Fabrication of Gelatin-Based Electrospun Composite Fibers for Anti-Bacterial Properties and Protein Adsorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Influence of Gel Concentration on Fibers
2.2. Influence of CS Concentration on Fibers
2.3. Influence of HA Concentration and Particle Size on Fibers
2.4. Influence of the GO Concentration on Fibers
2.5. Test of Antibacterial Properties
2.6. Adsorption Performance of BSA
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Graphene Oxide and Reduction of Graphene Oxide Using the Hummers Method
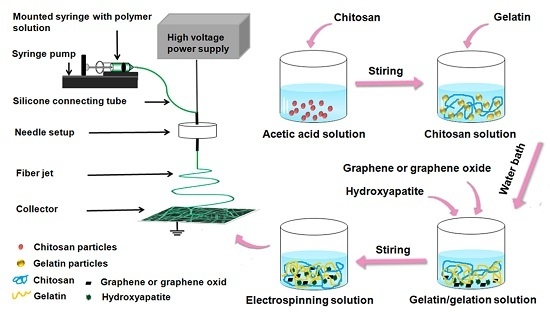
4.3. Configuration of Electrospinning Solution
4.4. Preparation of Electrospun Fibers
4.5. Test of Antibacterial Properties
4.6. Protein Adsorption
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C. Poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/hydroxyapatite nanofibrous scaffolds fabricated by electrospinning for bone tissue engineering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofman, K.; Tucker, N.; Stanger, J.; Staiger, M.; Marshall, S.; Hall, B. Effects of the molecular format of collagen on characteristics of electrospun fibres. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.K.; Chhabra, H.; Soni, V.P.; Bellare, J.R. Enhanced mechanical strength and biocompatibility of electrospun polycaprolactone-gelatin scaffold with surface deposited nano-hydroxyapatite. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 2376–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajkiewicz, P.; Kołbuk, D. Electrospinning of gelatin for tissue engineering—Molecular conformation as one of the overlooked problems. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 2009–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Feng, Y.; Fang, Z.; Xiao, R.; Yuan, W.; Khan, M. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun gelatin-heparin nanofibers as vascular tissue engineering. Macromol. Res. 2013, 21, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.X.; Li, H.F.; Sun, Z.Z.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, Y.F. Fabrication of mineralized electrospun PLGA and PLGA/gelatin nanofibers and their potential in bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, S.; Nethala, S.; Pattnaik, S.; Tripathi, A.; Moorthi, A.; Selvamurugan, N. Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial activity of a bio-composite scaffold containing chitosan/nano-hydroxyapatite/nano-silver for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, K.; Noguchi, K.; Hanafusa, Y.; Osawa, K.; Ogawa, K. Structural study of anhydrous tendon chitosan obtained via chitosan/acetic acid complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 26, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Nair, S.V.; Tokura, S.; Tamura, H.; Selvamurugan, N. Novel carboxymethyl derivatives of chitin and chitosan materials and their biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2010, 55, 675–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Su, G.; Li, L.; Gilbertson, B.O.; Yu, L.H.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.-P.; Yan, B. Size-Dependent Cell Uptake of Protein-Coated Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artiles, M.S.; Rout, C.S.; Fisher, T.S. Graphene-based hybrid materials and devices for biosensing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Qian, F.; Saltikov, C.W.; Jiao, Y.; Li, Y. Microbial reduction of graphene oxide by Shewanella. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Li, T.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Gao, C.; Zhang, S.; Xie, E. Graphene-based composite materials beneficial to wound healing. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2978–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, A.F.D.; Martinez, D.S.T.; Meira, S.M.M.; de Moraes, A.C.M.; Brandelli, A.; Filho, A.G.S.; Alves, O.L. Anti-adhesion and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles supported on graphene oxide sheets. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpio, I.E.M.; Santos, C.M.; Wei, X.; Rodrigues, D.F. Toxicity of a polymer-graphene oxide composite against bacterial planktonic cells, biofilms, and mammalian cells. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4746–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titov, A.V.; Král, P.; Pearson, R. Sandwiched Graphene−Membrane Superstructures. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goenka, S.; Sant, V.; Sant, S. Graphene-based nanomaterials for drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2014, 173, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Chang, H.; Chen, S.; Lai, C.; Khademhosseini, A.; Wu, H. Regulating Cellular Behavior on Few-Layer Reduced Graphene Oxide Films with Well-Controlled Reduction States. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabra, A.B.; Paula, A.J.; de Lima, R.; Alves, O.L.; Durán, N. Nanotoxicity of Graphene and Graphene Oxide. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirkhanzadeh, M. Direct formation of nanophase hydroxyapatite on cathodically polarized electrodes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1998, 9, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, K.R.; Mostafa, A.A. Preparation and bioactivity evaluation of hydroxyapatite-titania/chitosan-gelatin polymeric biocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Chung, W.-J.; Kim, G. A mechanically improved virus-based hybrid scaffold for bone tissue regeneration. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 55022–55032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Xia, L.; Gan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Jiang, X.; Chang, J. Tailoring the Nanostructured Surfaces of Hydroxyapatite Bioceramics to Promote Protein Adsorption, Osteoblast Growth, and Osteogenic Differentiation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8008–8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Zhitomirsky, I. Electrodeposition of composite hydroxyapatite–chitosan films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 94, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Weng, J. Investigation on process parameters of electrospinning system through orthogonal experimental design. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 3105–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Li, J. Room Temperature Ionic Liquid Based Polystyrene Nanofibers with Superhydrophobicity and Conductivity Produced by Electrospinning. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3420–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Yu, Q.; Qiu, Z.; Yan, Y. Effects of different ionic liquids on the electrospinning of a polyacrylonitrile polymer solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 2359–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, V.C.; Jachak, A.; Hurt, R.H.; Kane, A.B. Biological Interactions of Graphene-Family Nanomaterials: An Interdisciplinary Review. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of Graphene and Graphene Oxide Nanowalls Against Bacteria. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Liu, Z. Graphene in biomedicine: Opportunities and challenges. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuila, T.; Bose, S.; Khanra, P.; Mishra, A.K.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Recent advances in graphene-based biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4637–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Reagent | NaCl | KCl | KH2PO4 | Na2HPO4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (g·L−1) | 80.0 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 14.4 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, W. Fabrication of Gelatin-Based Electrospun Composite Fibers for Anti-Bacterial Properties and Protein Adsorption. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14100192
Gao Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Cui W. Fabrication of Gelatin-Based Electrospun Composite Fibers for Anti-Bacterial Properties and Protein Adsorption. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(10):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14100192
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ya, Yingbo Wang, Yimin Wang, and Wenguo Cui. 2016. "Fabrication of Gelatin-Based Electrospun Composite Fibers for Anti-Bacterial Properties and Protein Adsorption" Marine Drugs 14, no. 10: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14100192
APA StyleGao, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., & Cui, W. (2016). Fabrication of Gelatin-Based Electrospun Composite Fibers for Anti-Bacterial Properties and Protein Adsorption. Marine Drugs, 14(10), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14100192