The Anti-Viral Applications of Marine Resources for COVID-19 Treatment: An Overview
Abstract
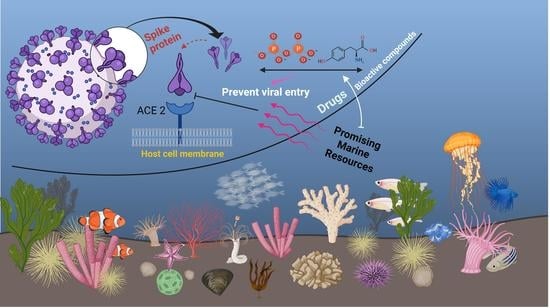
:1. Introduction
2. Marine Natural Polymer: Inorganic Polyphosphate for COVID-19 Treatment
3. Promising Compounds from Marine Algae, Bacteria, Sponges, and Fish for COVID-19 Treatment
4. Promising Advantages and Limitations of Marine Resources
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Velavan, T.; Meyer, C. The COVID-19 epidemic. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2020, 25, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Y.; Shang, J.; Graham, R.; Baric, R.S.; Li, F. Receptor recognition by novel coronavirus from Wuhan: An analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00127-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chien, C.; Yasmishyn, A.; Yang, Y.; Lai, W.; Luo, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chang, P.; et al. Highlight of immune pathogenic response and hematopathologic effect in SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-Cov-2 infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taglialatela-Scafati, O. New hopes for drugs against COVID-19 come from the sea. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Approves First Treatment for COVID-19. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-treatment-covid-19 (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- The Recovery Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19—Preliminary Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinner, C.D.; Gottlieb, R.L.; Criner, G.; Arribas López, J.R.; Cattelan, A.M.; Soriano Viladomiu, A.; Ogbuagu, O.; Malhotra, P.; Mullane, K.M.; Castagna, A.; et al. Effect of Remdesivir vs Standard Care on Clinical Status at 11 Days in Patients With Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium. Repurposed antiviral drugs for COVID-19—Interim WHO SOLIDARITY Trial Results. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 384, 497–511. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Peto, R.; Karim, Q.A.; Alejandria, M.; Restrepo, A.M.H.; García, C.H.; Kieny, M.P.; Malekzadeh, R.; Murthy, S.; Preziosi, M.-P. Repurposed antiviral drugs for COVID-19—Interim WHO SOLIDARITY trial results. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.D.; Lye, D.C.B.; Hui, D.S.; Marks, K.M.; Bruno, R.; Montejano, R.; Spinner, C.D.; Galli, M.; Ahn, M.Y.; Nahass, R.G.; et al. Remdesivir for 5 or 10 days in patients with severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—Preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hossary, E.M.; Cheng, C.; Hamed, M.M.; Hamed, A.N.E.-S.; Ohlsen, K.; Hentschel, U.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Antifungal potential of marine natural products. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 126, 631–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; El-Hossary, E.M.; Oelschlaeger, T.A.; Donia, M.S.; Quinn, R.J.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Potential of marine natural products against drug-resistant bacterial infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e237–e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shady, N.H.; El-Hossary, E.M.; Fouad, M.A.; Gulder, T.A.M.; Kamel, M.S.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Bioactive natural products of marine sponges from the genus Hyrtios. Molecules 2017, 22, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A. Collagen of extracellular matrix from marine invertebrates and its medical applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanium, D.; Hanna, L.; Maheshkumar, K.; Ponmurugan, K.; Al-dhabi, N.; Murugan, P. Immune stimulatory and anti-HIV-1 potential of extracts derived from marine brown algae Padina tetrastromatica. J. Complementary Integr. Med. 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izumida, M.; Suga, K.; Ishibashi, F.; Kubo, Y. The Spirocyclic Imine from a Marine Benthic Dinoflagellate, Portimine, Is a Potent Anti-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Therapeutic Lead Compound. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terasawa, M.; Hayashi, K.; Lee, J.B.; Nishiura, K.; Matsuda, K.; Hayashi, T.; Kawahara, T. Anti-influenza A virus activity of rhamnan sulfate from green algae Monostroma nitidum in mice with normal and compromised immunity. Mar. Drugs 2020, 28, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Neufurth, M.; Schepler, H.; Wang, S.; Tolba, E.; Schröder, H.C.; Wang, X.H. The biomaterial polyphosphate blocks stoichiometrically binding of the SARS-CoV-2 S-protein to the cellular ACE2 receptor. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 6603–6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Neufurth, M.; Wang, S.; Tan, R.; Schroder, H.C.; Wang, X. Morphogenetic (mucin expression) as well as potential anti-corona viral activity of the marine secondary metabolite polyphosphate on A549 cells. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufurth, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Schroder, H.C.; Müller, W.E.G. Caged dexamethasone/quercetin nanoparticles, formed of the morphogenetic active inorganic polyphosphate, are strong inducers of MUC5AC. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Neufurth, M.; Wang, S.; Schröder, H.C.; Wang, X. Polyphosphate Reverses the Toxicity of the Quasi-Enzyme Bleomycin on Alveolar Endothelial Lung Cells In Vitro. Cancers 2021, 13, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufurth, M.; Wang, X.H.; Tolba, E.; Lieberwirth, I.; Wang, S.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E.G. The inorganic polymer, polyphosphate, blocks binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to ACE2 receptor at physiological concentrations. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 182, 114215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, V.; Dae-Young Kong, D.Y.; Asadzadeh, F.; Marrone, L.; Siciliano, R.; Cerino, P.; Criscuolo, G.; Pisano, I.; Quarantelli, F.; Izzo, B.; et al. Long-chain polyphosphates impair SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication: A route for therapy in man. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Balasubramanian, S.A.; Oelschlaeger, T.; Grkovic, T.; Pham, N.B.; Quinn, R.J.; Hentschel, U. Potential of marine natural products against drug-resistant fungal, viral, and parasitic infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e30–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Bayer, K.; Hentschel, U. Diversity, abundance and natural products of marine sponge-associated actinomycetes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hossary, E.M.; Abdel-Halim, M.; Ibrahim, E.S.; Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; Nodwell, J.R.; Handoussa, H.; Abdelwahab, M.F.; Holzgrabe, U.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Natural Products Repertoire of the Red Sea. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahran, E.M.; Albohy, A.; Khalil, A.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Ahmed, H.A.; El-Hossary, E.M.; Bringmann, G.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Bioactivity potential of marine natural products from Scleractinia-associated microbes and in silico anti-SARS-COV-2 evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, D.; Patamia, V.; Scala, A.; Sciortino, M.T.; Piperno, A.; Rescifina, A. Putative inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease from a library of marine natural products: A virtual screening and molecular modeling study. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.T.; Ali, A.; Wang, Q.; Irfan, M.; Khan, A.; Zeb, M.T.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Chinnasamy, S.; Wei, D.Q. Marine natural compounds as potents inhibitors against the main protease of SARS-CoV-2-a molecular dynamic study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendyala, B.; Patras, A. In silico screening of food bioactive compounds to predict potential inhibitors of COVID-19 main protease (Mpro) and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). ChemRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, L.; Vernes, L.; Cadoret, J.-P. Docking and in silico toxicity assessment of Arthrospira compounds as potential antiviral agents against SARS-CoV-2. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 33, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nagle, V.; Gaikwad, M.; Pawar, Y.; Dasgupta, S. Marine red alga Porphyridium sp. as a source of sulfated polysaccharides (SPs) for combating against COVID-19. Preprints 2020, 2020040168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, P.S.; Oh, H.; Kwon, S.-J.; Jin, W.; Zhang, F.; Fraser, K.; Hong, J.J.; Linhardt, R.J.; Dordick, J.S. Sulfated polysaccharides effectively inhibit SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surti, M.; Patel, M.; Adnan, M.; Moin, A.; Ashraf, S.A.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Snoussi, M.; Deshpande, S.; Reddy, M.N. Ilimaquinone (marine sponge metabolite) as a novel inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 key target proteins in comparison with suggested COVID-19 drugs: Designing, docking and molecular dynamics simulation study. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 37707–37720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, A.; Le, N.T.; Selisko, B.; Eydoux, C.; Alvarez, K.; Guillemot, J.C.; Decroly, E.; Peersen, O.; Ferron, F.; Canard, B. Remdesivir and SARS-CoV-2: Structural requirements at both nsp12 RdRp and nsp14 Exonuclease active-sites. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, N.; Ehrlich, H.; Eisenhofer, G.; Ehrlich, A.; Meschke, S.; Ziegler, C.G.; Bornstein, S.R. Anti–tumorigenic and anti–metastatic activity of the sponge–derived marine drugs Aeroplysinin–1 and Isofistularin–3 against Pheochromocytoma in vitro. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovalchuk, V.; Voronkina, A.; Binnewerg, B.; Schubert, M.; Muzychka, L.; Wysokowski, M.; Tsurkan, M.; Bechmann, N.; Petrenko, I.; Fursov, A.; et al. Naturally drug loaded chitin: Isolation and applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drechsel, A.; Helm, J.; Ehrlich, H.; Pantovic, S.; Bornstein, S.; Bechmann, N. Anti-tumor activity vs. normal cell toxicity: Therapeutic potential of the bromotyrosines Aerothionin and Homoaerothionin in vitro. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnewerg, B.; Schubert, M.; Voronkina, A.; Muzychka, L.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Djurović, M.; Kovalchuk, V.; Tsurkan, M.; Martinovic, R.; et al. Marine biomaterials: Biomimetic and pharmacological potential of cultivated Aplysina aerophoba marine demosponge. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Vilas, J.A.; Martínez-Poveda, B.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.Á. Aeroplysinin-1, a sponge-derived multi-targeted bioactive marine drug. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, Y.; Shin, H.; Lee, M.K.; Kwon, O.S.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, C.W.; Lee, H.-R.; Kim, M. Antiviral activity of lambda-carrageenan against influenza viruses and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, A.; Arora, P.; Prajapati, S.K. Can Algal derived bioactive metabolites serve as potential therapeutics for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 like viral infection? Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 596374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Peng, H.R.; Wang, Q.L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Dong, X.P.; Wen, C.R.; Ai, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhu, B.W. Inhibitory activities of marine sulfated polysaccharides against SARS-CoV-2. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7415–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- From the Sea: A Marine Substance Can Inhibit COVID-19 Pathogen. Available online: https://climatechangeresearch.ca/press-release/ (accessed on 27 April 2021).
- Muzychka, L.; Voronkina, A.; Kovalchuk, V.; Smolii, O.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Youssef, D.; Ehrlich, I.; Ehrlich, H. Marine biomimetics: Bromotyrosines loaded chitinous skeleton as source of antibacterial agents. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Du, Y. Enzymatic preparation of κ-carrageenan oligosaccharides and their anti-angiogenic activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Mao, X.; Peng, X.; Tang, S. Effects of sulfate group in red seaweed polysaccharides on anticoagulant and cytotoxicity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Hao, C.; Zhang, X.-E.; Cui, Z.-Q.; Guan, H.-S. In vitro inhibitory effect of carrageenan oligosaccharide on influenza A H1N1 virus. Antivir. Res. 2011, 92, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yan, X.; Lin, J.; Wang, F.; Xu, W. Depolymerized products of lambda-carrageenan as a potent angiogenesis inhibitor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6910–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, M.; Jayaraman, G. Marine Sulfated Polysaccharides has potential antiviral drug candidates to treat Corona Virus disease (COVID-19). Carbohydr Res. 2021, 505, 108326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.; Wemheuer, B.; Laffy, P.W.; Webster, N.S.; Thomas, T. Taxonomic, functional and expression analysis of viral communities associated with marine sponges. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.E.; Steenhuis, P.; de Moraes, K.R.; van der Meer, J.; Thieltges, D.W.; Brussaard, C.P.D. Marine virus predation by non-host organisms. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascelli, C.; Laffy, P.W.; Botté, E.; Kupresanin, M.; Rattei, T.; Lurgi, M.; Ravasi, T.; Webster, N.S. Viral ecogenomics across the Porifera. Microbiome 2020, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadas, E.; Marie, D.; Shpigel, M.; Ilan, M. Virus predation by sponges is a new nutrient-flow pathway in coral reef food webs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1548–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinehart, K.L.; Shield, L.S.; Cohen-Parsons, M. Antiviral Substances. In Pharmaceutical and Bioactive Natural Products; Attaway, D.H., Zaborsky, O.R., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varijakzhan, D.; Loh, J.Y.; Yap, W.S.; Yusoff, K.; Seboussi, R.; Lim, S.E.; Lai, K.S.; Chong, C.M. bioactive compounds from marine sponges: Fundamentals and applications. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, S.; Kaur, M.; Minneman, K.P. Antiviral lead compounds from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs. 2010, 8, 2619–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamoda, A.M.; Fayed, B.; Ashmawy, N.S.; El-Shorbagi, A.A.; Hamdy, R.; Soliman, S.S.M. Marine sponge is a promising natural source of anti-SARS-CoV-2 scaffold. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 666664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pech-Puch, D.; Berastegui-Cabrera, J.; Pérez-Povedano, M.; Villegas-Hernández, H.; Guillén-Hernández, S.; Cautain, B.; Reyes, F.; Pachón, J.; Gómez, P.; Rodríguez, J.; et al. Antiviral and Antiproliferative Potential of Marine Organisms From the Yucatan Peninsula. Mexico Front. Mar. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udayangani, R.; Somasiri, G.; Wickramasinghe, I.; Kim, S. Potential health benefits of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae. Encycl. Mar. Biotech. 2020, 1, 629–635. [Google Scholar]
- Dryer, O. Covid-19: Remdesivir has little or no impact on survival, WHO trial shows. BMJ 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, R.; Luesch, H. Marine natural products: A new wave of drugs? Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shinde, P.; Banerjee, P.; Mandhare, A. Marine natural products as source of new drugs: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 283–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Marine Compound | Source | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Inorganic polyphosphate (polyP) [21,22,24,25] | Marine sponges, bacteria (ex. Cyanobacterium synepchcoccus) |
|
| Lambda-carrageenan [43] | Marine algae |
|
| Terphenyllin Tirandamycin A [29] | Scleractinia associated organisms |
|
| Phlorotannins (17 molecules) [30] | Sargassum spinuligerum brown algea |
|
| Five Marine compounds (C19H40O3, C16H30O2, C22H32O4, C21H26O3, C31H30Br6N4O11) [31] | Aplysindae Sponge, soft coral Pterogorgia citrina Petrosia strongylophora sp. |
|
| Phycocyanobilins (PCB) [32,33] | Cyanobacteria, algae rhodophytes |
|
| Sulfated Polysaccharides [34,35,44,45] | Cyanobacteria, brown algae (Saccharina japonica) |
|
| Bromotyrosines [40,41,46,47] | Marine sponges |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geahchan, S.; Ehrlich, H.; Rahman, M.A. The Anti-Viral Applications of Marine Resources for COVID-19 Treatment: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080409
Geahchan S, Ehrlich H, Rahman MA. The Anti-Viral Applications of Marine Resources for COVID-19 Treatment: An Overview. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(8):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080409
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeahchan, Sarah, Hermann Ehrlich, and M. Azizur Rahman. 2021. "The Anti-Viral Applications of Marine Resources for COVID-19 Treatment: An Overview" Marine Drugs 19, no. 8: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080409
APA StyleGeahchan, S., Ehrlich, H., & Rahman, M. A. (2021). The Anti-Viral Applications of Marine Resources for COVID-19 Treatment: An Overview. Marine Drugs, 19(8), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080409