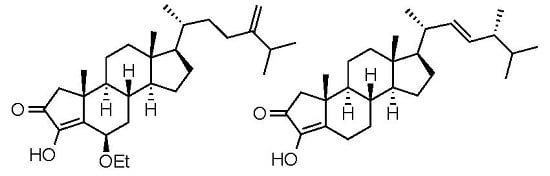
Crellasterones A and B: A-Norsterol Derivatives from the New Caledonian Sponge Crella incrustans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goad, J.; Akihisa, T. Analysis of Sterols; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh, Y.M.; Djerassi, C. Bioconversion of lanosterol into holotoxingonin, a triterpenoid from the sea cucumber Stichopus californicus. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1976, 24, 1057–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokke, W.C.; Tarchini, C.; Stierle, D.B.; Djerassi, C. Isolation, structure elucidation and partial synthesis of xestosterol, biosynthetically significant sterol from the sponge Xestospongia muta. J. Org. Chem. 1979, 44, 3385–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, R.G.; Baker, B.J. Marine sterols. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1991, 8, 465–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergquist, P.R.; Karuso, P.; Cambie, R.C.; Smith, D.J. Sterol composition and classification of the Porifera. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1991, 19, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Fusetani, N. Sokodosides, Steroid Glycosides with an Isopropyl Side Chain, from the Marine Sponge Erylus placenta. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 4884–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, V.; Stoilov, I.L.; Djerassi, C.; Karuso, P.; Poiner, A.; Scheuer, P.J. Biosynthetic studies of marine lipids. 20. Sequence of double-bond introduction in the sponge sterol 24.beta.-methylcholesta-5,7,22,25-tetraen-3.beta.-ol. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Auria, M.V.; Giannini, C.; Zampella, A.; Minale, L.; Debitus, C.; Roussakis, C. Crellastatin A: A Cytotoxic Bis-Steroid Sulfate from the Vanuatu Marine Sponge Crella sp. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 7382–7388. [Google Scholar]
- Zampella, A.; Giannini, C.; Debitus, C.; Roussakis, C.; D’Auria, M.V. Isolation and Structural Elucidation of Crellastatins B–H: Cytotoxic Bis(steroid) Derivatives from the Vanuatu Marine Sponge Crella sp. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 1999, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, C.; Zampella, A.; Debitus, C.; Menou, J.-L.; Roussakis, C.; D’Auria, M.V. Isolation and structural elucidation of the crellastatins I-M: Cytotoxic bis-steroid derivatives from the vanuatu marine sponge Crella sp. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 13749–13756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, S.; Imae, Y.; Takada, K.; Kikuchi, J.; Nakao, Y.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Shishicrellastatins, inhibitors of cathepsin B, from the marine sponge Crella (Yvesia) spinulata. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6594–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.S.; Mutka, T.; Vesley, B.; Amsler, M.O.; McClintock, J.B.; Amsler, C.D.; Perman, J.A.; Singh, M.P.; Maiese, W.M.; Zaworotko, M.J.; et al. Norselic Acids A–E, Highly Oxidized Anti-infective Steroids that Deter Mesograzer Predation, from the Antarctic Sponge Crella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1842–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wai Lam, L.; Cooke, P.; Pattenden, G.; Bandaranayake, W.; Wickramasinghe, W. Structure and total synthesis of benzylthiocrellidone, a novel dimedone-based vinyl sulfide from the sponge Crella spinulata. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1999, 8, 847–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Deng, Z.; Guan, H.; Ofwegen, L.V.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Steroids from the soft coral Dendronephthya sp. Steroids 2005, 70, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolit, A.; Walleser, P.M.; Yap, G.P.A.; Tius, M.A. Catalytic Enantioselective Nazarov Cyclization: Construction of Vicinal All-Carbon-Atom Quaternary Stereocenters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6180–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlrichs, R.; Bär, M.; Häser, M.; Horn, H.; Kölmel, C. Electronic structure calculations on workstation computers: The program system Turbomole. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1989, 162, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.-H.; Chao, C.-H.; Wang, G.-H.; Hung, K.-C.; Duh, C.-Y.; Chiang, M.Y.; Wu, Y.-C.; Wu, C.-C. The first A-nor-hippuristanol and two novel 4,5-secosuberosanoids from the Gorgonian Isis hippuris. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 6413–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.L.C.; McInnes, A.G.; Shimizu, S.; Smith, D.G.; Walter, J.A.; Idler, D.; Khalil, W. Identification of C-24 alkyl epimers of marine sterols by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Can. J. Chem. 1978, 56, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, G.; Serrar, M.; Hadid, Z. Steroid Derivatives and Use Thereof as Medicaments. U.S. Patent 7,186,756 B2, 6 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Deng, Z.W.; Xu, M.; Li, Q.; Lin, W.H. New A-nor steroids and their antifouling activity from the Chinese marine sponge Acanthella cavernosa. Steroids 2008, 73, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuno, M.N.; Pawlik, J.R.; Molinski, T.F. Phorbasterones A-D, Cytotoxic Nor-Ring A Steroids from the Sponge Phorbas amaranthus. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 731–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tischler, M.; Ayer, S.W.; Andersen, R.J.; Mitchell, J.F.; Clardy, J. Anthosterones A and B, ring A contracted steroids from the sponge Anthoracuata graceae. Can. J. Chem. 1988, 66, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, R.W.M.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Rützler, K.; de Voogd, N.J.; Alvarez de Glasby, B.; Hajdu, E.; Pisera, A.B.; Manconi, R.; Schoenberg, C.; et al. Catalogue of Life: 2016 Annual Checklist; Species 2000; Naturalis: Leiden, The Netherlands; Available online: http://www.catalogueoflife.org/annual-checklist/2016 (accessed on 1 April 2017).
- Łotowski, Z.; Morzycki, J.W.; Niewczas, I.S.; Zdanowicz, M. Synthesis of cis and trans Isomers of D-Ring Linked Bis-Steroid Pyrazines from 16α-Bromo-17-oxosteroids. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 2002, 67, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piggott, A.M.; Karuso, P. 9-Hydroxyfurodysinin-O-ethyl lactone: A new sesquiterpene isolated from the tropical marine sponge Dysidea arenaria. Molecules 2005, 10, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragini, K.; Fromont, J.; Piggott, A.M.; Karuso, P. Enantiodivergence in the Biosynthesis of Bromotyrosine Alkaloids from Sponges? J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djerassi, C.; Riniker, R.; Riniker, B. Optical Rotatory Dispersion Studies. VII.1 Application to Problems of Absolute Configurations2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1956, 78, 6362–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Massarani, S.M.; El-Gamal, A.A.; Al-Said, M.S.; Abdel-Kader, M.S.; Ashour, A.E.; Kumar, A.; Abdel-Mageed, W.M.; Al-Rehaily, A.J.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Fun, H.-K. Studies on the Red Sea Sponge Haliclona sp. for its Chemical and Cytotoxic Properties. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Position a | Crellasterone A (1) | Crellasterone B (2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 48.4, CH2 | α 2.23, d (18.8) | 47.3, CH2 | α 2.21, d (18.8) |
| β 2.16, d (18.8) | β 2.15, d (18.8) | |||
| 2 | 202.6, C | - | 201.6, C | - |
| 3 | 147.1, C | - | 144.1, C | - |
| 5 | 149.5, C | - | 154.8, C | - |
| 6 | 69.4, CH | 4.59, m | 22.4, CH2 | α 2.81, m |
| β 2.12, m | ||||
| 7 | 38.0, CH2 | α 2.03, m | 31.7, CH2 | α 1.87 m |
| β 1.14, m | β 0.95, m | |||
| 8 | 31.3, CH | 1.84, m | 35.9, CH | 1.48, m |
| 9 | 53.7, CH | 0.85, m | 53.9, CH | 0.86, m |
| 10 | 40.6, C | 40.6, C | ||
| 11 | 23.6, CH2 | α 1.16, m | 23.8, CH2 | α 1.37, m |
| β 1.56, m | β 1.52, m | |||
| 12 | 39.6, CH2 | α 1.99, m | 39.5, CH2 | α 1.97, m |
| β 1.14, m | β 1.16, m | |||
| 13 | 43.1, C | 42.9, C | ||
| 14 | 55.9, CH | 1.11, m | 55.9, CH | 1.12, m |
| 15 | 24.1, CH2 | α 1.34, m | 24.3, CH2 | α 1.55, m |
| β 1.58, m | β 1.07, m | |||
| 16 | 28.2, CH2 | α 1.83, m | 28.8, CH2 | α 1.67, m |
| β 1.26, m | β 1.20, m | |||
| 17 | 55.9, CH | 0.96, m | 55.8, CH | 0.99, m |
| 18 | 12.2, CH3 | 0.72, s | 12.3, CH3 | 0.71, s |
| 19 | 21.7, CH3 | 1.25, s | 20.3, CH3 | 1.13, s |
| 20 | 35.7, CH | 1.39, m | 40.3, CH | 1.99, m |
| 21 | 18.7, CH3 | 0.92, d (6.6) | 21.0, CH3 | 0.97, d (6.6) |
| 22 | 34.6, CH2 | α 1.12, m | 135.9, CH | 5.13, dd (15.2, 7.5) |
| β 1.51, m | ||||
| 23 | 31.0, CH2 | α 2.07, m | 132.0, CH | 5.14, dd (15.2, 7.8) |
| β 1.86, m | ||||
| 24 | 156.8, C | - | 43.1, CH | 1.81, m |
| 25 | 33.8, CH | 2.20, m | 33.2, CH | 1.43, m |
| 26 | 22.0, CH3 | 1.00, d (3.7) | 19.7, CH3 | 0.80, d (6.8) |
| 27 | 21.9, CH3 | 0.99, d (3.7) | 20.2, CH3 | 0.82, d (6.8) |
| 28 | 106.0, CH2 | α 4.69, m | 18.1, CH3 | 0.89, d (6.8) |
| β 4.63, m | ||||
| 29 | 64.1, CH2 | 3.41, q (7.0) | - | - |
| 30 | 15.2, CH3 | 1.16, t (7.0) | - | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ragini, K.; Piggott, A.M.; Karuso, P. Crellasterones A and B: A-Norsterol Derivatives from the New Caledonian Sponge Crella incrustans. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060177
Ragini K, Piggott AM, Karuso P. Crellasterones A and B: A-Norsterol Derivatives from the New Caledonian Sponge Crella incrustans. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(6):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060177
Chicago/Turabian StyleRagini, Kavita, Andrew M. Piggott, and Peter Karuso. 2017. "Crellasterones A and B: A-Norsterol Derivatives from the New Caledonian Sponge Crella incrustans" Marine Drugs 15, no. 6: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060177
APA StyleRagini, K., Piggott, A. M., & Karuso, P. (2017). Crellasterones A and B: A-Norsterol Derivatives from the New Caledonian Sponge Crella incrustans. Marine Drugs, 15(6), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060177