Structural and Functional Characterization of a Novel α-Conotoxin Mr1.7 from Conus marmoreus Targeting Neuronal nAChR α3β2, α9α10 and α6/α3β2β3 Subtypes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemical Identity of Synthetic Mr1.7 and Its Variants

2.2. Disulfide Bridge Pattern of Mr1.7 Is I-III, II-IV
| α-CTX | Amino Acid Sequence | Targets (IC50, nM) | α3β4/α3β2 | α2β4/α3β2 | α7/α3β2 | α9α10/α3β2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mr1.7 | PECCTHPACHVSHPELC * | α3β2 (53.1(48.0–58.8)), α9α10 (185.7(154.1–223.7)), α6/α3β2β3 (284.2(199.4–405.2)), α3β4 (>10,000), α7 (>10,000), α2β4 (>10,000), α2β2 (>10,000), α4β2 (>10,000), α4β4 (>10,000) | >188 | >188 | >188 | 3.5 |
| RaaMr1.7 | RPECCTHPACHVSHPELC * | α3β2 (41.2(22.5–75.5)) | ||||
| Mr1.7[P1A] | AECCTHPACHVSHPELC * | α3β2 (42.0(26.1–67.6)) | ||||
| Mr1.7[E2A] | PACCTHPACHVSHPELC * | α3β2 (11.8(8.4–16.7)), α9α10 (>10,000), α3β4 (>10,000), α7 (>10,000), α2β4 (>10,000) | >847 | >847 | >847 | >847 |
| Mr1.7[H10A] | PECCTHPACAVSHPELC * | α3β2 (123.4(96.5–157.6)) | ||||
| Mr1.7[H13A] | PECCTHPACHVSAPELC * | α3β2 (>10,000) | ||||
| Mr1.7[V11G] | PECCTHPACHGSHPELC * | α3β2 (137.8(114.5–165.7)) | ||||
| Mr1.7[S12N] | PECCTHPACHVNHPELC * | α3β2 (11.5(9.4–13.9)), α3β4 (849.9(477.4–1523.6)), α7 (220.3(136.4–355.9)), α2β4 (367.3(215.7–625.6)), α9α10 (>10,000) | 74 | 32 | 17 | >870 |
| Mr1.7[H13N] | PECCTHPACHVSNPELC * | α3β2 (541.4(395.1–742.0)), α9α10 (1833(1033–3250)), α3β4 (>10000), α7 (2423(1785–3289)), α2β4 (>10,000), α4β2 (>10,000), α2β2 (>10,000), α4β4 (>10,000) | >18.5 | >18.5 | 4.5 | 3.5 |
| Mr1.7[E2A,S12N] | PACCTHPACHVNHPELC * | α3β2 (6.4(5.1–7.9)), α3β4 (556.3(385.4–803.1)), α7 (590.8(447.0–781.0)), α2β4 (3489(2503–4863)), α9α10 (>10,000) | 88 | 594 | 109 | >1563 |
| Mr1.7[V11G,S12N] | PECCTHPACHGNHPELC * | α3β2 (28.4(24.8–32.5)) | ||||
| Mr1.7[E2G,V11G,S12N,Δ1] | GCCTHPACHGNHPELC * | α3β2 (4.4(3.7–5.3)), α3β4 (124.9(80.9–192.7)), α2β4 (389.9(250.3–607.5)), α9α10 (>10,000), α7 (>10,000) | 27 | 89 | >2272 | >2272 |
2.3. NMR Assignments and Structural Calculations of Mr1.7
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| NOE distance constraints | 156 |
| Intra-residue | 96 |
| Sequential | 42 |
| Medium range | 15 |
| Long range | 3 |
| NMR constraint violations | |
| H bond constraints | 1 |
| Dihedral constraints | 5 |
| Cyana target function (Å) | 0.37 ± 0.05 |
| RMSD to mean coordinates | |
| Mean global backbone atoms RMSD | 0.66 ± 0.15 |
| Mean global heavy atoms RMSD | 1.22 ± 0.18 |
| Rachandran statistics from PROCHECK-NMR | |
| Most favored regions, % | 47.7 |
| Additional allowed regions, % | 43.1 |
| Generously allowed regions, % | 9.2 |
| Disallowed regions, % | 0.0 |


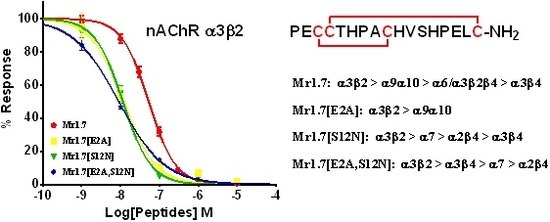
2.4. Potency of Mr1.7 at the Rat Neuronal nAChRs

2.5. Key Residues of the N-Terminal Sequence Affect the Potency and Selectivity of Mr1.7 for nAChR α3β2
2.6. Key Residues of the Loop2 Region Affect the Potency and Selectivity of Mr1.7 for nAChR α3β2


| α-CTX | Amino acids sequence a | Targets (IC50, nM) b | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mr1.7 | PETHSHEL * | α3β2 (53.1), α9α10 (187.5) | This work |
| Mr1.8 (MrIC) | PETHSEL * | α3β2 (541.4), α9α10 (1833), α7 (2423) | This work |
| PeIA | SHEL * | α3β2 (23), α9α10 (6.9), α3β4 (480), α7 (1800) | [26] |
| RegIIA | NHI * | α3β2 (33), α3β4 (97), α7 (103), α9α10 (>1000) | [27] |
| OmIA | NHIG * | α3β2 (11.0), α7 (27.1) | [28] |
| LsIA | SNRNI * | α3β2 (10.3), α7 (10.1) | [17] |
| ArIA | IRDENRHVRRR # | α3β2 (18.0), α7 (6.0) | [29] |
| GID | IRDγNRHV # | α3β2 (3.1), α4β2 (152), α7 (4.5) | [30] |
| ArIB | DENRHVRRR # | α3β2 (60.1), α7 (1.8) | [29] |
| TxIA | RPIADL * | α3β2 (3.6), α7 (392) | [31] |
| PnIA | LPAADY * | α3β2 (9.6), α7 (252) | [32] |
| AnIA | AAQDY * | α3β2 (5.8) | [16] |
| AnIB | GAAQDY * | α3β2 (0.3), α7 (76) | [16] |
| GIC | AGQHI * | hα3β2 (1.1), hα4β2 (309), hα3β4 (755) | [33] |
| Lo1a | ENRTHEVD * | α7 (3240) | [34] |
| Vc1.1 | DRNYDHEI * | α3β2 (5532), α9α10 (109), α3β4 (4200), α7 (7123) | [35] |
| MII | NVHLEHSNL * | α3β2 (0.5), α7 (~200) | [36] |
| TxID | VSAMSI- * | α3β4 (12.5), α2β4 (4550) | [37] |
| BuIA | TPAVLY--- * | α3β2 (5.7), α3β4 (28), α4β4 (69.9), α2β4 (121), α7 (272), α2β2 (800) | [38] |

| α-CTX | koff | t1/2 a | kobs b | kon | Ki c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min−1 | min | min−1 | min−1M−1 | M−9 | |
| Mr1.7 | 0.187 ± 0.016 | 3.710 (3.165–4.480) | 0.735 ± 0.064 | 0.548 × 107 | 34.093 |
| Mr1.7[E2A] | 0.168 ± 0.023 | 4.129 (3.236–5.702) | 0.686 ± 0.040 | 0.518 × 107 | 32.401 |
| Mr1.7[S12N] | 0.244 ± 0.038 | 2.836 (2.150–4.164) | 1.024 ± 0.073 | 0.780 × 107 | 31.349 |
| Mr1.7[E2A,S12N] | 0.104 ± 0.014 | 6.688 (5.263–9.170) | 0.546 ± 0.031 | 0.443 × 107 | 23.402 |
| Mr1.7[E2G,V11G,S12N,Δ1] | 0.211 ± 0.017 | 3.286 (2.842–3.894) | 1.460 ± 0.2516 | 0.125 × 108 | 16.884 |
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptide Synthesis
4.2. Analysis of Disulfide Bridges
4.3. NMR Spectroscopy and Structural Calculation
4.4. Inhibitory Activity to nAChR Subunits Expressed on Oocyte
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hogg, R.C.; Raggenbass, M.; Bertrand, D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: From structure to brain function. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 147, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zoli, M.; Pistillo, F.; Gotti, C. Diversity of native nicotinic receptor subtypes in mammalian brain. Neuropharmacology 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K.A.; Patwardhan, A.M.; Akopian, A.N. Receptor and channel heteromers as pain targets. Pharm. Basel 2012, 5, 249–278. [Google Scholar]
- Becchetti, A.; Aracri, P.; Meneghini, S.; Brusco, S.; Amadeo, A. The role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in autosomal dominant nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, S.; Maskos, U. Role of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in Alzheimer’s disease pathology and treatment. Neuropharmacology 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaias, I.U.; Spiegel, J.; Brumberg, J.; Cosgrove, K.P.; Marotta, G.; Oishi, N.; Higuchi, T.; Kusters, S.; Schiller, M.; Dillmann, U.; et al. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor density in cognitively intact subjects at an early stage of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, E.X.; Pereira, E.F.; Alkondon, M.; Rogers, S.W. Mammalian nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: From structure to function. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 73–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasoli, F.; Gotti, C. Structure of neuronal nicotinic receptors. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lebbe, E.K.; Peigneur, S.; Wijesekara, I.; Tytgat, J. Conotoxins targeting nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2970–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, T.; Wittenauer, S.; McIntosh, J.M.; Vincler, M. Spinal [alpha]3[beta]2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors tonically inhibit the transmission of nociceptive mechanical stimuli. Brain Res. 2008, 1229, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, E.; Elgoyhen, A.B.; Gomez-Casati, M.E.; Knipper, M.; Vetter, D.E.; Fuchs, P.A.; Glowatzki, E. Developmental regulation of nicotinic synapses on cochlear inner hair cells. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 7814–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napier, I.A.; Klimis, H.; Rycroft, B.K.; Jin, A.H.; Alewood, P.F.; Motin, L.; Adams, D.J.; Christie, M.J. Intrathecal alpha-conotoxins Vc1.1, AuIB and MII acting on distinct nicotinic receptor subtypes reverse signs of neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 2202–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Cinci, L.; Micheli, L.; Zanardelli, M.; Pacini, A.; McIntosh, J.M.; Ghelardini, C. Alpha-conotoxin RgIA protects against the development of nerve injury-induced chronic pain and prevents both neuronal and glial derangement. Pain 2014, 155, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.D.; Norton, R.S. Conotoxin gene superfamilies. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 6058–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard, E.L.; Nevin, S.T.; Loughnan, M.L.; Nicke, A.; Clark, R.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J.; Adams, D.J.; Craik, D.J.; Daly, N.L. Inhibition of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes by alpha-conotoxin GID and analogues. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4944–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loughnan, M.L.; Nicke, A.; Jones, A.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Chemical and functional identification and characterization of novel sulfated alpha-conotoxins from the cone snail Conus anemone. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inserra, M.C.; Kompella, S.N.; Vetter, I.; Brust, A.; Daly, N.L.; Cuny, H.; Craik, D.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Adams, D.J.; Lewis, R.J. Isolation and characterization of alpha-conotoxin LsIA with potent activity at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, R.B.; DelaCruz, R.G.; Grose, J.H.; McIntosh, J.M.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M. Critical residues influence the affinity and selectivity of alpha-conotoxin MI for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 13310–13315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Dutertre, S.; Vetter, I.; Christie, M.J. Conus venom peptide pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 259–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essack, M.; Bajic, V.B.; Archer, J.A. Conotoxins that confer therapeutic possibilities. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1244–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, N.; Wu, C.; Jiang, J.; Yue, J.; Jing, Y.; Dai, Q. Diversity and evolution of conotoxins in Conus virgo, Conus eburneus, Conus imperialis and Conus marmoreus from the south china sea. Toxicon 2012, 60, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, F.; Du, W. Solution structure of a novel alpha-conotoxin with a distinctive loop spacing pattern. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Du, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Ding, J.; Jiang, L.; Dai, Q. Characterization of a T-superfamily conotoxin TxVC from Conus textile that selectively targets neuronal nAChR subtypes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 454, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, N.L.; Callaghan, B.; Clark, R.J.; Nevin, S.T.; Adams, D.J.; Craik, D.J. Structure and activity of alpha-conotoxin PeIA at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes and GABA(B) receptor-coupled N-type calcium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 10233–10237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, A.H.; Vetter, I.; Dutertre, S.; Abraham, N.; Emidio, N.B.; Inserra, M.; Murali, S.S.; Christie, M.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Mric, a novel alpha-conotoxin agonist in the presence of PNU at endogenous alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, J.M.; Plazas, P.V.; Watkins, M.; Gomez-Casati, M.E.; Olivera, B.M.; Elgoyhen, A.B. A novel alpha-conotoxin, PeIA, cloned from Conus pergrandis, discriminates between rat alpha9alpha10 and alpha7 nicotinic cholinergic receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30107–30112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, A.; Kompella, S.N.; Akondi, K.B.; Melaun, C.; Daly, N.L.; Luetje, C.W.; Alewood, P.F.; Craik, D.J.; Adams, D.J.; Mari, F. RegIIA: An alpha4/7-conotoxin from the venom of Conus regius that potently blocks α3β4 nAChRs. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talley, T.T.; Olivera, B.M.; Han, K.H.; Christensen, S.B.; Dowell, C.; Tsigelny, I.; Ho, K.Y.; Taylor, P.; McIntosh, J.M. Alpha-conotoxin OmIA is a potent ligand for the acetylcholine-binding protein as well as alpha3beta2 and alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 24678–24686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteaker, P.; Christensen, S.; Yoshikami, D.; Dowell, C.; Watkins, M.; Gulyas, J.; Rivier, J.; Olivera, B.M.; McIntosh, J.M. Discovery, synthesis, and structure activity of a highly selective alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 6628–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicke, A.; Loughnan, M.L.; Millard, E.L.; Alewood, P.F.; Adams, D.J.; Daly, N.L.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J. Isolation, structure, and activity of GID, a novel alpha 4/7-conotoxin with an extended N-terminal sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3137–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutertre, S.; Ulens, C.; Buttner, R.; Fish, A.; van Elk, R.; Kendel, Y.; Hopping, G.; Alewood, P.F.; Schroeder, C.; Nicke, A.; et al. AChBP-targeted alpha-conotoxin correlates distinct binding orientations with nAChR subtype selectivity. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3858–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopping, G.; Wang, C.I.; Hogg, R.C.; Nevin, S.T.; Lewis, R.J.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. Hydrophobic residues at position 10 of alpha-conotoxin PnIA influence subtype selectivity between alpha7 and alpha3beta2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 91, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McIntosh, J.M.; Dowell, C.; Watkins, M.; Garrett, J.E.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M. Alpha-conotoxin GIC from Conus geographus, a novel peptide antagonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33610–33615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebbe, E.K.; Peigneur, S.; Maiti, M.; Devi, P.; Ravichandran, S.; Lescrinier, E.; Ulens, C.; Waelkens, E.; D’Souza, L.; Herdewijn, P.; et al. Structure-function elucidation of a new alpha-conotoxin, Lo1a, from Conus longurionis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 9573–9583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halai, R.; Clark, R.J.; Nevin, S.T.; Jensen, J.E.; Adams, D.J.; Craik, D.J. Scanning mutagenesis of alpha-conotoxin Vc1.1 reveals residues crucial for activity at the alpha9alpha10 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 20275–20284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartier, G.E.; Yoshikami, D.; Gray, W.R.; Luo, S.; Olivera, B.M.; McIntosh, J.M. A new alpha-conotoxin which targets alpha3beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7522–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Zhangsun, D.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Christensen, S.; Harvey, P.J.; Akcan, M.; Craik, D.J.; McIntosh, J.M. Characterization of a novel alpha-conotoxin TxID from Conus textile that potently blocks rat alpha3beta4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9655–9663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, L.; Dowell, C.; Watkins, M.; Stitzel, J.A.; Olivera, B.M.; McIntosh, J.M. Alpha-conotoxin BuIA, a novel peptide from Conus bullatus, distinguishes among neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, A.; Starobova, H.; Inserra, M.C.; Jin, A.H.; Deuis, J.R.; Dutertre, S.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Daly, N.L.; Vetter, I. Alpha-conotoxin MrIC is a biased agonist at alpha nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 92, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, R.C.; Miranda, L.P.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Adams, D.J. Single amino acid substitutions in alpha-conotoxin PnIA shift selectivity for subtypes of the mammalian neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 36559–36564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hone, A.J.; Ruiz, M.; Scadden, M.; Christensen, S.; Gajewiak, J.; Azam, L.; McIntosh, J.M. Positional scanning mutagenesis of alpha-conotoxin PeIA identifies critical residues that confer potency and selectivity for alpha6/alpha3beta2beta3 and alpha3beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 25428–25439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiembob, D.L.; Roberts, R.L.; Luetje, C.W.; McIntosh, J.M. Determinants of alpha-conotoxin BuIA selectivity on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor beta subunit. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 11200–11207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Sheng, Z.; Geiger, J.H.; Castellino, F.J.; Prorok, M. Helix-helix interactions between homo- and heterodimeric gamma-carboxyglutamate-containing conantokin peptides and their derivatives. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 12641–12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Du, W. Solution structure of Hyp10Pro variant of conomarphin, a cysteine-free and d-amino-acid containing conopeptide. Toxicon 2009, 54, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guntert, P. Automated NMR structure calculation with Cyana. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton N. J. 2004, 278, 353–378. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, N.; Du, W.; Dai, Q. Structural and Functional Characterization of a Novel α-Conotoxin Mr1.7 from Conus marmoreus Targeting Neuronal nAChR α3β2, α9α10 and α6/α3β2β3 Subtypes. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3259-3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063259
Wang S, Zhao C, Liu Z, Wang X, Liu N, Du W, Dai Q. Structural and Functional Characterization of a Novel α-Conotoxin Mr1.7 from Conus marmoreus Targeting Neuronal nAChR α3β2, α9α10 and α6/α3β2β3 Subtypes. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(6):3259-3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063259
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuo, Cong Zhao, Zhuguo Liu, Xuesong Wang, Na Liu, Weihong Du, and Qiuyun Dai. 2015. "Structural and Functional Characterization of a Novel α-Conotoxin Mr1.7 from Conus marmoreus Targeting Neuronal nAChR α3β2, α9α10 and α6/α3β2β3 Subtypes" Marine Drugs 13, no. 6: 3259-3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063259
APA StyleWang, S., Zhao, C., Liu, Z., Wang, X., Liu, N., Du, W., & Dai, Q. (2015). Structural and Functional Characterization of a Novel α-Conotoxin Mr1.7 from Conus marmoreus Targeting Neuronal nAChR α3β2, α9α10 and α6/α3β2β3 Subtypes. Marine Drugs, 13(6), 3259-3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063259