Anti-Pigmentary Effect of (-)-4-Hydroxysattabacin from the Marine-Derived Bacterium Bacillus sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of (-)-4-Hydroxysattabacin and (-)-Sattabacin
2.2. Effect of (-)-4-Hydroxysattabacin on the Melanin Synthesis and Cell Viability of B16F10 Cell
2.3. Mechanism Underlying the Anti-Melanogenic Activities of (-)-4OH-ST
2.4. Effect of (-)-4-Hydroxysattabacin on the Melanin Synthesis and Cell Viability of Human Melanoma Cells
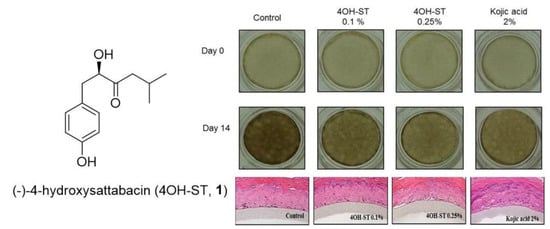
2.5. Effects of (-)-4OH-ST Using an Artificial Human Epidermis, KeraskinTM and MelanoDermTM
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Strain and Cultivation
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Cell Culture
3.5. Melanin Assay and Cell Viability Assay (WST-1 or MTT)
3.6. Mushroom Tyrosinase Inhibition Assay
3.7. RNA Isolation
3.8. Real-Time PCR
3.9. Western Blot Analysis
3.10. Hypopigmenting Effect of 4OH-ST (1) Using the Pigmented Human Epidermal 3D Skin Model, MelanodermTM
3.11. Statistics Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costin, G.E.; Hearing, V.J. Human skin pigmentation: Melanocytes modulate skin color in response to stress. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 976–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K. Quantitative analysis of eumelanin and pheomelanin in humans, mice, and other animals: A comparative review. Pigment Cell Res. 2003, 16, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briganti, S.; Camera, E.; Picardo, M. Chemical and Instrumenatal Approaches to Treat Hyperpigmentation. Pigment Cell Res. 2003, 16, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Park, H.; Jeon, S.W.; Bang, J.; Chung, K.Y.; Choi, D.W.; Kim, E.; Lim, K.M. Novel anti-melanogenic hexapeptoids, PAL-10 and PAL-12. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2015, 307, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Gao, J. The use of botanical extracts as topical skin-lightening agents for the improvement of skin pigmentation disorders. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2008, 13, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessinioti, C.; Stratigos, A.J.; Rigopoulos, D.; Katsambas, A.D. A review of genetic disorders of hypopigmentation: Lessons learned from the biology of melanocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 2009, 18, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Jung, S.H. Downregulation of melanogenesis: Drug discovery and therapeutic options. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Namasivayam, V. Skin whitening agents: Medicinal chemistry perspective of tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 403–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillbro, J.M.; Olsson, M.J. The melanogenesis and mechanisms of skin-lightening agents-existing and new approaches. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2011, 33, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedley, S.J.; Gawkrodger, D.J.; Weetman, A.P.; Macneil, S. alpha-MSH and melanogenesis in normal human adult melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 1998, 11, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegrist, W.; Solca, F.; Stutz, S.; Giuffre, L.; Carrel, S.; Girard, J.; Eberle, A.N. Characterization of receptors for a-Melanocyte-stimulating Hormone on Human Melanoma Cells. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 6352–6358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, E.; Funasaka, Y.; Kondoh, H.; Chakraborty, A.K.; Mishima, Y.; Ichihashi, M. Expression of tyrosinase, TRP-1 and TRP-2 in ultraviolet-irradiated human melanomas and melanocytes: TRP-2 protects melanoma cells from ultraviolet B induced apoptosis. Melanoma Res. 1999, 9, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, Y.; Tanigawa, T.; Abe, H.; Fujiwara, Y. Melanogenesis inhibition by an oolong tea extract in b16 mouse melanoma cells and UV-induced skin pigmentation in brownish guinea pigs. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, T.J.; Lei, T.C.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Batzer, J.; Wolber, R.; Hearing, V.J. Reconstituted 3-dimensional human skin of various ethnic origins as an in vitro model for studies of pigmentation. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 318, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampis, G.; Deidda, D.; Maullu, C.; Madeddu, M.A.; Pompei, R. Sattabacins and Sattazolins: New Biologically Active Compounds with Antiviral Properties Extracted from a Bacillus sp. J. Antibiot. 1995, 48, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancha, S.R.; Regnery, C.M.; Dahlke, J.R.; Miller, K.A.; Blake, D.J. Antiviral activity of (+)-sattabacin against varicella zoster. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuemei, L.; Yu, T.-K.; Kwak, J.; Son, B.-Y.; Seo, Y.; Zee, O.-P.; Ahn, J.-W. Soraphinol C, a New Free -Radical Scavenger from Sorangium cellulosum. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 520–522. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J-S.; Kagaya, N.; Hashimoto, J.; Izumikawa, M.; Yabe, S.; Shin-ya, K.; Nishiyama, M.; Kuzuyama, T. Identification and Biosynthesis of New Acyloins from Bacterium Thermosporothrix hazakensis SK20-1T. Chembiochem 2014, 15, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, K.S.; Park, K.J.; Park, S.M.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, C.G. Down-regulation of tyrosinase, TRP-1, TRP-2 and MITF expressions by citrus press-cakes in murine B16 F10 melanoma. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Jang, W.-H.; Jung, H.-S.; Heo, Y.; Park, Y.-H.; Bae, S.; Lim, K.-M.; Seo, S. Keraskin-VM: A novel reconstructed human epidermis model for skin irritation tests. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.; Hughes, J.; Hong, M.; Jia, Q.; Orndorff, S. Modulation of melanogenesis by aloesin: A competitive inhibitor of tyrosinase. Pigment Cell Res. 2002, 15, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Shin, S.; Lee, J.-A.; Park, D.; Lee, J.; Jung, E. Inhibition of melanogenesis by Gaillardia aristata flower extract. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Kawai, K.; Kawai, K. Contact allergy to kojic acid in skin care products. Contact Dermat. 1995, 32, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gavin, J.; Gonzalez-Vilas, D.; Fernandez-Redondo, V.; Toribio, J. Pigmented contact dermatitis due to kojic acid. A paradoxical side effect of a skin lightener. Contact Dermat. 2010, 62, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boissy, R.E. Melanosome transfer to and translocation in the keratinocyte. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 12, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.; Leutou, A.S.; Jeong, H.; Kim, D.; Seong, C.N.; Nam, S.-J.; Lim, K.-M. Anti-Pigmentary Effect of (-)-4-Hydroxysattabacin from the Marine-Derived Bacterium Bacillus sp. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15050138
Kim K, Leutou AS, Jeong H, Kim D, Seong CN, Nam S-J, Lim K-M. Anti-Pigmentary Effect of (-)-4-Hydroxysattabacin from the Marine-Derived Bacterium Bacillus sp. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(5):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15050138
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyuri, Alain S. Leutou, Haein Jeong, Dayoung Kim, Chi Nam Seong, Sang-Jip Nam, and Kyung-Min Lim. 2017. "Anti-Pigmentary Effect of (-)-4-Hydroxysattabacin from the Marine-Derived Bacterium Bacillus sp." Marine Drugs 15, no. 5: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15050138
APA StyleKim, K., Leutou, A. S., Jeong, H., Kim, D., Seong, C. N., Nam, S. -J., & Lim, K. -M. (2017). Anti-Pigmentary Effect of (-)-4-Hydroxysattabacin from the Marine-Derived Bacterium Bacillus sp. Marine Drugs, 15(5), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15050138