chitin deacetylase from Aspergillus nidulans and its role in cell wall degradation. Curr. Microbiol. 1995, 30, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Win, N.N.; Stevens, W.F. Shrimp chitin as substrate for fungal chitin deacetylase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 57, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Park, R.-D.; Muzzarelli, R.A.A. Chitin deacetylases: Properties and applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Vázquez, J.A.; Rodríguez-Amado, I.; Montemayor, M.I.; Fraguas, J.; González, M.D.P.; Murado, M.A. Chondroitin Sulfate, Hyaluronic Acid and Chitin/Chitosan Production Using Marine Waste Sources: Characteristics, Applications and Eco-Friendly Processes: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 747-774. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11030747
Vázquez JA, Rodríguez-Amado I, Montemayor MI, Fraguas J, González MDP, Murado MA. Chondroitin Sulfate, Hyaluronic Acid and Chitin/Chitosan Production Using Marine Waste Sources: Characteristics, Applications and Eco-Friendly Processes: A Review. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(3):747-774. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11030747
Chicago/Turabian StyleVázquez, José Antonio, Isabel Rodríguez-Amado, María Ignacia Montemayor, Javier Fraguas, María Del Pilar González, and Miguel Anxo Murado. 2013. "Chondroitin Sulfate, Hyaluronic Acid and Chitin/Chitosan Production Using Marine Waste Sources: Characteristics, Applications and Eco-Friendly Processes: A Review" Marine Drugs 11, no. 3: 747-774. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11030747
APA StyleVázquez, J. A., Rodríguez-Amado, I., Montemayor, M. I., Fraguas, J., González, M. D. P., & Murado, M. A. (2013). Chondroitin Sulfate, Hyaluronic Acid and Chitin/Chitosan Production Using Marine Waste Sources: Characteristics, Applications and Eco-Friendly Processes: A Review. Marine Drugs, 11(3), 747-774. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11030747