Molecular and Chemical Analysis of the Lipopolysaccharide from Aeromonas hydrophila Strain AH-1 (Serotype O11)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
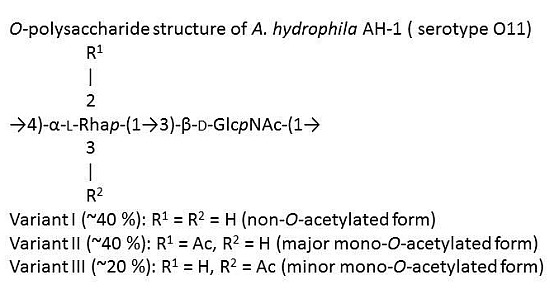
2.1. Chemical Structure of the A. Hydrophila AH-1 O11-Polysaccharide


| Sugar Residue | Nucleus | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 (6a, 6b) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| →3)-β-d-GlcpNAc-(1→ | 1H | 4.78 | 3.76 | 3.61 | 3.49 | 3.42 | 3.74, 3.90 |
| 13C | 102.0 | 56.9 | 82.9 | 69.9 | 77.0 | 62.1 | |
| →4)-α-l-Rhap-(1→ | 1H | 4.84 | 3.74 | 3.81 | 3.60 | 3.97 | 1.26 |
| 13C | 102.2 | 72.1 | 71.5 | 81.3 | 68.5 | 18.1 |

2.2. O11-Antigen LPS Biosynthesis Gene Cluster (wbO11)

| ORF | Protein Name | Protein Size | Predicted Function | Homologous Protein with Known Function | Percentage Identity/Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O-antigen LPS (wb) cluster | |||||
| 1 | RmlB | 361 | dTDP-glucose-4-6-dehydratase | RmlB multispecies Aeromonas | 100/100 |
| 2 | RmlD | 295 | dTDP-4-dehydro-rhamnose reductase | RmlD multispecies Aeromonas | 100/100 |
| 3 | RmlA | 292 | Glucose-1-phosphate thymildylyl transferase | RmlA multispecies Aeromonas | 100/100 |
| 4 | RmlC | 186 | dTDP-4-dehydro-rhamnose 3,5-epimerase | RmlC multispecies Aeromonas | 93/100 |
| Inserted S-layer protein cluster | |||||
| 17 | Wzm | 272 | ABC-2 type transporter permease | Wzm multispecies Aeromonas | 98/99 |
| 18 | Wzt | 438 | ABC transporter ATP binding protein | Wzt multispecies Aeromonas | 100/100 |
| 19 | WbbB | 1116 | N-acetyl glucosaminyl transferase | WbbB Klebsiella pneumonaie | 79/87 |
| 20 | acyltrans | 358 | Acyl transferase family 3 | Acyltransferase Serratia marcescens | 45/65 |
| 21 | WbbL | 268 | Rhamnosyl transferase | Glucosyl transferase family 2 A. veronii Rhmanosyl transferase E. coli | 100/10043/67 |
| 22 | UDP-ep | 318 | NAD-dependent dehydratase or UDP-sugar epimerase | NAD-dependent dehydratase or UDP-sugar epimerase multispecies Aeromonas | 100/100 |
| S-layer protein cluster | |||||
| 5 | SpsE | 551 | S-layer secretion system protein E | Type II secretion system (T2SS) protein E A. hydrophila | 100/100 |
| 6 | SpsF | 399 | S-layer secretion system protein F | Type II secretion system(T2SS) protein F A. hydrophila | 100/100 |
| 7 | SpsG | 144 | S-layer secretion system protein G | Type II secretion system (T2SS) protein G A. hydrophila | 99/100 |
| 8 | SpsH | 123 | S-layer secretion system protein H | Type II secretion system (T2SS) protein H A. hydrophila | 98/99 |
| 9 | SpsI | 139 | S-layer secretion system protein I | Type II secretion system (T2SS) protein I A. hydrophila | 99/100 |
| 10 | SpsJ | 201 | S-layer secretion system protein J | Type II secretion system (T2SS) protein J A. hydrophila | 98/99 |
| 11 | SpsK | 340 | S-layer secretion system protein K | Type II secretion system (T2SS) protein K A. hydrophila | 100/100 |
| 12 | SpsL | 252 | S-layer secretion system protein L | Type II secretion system (T2SS) protein L A. hydrophila | 94/95 |
| 13 | SpsM | 198 | Putative S-layer secretion system protein M | ORF1 hypothetical protein for S-layer secretion A. hydrophila | 100/100 |
| 14 | Orf2 | 166 | Putative S-layer hypothetical protein secretion system | ORF2 hypothetical protein for S-layer secretion A. hydrophila | 98/99 |
| 15 | SpsD | 743 | S-layer secretion system protein D | Type II secretion system (T2SS) protein D A. hydrophila | 100/100 |
| 16 | VapA | 469 | Surface layer protein | Paracrystaline surface layer protein A. hydrophila | 100/100 |
2.3. Mutant Isolation and Characterization



3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Growth Conditions
| Strain or Plasmid | Relevant Characteristics | Reference or Source |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli strains | ||
| DH5α | F-end A hsdR17 (rK- mK+) supE44 thi-1 recA1 gyr-A96 _80lacZM15 | [30] |
| MC1061 | thi thr1 leu6 proA2 his4 argE2 lacY1 galK2 ara14 xyl5, supE44,λpir | [31] |
| A. hydrophila strains | ||
| AH-1 | O11, Wild type | [32] |
| AH-1ΔrmlB | AH-1 rmlB in frame mutant unable to produce O11-antigen LPS | This study |
| AH-1Δwzt | AH-1 wzt in frame mutant unable to produce O11-antigen LPS | This study |
| AH-1ΔwbbB | AH-1 wbbB in frame mutant unable to produce O11-antigen LPS | This study |
| AH-1ΔwbbL | AH-1 wbbL in frame mutant unable to produce O11-antigen LPS | This study |
| AH-1ΔUDP-ep | AH-1 UDP-ep in frame mutant, able to produce O11-antigen LPS | This study |
| AH-1ΔvapA | AH-1 vapA in frame mutant, unable to produce S-layer but able to produce O11-antigen LPS | This study |
| AH-3ΔwahA | AH-3 wahA LPS-core in frame mutant | [15] |
| AH-3ΔwaaF | AH-3 waaF LPS-core in frame mutant | [15] |
| AH-3ΔwaaC | AH-3 waaC LPS-core in frame mutant | [15] |
| Plasmids | ||
| pGEMT easy | PCR generated DNA fragment cloning vector Amp R | Promega |
| pBAD33-Cm | Arabinose-inducible expression vector, Cm R | [33] |
| pDM4 | Suicide plasmid, Sacarose, Cm R | [31] |
| pLA2917 | Cosmid vector, Km R, Tc R | [19] |
4.2. General DNA Methods
4.3. DNA Sequencing and Computer Analysis of Sequence Data
4.4. Mutant Construction
4.5. Plasmid Constructions and Mutant Complementation Studies
4.6. LPS Isolation and SDS-PAGE
4.7. Large-Scale Isolation of LPS Plus Isolation and O-Deacetylation of the O-Polysaccharide
4.8. Sugar Analysis and NMR Spectroscopy
4.9. OM Protein and S-Layer Isolation and Characterization
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nazarenko, E.L.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. The structural diversity of carbohydrate antigens of selected gram-negative marine bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1914–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature. Available online: http://www.bacterio.net (accessed on 9 April 2015).
- MacDonell, M.T.; Swartz, D.G.; Ortiz-Conde, B.A.; Last, G.A.; Colwell, R.R. Ribosomal RNA phylogenies for the vibrio-enteric group of eubacteria. Microbiol. Sci. 1986, 3, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Romanenko, L.A.; Schumann, P.; Zhukova, N.V.; Rohde, M.; Mikhailov, V.V.; Stackebrandt, E. Marinobacter bryozoorum sp. nov. and Marinobacter sediminum sp. nov., novel bacteria from the marine environment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.T.; Shieh, W.Y. Zobellella denitrificans gen. nov., sp. nov. and Zobellella taiwanensis sp. nov., denitrifying bacteria capable of fermentative metabolism. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Carnahan, A.; Joseph, S.W. Order XII. Aeromonadales. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; Brenner, D.J., Krieg, N.R., Staley, J.T., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 2, PartB II; pp. 556–597. [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki, R.; Shimada, T. O-serogrouping scheme for mesophilic Aeromonas strains. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1984, 37, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.V.; Gross, R.J.; Cheasty, T.; Rowe, B. Extended serogrouping scheme for motile, mesophilic Aeromonas species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miñana-Galbis, D.; Farfán, M.; Lorén, J.G.; Fusté, M.C. The reference strain Aeromonas hydrophila CIP 57.50 should be reclassified as Aeromonas salmonicida CIP 57.50. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozińska, A.; Pękala, A. Characteristics of disease spectrum in relation to species, serogroups, and adhesion ability of motile aeromonads in fish. Sci. World J. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L.; Khashe, S.; Kellogg, G.H.; Shimada, T. Further studies on biochemical characteristics and serologic properties of the genus Aeromonas. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1930–1933. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dooley, J.S.; Lallier, R.; Shaw, D.H.; Trust, T.J. Electrophoretic and immunochemical analyses of the lipopolysaccharides from various strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 164, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shaw, D.H.; Squires, M.J. O-antigen structure in a virulent strain of Aeromonas hydrophila. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1984, 24, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, N.; Canals, R.; Lacasta, A.; Kondakova, A.N.; Lindner, B.; Knirel, Y.A.; Merino, S.; Regué, M.; Tomás, J.M. Molecular analysis of three Aeromonas hydrophila AH-3 (serotype O34) lipopolysaccharide core biosynthesis gene clusters. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 3176–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westphal, O.; Jann, K. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide extraction with phenol-water and further application of the procedure. Methods Carbohydr. Chem. 1965, 5, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Duus, J.Ø.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Bock, K. Carbohydrate structural determination by NMR spectroscopy: Modern methods and limitations. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 4589–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Pietras, H.; Duda, K.A.; Kozinska, A.; Pekala, A.; Holst, O. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of Aeromonas sobria strain Pt312. Carbohydr. Res. 2015, 403, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueras, M.M.; Merino, S.; Aguilar, A.; Benedí, V.J.; Tomás, J.M. Cloning, sequencing and role in serum susceptibility of porin II from mesophilic Aeromonas sp. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, N.; Canals, R.; Saló, M.T.; Vilches, S.; Merino, S.; Tomás, J.M. The Aeromonas hydrophila wb*O34 gene cluster: genetics and temperature regulation. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 4198–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artsimovitch, I.; Landick, R. The transcriptional regulator RfaH stimulates RNA chain synthesis after recruitment to elongation complexes by the exposed nontemplate DNA strand. Cell 2002, 109, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.J.; Hughes, C.; Koronakis, V. RfaH and the ops element, components of a novel system controlling bacterial transcription elongation. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 26, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Vinogradov, E.; Jimenez, N.; Merino, S.; Tomás, J.M. Structural studies on the R-type lipopolysaccharide of Aeromonas hydrophila. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saigi, F.; Climent, N.; Piqué, N.; Sanchez, C.; Merino, S.; Rubirés, X.; Aguilar, A.; Tomás, J.M.; Regué, M. Genetic analysis of the Serratia marcescens N28b O4 antigen gene cluster. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, L.; Merino, S.; Regué, M.; Rodríguez, F.; Tomás, J.M. A Klebsiella pneumoniae O-antigen heteropolysaccharide (O12) requiring an ABC-2-trasnporter dependent pathway. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, P.; Kanehisa, M.; DeLisi, C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 815, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquilini, E.; Tomás, J.M. Lipopolysaccharides (Endotoxins). In Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro, E.E.; Kay, W.W.; Ainsworth, T.; Chamberlain, J.B.; Buckley, J.T.; Trust, T.J. Loss of virulence during culture of Aeromonas salmonicida at high temperature. J. Bacteriol. 1981, 148, 393–400. [Google Scholar]
- Belland, R.J.; Trust, T.J. Synthesis, export, and assembly of Aeromonas salmonicida A-layer analysed by transposon mutagenesis. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 163, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J. Mol. Biol. 1983, 166, 557–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milton, D.L.; O’Toole, R.; Horstedt, P.; Wolf-Watz, H. Flagellin A is essential for the virulence of Vibrio anguillarum. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.B.; Srinivasa Rao, P.S.; Lee, H.C.; Vilches, S.; Merino, S.; Tomás, J.M.; Leung, K.Y. A Type III secretion system is required for Aeromonas hydrophila AH-1 pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, L.M.; Belin, D.; Carson, M.J.; Beckwith, J. Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 4121–4130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchcock, P.J.; Brown, T.M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J. Bacteriol. 1983, 154, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sawardeker, J.S.; Sloneker, J.H.; Jeanes, A. Spectrophotometric determination of high molecular weight quaternary ammonium cations in polysaccharides. Anal. Chem. 1965, 37, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmalm, G.; Leontein, K. Structural studies of the Escherichia coli O127 O-antigen polysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res. 1993, 247, 87–89. [Google Scholar]
- Esteve, C.; Amaro, C.; Toranzo, A.E. O-serogrouping and surface components of Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas jandaei pathogenic for eels. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1994, 117, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, J.S.G.; Trust, T.J. Surface protein composition of Aeromonas hydrophila strains virulent for fish: Identification of a surface array protein. J. Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merino, S.; Rubires, X.; Aguilar, A.; Albertí, S.; Hernández-Allés, S.; Benedí, V.J.; Tomás, J.M. Mesophilic Aeromonas sp. serogroup O:11 resistance to complement-mediated killing. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 5302–5309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merino, S.; Nogueras, M.M.; Aguilar, A.; Rubires, X.; Albertí, S.; Benedí, V.J.; Tomás, J.M. Activation of the complement classical pathway (C1q binding) by mesophilic Aeromonas outer membrane protein. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 3825–3831. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merino, S.; Canals, R.; Knirel, Y.A.; Tomás, J.M. Molecular and Chemical Analysis of the Lipopolysaccharide from Aeromonas hydrophila Strain AH-1 (Serotype O11). Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2233-2249. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13042233
Merino S, Canals R, Knirel YA, Tomás JM. Molecular and Chemical Analysis of the Lipopolysaccharide from Aeromonas hydrophila Strain AH-1 (Serotype O11). Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(4):2233-2249. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13042233
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerino, Susana, Rocío Canals, Yuriy A. Knirel, and Juan M. Tomás. 2015. "Molecular and Chemical Analysis of the Lipopolysaccharide from Aeromonas hydrophila Strain AH-1 (Serotype O11)" Marine Drugs 13, no. 4: 2233-2249. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13042233
APA StyleMerino, S., Canals, R., Knirel, Y. A., & Tomás, J. M. (2015). Molecular and Chemical Analysis of the Lipopolysaccharide from Aeromonas hydrophila Strain AH-1 (Serotype O11). Marine Drugs, 13(4), 2233-2249. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13042233