Mechanisms of Bioactivities of Fucoidan from the Brown Seaweed Fucus vesiculosus L. of the Barents Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
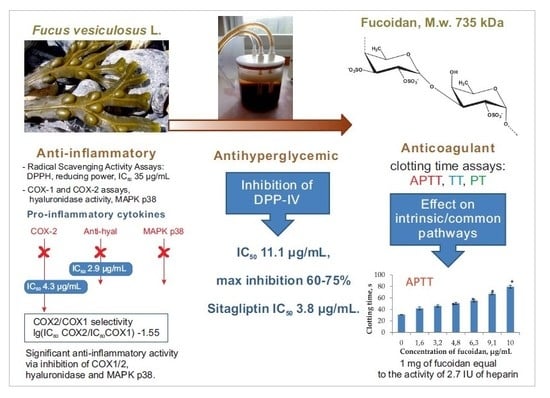
2.1. Radical Scavenging Activities
2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activities
2.3. Anti-Hyperglycemic Activity
2.4. Anti-Coagulant Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.1.1. Fucoidan
3.1.2. Chemicals
3.2. Radical Scavenging Activity Assays
3.2.1. 1, 1-Diphenyl-2-picryl hydrazil Radical Scavenging Activities
3.2.2. Reducing Power
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity Assays
3.3.1. Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase
3.3.2. Hyaluronidase Activity
3.3.3. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
3.3.4. Western Blotting
3.4. Anti-Hyperglycemic Activity Assay
3.5. Anti-Coagulant Activity Assay
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Guerrero, A.J.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Nakamura, F.; Fusetani, N. Marine pharmacology in 2014–2015: Marine compounds with antibacterial, antidiabetic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, antiviral, and anthelmintic activities; affecting the immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usov, A.I.; Bilan, M.I. Fucoidans—Sulfated polysaccharides of brown algae. Russ. Chem. Revs. 2009, 78, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushakova, N.A.; Morozevich, G.E.; Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Usov, A.I.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E. Anticoagulant activity of fucoidans from brown algae. Biomed. Khim. 2008, 54, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ale, M.T.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Important determinants for fucoidan bioactivity: A critical review of structure-function relations and extraction methods for fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from brown seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2106–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ale, M.T.; Meyer, A.S. Fucoidans from brown seaweeds: An update on structures, extraction techniques and use of enzymes as tools for structural elucidation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8131–8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z. Antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharide fractions extracted from Laminaria japonica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, M.; Cao, Q.; Ji, A.; Liang, H.; Song, S. Biological activities of fucoidan and the factors mediating its therapeutic effects: A review of recent studies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koh, H.S.A.; Lu, J.; Zhou, W. Structure characterization and antioxidant activity of fucoidan isolated from Undaria pinnatifida grown in New Zealand. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 212, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.A.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, S.Y.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Wang, L.; Abetunga, D.T.U.; Kim, W.-S.; Lee, D.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. Fucoidan isolated from Padina commersonii inhibit LPS-induced inflammation in macrophages blocking TLR/NF-κB signal pathway. Carbohydr. Ppolym. 2019, 224, 115195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.S.; Sanjeewa, K.A.; Samarakoon, K.W.; Lee, W.W.; Kim, H.-S.; Ranasinghe, P.; Gunasekara, U.K.D.S.S.; Jeon, Y.J. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functionality of ten Sri Lankan seaweed extracts obtained by carbohydrase assisted extraction. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Liu, C.G.; Tian, Y.J.; Gao, D.H.; Li, W.S.; Ma, H.L. Inhibitory effect of fucoidan on hypoglycemia in diabetes mellitus anim. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 8529–8534. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, I.S.; Ryu, B.; Ahn, G.; Yeo, I.K.; Jeon, Y.J. Therapeutic potential of algal natural products against metabolic syndrome: A review of recent developments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irhimeh, M.R.; Fitton, J.H.; Lowenthal, R.M. Pilot clinical study to evaluate the anticoagulant activity of fucoidan. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2009, 20, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Song, H.; Li, P. Potential antioxidant and anticoagulant capacity of low molecular weight fucoidan fractions extracted from Laminaria japonica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 46, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.B.; Zhang, Z.S.; Hou, Z.S.; Zhang, H. In vitro anticoagulant activity of fucoidan derivatives from brown seaweed Laminaria japonica. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2011, 29, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Xue, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B. Antithrombotic activity of oral administered low molecular weight fucoidan from Laminaria japonica. Thromb. Res. 2016, 144, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylova, N.V.; Ermakova, S.P.; Lavrov, V.F.; Leneva, I.A.; Kompanets, G.G.; Iunikhina, O.V.; Nosik, M.N.; Ebralidze, L.K.; Falynskova, I.N.; Silchenko, A.S.; et al. The comparative analysis of antiviral activity of native and modified fucoidans from brown algae Fucus evanescens in vitro and in vivo. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N.; Faustova, N.M.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Kosman, V.M.; Vuorela, H.; Makarov, V.G. Pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus after oral administration to rats. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitton, J.H.; Stringer, D.N.; Park, A.Y.; Karpiniec, S.S. Therapies from fucoidan: New developments. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oka, S.; Okabe, M.; Tsubura, S.; Mikami, M.; Imai, A. Properties of fucoidans beneficial to oral healthcare. Odontology 2020, 108, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitton, J.H.; Dell’Acqua, G.; Gardiner, V.-A.; Karpiniec, S.S.; Stringer, D.N.; Davis, E. Topical benefits of two fucoidan-rich extracts from marine macroalgae. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Vuorela, H. The pharmacokinetics of fucoidan after topical application to rats. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, K.; Joseph, D.; Joy, M.; Raola, V.K. Characterization of substituted aryl meroterpenoids from red seaweed Hypnea musciformis as potential antioxidants. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, A.N.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Antioxidant phytochemicals for the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases. Molecules 2015, 20, 21138–21156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgate, S.T.; Peters-Golden, M.; Panettieri, R.A.; Henderson, W.R. Roles of cysteinyl leukotrienes in airway inflammation, smooth muscle function, and remodeling. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.A. High-through screening assays for cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase, the targets for inflammatory disorders. Ind. J. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 48, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala, J. The p38 MAP kinase pathway as a therapeutic target in inflammatory disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2004, 4, 372–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Sharrocks, A.D.; Whitmarsh, A.J. Transcriptional regulation by the MAP kinase signaling cascades. Gene 2003, 320, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsube, T.; Yamasaki, Y.; Iwamoto, M.; Oka, S. Hyaluronidase-inhibiting polysaccharide isolated and purified from hot water extract of sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2003, 9, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elzoghby, A.O.; Freag, M.S.; Elkhodairy, K.A. Biopolymeric nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery to brain tumors. In Nanotechnology-Based Targeted Drug Delivery Systems for Brain Tumors; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havale, S.H.; Pal, M. Medicinal chemistry approaches to the inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1783–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.D.; Liu, X.; Hao, J.J.; Cai, C.; Fan, F.; Dun, Y.L.; Zhao, X.L.; Liu, X.X.; Li, C.X.; Yu, G.L. In vitro and in vivo hypoglycemic effects of brown algal fucoidans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dürig, J.; Bruhn, T.; Zurborn, K.-H.; Gutensohn, K.; Bruhn, H.D.; Béress, L. Anticoagulant fucoidan fractions from fucus vesiculosus induce platelet activation in vitro. Thromb. Res. 1997, 85, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.; Muffler, K.; Hahn, T.; Rupp, S.; Finkelmeier, D.; Burger-Kentischer, A.; Ulber, R. Physicochemical and biological characterization of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus purified by dye affinity chromatography. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lahrsen, E.; Schoenfeld, A.K.; Alban, S. Size-dependent pharmacological activities of differently degraded fucoidan fractions from Fucus vesiculosus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jönsson, M.; Allahgholi, L.; Sardari, R.R.; Hreggviðsson, G.O.; Nordberg Karlsson, E. Extraction and modification of macroalgal polysaccharides for current and next-generation applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luthuli, S.; Wu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wu, M.; Tong, H. Therapeutic effects of fucoidan: A review on recent studies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fletcher, H.R.; Biller, P.; Ross, A.B.; Adams, J.M.M. The seasonal variation of fucoidan within three species of brown macroalgae. Algal Res. 2017, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seyoum, A.; Asres, K.; El-Fiky, F.K. Structure–radical scavenging activity relationships of flavonoids. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.J.; Aida, W.M.W.; Maskat, M.T.; Mamot, S.; Ropien, J.; Mohd, D.M. Isolation and antioxidant capacity of fucoidan from selected Malaysian seaweeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 42, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Macquarrie, D. Microwave assisted extraction of sulfated polysaccharides (fucoidan) from ascophyllum nodosum and its antioxidant activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 129, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Jasso, R.; Mussatto, S.; Pastrana, L.; Aguilar, C.; Teixeira, J. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of sulphated polysaccharides extracted from Fucus vesiculosus using different hydrothermal processes. Chem. Pap. 2014, 68, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, K.; Chiu, F.; Ng, K. Identification and quantification of antioxidants in Fructus lycii. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, P. Extraction, structural characterization, and potential antioxidant activity of the polysaccharides from four seaweeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phull, A.R.; Kim, S.J. Fucoidan as bio-functional molecule: Insights into the antiinflammatory potential and associated molecular mechanisms. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.; Ulber, R. Fucoidans: Downstream processes and recent applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, D.; Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S. In vitro antioxidant activities of sulfated polysaccharide fractions extracted from Corallina officinalis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.; Hahn, T.; Finkelmeier, D.; Burger-Kentischer, A.; Rupp, S.; Krämer, R.; Ulber, R. Phenomenological investigation of the cytotoxic activity of fucoidan isolated from Fucus vesiculosus. Process Biochem. 2019, 81, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Viñas, M.; Flórez-Fernández, N.; González-Muñoz, M.J.; Domínguez, H. Influence of molecular weight on the properties of Sargassum muticum fucoidan. Algal Res. 2019, 38, 101393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, W.; Hamid, N.; Liu, T.; Lu, J.; White, W.L. Fucoidan from New Zealand Undaria pinnatifida: Monthly variations and determination of antioxidant activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, S.N.; Shanmugam, S.; Subramanian, B.; Jaganathan, R. Cytotoxic effect of fucoidan extracted from Sargassum cinereum on colon cancer cell line HCT-15. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jónsdóttir, R.; Ólafsdóttir, G. Total phenolic compounds, radical scavenging and metal chelation of extracts from Icelandic seaweeds. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parys, S.; Kehraus, S.; Krick, A.; Glombitza, K.W.; Carmeli, S.; Klimo, K.; Gerhauser, C.; Konig, G.M. In vitro chemopreventive potential of fucophlorethols from the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus L. by anti-oxidant activity and inhibition of selected cytochrome P450 enzymes. Phytochemistry. 2010, 71, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouzeau, J.Y.; Terlain, B.; Abid, A.; Nédélec, E.; Netter, P. Cyclo-oxygenase isoenzymes. How recent findings affect thinking about nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Drugs 1997, 53, 563–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.L.; DeWitt, D.L.; Garavito, R.M. Cyclooxygenases: Structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 145–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, H.Y.; Han, M.H.; Park, C.; Jin, C.Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Choi, I.W.; Kim, N.D.; Nam, T.J.; Kwon, T.K.; Choi, Y.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of fucoidan through inhibition of NF-κB, MAPK and Akt activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglia cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewi, L. In silico analysis of the potential of the active compounds fucoidan and alginate derived from Sargassum sp. as inhibitors of COX-1 and COX-2. Med Arch. 2016, 70, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Ko, C.I.; Ahn, G.; You, S.; Kim, J.S.; Heu, M.S.; Kim, J.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Molecular characteristics and anti-inflammatory activity of the fucoidan extracted from Ecklonia cava. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phull, A.R.; Majid, M.; Haq, I.U.; Khan, M.R.; Kim, S.J. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of anti-arthritic, antioxidant efficacy of fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida (Harvey) Suringar. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.D.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, T.; Jang, S.-A.; Kang, S.C.; Koo, H.J.; Sohn, E.; Bak, J.P.; Namkoong, S.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus protects against alcohol-induced liver damage by modulating inflammatory mediators in mice and HepG2 cells. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1051–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayawardena, T.U.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Lee, W.W.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.S.; Jeon, Y.J. Isolation and purification of fucoidan fraction in Turbinaria ornata from the Maldives; Inflammation inhibitory potential under LPS stimulated conditions in in-vitro and in-vivo models. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Public Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation. Online State Register of Medicinal Preparations. 2018. Available online: http://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=e8ad7e7f-98c1-4389-a6d6-1fc8c4cd969a&t= (accessed on 22 May 2020).
- Rosoiu, N.; Nita, R.; Olariu, L.; Drumea, V.; Ene, D.M. Original bioactive complexes rich in glycosaminoglycans obtained from small fish. Roum. Soc. Biol. Sci. 2008, 13, 3944–3954. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.J.; Lee, O.H.; Lee, B.Y. Fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide, inhibits adipogenesis through the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Life Sci. 2010, 22, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.; Fernando, I.P.; Kim, E.A.; Ahn, G.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory activity of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from an enzymatic digest of brown seaweed Sargassum horneri in RAW 264.7 cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2017, 11, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unnikrishnan, P.S.; Suthindhiran, K.; Jayasri, M.A. Inhibitory potential of Turbinaria ornata against key metabolic enzymes linked to diabetes. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 783895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unnikrishnan, P.S.; Suthindhiran, K.; Jayasri, M.A. Antidiabetic potential of marine algae by inhibiting key metabolic enzymes. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, A.P.; Gailani, D. The intrinsic pathway of coagulation as a target for antithrombotic therapy. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2016, 30, 1099–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Song, L.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, P. Sulfated polysaccharides isolated from cloned Grateloupia filicina and their anticoagulant activity. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 612352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athukorala, Y.; Jung, W.K.; Park, P.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, S.K.; Vasanthan, T.; Jeon, Y.J. Evaluation of biomolecular interactions of sulfated polysaccharide isolated from Grateloupia filicina on blood coagulation factors. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 503–511. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Till, S.; Knappe, S.; Quinn, C.; Catarello, J.; Ray, G.J.; Scheiflinger, F.; Szabo, C.M.; Dockal, M. Screening of complex fucoidans from four brown algae species as procoagulant agents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinsksya, E.D.; Makarova, M.N.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N. Effects of ultrasound treatment on the chemical composition and anticoagulant properties of dry Fucus extract. Pharm. Chem. J. 2015, 49, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, T.T.T.; Tran, V.T.T.; Yuguchi, Y.; Bui, L.M.; Nguyen, T.T. Structure of fucoidan from brown seaweed Turbinaria ornata as studied by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESIMS) and small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) techniques. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2431–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imbs, T.I.; Skriptsova, A.V.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Antioxidant activity of fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides obtained from Fucus evanescens by different extraction methods. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarov, U.S.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Laakso, I.; Seppänen-Laakso, T.; Urakova, I.N.; Vuorela, H.; Makarov, V.G.; Shikov, A.N. Metabolite profiling and mechanisms of bioactivity of snake autolysate—A traditional Uzbek medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 250, 112459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.O.; Barrowcliffe, T.W.; Holmer, E.; Johnson, E.A.; Sims, G.E.C. Anticoagulant properties of heparin fractionated by affinity chromatography on matrix-bound antithrombin III and by gel filtration. Thromb. Res. 1976, 9, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, A.J. The clinical application of the hippuric acid and the prothrombin tests. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1940, 10, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denson, K.W.; Bonnar, J. The measurement of heparin: A method based on the potentiation of anti-factor Xa. Thromb. Haemost. 1973, 30, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Z.; Zhang, R.Y.; Bai, J. An anti-oxidative therapy for ameliorating cardiac injuries of critically ill COVID-19-infected patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X.; et al. The use of anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of people with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): The experience of clinical immunologists from China. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 214, 108393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thachil, J.; Tang, N.; Gando, S.; Falanga, A.; Cattaneo, M.; Levi, M.; Clarck, C.; Iba, T. ISTH interim guidance on recognition and management of coagulopathy in COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | IC50 (mg mL−1) | AEAC (mgAA/100 g) |
|---|---|---|
| Fucoidan | 0.035 ± 0.002 | 914 ± 28 |
| Quercetin | 0.026 ± 0.001 | 1231 ± 56 |
| Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) | 0.00059 ± 0.00005 | 54237 ± 22 |
| Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) | 0.00092 ± 0.00003 | 34783 ± 14 |
| Ascorbic acid (AA) | 0.00032 ± 0.00002 |
| Sample, Concentration | Percentage of MAPK p38 (%) |
|---|---|
| Intact cells (no stimulation with LPS) | 23.0 ± 1.2 |
| Control cells stimulated with LPS (1 μg mL−1) | 100 |
| SB203580 (1.88 μg mL−1) + LPS | 41.0 ± 1.8 |
| Fucoidan (0.25 μg mL−1) + LPS | 17.0 ± 0.6 |
| Fucoidan (0.125 μg mL−1) + LPS | 20.0 ± 0.5 |
| Fucoidan (0.05 μg mL−1) + LPS | 31.0 ± 0.9 |
| Fucoidan (0.025 μg mL−1) + LPS | 53.0 ± 0.8 |
| Fucoidan (0.0125 μg mL−1) + LPS | 56.0 ± 0.9 |
| Fucoidan (0.00625 μg mL−1) + LPS | 77.0 ± 0.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Shikov, A.N. Mechanisms of Bioactivities of Fucoidan from the Brown Seaweed Fucus vesiculosus L. of the Barents Sea. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050275
Pozharitskaya ON, Obluchinskaya ED, Shikov AN. Mechanisms of Bioactivities of Fucoidan from the Brown Seaweed Fucus vesiculosus L. of the Barents Sea. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(5):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050275
Chicago/Turabian StylePozharitskaya, Olga N., Ekaterina D. Obluchinskaya, and Alexander N. Shikov. 2020. "Mechanisms of Bioactivities of Fucoidan from the Brown Seaweed Fucus vesiculosus L. of the Barents Sea" Marine Drugs 18, no. 5: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050275
APA StylePozharitskaya, O. N., Obluchinskaya, E. D., & Shikov, A. N. (2020). Mechanisms of Bioactivities of Fucoidan from the Brown Seaweed Fucus vesiculosus L. of the Barents Sea. Marine Drugs, 18(5), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050275