The Anti-Obesity Effect of Polysaccharide-Rich Red Algae (Gelidium amansii) Hot-Water Extracts in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Hamsters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Carbohydrate Content and Monosaccharide Composition
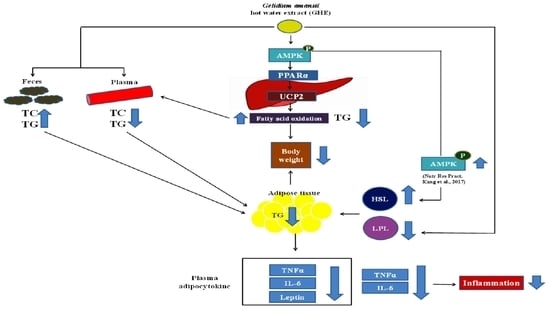
2.2. Effects of GHE on Body and Tissue Weights in HF Diet-Fed Hamsters
2.3. Effects of GHE on Plasma, Liver, and Fecal Lipids and Adipocytokines in HF Diet-Fed Hamsters
2.4. Effects of GHE on TG Contents and Lipolysis Rate and LPL Activity in Adipose Tissues and Lipid Metabolism-Related Protein Expressions in the Livers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Solvents
4.2. Hot-Water Extract of GA (GHE)
4.3. Analysis of Carbohydrate Content and Monosaccharide Composition
4.4. Animals and Treatments
4.5. Collection of Blood and Tissue Samples
4.6. Determination of Plasma Lipids
4.7. Determination of Plasma Glucose, Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNF-α), Interleukin 6 (IL-6), and Leptin
4.8. Determination of Liver Lipids, Fecal Lipids, and Bile Acid Levels
4.9. Lipolysis Rate Measurement
4.10. Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) Activity
4.11. Western Blot Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aubin, M.C.; Lajoie, C.; Clément, R.; Gosselin, H.; Calderone, A.; Perrault, L.P. Female rats fed a high-fat diet were associated with vascular dysfunction and cardiac fibrosis in the absence of overt obesity and hyperlipidemia: Therapeutic potential of resveratrol. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, A.G.; Cote, C.; Couto, J.; Daskiran, M.; Gunnarsson, C.; Haas, K.; Haas, S.; Nigam, S.C.; Schuette, R. Prevalence of obesity, type II diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension in the United States: Findings from the GE Centricity Electronic Medical Record database. Popul. Health Manag. 2010, 13, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, M.R.; Benício, M.H.; Latorre, M.R.; Jardim, P.C. Waist circumference and body mass index as predictors of hypertension. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2006, 87, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J. A comprehensive review on metabolic syndrome. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 943162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.S.; Wu, J.C.; Pan, M.H. Molecular mechanism on functional food bioactives for anti-obesity. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 2, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.J.; Goodrick, G.K. A functional food product for management of weight. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2002, 42, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labropoulos, K.C.; Niesz, D.E.; Danforth, S.C.; Kevrekidis, P.G. Dynamic rheology of agar gels: Theory and experiments. Part I. Development of a rheological model. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 50, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Tu, C.J.; Wu, H.T. Growth-inhibitory effects of the red alga gelidium amansii on cultured cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Tang, F.; Zuo, S.H. An experimental study on the hypoglycemic effect of agar polysaccharide in diabetic rats. Health Med. Res. Pract. 2011, 4, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, H.; Yamamoto, R.; Hirao, K.; Tochikubo, O. Effects of agar (kanten) diet on obese patients with impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2005, 7, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.H.; Yao, H.T.; Chiang, M.T. Red algae (Gelidium amansii) hot water extracts ameliorate lipid metabolism in hamsters fed a high fat diet. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.J.; Lee, O.H.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, B.Y. Extract from edible red seaweed (Gelidium amansii) inhibits lipid accumulation and ros production during differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2012, 17, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.C.; Kang, N.; Kim, S.Y.; Lima, I.S.; Ko, S.C.; Kim, Y.T.; Kim, Y.B.; Jeung, H.D.; Choi, K.S.; Jeon, Y.J. Popular edible seaweed, Gelidium amansii prevents against diet-induced obesity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Jiao, R.; Peng, C.; Wong, Y.M.; Yeung, V.S.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.Y. Choosing hamsters but not rats as a model for studying plasma cholesterol-lowering activity of functional foods. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Huang, C.; Liao, X.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Feng, R.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Beneficial effects of mangiferin on hyperlipidemia in high-fat-fed hamsters. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuem, N.; Song, S.J.; Yu, R.; Yun, J.W.; Park, T. Oleuropein attenuates visceral adiposity in high-fat diet-induced obese mice through the modulation of WNT10b-and galanin-mediated signalings. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 2166–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Choi, G.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.K. Dohaekseunggi-tang extract inhibits obesity, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landin, K.; Holm, G.; Tengborn, L.; Smith, U. Guar gum improves insulin sensitivity, blood lipids, blood pressure, and fibrinolysis in healthy men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 56, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkiewski, M. Effect of guar gum on body-weight, hunger ratings and metabolism in obese subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 1984, 52, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, A.M.; Yanovski, J.A.; Calis, K.A. Orlistat, a new lipase inhibitor for the management of obesity. Pharmacotherapy 2000, 20, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Choe, S.S.; Jang, H.; Kim, J.; Jeong, H.W.; Jo, H.; Tadi, S.; Park, M.G.; Kwak, T.H.; Kim, J.M.; et al. AMPK activation with glabridin ameliorates adiposity and lipid dysregulation in obesity. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.; Xing, Y.; Wang, D.Q.; Howles, P.; Basford, J.E.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Y.Q.; Hui, D.Y.; Woods, S.C.; Liu, M. Ginsenoside Rb1 reduces fatty liver by activating AMP-activated protein kinase in obese rats. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, P.; Kai, Q.; Gao, J.; Lian, Z.Q.; Wu, C.M.; Wu, C.A.; Zhu, H.B. Cordycepin prevents hyperlipidemia in hamsters fed a high-fat diet via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 113, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.J.; Lee, G.Y.; Chung, J.J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, J.B. Adiponectin increases fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle cells by sequential activation of AMP-activated protein kinase, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, M.; Masaki, T.; Nishimura, J.; Seike, M.; Yoshimatsu, H. The effects of branched-chain amino acid granules on the accumulation of tissue triglycerides and uncoupling proteins in diet-induced obese mice. Endocr. J. 2011, 58, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ide, T.; Moriuchi, H.; Nihimoto, K. Hypolipidemic effects of guar gum and its enzyme hydrolysate in rats fed highly saturated fat diets. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 1991, 35, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, M.S.; Ahmad, A.; Sharif, M.K. Influence of pectin and guar gum composite flour on plasma biochemical profile of streptozotocin-induced diabetic male albino rats. Int. J. Food Prop. 2007, 10, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsdottir, G.; Xu, J.; Molin, G.; Ahrne, S.; Nyman, M. High-fat diet reduces the formation of butyrate, but increases succinate, inflammation, liver fat and cholesterol in rats, while dietary fiber counteracts these effects. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, A.C.; Sgarbieri, V.C. Guar gum effects on food intake, blood serum lipids and glucose levels of Wistar rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1998, 53, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittas, A.G.; Joseph, N.A.; Greenberg, A.S. Adipocytokines and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, P.A.; Ranganathan, S.; Li, C.; Wood, L.; Ranganathan, G. Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, E745–E751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.C.; Chang, C.J.; Yang, T.H.; Chiang, M.T. Long-term feeding of red algae (Gelidium amansii) ameliorates glucose and lipid metabolism in a high fructose diet-impaired glucose tolerance rat model. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Eckel, R.H. Lipoprotein lipase: From gene to obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E271–E288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, M.J.; Holmes, A.G.; Pinnamaneni, S.K.; Garnham, A.P.; Steinberg, G.R.; Kemp, B.E.; Febbraio, M.A. Regulation of HSL serine phosphorylation in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 290, E500–E508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Besten, G.; Gerding, A.; van Dijk, T.H.; Ciapaite, J.; Bleeker, A.; van Eunen, K.; Havinga, R.; Groen, A.K.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Bakker, B.M. Protection against the Metabolic Syndrome by Guar Gum-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Depends on Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Lee, H.A.; Kim, H.J.; Han, J.S. Gelidium amansii extract ameliorates obesity by down-regulating adipogenic transcription factors in diet-induced obese mice. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2017, 11, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wi, S.G.; Kim, H.J.; Mahadevan, S.A.; Yang, D.J.; Bae, H.J. The potential value of the seaweed Ceylon moss (Gelidium amansii) as an alternative bioenergy resource. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6658–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). Official Methods of Analysis, 16th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC): Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldi, T.R.I.; Margiotta, G.; Zambonin, C.G. Determination of sugars and alditols in food samples by HPAEC with integrated pulsed amperometric detection using alkaline eluents containing barium or strontium ions. Food Chem. 1998, 62, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Solane, G.M. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, S.E.; Goldford, S. A sensitive enzymatic method of determination of free and esterified tissue cholesterol. Clin. Chim. Acta 1977, 79, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.H.; Lai, M.H. Fermentation of resistant rice starch produces propionate reducing serum and hepatic cholesterol in rats. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1991–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.J.; Barnard, R.J. Effect of diet on fat cell size and hormone-sensitive lipase activity. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 1999, 87, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusunoki, M.; Hara, T.; Tsutsumi, K.; Nakamura, T.; Miyata, T.; Sakakibara, F.; Sakamoto, S.; Ogawa, H.; Nakaya, Y.; Storlien, L.H. The lipoprotein lipase activator, NO-1886, suppresses fat accumulation and insulin resistance in rats fed a high-fat diet. Diabetologia 2000, 43, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Molar Ratio of Monosaccharide Composition (100%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuc | Rha | Ara | Gal | Glc | Man | Xyl | GalA | GlcA |
| 8.3 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± <0.1 | nd | 86.0 ± 0.5 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± <0.1 | 1.1 ± <0.1 | nd | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| Parameters | Con | HF | GG | GHE | OL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial body weight (g) | 106.4 ± 6.7 b | 118.4 ± 7.4 a | 115.9 ± 5.6 a | 116.9 ± 5.6 a | 116.2 ± 8.2 a |
| Final body weight (g) | 110.6 ± 8.7 d | 133.7 ± 9.4 a | 125.7 ± 3.0 b | 121.9 ± 3.9 bc | 115.5 ± 8.6 cd |
| Body weight gain (g) | 4.2 ± 7.9 bc | 15.3 ± 4.5 a | 9.8 ± 3.8 b | 5.0 ± 4.5 bc | -0.7 ± 5.2 c |
| Food intake (g/days) | 8.3 ± 0.3 b | 8.1 ± 0.4 bc | 7.8 ± 0.4 c | 7.8 ± 0.4 c | 9.3 ± 0.3 a |
| Feed efficiency ratio (%) | 0.7 ± 1.4 cd | 2.7 ± 0.8 a | 1.8 ± 0.7 ab | 0.9 ± 0.8 bc | −0.1 ± 0.8 d |
| Fasting body weight (g) | 108.3 ± 8.3 d | 130.6 ± 9.5 a | 123.5 ± 4.3 ab | 119.3 ± 3.8 bc | 113.2 ± 9.2 cd |
| Liver weight (g) | 3.2 ± 0.3 d | 6.1 ± 0.3 a | 5.1 ± 0.3 b | 5.0 ± 0.1 b | 3.6 ± 0.2 c |
| Relative liver weight (g/100 g BW) | 3.0 ± 0.2 d | 4.7 ± 0.2 a | 4.1 ± 0.1 b | 4.2 ± 0.1 b | 3.2 ± 0.2 c |
| Perirenal fat (g) | 1.0 ± 0.3 c | 2.0 ± 0.2 a | 1.8 ± 0.1 a | 1.5 ± 0.2 b | 1.2 ± 0.2 c |
| Paraepididymal fat (g) | 0.7 ± 0.2 d | 1.7 ± 0.2 a | 1.3 ± 0.1 b | 1.1 ± 0.2 c | 0.9 ± 0.2 c |
| White adipose tissue weight (g) | 1.7 ± 0.6 e | 3.6 ± 0.4 a | 3.1 ± 0.2 b | 2.6 ± 0.3 c | 2.1 ± 0.5 d |
| Relative white adipose tissue weight (g/100 g BW) | 1.5 ± 0.4 d | 2.8 ± 0.2 a | 2.5 ± 0.2 a | 2.1 ± 0.2 b | 1.8 ± 0.3 c |
| Parameters | Con | HF | GG | GHE | OL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 148.8 ± 13.6 a | 153.3 ± 12.5 a | 144.2 ± 21.1 a | 144.9 ± 23.1 a | 161.0 ± 15.7 a |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 58.4 ± 13.9 c | 173.7 ± 34.7 a | 139.3 ± 27.6 b | 128.1 ± 21.2 b | 119.8 ± 28.1 b |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 80.6 ± 13.4 d | 390.1 ± 76.9 a | 252.4 ± 31.7 b | 285.9 ± 42.0 b | 136.4 ± 22.5 c |
| Leptin (pg/mL) | 245.4 ± 81.3 d | 818.6 ± 241.9 a | 607.9 ± 232.0 b | 484.0 ± 155.5 bc | 352.5 ± 134.2 cd |
| TNFα (pg/mL) | 37.7 ± 1.4 d | 53.8 ± 1.2 a | 40.5 ± 1.8 b | 39.2 ± 2.1 bc | 37.3 ± 0.7 cd |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 10.5 ± 1.5 b | 21.5 ± 8.2 a | 11.8 ± 3.2 b | 10.2 ± 3.4 b | 8.8 ± 2.1 b |
| Lipids | Con | HF | GG | GHE | OL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | |||||
| Total cholesterol (mg/g Liver) | 5.9 ± 1.9 d | 71.2 ± 6.4 a | 42.8 ± 5.8 b | 40.4 ± 6.5 b | 17.0 ± 6.7 c |
| Total cholesterol (mg/Liver) | 19.1 ± 7.3 d | 434.1 ± 44.1 a | 218.3 ± 31.9 b | 201.2 ± 31.3 b | 61.0 ± 21.6 c |
| Triglyceride (mg/g Liver) | 2.9 ± 0.4 d | 9.5 ± 1.1 a | 7.8 ± 1.7 b | 6.1 ± 1.6 c | 7.3 ± 1.5 bc |
| Triglyceride (mg/Liver) | 9.2 ± 1.7 d | 57.6 ± 5.6 a | 39.4 ± 7.9 b | 30.6 ± 7.9 c | 26.6 ± 5.9 c |
| Feces | |||||
| Total cholesterol (mg/g feces) | 3.7 ± 0.5 d | 4.7 ± 0.9 cd | 5.0 ± 1.3 c | 10.3 ± 1.1 a | 7.1 ± 1.5 b |
| Total cholesterol (mg/day) | 4.3 ± 0.6 b | 5.5 ± 1.3 b | 5.3 ± 1.7 b | 11.8 ± 1.6 a | 12.5 ± 3.5 a |
| Triglyceride (mg/g feces) | 3.2 ± 0.2 c | 3.5 ± 0.3 c | 4.7 ± 0.5 b | 4.7 ± 0.3 b | 106.4 ± 13.8 a |
| Triglyceride (mg/day) | 3.8 ± 0.4 c | 4.0 ± 0.5 c | 5.0 ± 0.7 b | 5.5 ± 0.7 b | 185.5 ± 29.4 a |
| Composition | Con | HF | GG | GHE | OL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chow diet | 100 | 86.9 | 86.9 | 86.9 | 86.9 |
| Coconut oil | - | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Soybean oil | - | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Cholesterol | - | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Cellulose | - | 3 | - | - | 3 |
| Gelidium amansii hot-water extract | - | - | - | 3 | - |
| Guar gum | - | - | 3 | - | |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Orlistat | - | - | - | - | 200 mg/kg diet |
| Kcal (100 g) | 345.6 | 396.3 | 395.9 | 396.9 | 396.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, T.-H.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Lu, T.-J.; Liu, S.-H.; Chiang, M.-T. The Anti-Obesity Effect of Polysaccharide-Rich Red Algae (Gelidium amansii) Hot-Water Extracts in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Hamsters. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090532
Yang T-H, Chiu C-Y, Lu T-J, Liu S-H, Chiang M-T. The Anti-Obesity Effect of Polysaccharide-Rich Red Algae (Gelidium amansii) Hot-Water Extracts in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Hamsters. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(9):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090532
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Tsung-Han, Chen-Yuan Chiu, Ting-Jang Lu, Shing-Hwa Liu, and Meng-Tsan Chiang. 2019. "The Anti-Obesity Effect of Polysaccharide-Rich Red Algae (Gelidium amansii) Hot-Water Extracts in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Hamsters" Marine Drugs 17, no. 9: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090532
APA StyleYang, T. -H., Chiu, C. -Y., Lu, T. -J., Liu, S. -H., & Chiang, M. -T. (2019). The Anti-Obesity Effect of Polysaccharide-Rich Red Algae (Gelidium amansii) Hot-Water Extracts in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Hamsters. Marine Drugs, 17(9), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090532