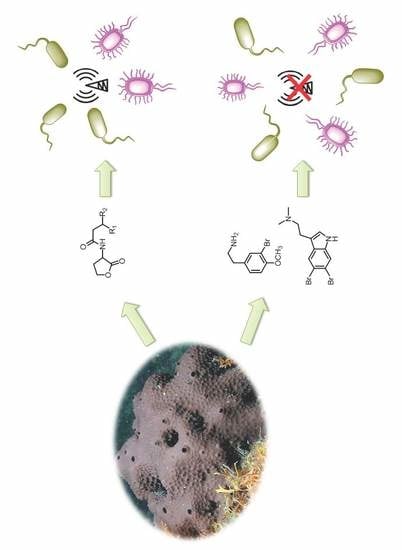
Identification of Quorum Sensing Activators and Inhibitors in The Marine Sponge Sarcotragus spinosulus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Taxonomic Identification of Sponge
2.2. Identification of AHLs in Sarcotragus spinosulus Crude Extracts
2.3. Bioassay-guided Isolation and Structural Elucidation of 1 and 2
2.4. Determination of Non-Inhibitory Concentration (NIC)
2.5. Dose-Dependent Quantification of Bioluminescence for QSI Assay
2.6. Inhibition of Production of the Virulence Factors Pyocyanin and Protease
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Sponge Sampling
3.2. Taxonomic Identification of Sponge
3.3. Microbial Enrichment by Cell Separation and Its Extraction
3.4. Crude Extracts Preparation and Preliminary Screening for QSI Activity
3.5. AHLs Identification Using LC-HRMS/MS Analysis
3.6. Bioassay-Guided Purification and Identification of Molecules with QSI Activity
3.7. Determination of Non-Inhibitory Concentration (NIC)
3.8. Dose-Dependent Quantification of Bioluminescence for QSI Assay
3.9. Inhibition of Production of Virulence Factors—Pyocyanin and Protease
3.10. Statistical Analysis
3.11. Data Deposition
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasko, D.A.; Sperandio, V. Anti-virulence strategies to combat bacteria-mediated disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaSarre, B.; Federle, M.J. Exploiting Quorum Sensing to Confuse Bacterial Pathogens. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2013, 77, 73–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López, D.; Vlamakis, H.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Paracrine signaling in a bacterium. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rutherford, S.T.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial Quorum Sensing: Its Role in Virulence and Possibilities for Its Control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a012427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cegelski, L.; Marshall, G.R.; Eldridge, G.R.; Hultgren, S.J. The biology and future prospects of antivirulence therapies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.H.; Wang, L.H.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, L.H. Quenching quorum-sensing-dependent bacterial infection by an N-acyl homoserine lactonase. Nature 2001, 411, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H.; Xu, J.L.; Li, X.Z.; Zhang, L.H. AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3526–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.T.; Schweizer, H.P. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (FabI): A target for the antimicrobial triclosan and its role in acylated homoserine lactone synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 5489–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.; Yin, B.; Qian, L.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, S. Screening for novel quorum-sensing inhibitors to interfere with the formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Rybtke, M.T.; Jakobsen, T.H.; Hentzer, M.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Computer-aided identification of recognized drugs as Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2432–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawlik, J.R. The Chemical Ecology of Sponges on Caribbean Reefs: Natural Products Shape Natural Systems. BioScience 2011, 61, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martins, M.L.; Pinto, U.M.; Riedel, K.; Vanetti, M.C.; Mantovani, H.C.; de Araujo, E.F. Lack of AHL-based quorum sensing in Pseudomonas fluorescens isolated from milk. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esteves, A.I.S.; Hardoim, C.C.P.; Xavier, J.R.; Gonçalves, J.M.S.; Costa, R. Molecular richness and biotechnological potential of bacteria cultured from Irciniidae sponges in the north-east Atlantic. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 85, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hentschel, U.; Piel, J.; Degnan, S.M.; Taylor, M.W. Genomic insights into the marine sponge microbiome. Nat. Rev. Micro 2012, 10, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piel, J.; Hui, D.; Wen, G.; Butzke, D.; Platzer, M.; Fusetani, N.; Matsunaga, S. Antitumor polyketide biosynthesis by an uncultivated bacterial symbiont of the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16222–16227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, M.C.; Mori, T.; Ruckert, C.; Uria, A.R.; Helf, M.J.; Takada, K.; Gernert, C.; Steffens, U.A.; Heycke, N.; Schmitt, S.; et al. An environmental bacterial taxon with a large and distinct metabolic repertoire. Nature 2014, 506, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zan, J.; Fuqua, C.; Hill, R.T. Diversity and functional analysis of luxS genes in Vibrios from marine sponges Mycale laxissima and Ircinia strobilina. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esposito, G.; Teta, R.; Della Sala, G.; Pawlik, J.R.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Isolation of Smenopyrone, a Bis-gamma-Pyrone Polypropionate from the Caribbean Sponge Smenospongia aurea. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saurav, K.; Burgsdorf, I.; Teta, R.; Esposito, G.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Costantino, V.; Steindler, L. Isolation of Marine Paracoccus sp. Ss63 from the Sponge Sarcotragus sp. and Characterization of its Quorum-Sensing Chemical-Signaling Molecules by LC-MS/MS Analysis. Israel J. Chem. 2016, 56, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.E.; Keshavan, N.D. Messing with Bacterial Quorum Sensing. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 859–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gardères, J.; Taupin, L.; Saïdin, J.; Dufour, A.; Le Pennec, G. N-acyl homoserine lactone production by bacteria within the sponge Suberites domuncula (Olivi, 1792) (Porifera, Demospongiae). Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, N.M.; Cicirelli, E.M.; Kan, J.; Chen, F.; Fuqua, C.; Hill, R.T. Diversity and quorum-sensing signal production of Proteobacteria associated with marine sponges. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britstein, M.; Saurav, K.; Teta, R.; Sala, G.D.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Stoppelli, N.; Zoccarato, L.; Costantino, V.; Steindler, L. Identification and chemical characterization of N-acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing signals across sponge species and time. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fix182. [Google Scholar]
- Saurav, K.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Haber, M.; Burgsdorf, I.; Oliviero, G.; Costantino, V.; Morgenstern, D.; Steindler, L. In Search of Alternative Antibiotic Drugs: Quorum-Quenching Activity in Sponges and their Bacterial Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skindersoe, M.E.; Ettinger-Epstein, P.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bjarnsholt, T.; de Nys, R.; Givskov, M. Quorum Sensing Antagonism from Marine Organisms. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mai, T.; Tintillier, F.; Lucasson, A.; Moriou, C.; Bonno, E.; Petek, S.; Magre, K.; Al Mourabit, A.; Saulnier, D.; Debitus, C. Quorum sensing inhibitors from Leucetta chagosensis Dendy, 1863. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 311–317. [Google Scholar]
- Dobretsov, S.; Teplitski, M.; Bayer, M.; Gunasekera, S.; Proksch, P.; Paul, V.J. Inhibition of marine biofouling by bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors. Biofouling 2011, 27, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.F.M.; Goh, H.C.; Lim, S.C.; Pang, L.M.; Chin, J.S.F.; Tan, K.S.; Liang, Z.-X.; Yang, L.; Glukhov, E.; Gerwick, W.H.; et al. Integrated Genomic and Metabolomic Approach to the Discovery of Potential Anti-Quorum Sensing Natural Products from Microbes Associated with Marine Samples from Singapore. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Teplitski, M.; Robinson, J.B.; Bauer, W.D. Plants secrete substances that mimic bacterial N-acyl homoserine lactone signal activities and affect population density-dependent behaviors in associated bacteria. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2000, 13, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manefield, M.; de Nys, R.; Kumar, N.; Read, R.; Givskov, M.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S. Evidence that halogenated furanones from Delisea pulchra inhibit acylated homoserine lactone (AHL)-mediated gene expression by displacing the AHL signal from its receptor protein. Microbiology 1999, 145, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keshavan, N.D.; Chowdhary, P.K.; Haines, D.C.; Gonzalez, J.E. L-Canavanine made by Medicago sativa interferes with quorum sensing in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 8427–8436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Igarashi, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Fukuda, T.; Shojima, A.; Nakayama, J.; Carro, L.; Trujillo, M.E. Arthroamide, a Cyclic Depsipeptide with Quorum Sensing Inhibitory Activity from Arthrobacter sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2827–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, R.M.; Dobretsov, S.; Al-Fori, M.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Sudesh, K.; Paul, V.J. Quorum-sensing inhibitory compounds from extremophilic microorganisms isolated from a hypersaline cyanobacterial mat. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gross, H.; Goeger, D.E.; Hills, P.; Mooberry, S.L.; Ballantine, D.L.; Murray, T.F.; Valeriote, F.A.; Gerwick, W.H. Lophocladines, Bioactive Alkaloids from the Red Alga Lophocladia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costantino, V.; Della Sala, G.; Saurav, K.; Teta, R.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Mangoni, A.; Steindler, L. Plakofuranolactone as a Quorum Quenching Agent from the Indonesian Sponge Plakortis cf. lita. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tello, E.; Castellanos, L.; Arévalo-Ferro, C.; Duque, C. Disruption in Quorum-Sensing Systems and Bacterial Biofilm Inhibition by Cembranoid Diterpenes Isolated from the Octocoral Eunicea knighti. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilabert, M.; Ramos, A.N.; Schiavone, M.M.; Arena, M.E.; Bardón, A. Bioactive Sesqui- and Diterpenoids from the Argentine Liverwort Porella chilensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, A.; Iacovidou, M.; Hirokawa, E.; Soll, C.E.; Trujillo, M. 17-Hydroxycyclooctatin, a Fused 5−8−5 Ring Diterpene, from Streptomyces sp. MTE4a. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bojko, B.; Onat, B.; Boyaci, E.; Psillakis, E.; Dailianis, T.; Pawliszyn, J. Application of in situ Solid-Phase Microextraction on Mediterranean Sponges for Untargeted Exometabolome Screening and Environmental Monitoring. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doberva, M.; Stien, D.; Sorres, J.; Hue, N.; Sanchez-Ferandin, S.; Eparvier, V.; Ferandin, Y.; Lebaron, P.; Lami, R. Large Diversity and Original Structures of Acyl-Homoserine Lactones in Strain MOLA 401, a Marine Rhodobacteraceae Bacterium. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataldi, T.R.I.; Bianco, G.; Abate, S.; Losito, I. Identification of unsaturated N-acylhomoserine lactones in bacterial isolates of Rhodobacter sphaeroides by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization-hybrid linear ion trap-Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Sala, G.; Teta, R.; Esposito, G.; Costantino, V. Chapter 1—The Chemical Language of Gram-Negative Bacteria. In Quorum Sensing; Tommonaro, G., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, G.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L.; Mai, L.H.; Longeon, A.; Teta, R.; Meijer, L.; Van Soest, R.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Chloromethylhalicyclamine B, a Marine-Derived Protein Kinase CK1δ/ε Inhibitor. J. Nat.Prod. 2016, 79, 2953–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longeon, A.; Copp, B.R.; Quevrain, E.; Roue, M.; Kientz, B.; Cresteil, T.; Petek, S.; Debitus, C.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L. Bioactive indole derivatives from the South Pacific marine sponges Rhopaloeides odorabile and Hyrtios sp. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollica, A.; Locatelli, M.; Stefanucci, A.; Pinnen, F. Synthesis and bioactivity of secondary metabolites from marine sponges containing dibrominated indolic systems. Molecules 2012, 17, 6083–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, T.A. Phenethylamine and related compounds in plants. Phytochemistry 1977, 16, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.D. Mammalian central nervous system trace amines. Pharmacologic amphetamines, physiologic neuromodulators. J. Neurochem. 2004, 90, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynnes, T.; Horne, S.M.; Prüß, B.M. ß-Phenylethylamine as a novel nutrient treatment to reduce bacterial contamination due to Escherichia coli O157:H7 on beef meat. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, J.N.A.; van Soest, R.W.M. Systema Porifera, A Guide to the Classification of the Sponges; Hooper, J.N.A., Van Soest, R.W.M., Willenz, P., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 2, p. 1706. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Rot, C.; Goldfarb, I.; Ilan, M.; Huchon, D. Putative cross-kingdom horizontal gene transfer in sponge (Porifera) mitochondria. BMC Evol. Biol. 2006, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loytynoja, A.; Vilella, A.J.; Goldman, N. Accurate extension of multiple sequence alignments using a phylogeny-aware graph algorithm. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kishino, H.; Yano, T. Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence Limits on Phylogenies: An Approach Using the Bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgsdorf, I.; Slaby, B.M.; Handley, K.M.; Haber, M.; Blom, J.; Marshall, C.W.; Gilbert, J.A.; Hentschel, U.; Steindler, L. Lifestyle evolution in cyanobacterial symbionts of sponges. MBio 2015, 6, e00391-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClean, K.H.; Winson, M.K.; Fish, L.; Taylor, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Camara, M.; Daykin, M.; Lamb, J.H.; Swift, S.; Bycroft, B.W.; et al. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: Exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 1997, 143, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saurav, K.; Costantino, V.; Venturi, V.; Steindler, L. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors from the Sea Discovered Using Bacterial N-acyl-homoserine Lactone-Based Biosensors. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winson, M.K.; Swift, S.; Fish, L.; Throup, J.P.; Jorgensen, F.; Chhabra, S.R.; Bycroft, B.W.; Williams, P.; Stewart, G.S. Construction and analysis of luxCDABE-based plasmid sensors for investigating N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 163, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| AHLs | M+H (exp) | Rt | 454 | 455 | 456 | 457 | 460 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OHC6:1-AHL | 214.1073 | 1.73 | x | ||||
| C6-AHL | 200.1280 | 11.86 | x | ||||
| C8-AHL | 228.1593 | 15.39 | x | ||||
| C10:1-AHL | 254.1749 | 15.89 | x | x | x | ||
| OC10-AHL | 270.1697 | 17.46 | x | ||||
| C12-AHL | 284.2217 | 24.18 | x | ||||
| C14-AHL | 312.2527 | 27.63 | x | ||||
| OHC14-AHL | 328.2479 | 23.58 | x | ||||
| OHC16-AHL | 356.2794 | 25.18 | x | ||||
| OHC18-AHL | 384.3102 | 30.25 | x | ||||
| OC16-AHL | 354.2635 | 25.22 | x |
| AHLs | M+H (exp) | Rt | SCS-B | SCS-C | SCS-D | SCS-E | SCS-F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C10:1-AHL | 254.1749 | 15.89 | x | x | x | ||
| C6-AHL | 200.1280 | 11.86 | x | ||||
| C8:1-AHL | 226.1437 | 11.16 | x | x | |||
| C8-AHL | 228.1593 | 15.39 | x | ||||
| OC14-AHL | 326.2320 | 24.96 | x | x | |||
| OHC10-AHL | 272.1853 | 16.17 | x | ||||
| OHC12-AHL | 300.2168 | 20.08 | x | ||||
| OHC14:1-AHL | 326.2321 | 23.86 | x | ||||
| OHC14-AHL | 328.2479 | 23.58 | x | ||||
| OHC16-AHL | 356.2794 | 25.18 | x | ||||
| OHC18-AHL | 384.3102 | 30.25 | x | ||||
| OHC6:1-AHL | 214.1073 | 1.73 | x | ||||
| OHC8-AHL | 244.1544 | 10.46 | x | x | |||
| OC12-AHL | 298.0009 | 21.44 | x |
| AHLs | M+H (exp) | rt | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC10-AHL | 270.1697 | 17.44 | x | |||||
| OHC14:1-AHL | 326.2321 | 23.86 | x | |||||
| C16-AHL | 340.2845 | 30.71 | L | x | L | L | L | |
| OC16-AHL | 354.2635 | 25.22 | L | x | x | L | L | |
| C18-AHL | 368.3148 | 33.88 | L | x | x | L | L | |
| OC18-AHL | 382.2946 | 31.26 | L | x | x | L | L | |
| OHC18-AHL | 384.3103 | 29.95 | L | x | x | L | L | |
| C18:1-AHL | 366.2998 | 31.45 | L | x | x | L | L | |
| C19-AHL | 382.3312 | 32.83 | L | x | x | L | L | |
| OC19-AHL | 396.3104 | 30.20 | L | x | x | L | L |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saurav, K.; Borbone, N.; Burgsdorf, I.; Teta, R.; Caso, A.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Esposito, G.; Britstein, M.; Steindler, L.; Costantino, V. Identification of Quorum Sensing Activators and Inhibitors in The Marine Sponge Sarcotragus spinosulus. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18020127
Saurav K, Borbone N, Burgsdorf I, Teta R, Caso A, Bar-Shalom R, Esposito G, Britstein M, Steindler L, Costantino V. Identification of Quorum Sensing Activators and Inhibitors in The Marine Sponge Sarcotragus spinosulus. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(2):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18020127
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaurav, Kumar, Nicola Borbone, Ilia Burgsdorf, Roberta Teta, Alessia Caso, Rinat Bar-Shalom, Germana Esposito, Maya Britstein, Laura Steindler, and Valeria Costantino. 2020. "Identification of Quorum Sensing Activators and Inhibitors in The Marine Sponge Sarcotragus spinosulus" Marine Drugs 18, no. 2: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18020127
APA StyleSaurav, K., Borbone, N., Burgsdorf, I., Teta, R., Caso, A., Bar-Shalom, R., Esposito, G., Britstein, M., Steindler, L., & Costantino, V. (2020). Identification of Quorum Sensing Activators and Inhibitors in The Marine Sponge Sarcotragus spinosulus. Marine Drugs, 18(2), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18020127