Purification, Characterization and Evaluation of Inhibitory Mechanism of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Pearl Oyster (Pinctada fucata martensii) Meat Protein Hydrolysate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
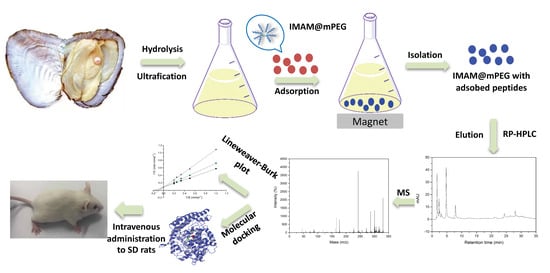
2.1. Separation and Purification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from POMPH
2.2. Characterization of Purified ACE Inhibitory Peptides
2.3. Activity-structure Relationship of the Isolated ACE Inhibitory Peptides
2.4. Evaluation of Inhibition Pattern of Purified ACE Inhibitory Peptides
2.5. Molecular Docking
2.6. Antihypertensive Studies of POMPH on SD rats
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Pearl Oyster Meat Protein
3.3. Preparation of IMAM@mPEG
3.4. Separation and Purification of ACE Inhibitory Peptide from POMPH
3.5. In Vitro Assay of ACE Inhibitory Activity
3.6. Identification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides by Mass Spectrometry
3.7. Determination of Inhibition Pattern
3.8. Molecular Docking
3.9. Evaluation of Antihypertensive Activity of POMPH in SD Rats
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization, 2014 Global Noncommunicable Diseases Report. Available online: http://www.who.int/nmh/publications/ncd-status-report-2014/en/ (accessed on 2 August 2019).
- Hippauf, F.; Huettner, C.; Lunow, D.; Borchardt, L.; Henle, T.; Kaskel, S. Towards a continuous adsorption process for the enrichment of ACE-inhibiting peptides from food protein hydrolysates. Carbon 2016, 107, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, X.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ulaah, S. Isolation, purification and the anti-hypertensive effect of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from Ruditapes philippinarum fermented with Bacillus natto. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5230–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.; Tian, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ryu, M.; Wang, H.; Ng, T. Isolation of an angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory protein with antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats from the edible wild mushroom leucopaxillus tricolor. Molecular 2015, 20, 10141–10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhao, W.; Ding, L.; Shiuan, D.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Identification and the molecular mechanism of a novel myosin-derived ACE inhibitory peptide. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Geng, L.; Sui, Z.; Zhang, Q. Antihypertensive effects of two novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis (Rhodophyta) in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, L.; Zhu, J.; Huang, F.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Ding, G. Identification and molecular docking study of a novel angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from enzymatic hydrolysates of Cyclina sinensis. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheih, I.; Fang, T.; Wu, T. Isolation and characterisation of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from the algae protein waste. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslan, J.; Kamal, S.M.M.; Yunos, K.F.M.; Abdullah, N. Assessment on multilayer ultrafiltration membrane for fractionation of tilapia by-product protein hydrolysate with angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 173, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Q.; Xue, B.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Ou, S.; Peng, X. Angiotensin-i-converting enzyme inhibitory activities and in vivo antihypertensive effects of sardine protein hydrolysate. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, H2831–H2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.; Vo, T.; Ryu, B.; Kim, S. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Pacific cod skin gelatin using ultrafiltration membranes. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishkaei, M.S.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Abdul-Hamid, A.; Ismail, A.; Saari, N. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory and anti-hypertensive effect of protein hydrolysate from actinopyga lecanora (sea cucumber) in rats. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Regenstein, J.; Zhao, M.; Ren, J. Purification and characterization of an antioxidant protein from pearl oyster (Pinctada fucata martensii). J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2015, 24, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, N.; Tong, Z.; Liao, D. Optimation technical conditions for preparing antihypertensive-peptides(ACEI) from Pinctada martensii with alkali protease hydrolysis. Mar. Sci. 2008, 32, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Sun, L.; Zhuang, Y. Preparation and identification of novel inhibitory angiotensin-I-converting enzyme peptides from tilapia skin gelatin hydrolysates: Inhibition kinetics and molecular docking. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5251–5259. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wu, S.; Zhou, L.; Wang, F.; Lan, X.; Sun, J.; Tong, Z.; Liao, D. Separation and characterization of angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from saurida elongata proteins hydrolysate by IMAC-Ni2+. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewissen, B.G.; Pauly, A.; Celus, I.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Inhibition of angiotensin I-converting enzyme by wheat gliadin hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ortega, O.; Porath, J.; Guzmán, R. Adsorption of peptides and small proteins with control access polymer permeation to affinity binding sites. Part I: Polymer permeation-immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography separation adsorbents with polyethylene glycol and immobilized metal ions. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1227, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ortega, O.; Porath, J.; Guzmán, R. Adsorption of peptides and small proteins with control access polymer permeation to affinity binding sites. Part II: Polymer permeation-ion exchange separation adsorbents with polyethylene glycol and strong anion exchange group. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1227, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, R.; Hordur, G.K. ACE-inhibitory activity of tilapia protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 582–588. [Google Scholar]
- Picot, L.; Ravallec, R.; Fouchereau-Peron, M.; Vandanjon, L.; Jaouen, P.; Chaplain-Derouiniot, M.; Guerard, F.; Chabeaud, A.; LeGal, Y.; Alvarez, O.M.; et al. Impact of ultrafiltration and nanofiltration of an industrial fish protein hydrolysate on its bioactive properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mooney, J.T.; Fredericks, D.P.; Hearn, M.T.W. Application of an IMAC cassette for the purification of N-terminally tagged proteins. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 120, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-ledesma, B.; Contreras, M.; Recio, I. Antihypertensive peptides: Production, bioavailability and incorporation into foods. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 165, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Le, G.; Shi, Y.; Shrestha, S. Angiotensin I–converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins and their physiological and pharmacological effects. Nutr. Res. 2004, 24, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, A.; Jo, C.; Kang, K.; Lee, M. Antimicrobial and human cancer cell cytotoxic effect of synthetic angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ning, D.; Wang, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, F.; Zhao, L.; Cao, Y. Application and structure-activity relationship of antihypertensive peptides derived from milk protein. China Dairy Ind. 2015, 43, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Chaudhary, K.; Sharma, M.; Nagpal, G.; Chauhan, J.S.; Singh, S.; Gautam, A.; Raghava, G.P. AHTPDB: A comprehensive platform for analysis and presentation of antihypertensive peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D956–D965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbana, C.; Boye, J.I. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory properties of lentil protein hydrolysates: Determination of the kinetics of inhibition. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Su, Y.; Yang, Y. ACE inhibitory peptides and antioxidant peptides derived from in vitro digestion hydrolysate of hen egg white lysozyme. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahna, C.; Jeonb, Y.; Kimc, Y.; Jea, J. Angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from salmon byproduct protein hydrolysate by alcalase hydrolysis. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 2240–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, B.; Zarei, M.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Philip, R.; Bakar, J.; Hamid, A.A.; Saari, N. Purification and characterization of angiotensin converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides derived from Stichopus horrens: Stability study against the ACE and inhibition kinetics. J. Func. Foods 2016, 20, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Qian, Z.; Kim, S. A novel angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from tuna frame protein hydrolysate and its antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balti, R.; Bougatef, A.; Sila, A.; Guillochon, D.; Dhulster, P.; Arroume, N. Nine novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) muscle protein hydrolysates and antihypertensive effect of the potent active peptide in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Cui, J.; Bai, X.; Du, Z.; Miyaguchi, Y.; Lin, B. Purification and identification of a ACE inhibitory peptide from oyster proteins hydrolysate and the antihypertensive effect of hydrolysate in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.; Lin, T.; Chen, J.; Pan, B. The inhibitory effects of freshwater clam (Corbicula fluminea, Muller) muscle protein hydrolysates on angiotensin Ⅰ converting enzyme. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 2276–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Du, J.; Jia, J.; Kuang, C. Production of ACE inhibitory peptides from sweet sorghum grain protein using alcalase: Hydrolysis kinetic, purification and molecular docking study. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesh, R.; Schwager, S.L.U.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Crystal structure of the human angiotensin-converting enzyme-lisinopril complex. Nature 2003, 421, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Guan, Y.; Liu, H. Synthesis of magnetic silica nanospheres with metal ligands and application in affinity separation of proteins. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 275, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuoq, F.; Masion, A.; Labille, J.; Rose, J.; Ziarelli, F.; Prelot, B.; Bottero, J. Preparation of amino-functionalized silica in aqueous conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 266, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chi, Z.; Xu, J. A pH-responsive polymer based on dynamic imine bonds as a drug delivery material with pseudo target release behavior. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Liao, D.; Wu, S.; Wang, F.; Sun, J.; Tong, Z. Rapid purification and characterization of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from lizard fish protein hydrolysates with magnetic affinity separation. Food Chem. 2015, 182, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Standard. Laboratory Animal–Requirements of Environment and Housing Facilities. 2010. Available online: https://www.codeofchina.com/standard/GB14925-2010.html (accessed on 1 October 2011).
- World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [CrossRef]
- Guiding Principles in the Care and Use of Animals. J. Neurophysiol. 1986, 55, U201.
- Ikeda, K.; Gutierrez, O.G.; Yamori, Y. Dietary Ng-nitro-L-arginine induces sustained hypertension in normotensive wistar-kyoto rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1992, 19, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Han, J.; Zhou, M.; Ren, H.; Pan, Q.; Zheng, C.; Zheng, Q. Neuroprotective effect of scutellarin on ischemic cerebral injury by down-regulating the expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme and AT1 receptor. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar]






| Fraction | T-POMPH | D-POMPH | Eluate of IMAM@mPEG |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACE Inhibitory Activity (%) | 32.91 ± 1.37 | 55.25 ± 3.24 | 84.14 ± 2.63 |
| Amino Sequence | Source | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| VWYHT | Izumi Shrimp | 28.3 |
| IWHHT | Fish (Dried Bonito) | 5.1 |
| HLPLPLL | Casein | 34.4 |
| HLPLP | Milk proteins | 41 |
| HLL | No detected | 22.2 |
| GW | Soybean | 30 |
| GWAP | Fish (Sardine muscle) | 3.86 |
| AGW | Milk derived | <10 |
| IGW | Meat protein | <10 |
| WA | Fish (Salmon) | 277.3 |
| Source | Amino Sequence | Inhibition Pattern | IC50 (μM) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuna frame protein | GDLGKTTTVSN-WSPPKYKDTP | Non-competitive | 11.28 | [33] |
| Cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) muscle protein | VELYP | Non-competitive | 5.22 | [34] |
| Oyster protein | VVYPWTTQRF | Non-competitive | 66 | [35] |
| Salmon byproduct protein | FEDYVPLSCF | Mixed inhibition | 10.77 | [31] |
| VWDPPKFD | Non-competitive | 9.1 | ||
| Stichopus horrens | CRQHTLGHNT-QTSIAQ | Non-competitive | 80 | [32] |
| EVSQGRP | Mixed inhibition | 50 | ||
| Freshwater clam (Corbicula fluminea, Muller) muscle protein | VKP | Competitive | 3.7 | [36] |
| VKK | Competitive | 1045 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Lan, X.; Yaseen, M.; Wu, S.; Feng, X.; Zhou, L.; Sun, J.; Liao, A.; Liao, D.; Sun, L. Purification, Characterization and Evaluation of Inhibitory Mechanism of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Pearl Oyster (Pinctada fucata martensii) Meat Protein Hydrolysate. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080463
Liu P, Lan X, Yaseen M, Wu S, Feng X, Zhou L, Sun J, Liao A, Liao D, Sun L. Purification, Characterization and Evaluation of Inhibitory Mechanism of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Pearl Oyster (Pinctada fucata martensii) Meat Protein Hydrolysate. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(8):463. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080463
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Pengru, Xiongdiao Lan, Muhammad Yaseen, Shanguang Wu, Xuezhen Feng, Liqin Zhou, Jianhua Sun, Anping Liao, Dankui Liao, and Lixia Sun. 2019. "Purification, Characterization and Evaluation of Inhibitory Mechanism of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Pearl Oyster (Pinctada fucata martensii) Meat Protein Hydrolysate" Marine Drugs 17, no. 8: 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080463
APA StyleLiu, P., Lan, X., Yaseen, M., Wu, S., Feng, X., Zhou, L., Sun, J., Liao, A., Liao, D., & Sun, L. (2019). Purification, Characterization and Evaluation of Inhibitory Mechanism of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Pearl Oyster (Pinctada fucata martensii) Meat Protein Hydrolysate. Marine Drugs, 17(8), 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080463