Successful Approaches for a Red Seaweed Biorefinery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Red Seaweed
3. Seaweed Biorefinery
4. Biorefinery Strategies
4.1. Agarophytes
4.1.1. Agar Extraction Wastes
Agar-Low Molecular Weight Carbohydrates
Agar-Bioethanol
Agar-Methane
Agar-Biochar
4.1.2. Protein Extraction Wastes
Phycobiliproteins-Ethanol
Proteins-Bio-Oil-Biochar
Lipids-Fertilizers-Agar-Bioethanol
4.2. Carragenophytes
4.2.1. Carrageenan Extraction Wastes
Agricultural Bio-Stimulant and Carrageenan
Carrageenan-Ethanol
4.2.2. Processing of the Whole Seaweed
Biochar and Sugars
Bioactives-Carrageenan
Iodine-Lipids-Carrageenan-Cellulose
Carrageenan, Ethanol, Biofertilizer, and Biogas
Fertilizers and Chemicals
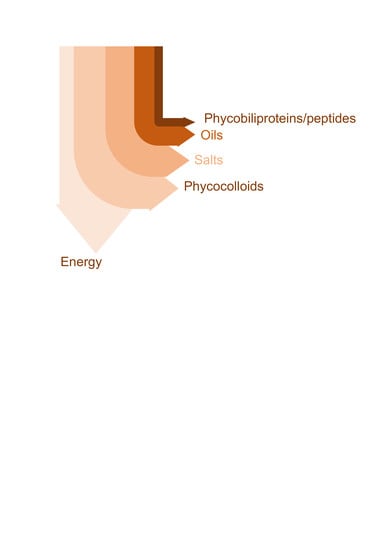
4.3. Porphyran Rich Seaweeds
Phycocolloids-Peptides
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Hal, J.W.; Huijgen, W.J.J.; López-Contreras, A.M. Opportunities and challenges for seaweed in the biobased economy. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerton, F.M.; Yan, N. Fuels, Chemicals and Materials from the Oceans and Aquatic Sources; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bayu, A.; Handayani, T. 3rd international conference on biomass: Accelerating the technical development and commercialization for sustainable bio-based products and energy. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Bogor, Indonesia, 1–2 August 2018; IOP: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; 478p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, R.S.; Reddy, C.R.K.; Jha, B. Characterization of agarophytic seaweeds from the biorefinery context. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghel, R.S.; Trivedi, N.; Gupta, V.; Neori, A.; Reddy, C.R.K.; Lali, A.; Jha, B. Biorefining of marine macroalgal biomass for production of biofuel and commodity chemicals. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbot, Y.N.; Al-Ghaili, H.; Benz, R. A review on the valorization of macroalgal wastes for biomethane production. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurens, L.M.L.; Chen-Glasser, M.; McMillan, J.D. A perspective on renewable bioenergy from photosynthetic algae as feedstock for biofuels and bioproducts. Algal Res. 2017, 24, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.D.; Flórez-Fernández, N.; Domínguez, H. Integral utilization of red seaweed for bioactive production. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balina, K.; Romagnoli, F.; Blumberga, D. Seaweed biorefinery concept for sustainable use of marine resources. Energy Procedia 2018, 128, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.D.; Kraan, S.; Domínguez, H. Seaweed biorefinery. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 335–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhukhan, J.; Gadkari, S.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Ng, K.S.; Shemfe, M.; Torres-García, E.; Lynch, J. Novel macroalgae (seaweed) biorefinery systems for integrated chemical, protein, salt, nutrient and mineral extractions and environmental protection by green synthesis and life cycle sustainability assessments. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 2635–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.A.; Lim, S.R.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.M. Potentials of macroalgae as feedstocks for biorefinery. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.A.; Nam, C.; Woo, S.; Park, J. Response surface method for optimization of phenolic compounds production by lignin pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 120, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesário, M.T.; da Fonseca, M.M.R.; Marques, M.M.; de Almeida, M.C.M.D. Marine algal carbohydrates as carbon sources for the production of biochemicals and biomaterials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 798–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, L.; Meyer, A.S. Potentials and possible safety issues of using biorefinery products in food value chains. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuela, A.; Robledo, D.; Bourgougnon, N.; Bedoux, G.; Hernández-Núñez, E.; Freile-Pelegrín, Y. Environmentally friendly valorization of Solieria filiformis (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) from IMTA using a biorefinery concept. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, S.M.G.; Carvalho, L.J.; Silva, P.S.; Rodrigues, M.R.; Pereira, O.; Pereira, L. Bioproducts from seaweeds: A review with special focus on the Iberian Peninsula. Curr. Org. Chem. 2014, 18, 896–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghetta, M.; Hou, X.; Bastianoni, S.; Bjerre, A.B.; Thomsen, M. Life cycle assessment of macroalgal biorefinery for the production of ethanol, proteins and fertilizers—A step towards a regenerative bioeconomy. J. Clean Prod. 2016, 137, 1158–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins: Biochemistry, bioactivity and production. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, R.E.; Martínez-Augustin, O.; Drago, S.R. Bioactive properties of peptides obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis from protein byproducts of Porphyra columbina. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, D.Y.; Israel, A.; Abelson, A. A novel two-stage seaweed integrated multi-trophic aquaculture. Rev. Aquacult. 2019, 11, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalegerie, F.; Lajili, S.; Bedoux, G.; Taupin, L.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Connan, S. Photo-protective compounds in red macroalgae from Brittany: Considerable diversity in mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs). Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 147, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uribe, E.; Vega-Gálvez, A.; Heredia, V.; Pastén, A.; di Scala, K. An edible red seaweed (Pyropia orbicularis): Influence of vacuum drying on physicochemical composition, bioactive compounds, antioxidant capacity, and pigments. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosemary, T.; Arulkumar, A.; Paramasivam, S.; Mondragon-Portocarrero, A.; Miranda, J.M. Biochemical, micronutrient and physicochemical properties of the dried red seaweeds Gracilaria edulis and Gracilaria corticata. Molecules 2019, 24, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, N.; Valente, S.; Ferraz, S.; Barreto, M.C.; Pinheiro de Carvalho, M.A.A. Nutraceutical potential of Asparagopsis taxiformis (Delile) Trevisan extracts and assessment of a downstream purification strategy. Heliyon 2018, 4, 00957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.T.; Matanjun, P. Chemical composition and physicochemical properties of tropical red seaweed, Gracilaria changii. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øverland, M.; Mydland, L.T.; Skrede, A. Marine macroalgae as sources of protein and bioactive compounds in feed for monogastric animals. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibbetts, S.M.; Milley, J.E.; Lall, S.P. Nutritional quality of some wild and cultivated seaweeds: Nutrient composition, total phenolic content and in vitro digestibility. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 3575–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez–Hernández, G.B.; Castillejo, N.; Carrión–Monteagudo, M.D.M.; Artés, F.; Artés-Hernández, F. Nutritional and bioactive compounds of commercialized algae powders used as food supplements. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2018, 24, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, R.; Pandima Devi, K. Evaluation of physicochemical properties, proximate and nutritional composition of Gracilaria edulis collected from Palk Bay. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francavilla, M.; Franchi, M.; Monteleone, M.; Caroppo, C. The red seaweed Gracilaria gracilis as a multi products source. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guihéneuf, F.; Gietl, A.; Stengel, D.B. Temporal and spatial variability of mycosporine-like amino acids and pigments in three edible red seaweeds from western Ireland. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2573–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Bijo, A.J.; Mantri, V.A.; Reddy, C.R.K.; Jha, B. Fatty acid profiling of tropical marine macroalgae: An analysis from chemotaxonomic and nutritional perspectives. Phytochemistry 2013, 86, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupérez, P. Mineral content of edible marine seaweeds. Food Chem. 2002, 79, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kumari, P.; Trivedi, N.; Shukla, M.K. Minerals, PUFAs and antioxidant properties of some tropical seaweeds from Saurashtra coast of India. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Circuncisão, A.R.; Catarino, M.D.; Cardoso, S.M.; Silva, A.M.S. Minerals from macroalgae origin: Health benefits and risks for consumers. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matanjun, P.; Mohamed, S.; Noordin, M.M.; Muhammad, K. Nutrient content of tropical edible seaweeds, Eucheuma cottonii, Caulerpa lentillifera and Sargassum polycystum. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Sharma, M.; Maiti, P.; Prasad, K.; Meena, R.; Siddhanta, A.K.; Bhatt, P.; Ijardar, S.; Mohandas, V.P.; Ghosh, A.; et al. Fuel intermediates, agricultural nutrients and pure water from Kappaphycus alvarezii seaweed. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17989–17997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, N.; Ferraz, S.; Valente, S.; Barreto, M.C.; Pinheiro de Carvalho, M.A.A. Biochemical composition, nutritional value, and antioxidant properties of seven seaweed species from the Madeira Archipelago. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, Y.Y.; Lee, K.T.; Chen, W.H.; Lin, S.C.; Sheen, H.K.; Tan, I.S. Dilute sulfuric acid hydrolysis of red macroalgae Eucheuma denticulatum with microwave-assisted heating for biochar production and sugar recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Ordóñez, E.; Jiménez Escrig, A.; Rupérez Antón, P. Dietary fibre and physicochemical properties of several edible seaweeds from the northwestern Spanish coast. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2289–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francavilla, M.; Manara, P.; Kamaterou, P.; Monteleone, M.; Zabaniotou, A. Cascade approach of red macroalgae Gracilaria gracilis sustainable valorization by extraction of phycobiliproteins and pyrolysis of residue. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Kumar, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, S.; Sahoo, D.; Kuhad, R.C. Process development for the production of bioethanol from waste algal biomass of Gracilaria verrucosa. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessami, M.J.; Phang, S.M.; Sohrabipoor, J.; Zafar, F.F.; Aslanzadeh, S. The bio-methane potential of whole plant and solid residues of two species of red seaweeds: Gracilaria manilaensis and Gracilariopsis persica. Algal Res. 2019, 42, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Cedeno, F.R.; Solórzano-Chávez, E.G.; de Oliveira, L.E.; Gelli, V.C.; Monti, R.; de Oliveira, S.C.; Masarin, F. Sequential enzymatic and mild-acid hydrolysis of by-product of carrageenan process from Kappaphycus alvarezii. Bioenerg. Res. 2019, 12, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Pacual, N.; Montero, M.P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Antioxidant film development from unrefined extracts of brown seaweeds Laminaria digitata and Ascophyllum nodosum. Food Hydrocolloids 2014, 37, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ordóñez, E.; Jiménez-Escrig, A.; Rupérez, P. Bioactivity of sulfated polysaccharides from the edible red seaweed Mastocarpus stellatus. Bioact. Carbohydr. Dietary Fibre 2014, 3, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, R.E.; Alaiz, M.; Vioque, J.; Drago, S.R. Enzyme proteolysis enhanced extraction of ACE inhibitory and antioxidant compounds (peptides and polyphenols) from Porphyra columbina residual cake. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, R.E.; Salgado, P.R.; Drago, S.R.; González, R.J.; Mauri, A.N. Development of naturally activated edible films with antioxidant properties prepared from red seaweed Porphyra columbina biopolymers. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, E.; Melo, T.; Moreira, A.S.P.; Bernardo, C.; Helguero, L.; Ferreira, I.; Cruz, M.T.; Rego, A.M.; Domingues, P.; Calado, R.; et al. Valorization of lipids from Gracilaria sp. through lipidomics and decoding of antiproliferative and anti-inflammatory activity. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, S.; Stokes, J. Valorisation to biogas of macroalgal waste streams: A circular approach to bioproducts and bioenergy in Ireland. Chem. Pap. 2017, 71, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Ingle, K.N.; Golberg, A. Macroalgae (seaweed) for liquid transportation biofuel production: What is next? Algal Res. 2016, 14, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, R.S.; Trivedi, N.; Reddy, C.R.K. A simple process for recovery of a stream of products from marine macroalgal biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, J.A.; Turner, L.B.; Adams, J.M.M.; Barrento, S.; Dyer, P.W.; Theodorou, M.K. Species variation in the effects of dewatering treatment on macroalgae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2305–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seghetta, M.; Romeo, D.; D´Este, M.; Alvarado-Morales, M.; Angelidaki, I.; Bastianoni, S.; Thomsen, M. Seaweed as innovative feedstock for energy and feed—Evaluating the impacts through a life cycle assessment. J. Cleaner Prod. 2017, 150, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M.M.; Schmidt, A.; Gallagher, J.A. The impact of sample preparation of the macroalgae Laminaria digitata on the production of the biofuels bioethanol and biomethane. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M.M.; Bleathman, G.; Thomas, D.; Gallagher, J.A. The effect of mechanical pre-processing and different drying methodologies on bioethanol production using the brown macroalga Laminaria digitata (Hudson) JV Lamouroux. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 2463–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.M.; Sahoo, B.; Panda, J.; Kumar, A. Microwave-induced synthesis of substituted isoxazoles as potential antimicrobial agents. Curr. Microwave Chem. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khambhaty, Y.; Mody, K.; Gandhi, M.R.; Thampy, S.; Maiti, P.; Brahmbhatt, H.; Eswaran, K.; Ghosh, P.K. Kappaphycus alvarezii as a source of bioethanol. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, J.; Brentner, L.B.; Ramirez, A.; Patel, M.K. Conceptual design of sustainable integrated microalgae biorefineries: Parametric analysis of energy use, greenhouse gas emissions and techno-economics. Algal Res. 2016, 17, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasuga, K.; Yamanashi, T.; Nakayama, S.; Ono, S. Discolored red seaweed Pyropia yezoensis with low commercial value is a novel resource for production of agar polysaccharides. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Yu, I.K.M.; Cho, D.-W.; Wang, D.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zhang, S.; Ding, S.; Wang, L.; Ok, Y.S. Microwave-assisted low-temperature hydrothermal treatment of red seaweed (Gracilaria lemaneiformis) for production of levulinic acid and algae hydrochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Meireles, F.; Abreu, H.T.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J. A comparative analysis of carrageenans produced by underutilized versus industrially utilized macroalgae (Gigartinales Rhodophyta). In Marine Algae Extracts Processes Products and Applications; Kim, S.-K., Chojnacka, K., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 277–294. [Google Scholar]
- Lebbar, S.; Fanuel, M.; Le Gall, S.; Falourd, X.; Ropartz, D.; Bressollier, P.; Gloaguen, V.; Faugeron-Girard, C. Agar extraction by-products from Gelidium sesquipedale as a source of glycerol-galactosides. Molecules 2018, 19, 3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, B.; Li, Y.X.; Kang, K.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, D.G. Floridoside from Laurencia undulata promotes osteogenic differentiation in murine bone marrow mesenchymal cells. J. Funct. Food 2015, 19, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, G.; Sahoo, D.; Kuhad, R.C. Bioethanol production from Gracilaria verrucosa, a red alga, in a biorefinery approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez, A.; Gascó, G.; Ruiz, B.; Fuente, E. Hydrochars from industrial macroalgae Gelidium sesquipedale biomass wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Paul, N.A.; Dworjanyn, S.A.; Bird, M.I.; de Nys, R. Biochar from commercially cultivated seaweed for soil amelioration. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, M.P.; Merlyn, R.; Arunkumar, K.; Perumal, K. Characterization, pretreatment and saccharification of spent seaweed biomass for bioethanol production using baker’s yeast. Biomass Bioenerg. 2016, 90, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinita, M.D.N.; Marhaeni, B.; Jeong, G.T.; Hong, Y.K. Sequential acid and enzymatic hydrolysis of carrageenan solid waste for bioethanol production: A biorefinery approach. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.X.; Mi, Y.; Cao, W.X.; Lim, P.E.; Xue, C.H.; Tang, Q.J. A pilot study on anti-obesity mechanisms of Kappaphycus alvarezii: The role of native κ-carrageenan and the leftover sans-carrageenan fraction. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.; Seth, A. Recovery ratio and quality of an agricultural bio-stimulant and semi-refined carrageenan co-produced from the fresh biomass of Kappaphycus alvarezii with respect to seasonality. Algal Res. 2018, 32, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaran, K.; Ghosh, P.K.; Siddhata, A.K.; Patolia, J.S.; Periyasamy, C.; Mehta, A.S.; Mody, K.H.; Ramavat, B.K.; Prasad, K.; Rajyaguru, M.R. Integrated Method for Production of Carrageenan and Liquid Fertilizer from Fresh Seaweeds. U.S. Patent 6893479 B2, 17 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, I.S.; Lee, K.T. Enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of seaweed solid wastes for bioethanol production: An optimization study. Energy 2014, 78, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khambhaty, Y.; Ojha, K.; Akshaya, R.; Charyulu, E.M. An eco-friendly approach towards treatment of tannery lime liquor using halo tolerant alkaliphile of extreme origin. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinita, M.D.N.; Marhaeni, B.; Hong, Y.K.; Jeong, G.T. Enzymatic saccharification of agar waste from Gracilaria verrucosa and Gelidium latifolium for bioethanol production. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 3201–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.D.; Flórez-Fernández, N.; Domínguez, H. Mastocarpus stellatus red seaweed as a promising source of healthy compounds. In Book of Abstracts, Proceedings of the 3rd Annual Meeting: From Bed to Bedside: Diagnosis, Therapy and Data Analysis, Vigo, Spain, 1–2 July 2019; University of Vigo: Vigo, Spain, 2019; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- Schiener, P.; Zhao, S.; Theodoridou, K.; Carey, M.; Mooney-McAuley, K.; Greenwell, C. The nutritional aspects of biorefined Saccharina latissima, Ascophyllum nodosum and Palmaria palmata. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2017, 7, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, K.; Vitkin, E.; Robin, A.; Yakhini, Z.; Mishori, D.; Golberg, A. Macroalgae biorefinery from Kappaphycus alvarezii: Conversion modeling and performance prediction for India and Philippines as examples. Bioenerg. Res. 2018, 11, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Ghosh, A.; Prasad, K.; Singh, S.; Bhatt, N.; Zodape, S.T.; Chaudhary, J.P.; Chaudhari, J.; Chatterjee, P.B.; Seth, A. Elimination of gibberellin from Kappaphycus alvarezii seaweed sap foliar spray enhances corn stover production without compromising the grain yield advantage. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 75, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Seaweed Genus | Carbohydrates | Protein | Lipids | Minerals | Phenolics | Chla/Car (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asparagopsis | 40.5 | 17.6 | 6.62 | 23.76 | 0.06 | 0.03/0.01 | [39] |
| Chondrus | 50.20–64.6 | 6.7–18.1 | 2.46–4.20 | 19.8–22.8 | 0.04–0.43 | 0.06/0.02 | [28,29,39] |
| Eucheuma | 65.82 | 4.9 | 0.10 | 17.3 | [40] | ||
| Galaxaura | 10.28 | 2.80 | 1.43 | 84.36 | [39] | ||
| Grateulopia | 73.37 | 4.9 | 2.97 | 16.60 | 0.02 | 0.18/0.13 | [39] |
| Gelidium | 23.5–25.2 2; 10.6–12.2 3 | 18.4–19.3 | 1.1–1.3 | [4] | |||
| Gelidiella | 24.52; 9.83 | 14.9 | 1.4 | [4] | |||
| Gelidiopsis | 11.43 | 17.6 | 1.3 | [4] | |||
| Gigartina | 29.31 1 | 15.6 | 0.57 | 34.56 | [41] | ||
| Gracilaria | 24.8–78.7; 11.2–56.6 2; 3.8–6.1 3 | 0.6–45.0 | 0.3–7.1 | 7.4–40.3 | 0.001–0.06/0.001–0.007 | [4,24,26,30,31,42,43,44] | |
| Graciliaropsis | 77.7 | 10.5 | 0.8 | [44] | |||
| Kappaphycus | 57.2 | 2.6 | 5.2 | 15.8 | [45] | ||
| Mastocarpus | 60.4; 31.70 1 | 12.1–21.4 | 0.39 | 15.6–24.9 | [41,46] | ||
| Nemalion | 31.43 | 3.80 | 2.17 | 60.64 | 0.06 | 0.09/0.01 | [39] |
| Solieria | 18.8–22.5 | 8.1–8.3 | 2.1–2.5 | [16] | |||
| Palmaria | 31.7–59.0 | 10.7–31.4 | 4.9–12.9 | 9.0–23.7 | 0.48–0.55 | [28,29] | |
| Porphyra | 39.0–64.01 | 22.3–53.9 | 1.3 | 0.5–16.4 | 0.27–0.35 | 0.18–0.35/0.03–0.06 | [20,23,29] |
| Properties | AC, AT, AV, Ave, FP | AO, AH | AAt, ACh, AD, AH, AI, AP, AT, IS | DMS | AAt, AI, AO, AP, AT | AI, AO, AT | |
| References | [8,11,17,47] | [19,20,48,49] | [26,33,35,50] | [36] | [3,27] | [25] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez-Viñas, M.; Flórez-Fernández, N.; Torres, M.D.; Domínguez, H. Successful Approaches for a Red Seaweed Biorefinery. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110620
Álvarez-Viñas M, Flórez-Fernández N, Torres MD, Domínguez H. Successful Approaches for a Red Seaweed Biorefinery. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(11):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110620
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez-Viñas, Milena, Noelia Flórez-Fernández, M. Dolores Torres, and Herminia Domínguez. 2019. "Successful Approaches for a Red Seaweed Biorefinery" Marine Drugs 17, no. 11: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110620
APA StyleÁlvarez-Viñas, M., Flórez-Fernández, N., Torres, M. D., & Domínguez, H. (2019). Successful Approaches for a Red Seaweed Biorefinery. Marine Drugs, 17(11), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110620