Bioactive Diphenyl Ethers and Isocoumarin Derivatives from a Gorgonian-Derived Fungus Phoma sp. (TA07-1)
Abstract
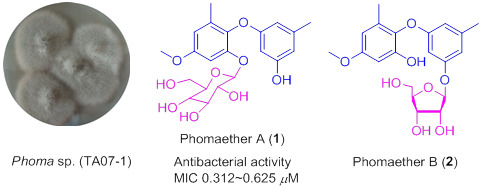
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Materials
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Methanolysis of Compound 1
3.5. Methanolysis of Compound 2
3.6. Biological Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, S.L.; Wang, M.; Feng, Q.; Lin, Y.Y.; Zhao, H.E. A study on biological activity of marine fungi from different habitats in coastal regions. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1966–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, J.I. Search for new bioactive marine natural products and application to drug development. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, R.K.; Xu, Z.R. Biomedical compounds from marine organisms. Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.M.; Xu, R.F.; Gu, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L. Biological and chemical diversity of coral-derived microorganisms. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 3707–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, I.E.; Gross, H.; Pontius, A.; Kehraus, S.; Krick, A.; Kelter, G.; Maier, A.; Fiebig, H.H.; König, G.M. Epoxyphomalin A and B, prenylated polyketides with potent cytotoxicity from the marine-derived fungus Phoma sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5014–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.P.; Dong, T.H.; Zhu, W.M. Thiodiketopiperazines from the marine-derived fungus Phoma sp. OUCMDZ-1847. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loesgen, S.; Bruhn, T.; Meindl, K.; Dix, I.; Schulz, B.; Zeeck, A.; Bringmann, G. (+)-Flavipucine, the missing member of the pyridione epoxide family of fungal antibiotics. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 2011, 5156–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.H.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Gloer, J.B.; Wicklow, D.T. Phomalevones A–C: Dimeric and pseudodimeric polyketides from a fungicolous Hawaiian isolate of Phoma sp. (Cucurbitariaceae). J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Shao, C.L.; Meng, H.; She, Z.G.; Wang, C.Y. Anti-respiratory syncytial virus prenylated dihydroquinolone derivatives from the gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. XS-20090B15. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2720–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.L.; Shao, C.L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, K.L.; Guan, F.F.; Shi, T.; Wang, C.Y. Azaphilone and diphenyl ether derivatives from a gorgonian-derived strain of the fungus Penicillium pinophilum. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2310–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Yang, Q.; Shao, C.L.; Kong, C.J.; Zheng, J.J.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, C.Y. Bioactive 7-oxabicyclic [6.3.0] lactam and 12-membered macrolides from a gorgonian-derived Cladosporium sp. fungus. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4171–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.L.; Xu, R.F.; Wei, M.Y.; She, Z.G.; Wang, C.Y. Structure and absolute configuration of fumiquinazoline L, an alkaloid from a gorgonian-derived Scopulariopsis sp. fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.P.; Cao, F.; Shao, C.L.; Chen, M.; Liu, H.J.; Zheng, C.J.; Wang, C.Y. Subergorgiaols A–L, 9, 10-secosteroids from the South China Sea gorgonian Subergorgia rubra. Steroids 2015, 94, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, H.A.; Gloer, J.B. Interference competition among natural fungal competitors: An antifungal metabolite from the coprophilous fungus Preussia fleischhakii. J. Nat. Prod. 1988, 51, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.O.; Breinholt, J. Dichlorodiaportin, diaportinol, and diaportinic acid: Three novel isocoumarins from Penicillium nalgiovense. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1182–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, A.H.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Wray, V.; Müller, W.E.G.; Kozytska, S.; Hentschel, U.; Proksch, P.; Ebel, R. Bioactive metabolites from the endophytic fungus Ampelomyces sp. isolated from the medicinal plant Urospermum picroides. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.; Shizuri, Y.; Yamamura, S.; Kawai, K.; Furukawa, H. Three new phenolic metalolites from Penicillium species. Heterocycles 1991, 32, 297–305. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, F.; Qi, J.; Song, X.C.; Hu, Z.F.; Zhu, D.N.; Yu, B.Y. Homoisoflavonoids from the fibrous roots of Polygonatum odoratum with glucose uptake-stimulatory activity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornsakulkarn, J.; Thongpanchang, C.; Lapanun, S.; Srichomthong, K. Isocoumarin glucosides from the scale insect fungus Torrubiella tenuis BCC 12732. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1341–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Zhu, T.J.; Liu, H.B.; Fang, Y.C.; Zhu, W.M.; Gu, Q.Q. Cytotoxic polyketides from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus glaucus. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, B.S.; Cho, Y.; Lee, I.K.; Cho, S.M.; Lee, T.H.; Yoo, I.D. Sterins A and B, new antioxidative compounds from Stereum hirsutum. J. Antibiot. 2002, 55, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serianni, A.S.; Barker, R. [13C]-Enriched tetroses and tetrofuranosides: An evaluation of the relationship between NMR parameters and furanosyl ring conformation. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 3292–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.L.; Ma, X.H.; Xie, Y.Y.; Cai, S.X.; Zhu, T.J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Li, D.H. Aromatic polyketides from a sponge-derived fungus Metarhizium anisopliae mxh-99 and their antitubercular activities. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appendino, G.; Gibbons, S.; Giana, A.; Pagani, A.; Grassi, G.; Stavri, M.; Smith, E.; Rahman, M.M. Antibacterial cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa: A structure-activity study. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirven, L.A.; Thornsberry, C. Minimum bactericidal concentration of sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim for Haemophilus influenzae: Correlation with prophylaxis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1978, 14, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis, P.N.; Wright, C.W.; Anderson, M.M.; Gupta, M.P.; Phillipson, J.D. A microwell cytotoxicity assay using Artemia salina (brine shrimp). Planta Med. 1993, 59, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 ) and HMBC (
) and HMBC (  ) correlations for compounds 1–3.
) correlations for compounds 1–3.
| Position | 1, δC Type | 1, δH Mult. (J in Hz) | 2, δC Type | 2, δH Mult. (J in Hz) | 3, δC Type | 3, δH Mult. (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 135.2 C | 135.6 C | 134.7 C | |||
| 2 | 150.9 C | 151.8 C | 147.5 C | |||
| 3 | 100.82 CH | 6.69, d (2.9) | 101.4 CH | 6.35, d (2.9) | 100.0 CH | 6.49, s |
| 4 | 156.3 C | 158.7 C | 151.7 C | |||
| 5 | 108.5 CH | 6.51, d (2.8) | 107.8 CH | 6.31, d (2.9) | 141.3 C | |
| 6 | 132.4 C | 134.0 C | 127.2 C | |||
| 1′ | 159.3 C | 160.7 C | 160.8 C | |||
| 2′ | 99.2 CH | 5.93, brs | 102.6 CH | 6.39, brs | 100.3 CH | 6.02, brs |
| 3′ | 158.2 C | 159.8 C | 159.4 C | |||
| 4′ | 109.4 CH | 6.18, brs | 111.7 CH | 6.60, brs | 110.4 CH | 6.24, brs |
| 5′ | 139.5 C | 141.3 C | 141.4 C | |||
| 6′ | 106.6 CH | 6.08, brs | 110.4 CH | 6.29, brs | 108.1 CH | 6.15, brs |
| 1″ | 100.76 CH | 4.82, d (7.8) | 102.3 CH | 5.55, d (4.5) | ||
| 2″ | 73.2 CH | 3.06, m | 73.4 CH | 4.13, dd (6.4, 4.5) | ||
| 3″ | 76.8 CH | 3.20, dd (8.9, 8.8) | 71.2 CH | 4.06, dd (6.5, 3.2) | ||
| 4″ | 69.8 CH | 3.08, m | 87.5 CH | 4.10, dt (3.5, 3.5) | ||
| 5″ | 77.3 CH | 3.30, ddd (8.4, 6.4, 2.0) | 63.2 CH2 | 3.69, dd (12.1, 3.4) | ||
| 3.63, dd (12.2, 3.8) | ||||||
| 6″ | 60.8 CH2 | 3.68, d (11.0) | ||||
| 3.40, d (11.0) | ||||||
| 4-OMe | 55.2 OCH3 | 3.73, s | 55.8 OCH3 | 3.74, s | 56.4 OCH3 | 3.81, s |
| 5-OMe | 61.0 OCH3 | 3.70, s | ||||
| 6-Me | 16.2 CH3 | 2.02, s | 16.5 CH3 | 2.03, s | 9.8 CH3 | 1.98, s |
| 3′-OH | 9.27, brs | |||||
| 5′-Me | 21.2 CH3 | 2.13, s | 21.8 CH3 | 2.24, s | 21.6 CH3 | 2.18, s |
| 2″-OH | 5.04, brs | |||||
| 3″-OH | 5.04, brs | |||||
| 4″-OH | 4.68, d (5.2) | |||||
| 6″-OH | 4.60, brs |
| Compounds | MIC/MBC (μM) | Test Ranges | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. albus | S. aureus | E. coli | V. parahaemolyticus | V. anguillarum | ||
| 1 | 0.312/0.625 | 0.625/0.625 | 0.625/1.25 | 0.625/2.50 | –/– | 0.039–20.0 |
| 3 | 0.625/1.25 | 0.312/0.625 | 1.25/5.00 | –/– | 10.0/– | 0.039–20.0 |
| 4 | 0.312/0.312 | 0.156/0.312 | 0.156/0.156 | 0.312/0.312 | 2.50/5.00 | 0.039–20.0 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.312/0.312 | 0.156/0.156 | 0.156/0.156 | 0.156/0.156 | 0.156/0.156 | 0.010–10.0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, T.; Qi, J.; Shao, C.-L.; Zhao, D.-L.; Hou, X.-M.; Wang, C.-Y. Bioactive Diphenyl Ethers and Isocoumarin Derivatives from a Gorgonian-Derived Fungus Phoma sp. (TA07-1). Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060146
Shi T, Qi J, Shao C-L, Zhao D-L, Hou X-M, Wang C-Y. Bioactive Diphenyl Ethers and Isocoumarin Derivatives from a Gorgonian-Derived Fungus Phoma sp. (TA07-1). Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(6):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060146
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Ting, Jun Qi, Chang-Lun Shao, Dong-Lin Zhao, Xue-Mei Hou, and Chang-Yun Wang. 2017. "Bioactive Diphenyl Ethers and Isocoumarin Derivatives from a Gorgonian-Derived Fungus Phoma sp. (TA07-1)" Marine Drugs 15, no. 6: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060146
APA StyleShi, T., Qi, J., Shao, C. -L., Zhao, D. -L., Hou, X. -M., & Wang, C. -Y. (2017). Bioactive Diphenyl Ethers and Isocoumarin Derivatives from a Gorgonian-Derived Fungus Phoma sp. (TA07-1). Marine Drugs, 15(6), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060146