Insight into the Mechanism of Action of Marine Cytotoxic Thiazinoquinones
Abstract
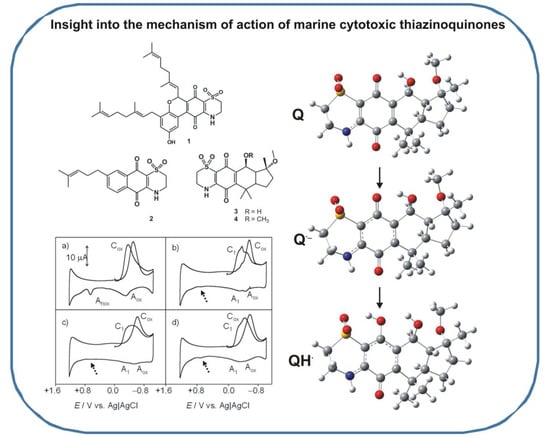
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. General Voltammetric Pattern
2.2. Interaction with ROS
2.3. Computational Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents, Compound Isolation, and Characterization
3.2. Electrochemical Studies
3.3. Computational Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zuman, P.; Perrin, C.L. Organic Polarography; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 1–316. ISBN 9780471985907. [Google Scholar]
- Doménech-Carbó, A.; de Carvalho, L.M.; Martini, M.; Valencia, D.P.; Cebrián-Torrejón, G. Electrochemical monitoring of the pharmacological activity of natural products. Stud. Nat. Prod. 2015, 45, 59–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Campos Rodrigues, T.; Rosenbaum, M.A. Microbial electroreduction: Screening for new cathodic biocatalysts. ChemElectroChem 2014, 1, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TerAvest, M.A.; Zajdel, T.J.; Ajo-Franklin, C.M. The Mtr pathway of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 couples substrate utilization to current production in Escherichia coli. ChemElectroChem 2014, 1, 1874–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doménech-Carbó, A.; Maciuk, A.; Figadère, B.; Poupon, E.; Cebrián-Torrejón, G. Solid-state electrochemical assay of heme-binding molecules for screening of drugs with antimalarial potential. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4014–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doménech-Carbó, A.; Cebrián-Torrejón, G.; De Miguel, L.; Tordera, V.; Rodrigues, D.; Assad-Kahn, S.; Fournet, A.; Figadère, B.; Vázquez, R.; Popuon, E. DsDNA, ssDNA, G-quadruplex DNA, and nucleosomal DNA electrochemical screening using canthin-6-one alkaloid-modified electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 115, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Albelda, M.T.; Inclán, M.; Valle-Algarra, F.M.; García-España, E.; Doménech-Carbó, A. Voltammetry of microparticles, scanning electrochemical microscopy and scanning tunneling microscopy applied to the study of dsDNA binding and damage by scorpiand-like polyamine receptors. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 720–721, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, F.; Schröder, U.; Gulabowski, R.; Doménech-Carbó, A. Electrochemistry of Immobilized Particles and Droplets, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–327. ISBN 978-3319108421. [Google Scholar]
- Doménech-Carbó, A.; Labuda, J.; Scholz, F. Electroanalytical chemistry for the analysis of solids: Characterization and classification (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 609–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Monte, D.; Ross, D.; Bellomo, G.; Eklow, L.; Orrenius, S. Alterations in intracellular thiol homeostasis during the metabolism of menadione by isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1984, 235, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.; Thor, H.; Orrenius, S.; Moldeus, P. Interaction of menadione (2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) with glutathione. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1985, 55, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigram, W.J.; Fuller, W.; Hamilton, L.D. Stereochemistry of intercalation: Interaction of daunomycin with DNA. Nat. New Biol. 1972, 235, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewey, K.M.; Rowe, T.C.; Yang, L.; Halligan, B.D.; Liu, L.F. Adriamycin-induced DNA damage mediated by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. Science 1984, 226, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommier, Y.; Schwartz, R.E.; Zwelling, L.A.; Kohn, K.W. Effects of DNA intercalating agents on topoisomerase II induced DNA strand cleavage in isolated mammalian cell nuclei. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 6406–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.M.; d’Arcy Doherty, M. Free radical mediated cell toxicity by redox cycling chemicals. Br. J. Cancer Suppl. 1987, 8, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samoilova, R.I.; Crofts, A.R.; Dikanov, S.A. Reaction of superoxide radical with quinone molecules. J. Phys. Chem. 2011, 115, 11589–11593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrax, J.; Beck, R.; Dejeans, N.; Glorieux, C.; Sid, B.; Pedrosa, R.C.; Benites, J.; Vásquez, D.; Valderrama, J.A.; Calderon, P.B. Redox-active quinones and ascorbate: An innovative cancer therapy that exploits the vulnerability of cancer cells to oxidative stress. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, B.; Gregory, J.L. Role of one-electron and two-electron reduction products of adriamycin and daunomycin in deoxyribonucleic acid binding. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1981, 30, 2626–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goormaghtigh, E.; Pollakis, G.; Ruysschaert, J.M. Mitochondrial membrane modifications induced by adriamycin-mediated electron transport. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1983, 32, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachur, N.R.; Gordon, S.L.; Gee, M.V.; Kohn, H. NADPH cytochrome P-450 reductase activation of quinone anticancer agents to free radicals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 954–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, F.; Crofts, A.R.; Kramer, D.M. Multiple Q-cycle bypass reactions at the Qo site of the cytochrome bc1 complex. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 7866–7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inbaraj, J.J.; Gandhisan, R.; Murugesan, R. ytotoxicity and superoxide anion generation by some naturally occurring quinones. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchekroun, M.N.; Myers, C.E.; Sinha, B.K. Free radical formation by ansamycin benzoquinone in human breast tumor cells: Implications for cytotoxicity and resistance. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 17, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Feng, L.; Oldham, E.A.; Keating, M.J.; Plunkett, W. Superoxide dismutase as a target for the selective killing of cancer cells. Nature (London) 2000, 407, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, A.; Fattorusso, E.; Luciano, P.; Macho, A.; Menna, M.; Muñoz, E. Antitumor effects of two novel naturally occurring terpene quinones isolated from the Mediterranean ascidian Aplidium conicum. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3410–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, A.; Fattorusso, E.; Luciano, P.; Menna, M.; Esposito, G.; Iuvone, T.; Pala, D. Conicaquinones A and B, two novel cytotoxic terpene quinones from the Mediterranean ascidian Aplidium conicum. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 5, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, M.; Aiello, A.; D’Aniello, F.; Imperatore, C.; Luciano, P.; Vitalone, R.; Irace, C.; Santamaria, R. Conithiaquinones A and B, tetracyclic cytotoxic meroterpenes from the Mediterranean ascidian Aplidium conicum. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 16, 3241–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperatore, C.; Persico, M.; Aiello, A.; Luciano, P.; Guiso, M.; Sanasi, M.F.; Taramelli, D.; Parapini, S.; Cebrián-Torrejón, G.; Doménech-Carbó, A.; et al. Marine inspired antiplasmodial thiazinoquinones: Synthesis, computational studies and electrochemical assays. RSC Adv. 2015, 7, 70689–70702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, T.; Tryk, D.A.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujishima, A. Electrochemical behavior of highly conductive boron-doped diamond electrodes for oxygen reduction in alkaline solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marselli, B.; Garcia-Gomez, J.; Michaud, P.A.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Comninellis, C. Electrogeneration of hydroxyl radicals on boron-doped diamond electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, D79–D83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapałka, A.; Foti, G.; Comninellis, C. The importance of electrode material in environmental electrochemistry: Formation and reactivity of free hydroxyl radicals on boron-doped diamond electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 2018–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enache, T.A.; Chiorcea-Paquim, A.-M.; Fatibello-Filho, O.; Oliveira-Brett, A.M. Hydroxyl radicals electrochemically generated in situ on a boron doped diamond electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 1342–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.Q. Electrochemistry of quinones. In The Chemistry of Quinonoid Compounds; Patai, S., Rappoport, Z., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 2, pp. 719–757. ISBN 9780471669296. [Google Scholar]
- Lovric, M.; Scholz, F. A model for the propagation of a redox reaction through microcrystals. J. Solid State Electrochem. 1997, 1, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovric, M.; Hermes, M.; Scholz, F. The effect of electrolyte concentration in the solution on the voltammetric response of insertion electrodes. J. Solid State Electrochem. 1998, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, K.B. Voltammetry at a three-phase junction. J. Solid State Electrochem. 1998, 2, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovric, M.; Scholz, F. A model for the coupled transport of ions and electrons in redox conductive microcrystals. J. Solid State Electrochem. 1999, 3, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, U.; Oldham, K.B.; Myland, J.C.; Mahon, P.J.; Scholz, F. Modelling of solid state voltammetry of immobilized microcrystals assuming an initiation of the electrochemical reaction at a three-phase junction. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2000, 4, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, T.; Sakai, T.; Ogura, K.; Yoshino, T. Oxygen reduction at electrochemically treated glassy carbon electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1986, 58, 1953–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, W.; McCreery, R.L. Isotope and surface preparation effects on alkaline dioxygen reduction at carbon electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1996, 410, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratsgar, S.; Deng, H.; Cortés-Salazar, F.; Scanlon, M.D.; Pribil, M.; Amstutz, V.; Karyakin, A.A.; Shahrokhian, S.; Girault, H.H. Oxygen reduction at soft interfaces catalyzed by in situ-generated reduced graphene oxide. ChemElectroChem 2014, 1, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinnouchi, R.; Anderson, A.B. Aqueous and surface redox potentials from self-consistently determined Gibbs energies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 8747–8750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.B.; Jinnouchi, R.; Uddin, J. Effective reversible potentials and onset potentials for O2 electroreduction on transition metal electrodes: Theoretical analysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofré, P.; Sawyer, D.T. Electrochemical reduction of dioxygen to perhydroxyl (HO2·) in aprotic solvents that contain Broensted acids. Anal. Chem. 1986, 58, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.; Hoey, B.M. The apparent inhibition of superoxide dismutase activity by quinones. J. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1986, 2, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossi, M.; Rega, N.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V. Energies, structures, and electronic properties of molecules in solution with the C-PCM solvation model. J. Comp. Chem. 2003, 24, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, R.G.; Szentplay, L.V.; Liu, S. Electrophilicity index. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 1922–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACD/Percepta; Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2015; Available online: http://www.acdlabs.com (accessed on 27 September 2017).
- Maple, J.R.; Hwang, M.J.; Stockfisch, T.P.; Dinur, U.; Waldman, M.; Ewig, C.S.; Hagler, A.T. Derivation of class II force fields. I. Methodology and quantum force field for the alkyl functional group and alkane molecules. J. Comput. Chem. 1994, 15, 162–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, R. Unconstrained optimization. In Practical Methods of Optimization, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1980; Volume 1, pp. 1–128. ISBN 978-0471277118. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, J.J. Optimization of parameters for semiempirical methods VI: More modifications to the NDDO approximations and re-optimization of parameters. J. Mol. Model. 2013, 19, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MOPAC2012; Stewart Computational Chemistry: Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 2012; Available online: http://OpenMOPAC.net (accessed on 27 September 2017).
- Baker, J. An algorithm for the location of transition states. J. Comput. Chem. 1986, 7, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, A.; Sullivan, E.; Mariam, Y.H. A semiempirical computational study of electron transfer reactivity of one- vs. two-ring model systems for anthracycline pharmacophores. I. A rationale for mode of action. J. Comput. Chem. 1996, 17, 204–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Compound | (Q → QH2) | Step 1 | Step 2i | Step 2ii | Step 3i | Step 3ii | Step 4i | Step 4ii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −752.9 | −98.0 | −277.2 | −267.3 | −92.8 | −99.3 | −284.9 | −288.3 |
| 2 | −742.2 | −90.6 | −278.1 | −270.8 | −85.2 | −95.9 | −288.3 | −284.9 |
| 3 | −750.6 | −96.6 | −275.2 | −268.8 | −90.0 | −100.4 | −288.7 | −284.7 |
| 4 | −749.6 | −93.1 | −278.5 | −271.4 | −88.2 | −95.4 | −289.8 | −289.7 |
| Compound | Q | Q•− | QH•i | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELUMO | Vertical EA | ω | ESOMO | Vertical IP | ESOMO | Vertical IP | Vertical EA | |
| 1 | −88.234 | 90.73 | 141.84 | −104.637 | 104.03 | −125.038 | 123.56 | 87.35 |
| 2 | −80.848 | 84.28 | 104.57 | −97.716 | 97.18 | −117.773 | 117.22 | 80.21 |
| 3 | −86.923 | 89.55 | 113.48 | −104.192 | 104.62 | −125.678 | 126.18 | 83.93 |
| 4 | −82.888 | 86.46 | 106.72 | −100.220 | 101.05 | −123.576 | 124.19 | 81.24 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imperatore, C.; Cimino, P.; Cebrián-Torrejón, G.; Persico, M.; Aiello, A.; Senese, M.; Fattorusso, C.; Menna, M.; Doménech-Carbó, A. Insight into the Mechanism of Action of Marine Cytotoxic Thiazinoquinones. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15110335
Imperatore C, Cimino P, Cebrián-Torrejón G, Persico M, Aiello A, Senese M, Fattorusso C, Menna M, Doménech-Carbó A. Insight into the Mechanism of Action of Marine Cytotoxic Thiazinoquinones. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(11):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15110335
Chicago/Turabian StyleImperatore, Concetta, Paola Cimino, Gerardo Cebrián-Torrejón, Marco Persico, Anna Aiello, Maria Senese, Caterina Fattorusso, Marialuisa Menna, and Antonio Doménech-Carbó. 2017. "Insight into the Mechanism of Action of Marine Cytotoxic Thiazinoquinones" Marine Drugs 15, no. 11: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15110335
APA StyleImperatore, C., Cimino, P., Cebrián-Torrejón, G., Persico, M., Aiello, A., Senese, M., Fattorusso, C., Menna, M., & Doménech-Carbó, A. (2017). Insight into the Mechanism of Action of Marine Cytotoxic Thiazinoquinones. Marine Drugs, 15(11), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15110335