A Versatile and Robust Serine Protease Inhibitor Scaffold from Actinia tenebrosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation of Two Low-Molecular-Mass Protease Inhibitors from A. tenebrosa
2.2. Sequence Analysis Reveals ATPI-I and ATPI-II Inhibitors Belong to the Kunitz-Type Family
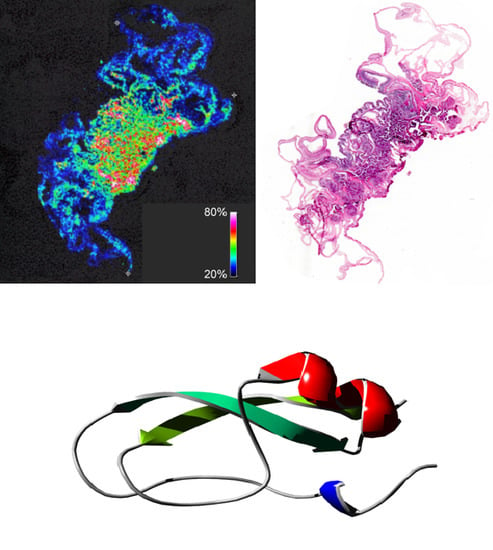
2.3. ATPI-I Is Localized to the Mesenteric Tissues of A. tenebrosa
2.4. ATPI-I and ATPI-II Have Distinctive Inhibitory Profiles toward the Closely Related Proteases KLK5, KLK7, and KLK14
2.5. Hydrogen-Bond Analysis Reveals Specific Interactions of ATPIs and KLKs
2.6. Sequence Diversity of Kunitz Domains in A. tenebrosa Inhibitors Indicates Functional Diversity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. A. tenebrosa Collection
4.2. Inhibitor Purification
4.3. Amino-Acid Sequence Determination Using LC–MS/MS
4.4. Transcriptomic Analysis
4.5. MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging
4.6. Synthesis of Peptide para-Nitroaniline (pNA) Substrates
4.7. Recombinant Production and Purification of KLKs
4.8. Kinetic Assays
4.9. Model Building and Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4.10. Sequence Consensus Analysis
4.11. In Silico Alanine Scanning
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hook, V.Y.; Azaryan, A.V.; Hwang, S.R.; Tezapsidis, N. Proteases and the emerging role of protease inhibitors in prohormone processing. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossovskaya, V.S.; Bunnett, N.W. Protease-activated receptors: Contribution to physiology and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 579–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clements, J.A.; Willemsen, N.M.; Myers, S.A.; Dong, Y. The tissue kallikrein family of serine proteases: Functional roles in human disease and potential as clinical biomarkers. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2004, 41, 265–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netzel-Arnett, S.; Hooper, J.D.; Szabo, R.; Madison, E.L.; Quigley, J.P.; Bugge, T.H.; Antalis, T.M. Membrane anchored serine proteases: A rapidly expanding group of cell surface proteolytic enzymes with potential roles in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedberg, J.E.; de Veer, S.J.; Harris, J.M. Natural and engineered kallikrein inhibitors: An emerging pharmacopoeia. Biol. Chem. 2010, 391, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swedberg, J.E.; Nigon, L.V.; Reid, J.C.; de Veer, S.J.; Walpole, C.M.; Stephens, C.R.; Walsh, T.P.; Takayama, T.K.; Hooper, J.D.; Clements, J.A.; et al. Substrate-guided design of a potent and selective kallikrein-related peptidase inhibitor for kallikrein 4. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.I.; Yang, Q.; Craik, C.S. Isolation of a high affinity inhibitor of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by phage display of ecotin. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 12250–12256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, A.; Baird, L.G. DX-88 and HAE: A developmental perspective. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2003, 29, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.A. FDA approves kallikrein inhibitor to treat hereditary angioedema. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2010, 67, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Lubenow, N. Recombinant hirudin in clinical practice: Focus on lepirudin. Circulation 2001, 103, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zucker, S.; Cao, J.; Chen, W.T. Critical appraisal of the use of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in cancer treatment. Oncogene 2000, 19, 6642–6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, J.; Hooper, J.; Dong, Y.; Harvey, T. The expanded human kallikrein (KLK) gene family: Genomic organisation, tissue-specific expression and potential functions. Biol. Chem. 2001, 382, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lose, F.; Batra, J.; O’Mara, T.; Fahey, P.; Marquart, L.; Eeles, R.A.; Easton, D.F.; Al Olama, A.A.; Kote-Jarai, Z.; Guy, M.; et al. Common variation in Kallikrein genes KLK5, KLK6, KLK12, and KLK13 and risk of prostate cancer and tumor aggressiveness. Urol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Veer, S.J.; Furio, L.; Swedberg, J.E.; Munro, C.A.; Brattsand, M.; Clements, J.A.; Hovnanian, A.; Harris, J.M. Selective Substrates and Inhibitors for Kallikrein-Related Peptidase 7 (KLK7) Shed Light on KLK Proteolytic Activity in the Stratum Corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brattsand, M.; Stefansson, K.; Lundh, C.; Haasum, Y.; Egelrud, T. A proteolytic cascade of kallikreins in the stratum corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briot, A.; Deraison, C.; Lacroix, M.; Bonnart, C.; Robin, A.; Besson, C.; Dubus, P.; Hovnanian, A. Kallikrein 5 induces atopic dermatitis-like lesions through PAR2-mediated thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression in Netherton syndrome. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarisbrick, I.A.; Linbo, R.; Vandell, A.G.; Keegan, M.; Blaber, S.I.; Blaber, M.; Sneve, D.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Rodriguez, M.; Diamandis, E.P. Kallikreins are associated with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis and promote neurodegeneration. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, H.; Laxmikanthan, G.; Lee, J.; Blaber, S.I.; Rodriguez, A.; Kogot, J.M.; Scarisbrick, I.A.; Blaber, M. Activation profiles and regulatory cascades of the human kallikrein-related peptidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 31852–31864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sotiropoulou, G.; Pampalakis, G.; Diamandis, E.P. Functional roles of human kallikrein-related peptidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32989–32994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prassas, I.; Eissa, A.; Poda, G.; Diamandis, E.P. Unleashing the therapeutic potential of human kallikrein-related serine proteases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourao, C.B.; Schwartz, E.F. Protease inhibitors from marine venomous animals and their counterparts in terrestrial venomous animals. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2069–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madio, B.; King, G.F.; Undheim, E.A.B. Sea Anemone Toxins: A Structural Overview. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fritz, H.; Brey, B.; Beress, L. Polyvalent isoinhibitors for trypsin, chymotrypsin, plasmin and kallikreins of sea anemones (Anemonia sulcata), isolation, inhibitory behavior and amino acid composition. Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 1972, 353, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiomi, K.; Ishikawa, M.; Yamanaka, H.; Kikuchi, T. Isolation and Properties of Four Serine Protease Inhibitors in the Sea Anemone Actinia equina. Nippon Suisan Gakk 1989, 55, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Fernández, R.; Perbandt, M.; Rehders, D.; Ziegelmüller, P.; Piganeau, N.; Hahn, U.; Betzel, C.; de los Ángeles Chávez, M.; Redecke, L. Three-dimensional Structure of a Kunitz-type Inhibitor in Complex with an Elastase-like Enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 14154–14165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prentis, P.J.; Pavasovic, A.; Norton, R.S. Sea Anemones: Quiet Achievers in the Field of Peptide Toxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishida, M.; Minagawa, S.; Miyauchi, K.; Shimakura, K.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Amino Acid Sequences of Kunitz-type Protease Inhibitors from the Sea Anemone Actinia equina. Fish. Sci. 1997, 63, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delfin, J.; Gonzalez, Y.; Diaz, J.; Chavez, M. Proteinase inhibitor from Stichodactyla helianthus: Purification, characterization and immobilization. Arch. Med. Res. 1994, 25, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, J.A.C. Digestion in sea anemones. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1959, 38, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basulto, A.; Pérez, V.M.; Noa, Y.; Varela, C.; Otero, A.J.; Pico, M.C. Immunohistochemical targeting of sea anemone cytolysins on tentacles, mesenteric filaments and isolated nematocysts of Stichodactyla helianthus. J. Exp. Zool. A Comp. Exp. Biol. 2006, 305, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, T.; Minagawa, S.; Nagai, H.; Ishida, M.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Novel peptide toxins from acrorhagi, aggressive organs of the sea anemone Actinia equina. Toxicon 2005, 46, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebens, K.P. Marine Flora and Fauna of the Eastern United States Anthozoa: Acitniaria, Corallimorpharia, Ceriantharia, and Zoanthidea. In NOAA Tech Rep NMFS; Pearce, J.B., Ed.; United States National Marine Fisheries Service: Seattle, WA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Krieger, E.; Koraimann, G.; Vriend, G. Increasing the precision of comparative models with YASARA NOVA--a self-parameterizing force field. Proteins 2002, 47, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, T.; Shiomi, K. Peptide toxins in sea anemones: Structural and functional aspects. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peigneur, S.; Billen, B.; Derua, R.; Waelkens, E.; Debaveye, S.; Béress, L.; Tytgat, J. A bifunctional sea anemone peptide with Kunitz type protease and potassium channel inhibiting properties. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ley, A.C.; Markland, W.; Ladner, R.C. Obtaining a family of high-affinity, high-specificity protein inhibitors of plasmin and plasma kallikrein. Mol. Divers. 1996, 2, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felber, L.M.; Kündig, C.; Borgoño, C.A.; Chagas, J.R.; Tasinato, A.; Jichlinski, P.; Gygi, C.M.; Leisinger, H.J.; Diamandis, E.P.; Deperthes, D.; et al. Mutant recombinant serpins as highly specific inhibitors of human kallikrein 14. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 2505–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.F. Tying pest insects in knots: The deployment of spider-venom-derived knottins as bioinsecticides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2437–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Veer, S.J.; Swedberg, J.E.; Akcan, M.; Rosengren, K.J.; Brattsand, M.; Craik, D.J.; Harris, J.M. Engineered protease inhibitors based on sunflower trypsin inhibitor-1 (SFTI-1) provide insights into the role of sequence and conformation in Laskowski mechanism inhibition. Biochem. J. 2015, 469, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedberg, J.E.; De Veer, S.J.; Sit, K.C.; Reboul, C.F.; Buckle, A.M.; Harris, J.M. Mastering the canonical loop of serine protease inhibitors: Enhancing potency by optimising the internal hydrogen bond network. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surm, J.M.; Smith, H.L.; Madio, B.; Undheim, E.A.; King, G.F.; Hamilton, B.R.; van der Burg, C.A.; Pavasovic, A.; Prentis, P.J. A process of convergent amplification and tissue-specific expression dominates the evolution of toxin and toxin-like genes in sea anemones. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 2272–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Betts, M.J.; Russell, R.B. Amino Acid Properties and Consequences of Substitutions. In Bioinformatics for Geneticists; Barnes, M.R., Gray, I.C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Borgoño, C.A.; Michael, I.P.; Shaw, J.L.; Luo, L.Y.; Ghosh, M.C.; Soosaipillai, A.; Grass, L.; Katsaros, D.; Diamandis, E.P. Expression and functional characterization of the cancer-related serine protease, human tissue kallikrein 14. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 2405–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michael, I.P.; Sotiropoulou, G.; Pampalakis, G.; Magklara, A.; Ghosh, M.; Wasney, G.; Diamandis, E.P. Biochemical and enzymatic characterization of human kallikrein 5 (hK5), a novel serine protease potentially involved in cancer progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 14628–14635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fry, B.G.; Vidal, N.; Van der Weerd, L.; Kochva, E.; Renjifo, C. Evolution and diversification of the Toxicofera reptile venom system. J. Proteom. 2009, 72, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M.S.; Liu, D.R. Methods for the directed evolution of proteins. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, T.H.; Link, A.J.; Tirrell, D.A. Evolution of a fluorinated green fluorescent protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13887–13890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chambers, M.C.; Maclean, B.; Burke, R.; Amodei, D.; Ruderman, D.L.; Neumann, S.; Gatto, L.; Fischer, B.; Pratt, B.; Egertson, J.; et al. A cross-platform toolkit for mass spectrometry and proteomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessner, D.; Chambers, M.; Burke, R.; Agus, D.; Mallick, P. ProteoWizard: open source software for rapid proteomics tools development. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2534–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Burg, C.A.; Prentis, P.J.; Surm, J.M.; Pavasovic, A. Insights into the innate immunome of actiniarians using a comparative genomic approach. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprioli, R.M.; Farmer, T.B.; Gile, J. Molecular imaging of biological samples: Localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 4751–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarnold, J.E.; Hamilton, B.R.; Welsh, D.T.; Pool, G.F.; Venter, D.J.; Carroll, A.R. High resolution spatial mapping of brominated pyrrole-2-aminoimidazole alkaloids distributions in the marine sponge Stylissa flabellata via MALDI-mass spectrometry imaging. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 2249–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Undheim, E.A.; Sunagar, K.; Hamilton, B.R.; Jones, A.; Venter, D.J.; Fry, B.G.; King, G.F. Multifunctional warheads: Diversification of the toxin arsenal of centipedes via novel multidomain transcripts. J. Proteomics. 2014, 102, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madio, B.; Peigneur, S.; Chin, Y.K.; Hamilton, B.R.; Henriques, S.T.; Smith, J.J.; Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Dekan, Z.; Boughton, B.A.; Alewood, P.F.; et al. PHAB toxins: A unique family of predatory sea anemone toxins evolving via intra-gene concerted evolution defines a new peptide fold. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 4511–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, M.L.; Hamilton, B.R.; Madio, B.; Morales, R.A.; Tonkin-Hill, G.Q.; Papenfuss, A.T.; Purcell, A.W.; King, G.F.; Undheim, E.A.; Norton, R.S. The Use of Imaging Mass Spectrometry to Study Peptide Toxin Distribution in Australian Sea Anemones. Aust. J. Chem. 2017, 70, 1235–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Undheim, E.A.; Hamilton, B.R.; Kurniawan, N.D.; Bowlay, G.; Cribb, B.W.; Merritt, D.J.; Fry, B.G.; King, G.F.; Venter, D.J. Production and packaging of a biological arsenal: Evolution of centipede venoms under morphological constraint. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4026–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, W.C.; White, P.D. Fmoc Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis: A Practical Approach; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Stefansson, K.; Brattsand, M.; Roosterman, D.; Kempkes, C.; Bocheva, G.; Steinhoff, M.; Egelrud, T. Activation of proteinase-activated receptor-2 by human kallikrein-related peptidases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egelrud, T.; Brattsand, M.; Kreutzmann, P.; Walden, M.; Vitzithum, K.; Marx, U.C.; Forssmann, W.G.; Mägert, H.J. hK5 and hK7, two serine proteinases abundant in human skin, are inhibited by LEKTI domain 6. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 153, 1200–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, R.A. Tight Binding Inhibitors, in Enzymes; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 305–317. [Google Scholar]
- MacKerell Jr, A.D.; Bashford, D.; Bellott, M.L.; Dunbrack Jr, R.L.; Evanseck, J.D.; Field, M.J.; Fischer, S.; Gao, J.; Guo, H.; Ha, S.; et al. All-atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and dynamics studies of proteins. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 3586–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD—Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kale, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Troshin, P.V.; Procter, J.B.; Barton, G.J. Java bioinformatics analysis web services for multiple sequence alignment--JABAWS:MSA. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2001–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingstone, C.D.; Barton, G.J. Protein sequence alignments: A strategy for the hierarchical analysis of residue conservation. Bioinformatics 1993, 9, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiss, G.A.; Watanabe, C.K.; Zhong, A.; Goddard, A.; Sidhu, S.S. Rapid mapping of protein functional epitopes by combinatorial alanine scanning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8950–8954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morrison, K.L.; Weiss, G.A. Combinatorial alanine-scanning. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2001, 5, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymkowitz, J.; Borg, J.; Stricher, F.; Nys, R.; Rousseau, F.; Serrano, L. The FoldX web server: An online force field. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W382–W388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Inhibitor | Amino-acid Sequence | Mass/Charge (Charge) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Observed | Calculated | ||
| ATPI-I | 1DANSFCQLPAVVGK14 | 753.47 (+2) | 753.37 (+2) |
| 15CRGYFPRYYYNTEAGK30 | 510.32 (+4) | 509.97 (+4) | |
| 22YYYNTEAGK30 | 554.97 (+2) | 554.75 (+2) | |
| 31CQQFIYGGCGGNR43 | 758.89 (+2) | 758.82 (+2) | |
| 31CQQFIYGGCGGNRNNFETVEDCR53 | 928.00 (+3) | 927.72 (+3) | |
| 44NNFETVEDCR53 | 642.39 (+2) | 642.27 (+2) | |
| 44NNFETVEDCRATCHSHA60 | 513.00 (+4) | 512.71 (+4) | |
| ATPI-II | 3NSFCNLPAVVGRCKGYFPR21 | 561.60 (+4) | 561.28 (+4) |
| 3NSFCNLPAVVGR15 | 667.53 (+2) | 667.34 (+2) | |
| 15CKGYFPR21 | 464.63 (+2) | 464.23 (+2) | |
| 22YFYNTEAGKCQR33 | 513.23 (+3) | 512.90 (+3) | |
| 34FIYGGCGGNRNNFETVDDCRATCHPRE60 | 641.54 (+5) | 641.28 (+5) | |
| Protease | Substrate | Ki (nM) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATPI-I | ATPI-II | ||
| Trypsin | Ac-YASR-pNA | 0.050 ± 0.007 | 0.080 ± 0.008 |
| Chymotrypsin | Ac-GRPY-pNA | 7.4 ± 1.2 | 2.9 ± 0.3 |
| KLK5 | Ac-YASR-pNA | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 21 ± 1 |
| KLK7 | KHLY-pNA | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 3.2 ± 0.2 |
| KLK14 | Ac-YASR-pNA | 13 ± 1 | 89 ± 7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Leahy, D.; Van Haeften, J.; Hartfield, P.; Prentis, P.J.; van der Burg, C.A.; Surm, J.M.; Pavasovic, A.; Madio, B.; Hamilton, B.R.; et al. A Versatile and Robust Serine Protease Inhibitor Scaffold from Actinia tenebrosa. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120701
Chen X, Leahy D, Van Haeften J, Hartfield P, Prentis PJ, van der Burg CA, Surm JM, Pavasovic A, Madio B, Hamilton BR, et al. A Versatile and Robust Serine Protease Inhibitor Scaffold from Actinia tenebrosa. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(12):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120701
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xingchen, Darren Leahy, Jessica Van Haeften, Perry Hartfield, Peter J. Prentis, Chloé A. van der Burg, Joachim M. Surm, Ana Pavasovic, Bruno Madio, Brett R. Hamilton, and et al. 2019. "A Versatile and Robust Serine Protease Inhibitor Scaffold from Actinia tenebrosa" Marine Drugs 17, no. 12: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120701
APA StyleChen, X., Leahy, D., Van Haeften, J., Hartfield, P., Prentis, P. J., van der Burg, C. A., Surm, J. M., Pavasovic, A., Madio, B., Hamilton, B. R., King, G. F., Undheim, E. A. B., Brattsand, M., & Harris, J. M. (2019). A Versatile and Robust Serine Protease Inhibitor Scaffold from Actinia tenebrosa. Marine Drugs, 17(12), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120701