New Discorhabdin B Dimers with Anticancer Activity from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
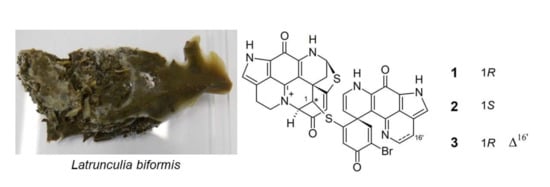
2.1. Purification and Structure Elucidation
2.2. Bioactivity Evaluation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Procedures
4.2. Sponge Material, Extraction, and Isolation
4.3. Anticancer and Cytotoxicity Assays
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samaai, T.; Gibbons, M.J.; Kelly, M.; Davies-Coleman, M. South African Latrunculiidae (Porifera: Demospongiae: Poecilosclerida): Descriptions of new species of Latrunculia du Bocage, Strongylodesma Lévi, and Tsitsikamma Samaai & Kelly. Zootaxa 2003, 371, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Samaai, T.; Govender, V.; Kelly, M. Cyclacanthia n.g. (Demospongiae: Poecilosclerida: Latrunculiidae incertea sedis), a new genus of marine sponges from South African waters, and description of two new species. Zootaxa 2004, 725, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez, B.; Bergquist, P.R.; Battershill, C.N. Taxonomic revision of the genus Latrunculia du Bocage (Porifera: Demospongiae: Latrunculiidae) in New Zealand. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 36, 151–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.; Sim-Smith, C.; Stone, R.; Samaai, T.; Reiswig, H.; Austin, W. New taxa and arrangements within the family Latrunculiidae (Demospongiae, Poecilosclerida). Zootaxa 2016, 4121, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; McCombs, J.D.; Munro, M.H.G. Discorhabdin C, a highly cytotoxic pigment from a sponge of the genus Latrunculia. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 5476–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G. Cytotoxic pigments from New Zealand sponges of the genus Latrunculia: Discorhabdin A, discorhabdin B and discorhabdin C. Tetrahedron 1988, 44, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G.; Higa, T.; Sakai, R. Discorhabdin D, an antitumor alkaloid from the sponges Latrunculia brevis and Prianos sp. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 4127–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, E.M.; Beukes, D.R.; Kelly, M.; Samaai, T.; Barrows, L.R.; Marshall, K.M.; Sincich, C.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Cytotoxic Pyrroloiminoquinones from four new species of South African latrunculid sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grkovic, T.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.-C.; Webb, V.L.; Ferreira, D.; Copp, B.R. Enantiomeric discorhabdin alkaloids and establishment of their absolute configurations using theoretical calculations of electronic circular dichroism spectra. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 9133–9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovic, T.; Copp, B.R. New natural products in the discorhabdin A- and B-series from New Zealand-sourced Latrunculia spp. sponges. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 6335–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovic, T.; Pearce, A.N.; Munro, M.H.G.; Blunt, J.W.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Copp, B.R. Isolation and characterization of diastereomers of discorhabdins H and K and assignment of absolute configuration to discorhabdins D, N, Q, S, T, and U. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Janussen, D.; Peifer, C.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Tasdemir, D. Targeted isolation of tsitsikammamines from the antarctic deep-sea sponge Latrunculia biformis by molecular networking and anticancer activity. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Hamann, M.T. Atkamine: A new pyrroloiminoquinone scaffold from the cold water Aleutian Islands Latrunculia sponge. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, F.J.; Peifer, C.; Janussen, D.; Tasdemir, D. New discorhabdin alkaloids from the Antarctic deep-sea sponge Latrunculia biformis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reyes, F.; Martín, R.; Rueda, A.; Fernandez, R.; Montalvo, D.; Gomez, C.; Sánchez-Puelles, J.M. Discorhabdins I and L, cytotoxic alkaloids from the sponge Latrunculia brevis. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Baker, B.J.; Grimwade, J.; Leonard, A.; McClintock, J.B. Discorhabdin alkaloids from the Antarctic sponge Latrunculia apicalis. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, G.; Pinkert, A.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G. Discorhabdin W, the first dimeric discorhabdin. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1796–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goey, A.K.L.; Chau, C.H.; Sissung, T.M.; Cook, K.M.; Venzon, D.J.; Castro, A.; Ransom, T.R.; Henrich, C.J.; McKee, T.C.; McMahon, J.B.; et al. Screening and biological effects of marine pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids: Potential inhibitors of the HIF-1α/p300 interaction. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.F.C.; Grkovic, T.; Pearce, A.N.; Copp, B.R. Investigation of the electrophilic reactivity of the cytotoxic marine alkaloid discorhabdin B. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 3092–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternhell, S. Correlation of interproton spin-spin coupling constants with structure. Q. Rev. Chem. Soc. 1969, 23, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.K.; Wang, X.J.; Sims, J.; Wang, B.; Pandey, P.; Welsh, C.L.; Stone, R.P.; Avery, M.A.; Doerksen, R.J.; Ferreira, D.; et al. Computationally assisted discovery and assignment of a highly strained and PANC-1 selective alkaloid from Alaska’s deep ocean. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4338–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Position | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| δH, Mult. (J in Hz) | δH, Mult. (J in Hz) | δH, Mult. (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 4.72 d (3.1) | 5.03 d (2.6) | 4.53 d (3.1) |
| 2 | 4.45 d (3.1) | 4.43 d (2.6) | 4.45 d (3.1) |
| 4 | 6.17 s | 6.27 s | 6.04 s |
| 7α | 2.71 dd (1.3, 12.0) | 2.76 dd (1.5, 11.7) | 2.31 dd (1.5, 12.0) |
| 7β | 2.91 dd (3.7, 12.0) | 2.95 dd (3.6, 11.7) | 2.38 dd (3.7, 12.0) |
| 8 | 5.62 dd (1.3, 3.7) | 5.58 dd (1.5, 3.6) | 5.30 dd (1.5, 3.7) |
| 14 | 7.15 s | 7.09 s | 7.13 s |
| 16 | 3.24 m | 3.03 m | 3.24 m |
| 3.10 ddd (2.6, 6.5, 16.3) | 3.07 ddd (2.7, 6.8, 16.3) | ||
| 17 | 4.13 ddd (2.6, 7.4, 13.9) | 3.91 m | 4.11 ddd (2.7, 7.3, 14.2) |
| 3.91 m | 3.89 m | ||
| 1’ | 7.89 s | 7.87 (s) | 7.91 s |
| 4’ | 6.66 s | 6.72 s | 6.48 s |
| 7’ | 4.79 d (7.5) | 4.82 d (7.5) | 4.21 d (7.5) |
| 8’ | 6.57 d (7.5) | 6.58 d (7.5) | 6.60 d (7.5) |
| 14’ | 7.25 s | 7.23 s | 8.15 s |
| 16’ | 2.98 m | 2.97 m | 7.64 d (6.0) |
| 17’ | 3.91 m | 3.91 m | 8.19 d (6.0) |
| TFA: Trifluoroacetic acid | |||
| Position | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| δCa | δCa | δC | |
| 1 | 46.0 (CH) | 44.9 (CH) | 45.8 (CH) |
| 2 | 65.6 (CH) | 68.0 (CH) | 66.1 (CH) |
| 3 | 182.3 (C) | 183.7 (C) | 182.3 (C) |
| 4 | 114.4 (CH) | 114.8 (CH) | 114.4 (CH) |
| 5 | 171.0 (C) | 174.4 (C) | 171.7 (C) |
| 6 | 46.6 (C) | 48.3 (C) | 47.0 (C) |
| 7 | 38.8 (CH2) | 39.2 (CH2) | 38.4 (CH2) |
| 8 | 63.8 (CH) | 62.8 (CH) | 63.6 (CH) |
| 10 | 148.6 (C) | 150.4 (C) | 148.4 (C) |
| 11 | 167.0 (C) | 167.0 (C) | / |
| 12 | 125.4 (C) | 125.8 (C) | 125.4 (C) |
| 14 | 127.5 (CH) | 127.5 (CH) | 127.4 (CH) |
| 15 | 119.4 (C) | 119.5 (C) | 119.4 (C) |
| 16 | 20.8 (CH2) | 20.7 (CH2) | 20.7 (CH2) |
| 17 | 52.9 (CH2) | 52.9 (CH2) | 52.9 (CH2) |
| 19 | 150.4 (C) | 150.6 (C) | 150.2 (C) |
| 20 | 101.1 (C) | 98.6 (C) | 101.2 (C) |
| 21 | 122.8 (C) | 122.7 (C) | 122.8 (C) |
| 1’ | 150.5 (CH) | 150.2 (CH) | 156.0 (CH) |
| 2’ | 124.3 (C) | 124.4 (C) | 120.0 (C) |
| 3’ | 176.2 (C) | 176.2 (C) | 178.4 (C) |
| 4’ | 122.3 (CH) | 121.9 (CH) | 118.7 (CH) |
| 5’ | 163.2 (C) | 164.7 (C) | 171.4 (C) |
| 6’ | 50.8 (C) | 50.7 (C) | 52.5 (C) |
| 7’ | 115.1 (CH) | 114.9 (CH) | 103.9 (CH) |
| 8’ | 126.9 (CH) | 126.4 (CH) | 128.8 (CH) |
| 10’ | 146.8 (C) | 147.2 (C) | 142.3 (C) |
| 11’ | 166.5 (C) | 166.5 (C) | / |
| 12’ | 125.6 (C) | 125.8 (C) | 120.9 |
| 14’ | 127.5 (CH) | 127.5 (CH) | 129.7 (CH) |
| 15’ | 120.9 (C) | 121.2 (C) | 126.3 (C) |
| 16’ | 19.3 (CH2) | 19.2 (CH2) | 115.9 (CH) |
| 17’ | 46.2 (CH2) | 46.1 (CH2) | 142.0 (CH) |
| 19’ | 159.9 (C) | 160.4 (C) | 148.4 (C) |
| 20’ | 95.8 (C) | 96.1 (C) | 108.0 (C) |
| 21’ | 123.2 (C) | 123.2 (C) | 121.0 (C) |
| IC50 Values (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|
| HCT-116 Cells | HaCaT Cells | |
| Compound 1 a | 0.16 | 0.56 |
| Compound 2 a | 2.01 | 4.69 |
| Negative (solvent) control b | - | - |
| Positive control c | 22.1 | 35.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Janussen, D.; Tasdemir, D. New Discorhabdin B Dimers with Anticancer Activity from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18020107
Li F, Janussen D, Tasdemir D. New Discorhabdin B Dimers with Anticancer Activity from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(2):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18020107
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Fengjie, Dorte Janussen, and Deniz Tasdemir. 2020. "New Discorhabdin B Dimers with Anticancer Activity from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis" Marine Drugs 18, no. 2: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18020107
APA StyleLi, F., Janussen, D., & Tasdemir, D. (2020). New Discorhabdin B Dimers with Anticancer Activity from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis. Marine Drugs, 18(2), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18020107