Neuronal Modulators from the Coral-Associated Fungi Aspergillus candidus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
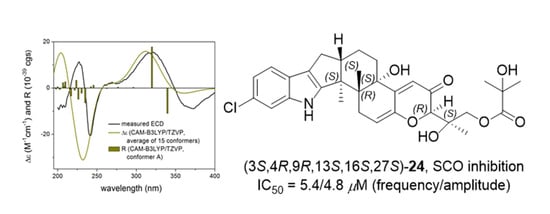
2. Results
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Material
3.3. Culture, Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Neuronal Modulatory Activity Assay In Vitro
3.5. Computational Section
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klich, M.A. Biogeography of Aspergillus species in soil and litter. Mycologia 2002, 94, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-K.; Xie, C.-L.; Xing, C.-P.; Wang, B.-Q.; Tian, X.-X.; Xia, J.-M.; Jia, L.-Y.; Pan, Y.-N.; Yang, X.-W. Cytotoxic p-terphenyls from the deep-sea-derived Aspergillus candidus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lu, F.; Bao, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, B.; Li, E.; Wang, Z.; Xie, L.; Guo, C.; Xue, Y.; et al. Terphenyl derivatives and terpenoids from a wheat-born mold Aspergillus candidus. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Inada, H.; Hayashi, A.; Higashimoto, K.; Pruksakorn, P.; Kamada, S.; Arai, M.; Ishida, S.; Kobayashi, M. Prenylterphenyllin and its dehydroxyl analogs, new cytotoxic substances from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus candidus IF10. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buttachon, S.; Ramos, A.A.; Inácio, Â.; Dethoup, T.; Gales, L.; Lee, M.; Costa, P.M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Sekeroglu, N.; Rocha, E.; et al. Bis-indolyl benzenoids, hydroxypyrrolidine derivatives and other constituents from cultures of the marine sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus candidus KUFA0062. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, T.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, S.; Xie, Y.Y.; Cui, Z.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Mao, Z.L. A new p-terphenyl derivative from the insect-derived fungus Aspergillus candidus Bdf-2 and the synergistic effects of terphenyllin. PeerJ 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L. Aspergivones A and B, two new flavones isolated from a gorgonian-derived Aspergillus candidus fungus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 31, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Che, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Prenylated p-terphenyls from a mangrove endophytic fungus, Aspergillus candidus LDJ-5. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Li, S.J.; Guo, Z.K.; Zhang, W.J.; Wei, W.; Tan, R.X.; Jiao, R.H. New p-terphenyls from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. YXf3. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Zhao, B.B.; Lu, C.H.; Huang, J.J.; Shen, Y.M. Two new p-terphenyl derivatives from the marine fungal strain Aspergillus sp. AF119. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, S.; Sun, S.; Zhou, H.; Kong, X.; Gu, Q. Prenylated polyhydroxy-p-terphenyls from Aspergillus taichungensis ZHN-7-07. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchelli, R.; Vining, L.C. Terphenyllin, a novel p-terphenyl metabolite from Aspergillus Candidus. J. Antibiot. 1975, 28, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munden, J.E.; Butterworth, D.; Hanscomb, G.; Verrall, M.S. Production of chlorflavonin, an antifungal metabolite of Aspergillus candidus. Appl. Microbiol. 1970, 19, 718–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamigauchi, T.; Sakazaki, R.; Nagashima, K.; Kawamura, Y.; Yasuda, Y.; Matsushima, K.; Tani, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Ishii, K.; Suzuki, R.; et al. Terprenins, novel immunosuppressants produced by Aspergillus candidus. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.-H.; Sun, Y.-Z.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Tang, H.; Li, J.; Su, L.; Zhuang, C.-L.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Zhang, W. Osteoclastogenesis regulation metabolites from the coral-associated fungus Pseudallescheria boydii TW-1024-3. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-L.; Li, R.; Li, J.; He, J.; Cao, Z.-Y.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Zheng, G.-L.; Zhang, W. Alternarin A, a drimane meroterpenoid, suppresses neuronal excitability from the coral-associated fungi Alternaria sp. ZH-15. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 2995–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Cai, F.Y.; Lauro, G.; Tang, H.; Su, L.; Wang, H.L.; Li, H.H.; Mándi, A.; Kurtán, T.; Riccio, R. Immunomodulatory biscembranoids and assignment of their relative and absolute configurations: Data set modulation in the density functional theory/nuclear magnetic resonance approach. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, X.B.; Lou, H.X. Structural and biological diversity of natural p-terphenyls. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-K. Natural terphenyls: developments since 1877. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 2209–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanets, E.V.; Yurchenko, A.N.; Smetanina, O.F.; Rasin, A.B.; Zhuravleva, O.I.; Pivkin, M.V.; Popov, R.S.; Von Amsberg, G.; Afiyatullov, S.S.; Dyshlovoy, S.A. Asperindoles A–D and a p-terphenyl derivative from the ascidian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. KMM 4676. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, S.-Z.; Pu, X.; Luo, G.; Zhao, L.-X.; Xu, L.-H.; Li, W.-J.; Luo, Y. Isolation and characterization of new p-terphenyls with antifungal, antibacterial, and antioxidant activities from halophilic actinomycete Nocardiopsis gilva YIM 90087. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2013, 61, 3006–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Tagami, K.; Minami, A.; Matsumoto, T.; Oikawa, H. Reconstitution of biosynthetic machinery for the synthesis of the highly elaborated indole diterpene penitrem. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday-Finch, S.C.; Wilkins, A.L.; Miles, C.O.; Tomoda, H.; Ōmura, S. Isolation and structure elucidation of lolilline, a possible biosynthetic precursor of the lolitrem family of tremorgenic mycotoxins. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 1997, 45, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ozaki, T.; Harada, M.; Miyasaka, T.; Sato, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Kanazawa, J.; Liu, C.; Maruyama, J.-I.; Adachi, M.; et al. Biosynthesis of indole diterpene lolitrems: Radical-induced cyclization of an epoxyalcohol affording a characteristic lolitremane skeleton. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 17996–18002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawada, K.; Arimura, A.; Tsuri, T.; Fuji, M.; Komurasaki, T.; Yonezawa, S.; Kugimiya, A.; Haga, N.; Mitsumori, S.; Inagaki, M.; et al. Total synthesis of terprenin, a highly potent and novel immunoglobulin E antibody suppressant. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, M.; Morita, A.; Kuwahara, S. Total synthesis of the tremorgenic indole diterpene paspalinine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 12833–12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, H.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Zhuang, C.-L.; Su, L.; Zheng, G.-L.; Zhang, W. Swinhoeisterols from the south china sea sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurobane, I.; Vining, L.C.; McInnes, A.G.; Smith, D.G. 3-Hydroxyterphenyllin, a new metabolite of Aspergillus candidus. Structure elucidation by H and C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Antibiot. 1979, 32, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belofsky, G.N.; Gloer, K.B.; Gloer, J.B.; Wicklow, D.T.; Dowd, P.F. New p-terphenyl and polyketide metabolites from the sclerotia of Penicillium raistrickii. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, C.; Yoshihira, K.; Natori, S.; Umeda, M. The structures of toxic metabolites of Aspergillus candidus. I. The compounds A and E, cytotoxic p-terphenyls. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1976, 24, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, A.; Takemura, A.; Koshimizu, K.; Nagano, H.; Kawazu, K. Candidusin A and B: New p-terphenyls with cytotoxic effects on sea urchin embryos. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1982, 46, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liao, Y.; Tang, C.; Huang, X.; Luo, Z.; Chen, J.; Cai, P. Cytotoxic and antibacterial compounds from the coral-derived fungus Aspergillus tritici SP2-8-1. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mándi, A.; Kurtán, T. Applications of OR/ECD/VCD to the structure elucidation of natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 889–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.S.; Yan, R.J.; Yu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Mándi, A.; Shen, L.; Kurtán, T.; Wu, J. Determination of the absolute configuration of super-carbon-chain compounds by a combined chemical, spectroscopic, and computational approach: Gibbosols A and B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13028–13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.G.; Goodman, J.M. Assigning stereochemistry to single diastereoisomers by GIAO NMR calculation: The DP4 probability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12946–12959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kashef, D.H.; Daletos, G.; Plenker, M.; Hartmann, R.; Mándi, A.; Kurtán, T.; Weber, H.; Lin, W.; Ancheeva, E.; Proksch, P. Polyketides and a dihydroquinolone alkaloid from a marine-derived strain of the fungus Metarhizium marquandii. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimblat, N.; Zanardi, M.M.; Sarotti, A.M. Beyond dp4: An improved probability for the stereochemical assignment of isomeric compounds using quantum chemical calculations of nmr shifts. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12526–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Cui, Y.; Nguyen, H.M.; Jenkins, D.P.; Wulff, H.; Pessah, I.N. Nanomolar bifenthrin alters synchronous Ca2+ oscillations and cortical neuron development independent of sodium channel activity. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, J.; Zou, X.; Zhao, F.; Guo, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; Feng, W.; Pessah, I.N.; et al. Saikosaponin d causes apoptotic death of cultured neocortical neurons by increasing membrane permeability and elevating intracellular Ca2+ concentration. Neurotoxicology 2019, 70, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinner, B.; Friedrich, O.; Zink, W.; Martin, E.; Fink, R.H.; Graf, B.M. Ketamine stereoselectively inhibits spontaneous Ca2+-oscillations in cultured hippocampal neurons. Anesth. Analg. 2005, 100, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nathalie, P.; Ana, M.L.M.; Shapiro, M.S. New in vitro phenotypic assay for epilepsy: Fluorescent measurement of synchronized neuronal calcium oscillations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84755. [Google Scholar]
- MacroModel. Schrödinger LLC, 2015. Available online: http://www.schrodinger.com/macromodel (accessed on 17 March 2021).
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Revision E.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, P.J.; Harada, N. ECD cotton effect approximated by the Gaussian curve and other methods. Chirality 2010, 22, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamo, C.; Barone, V. Exchange functionals with improved long-range behavior and adiabatic connection methods without adjustable parameters: The mPW and mPW1PW models. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 108, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierens, G.K. 1H and 13C NMR scaling factors for the calculation of chemical shifts in commonly used solvents using density functional theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2014, 35, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varetto, U. Molekel 5.4; Swiss National Supercomputing Centre: Manno, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]






| Position | 1 (in CDCl3) | 17 (in DMSO) | 18 (in DMSO) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δHa (J in Hz) | δCb, Type | δHc (J in Hz) | δCb, Type | δHa (J in Hz) | δCb, Type | |
| 1 | 125.7, C | 111.7, C | 112.6, C | |||
| 2 | 7.36, d (8.5) | 132.2, CH | 2.30, s | 9.5, CH3 | 2.25, s | 9.4, CH3 |
| 3 | 6.92, d (8.5) | 115.2, CH | ||||
| 4 | 154.8, C | 169.4, C | ||||
| 5 | 6.92, d (8.5) | 115.2, CH | 4.51, d (5.7) | 53.5, CH2 | 3.93, s | 31.6, CH2 |
| 6 | 7.36, d (8.5) | 132.2, CH | 152.2, C | 145.8, C | ||
| 1′ | 116.1, C | 119.1, C | 119.0, C | |||
| 2′ | 147.3, C | 146.9, C | 146.9, C | |||
| 3′ | 138.9, C | 135.9, C | 135.7, C | |||
| 4′ | 132.8, C | 129.0, C | 128.9, C | |||
| 5′ | 6.46, s | 104.0, CH | 6.57, s | 105.0, CH | 6.58, s | 105.2, CH |
| 6′ | 153.5, C | 149.6, C | 149.3, C | |||
| 1″ | 130.3, C | 128.6, C | 128.6, C | |||
| 2″ | 7.44, d (2.5) | 130.0, CH | 7.38, d (8.7) | 130.3, CH | 7.37, d (8.5) | 130.3, CH |
| 3″ | 130.2, C | 6.83, d (8.7) | 115.0, CH | 6.83, d (8.5) | 115.0, CH | |
| 4″ | 157.0, C | 156.5, C | 156.5, C | |||
| 5″ | 6.93, d (8.7) | 110.3, CH | 6.83, d (8.7) | 115.0, CH | 6.83, d (8.5) | 115.0, CH |
| 6″ | 7.45, dd (8.7, 2.5) | 127.2, CH | 7.38, d (8.7) | 130.3, CH | 7.37, d (8.5) | 130.3, CH |
| 1‴ | 3.38, d (7.5) | 28.7, CH2 | ||||
| 2‴ | 5.36, t (7.5) | 122.5, CH | ||||
| 3‴ | 132.8, C | |||||
| 4‴ | 1.73, s | 18.0, CH3 | ||||
| 5‴ | 1.75, s | 26.0, CH3 | ||||
| 4-OMe | 3.66, s | 52.1, CH3 | ||||
| 3′-OMe | 3.45, s | 60.8, CH3 | 3.71, s | 60.4, CH3 | 3.68, s | 60.3, CH3 |
| 6′-OMe | 3.74, s | 56.1, CH3 | 3.85, s | 55.7, CH3 | 3.85, s | 55.7, CH3 |
| 4″-OMe | 3.89, s | 55.6, CH3 | ||||
| 5-OH | 5.28, t (5.7) | |||||
| 2′-OH | 5.94, s | |||||
| 4″-OH | 9.51, s | 9.48, s | ||||
| Position | 22 (in CDCl3) | 23 (in CDCl3) | 24 (in DMSO) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δHa (J in Hz) | δCb, Type | δHc (J in Hz) | δCb, Type | δHa (J in Hz) | δCb, Type | |
| 1-NH | 7.70, s | 7.72, s | 10.96, s | |||
| 2 | 152.0, C | 152.8, C | 153.9, C | |||
| 3 | 52.0, C | 52.1, C | 50.4, C | |||
| 4 | 39.4, C | 39.4, C | 42.7, C | |||
| 5α | 1.87, dd (11.5, 9.2) | 27.3, CH2 | 1.84, ov d | 27.2, CH2 | 2.37, dd (17.0, 6.0) | 30.6, CH2 |
| 5β | 2.65, dd (11.5, 9.5) | 2.60, ov d | 3.02, d (17.0) | |||
| 6α | 2.23, dd (13.0, 9.2) | 31.1, CH2 | 2.12, dd (13.2, 9.0) | 30.7, CH2 | 5.69, m | 111.5, CH |
| 6β | 2.66, dd (13.0, 9.5) | 2.61, ov d | ||||
| 7 | 94.5, C | 94.0, C | 145.0, C | |||
| 9 | 4.05, d (2.0) | 84.0, CH | 4.81, d (2.4) | 79.2, CH | 4.25, d (1.5) | 82.1, CH |
| 10 | 196.5, C | 196.0, C | 194.7, C | |||
| 11 | 6.24, s | 120.7, CH | 6.22, s | 120.4, CH | 5.84, s | 116.1, CH |
| 12 | 158.9, C | 159.8, C | 154.5, C | |||
| 13 | 78.9, C | 78.8, C | 73.8, C | |||
| 14α | 2.00, ovd | 33.9, CH2 | 2.00, ov d | 33.8, CH2 | 1.93, ovd | 31.7, CH2 |
| 14β | 1.97, ovd | 1.96, dd (13.2, 4.8) | 1.83, ovd | |||
| 15α | 2.08, dd (13.0, 4.0) | 21.3, CH2 | 2.09, ov d | 21.3, CH2 | 1.92, ovd | 21.1, CH2 |
| 15β | 1.82, m | 1.82, ov d | 1.66, m | |||
| 16 | 2.83, m | 48.6, CH | 2.82, m | 48.7, CH | 2.72, m | 49.3, CH |
| 17α | 2.45, dd (13.2, 11.0) | 27.7, CH2 | 2.43, dd (13.2, 10.2) | 27.7, CH2 | 2.33, dd (13.0, 10.5) | 26.8, CH2 |
| 17β | 2.74, dd (13.2, 6.5) | 2.71, dd (13.2, 6.0) | 2.61, dd (13.0, 7.0) | |||
| 18 | 117.4, C | 117.5, C | 115.3, C | |||
| 19 | 125.3, C | 123.9, C | 123.3, C | |||
| 20 | 7.43, dd (6.7, 2.0) | 118.7, CH | 7.31, d (8.4) | 119.3, CH | 7.28, d (8.5) | 118.9, CH |
| 21 | 7.08, td (6.7, 2.0) | 119.9, CH | 7.04, dd (8.4, 1.8) | 120.4, CH | 6.92, dd (8.5, 2.0) | 118.8, CH |
| 22 | 7.10, td (6.7, 2.0) | 120.7, CH | 126.4, C | 123.9, C | ||
| 23 | 7.31, dd (6.7, 2.0) | 111.7, CH | 7.28, d (1.8) | 111.6, CH | 7.26, d (2.0) | 111.3, CH |
| 24 | 139.9, C | 140.2, C | 140.3, C | |||
| 25 | 1.38, s | 16.4, CH3 | 1.37, s | 16.4, CH3 | 1.29, s | 16.4, CH3 |
| 26 | 1.16, s | 24.5, CH3 | 1.14, s | 24.5, CH3 | 0.99, s | 19.7, CH3 |
| 27 | 66.8, C | 76.9, C | 74.3, C | |||
| 28α | 3.64, dd (12.0, 2.0) | 68.2, CH2 | 4.21, dd (13.2, 2.4) | 65.0, CH2 | 3.88, s | 67.9, CH2 |
| 28β | 3.75, d (12.0) | 3.69, d (13.2) | ||||
| 29 | 1.07, s | 18.9, CH3 | 1.37, s | 17.3, CH3 | 1.30, s | 21.9, CH3 |
| 1′ | 176.9, C | 175.5, C | ||||
| 2′ | 72.5, C | 71.3, C | ||||
| 3′ | 1.52, s | 27.4, CH3 | 1.29, s | 27.3, CH3 | ||
| 4′ | 1.53, s | 27.3, CH3 | 1.29, s | 27.3, CH3 | ||
| 13-OH | 4.98, s | |||||
| 27-OH | 5.06, d (1.5) | |||||
| 2′-OH | 5.26, s | |||||
| Compounds | SCOs EC50 (μM, Mean ± SEM) | 4-AP-induced SCOs EC50 (μM, Mean ± SEM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitude | Frequency | Amplitude | Frequency | |
| 6 | 10.28 ± 1.22 | 6.96 ± 0.73 | 28.45 ± 1.65 | 27.08 ± 2.94 |
| 17 | 3.86 ± 0.06 | 2.32 ± 0.67 | 3.70 ± 2.11 | 1.90 ± 1.04 |
| 18 | 1.85 ± 0.21 | 2.68 ± 0.04 | 3.88 ± 0.09 | 3.67 ± 0.01 |
| 24 | 5.62 ± 1.39 | 4.77 ± 0.14 | 6.05 ± 0.83 | 3.49 ± 0.51 |
| 9 | 7.48 ± 0.09 | 5.32 ± 3.92 I | N/T | N/T |
| 14 | 2.40 ± 0.57 | 0.26 ± 0.08 I | N/T | N/T |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, G.-Y.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; He, J.; Cao, Z.-Y.; Tang, H.; Mao, S.-C.; Zhang, W. Neuronal Modulators from the Coral-Associated Fungi Aspergillus candidus. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050281
Peng G-Y, Kurtán T, Mándi A, He J, Cao Z-Y, Tang H, Mao S-C, Zhang W. Neuronal Modulators from the Coral-Associated Fungi Aspergillus candidus. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(5):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050281
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Gao-Yang, Tibor Kurtán, Attila Mándi, Jing He, Zheng-Yu Cao, Hua Tang, Shui-Chun Mao, and Wen Zhang. 2021. "Neuronal Modulators from the Coral-Associated Fungi Aspergillus candidus" Marine Drugs 19, no. 5: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050281
APA StylePeng, G. -Y., Kurtán, T., Mándi, A., He, J., Cao, Z. -Y., Tang, H., Mao, S. -C., & Zhang, W. (2021). Neuronal Modulators from the Coral-Associated Fungi Aspergillus candidus. Marine Drugs, 19(5), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050281