Estrogenic Effects of Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Belowground and Aerial Parts of Spartina anglica
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Estrogenic Effects of Different Extracts from Belowground and Aerial Parts of S. anglica on MCF-7 Cells
2.2. Uterotrophic Activity of 50% Ethanol Extract from Belowground Part of S. anglica in the Immature Rat
2.3. Structure Elucidation of Compounds 1–5 from S. anglica
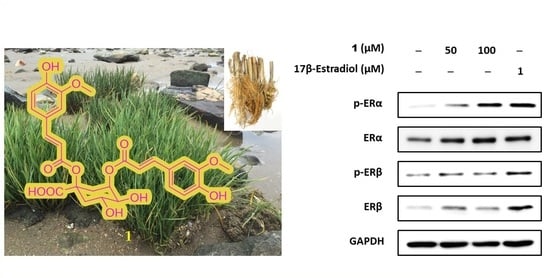
2.4. Estrogenic Effects of Compounds Isolated from Belowground Part of S. anglica on MCF-7 Cells
2.5. Anti-Proliferative Effect of Extracts and Compounds from S. anglica on MCF-7 Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation of Compounds from S. anglica
3.4. MCF-7 Culture
3.5. Determination of Estrogenic Effect in MCF-7 Cells
3.6. Determination of Anti-Proliferative Effect in MCF-7 Cells
3.7. Detection of Protein Expression in MCF-7 Cells
3.8. Animals
3.9. Uterotrophic Assay
3.10. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; O’Neill, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Holtzman, M.J.; Takemaru, K.I.; Korach, K.S.; Winuthayanon, W. Estrogen receptor α is required for oviductal transport of embryos. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sever, D.M.; Staub, N.L. Hormones, sex accessory structures, and secondary sexual characteristics in amphibians. In Hormones and Reproduction of Vertebrates; Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 83–98. [Google Scholar]
- Hausmann, M.; Slabbekoorn, D.; Van Goozen, S.H.; Cohen-Kettenis, P.T.; Güntürkün, O. Sex hormones affect spatial abilities during the menstrual cycle. Behav. Neurosci. 2000, 114, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messier, V.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; Barbat-Artigas, S.; Elisha, B.; Karelis, A.D.; Aubertin-Leheudre, M. Menopause and sarcopenia: A potential role for sex hormones. Maturitas 2011, 68, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greendale, G.A.; Lee, N.P.; Arriola, E.R. The menopause. Lancet 1999, 353, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidy, L. Biological aspects of menopause: Across the lifespan. Annu. Rev. Anthropol. 1994, 23, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco-Téllez, C.; Cortés-Bonilla, M.; Ortiz-Luna, G.; Sánchez-Zelayeta, L.; Méndez-Serrano, H.; Salazar-Jiménez, C.; Zavala-García, A.; Sánchez-Cevallos, A. Quality of life and menopause. In Quality of Life-Biopsychosocial Perspectives; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, D.; Rymer, J. Symptoms of the menopause. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2009, 23, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, P.K.; Agarwal, M. Postmenopausal syndrome. Indian J. Psychiatry 2015, 57, S222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Safi, Z.A.; Santoro, N. Menopausal hormone therapy and menopausal symptoms. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 101, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, J.S.; Brown, M. Estrogen receptor target gene: An evolving concept. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornstrom, L.; Sjoberg, M. Mechanisms of estrogen receptor signaling: Convergence of genomic and nongenomic actions on target genes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grodin, J.; Siiteri, P.; MacDonald, P. Source of estrogen production in postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1973, 36, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, H.D.; Humphrey, L.L.; Nygren, P.; Teutsch, S.M.; Allan, J.D. Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy: Scientific review. JAMA 2002, 288, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-L.; Weiss, N.S.; Newcomb, P.; Barlow, W.; White, E. Hormone replacement therapy in relation to breast cancer. JAMA 2002, 287, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietel, M. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), breast cancer and tumor pathology. Maturitas 2010, 65, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuzick, J. Hormone replacement therapy and the risk of breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 2344–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cos, P.; De Bruyne, T.; Apers, S.; Berghe, D.V.; Pieters, L.; Vlietinck, A.J. Phytoestrogens: Recent developments. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adlercreutz, H.; Mazur, W. Phyto-oestrogens and western diseases. Ann. Med. 1997, 29, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.K.; Hortobagyi, G.N. The evolving role of specific estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs). Surg. Oncol. 1999, 8, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.H.; Jeong, H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X.; Kim, S.; Jang, C.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Sohn, J.; Park, H.J.; Sung, N.H. Evaluation of the biological activity of Opuntia ficus indica as a tissue-and estrogen receptor subtype-selective modulator. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Prasain, J.K.; Barnes, S. Review of the methods used in the determination of phytoestrogens. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 777, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, I.L.; Savić-Gajić, I.M.; Tačić, A.D.; Savić, I.M. Classification and biological activity of phytoestrogens: A review. Adv. Technol. 2017, 6, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dixon, R.A. Phytoestrogens. Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 2004, 55, 225–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basu, P.; Maier, C. Phytoestrogens and breast cancer: In vitro anticancer activities of isoflavones, lignans, coumestans, stilbenes and their analogs and derivatives. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1648–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, J. Spartina marshes in southern England: VI. Pattern of invasion in Poole Harbour. J. Ecol. 1965, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumel, A.; Ainouche, M.; Misset, M.; Gourret, J.; Bayer, R. Genetic evidence for hybridization between the native and the introduced Spartina alterniflora (Poaceae) in South-West France: Spartina x neyrautii re-examined. Plant Syst. Evol. 2003, 237, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, A.V.; Evans, P.R. Spartina anglica in great Britain. In Focus on Nature Conservation, Liverpool University, United Kingdom, 10th November 1982; Doody, P., Ed.; Nature Conservancy Council: Cambridgeshire, UK, 1984; Volume 5, pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.-K.; Kil, J.; Joo, Y.-K.; Jung, Y.-S. Distribution and botanical characteristics of unrecorded alien weed Spartina anglica in Korea. Weed Turfgrass Sci. 2015, 4, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.J.; Park, S.; Kim, E.; Kwon, H.; Park, H.-J.; Nam, J.-W.; Roh, S.-S.; Choi, H. Antioxidant, pancreatic lipase inhibitory and tyrosinase inhibitory activities of extracts of the invasive plant Spartina anglica (cord-grass). Antioxidants 2021, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.A.; Park, E.J.; Lee, D.; Song, J.H.; Lee, H.L.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, Y.; Jung, K.; Kang, K.S.; Yoo, J.E. Estrogenic activity of sanguiin H-6 through activation of estrogen receptor α coactivator-binding site. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2019, 25, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrankό, L.; Clifford, M.N. An unambiguous nomenclature for the acyl-quinic acids commonly known as chlorogenic acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3602–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olennikov, D.N.; Kashchenko, N.I. 1,5-Di-O-isoferuloylquinic acid and other phenolic compounds from pollen of Calendula officinalis. Chem. Nat. Comp. 2014, 50, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzl, P.; Chaves, A.L.; Mayer, J.E.; Rao, I.M.; Nair, M.G. Roots of nutrient-deprived Brachiaria species accumulate 1,3-di-O-trans-feruloylquinic acid. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz-Böttcher, B.M.; Ernst, L.; Maier, H.G. New stereoisomers of quinic acid and their lactones. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1991, 1991, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizzi, L.; Scarpati, M.L. Constitution of cynarine, the active principle of the artichoke. Nature 1954, 174, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Ren, G. A determination of potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from azuki beans (Vigna angularis). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 6445–6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rho, T.; Yoon, K.D. Chemical constituents of Nelumbo nucifera seeds. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2017, 23, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.T.; Kim, Y.; Jang, H.-J.; Oh, H.-M.; Lim, C.-H.; Lee, S.W.; Rho, M.-C. Study of the UV light conversion of feruloyl amides from Portulaca oleracea and their inhibitory effect on IL-6-induced STAT3 activation. Molecules 2016, 21, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N. Simple antifungal metabolites from a marine sponge, Halichondria sp. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Comp. Biochem. 1994, 107, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paech, K.; Webb, P.; Kuiper, G.G.; Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Kushner, P.J.; Scanlan, T.S. Differential ligand activation of estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ at AP1 sites. Science 1997, 277, 1508–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Washbrook, E.; Sarwar, N.; Bates, G.J.; Pace, P.E.; Thirunuvakkarasu, V.; Taylor, J.; Epstein, R.J.; Fuller-Pace, F.V.; Egly, J.-M. Phosphorylation of human estrogen receptor α at serine 118 by two distinct signal transduction pathways revealed by phosphorylation-specific antisera. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4921–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hulka, B.S.; Moorman, P.G. Reprint of Breast cancer: Hormones and other risk factors. Maturitas 2008, 61, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.K.; Paganini-Hill, A.; Wan, P.C.; Pike, M.C. Effect of hormone replacement therapy on breast cancer risk: Estrogen versus estrogen plus progestin. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 328–332. [Google Scholar]
- Parrella, A.; Lavorgna, M.; Criscuolo, E.; Russo, C.; Isidori, M. Estrogenic activity and cytotoxicity of six anticancer drugs detected in water systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.J.; Hsu, Y.L.; Huang, Y.F.; Tsai, E.M. Molecular mechanisms of anticancer effects of phytoestrogens in breast cancer. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.Y.; Jo, M.S.; Lee, D.; Baek, S.E.; Baek, J.; Yu, J.S.; Kim, K.H. Dual effects of isoflavonoids from Pueraria lobata roots on estrogenic activity and anti-proliferation of MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 83, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.-Y.; Seo, C.-S.; Baek, S.-E.; Lee, J.; Shin, M.-S.; Kang, K.S.; Lee, S.; Yoo, J.-E. Analysis and identification of active compounds from Gami-Soyosan toxic to MCF-7 human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higashihara, N.; Shiraishi, K.; Miyata, K.; Oshima, Y.; Minobe, Y.; Yamasaki, K. Subacute oral toxicity study of bisphenol F based on the draft protocol for the “Enhanced OECD Test Guideline no. 407”. Arch. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Kim, G.J.; Kwon, H.; Nam, J.-W.; Baek, J.Y.; Shim, S.H.; Choi, H.; Kang, K.S. Estrogenic Effects of Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Belowground and Aerial Parts of Spartina anglica. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040210
Lee S, Kim GJ, Kwon H, Nam J-W, Baek JY, Shim SH, Choi H, Kang KS. Estrogenic Effects of Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Belowground and Aerial Parts of Spartina anglica. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(4):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040210
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sullim, Geum Jin Kim, Hyukbean Kwon, Joo-Won Nam, Ji Yun Baek, Sang Hee Shim, Hyukjae Choi, and Ki Sung Kang. 2021. "Estrogenic Effects of Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Belowground and Aerial Parts of Spartina anglica" Marine Drugs 19, no. 4: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040210
APA StyleLee, S., Kim, G. J., Kwon, H., Nam, J. -W., Baek, J. Y., Shim, S. H., Choi, H., & Kang, K. S. (2021). Estrogenic Effects of Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Belowground and Aerial Parts of Spartina anglica. Marine Drugs, 19(4), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040210