Structural Characterization and Spatial Mapping of Tetrodotoxins in Australian Polyclads
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Separation and Identification of TTX and Its Analogues Using HILIC-HRMS
2.2. Optimization of Flatworm Sample Preparation for TTX MALDI-MSI
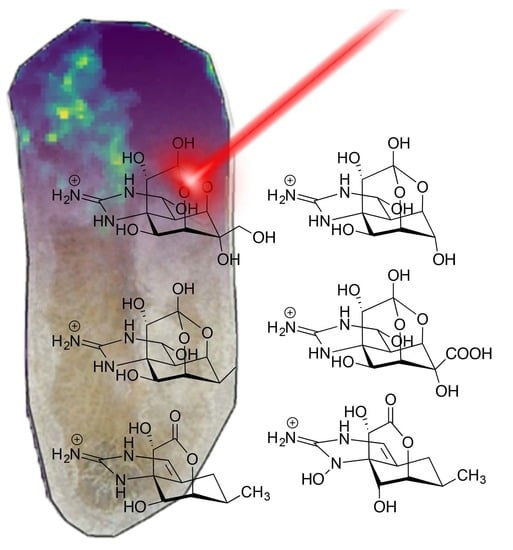
2.3. MALDI-MSI of Freeze Dried Stylochus sp. 1 Flatworms
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Flatworm Specimen Collection
4.2. Tetrodotoxin Analogue Separation and Analysis from Flatworms Using Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry
4.3. Spatial Mapping of TTX across Flatworms Using Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Imaging
4.4. Calibrant and Matrix Deposition
4.5. MALDI-TOF/TOF MS Data Acquisition
4.6. MALDI-TOF/TOF MS Data Analysis
4.7. Flatworm Specimen Identification
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, V.J.; Puglisi, M.P. Chemical mediation of interactions among marine organisms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, J.E.; De Nys, R.; Kumar, N.; Carson, D.G.; Steinberg, P.D. Induction of metamorphosis in the sea urchin Holopneustes purpurascens by a metabolite complex from the algal host Delisea pulchra. Biol. Bull. 2000, 198, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, J.E.; Carson, D.G.; De Nys, R.; Steinberg, P.D. Demographic consequences of an ontogenetic shift by a sea urchin in response to host plant chemistry. Ecology 2004, 85, 1355–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuso, P. Chemical ecology of the nudibranchs. In Bioorganic Marine Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; pp. 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, V.J.; Ritson-Williams, R. Marine chemical ecology. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 662–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglisi, M.P.; Sneed, J.M.; Sharp, K.H.; Ritson-Williams, R.; Paul, V.J. Marine chemical ecology in benthic environments. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1510–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patockaa, J.; Stredab, L. Brief review of natural nonprotein neurotoxins. ASA Newslett. 2002, 89, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.Z. Neurotoxins from marine dinoflagellates: A brief review. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 349–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A. Neurotoxins that act on voltage-sensitive sodium channels in excitable membranes. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1980, 20, 15–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bane, V.; Lehane, M.; Dikshit, M.; O’Riordan, A.; Furey, A. Tetrodotoxin: Chemistry, toxicity, source, distribution and detection. Toxins 2014, 6, 693–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chau, R.; Kalaitzis, J.A.; Neilan, B.A. On the origins and biosynthesis of tetrodotoxin. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 104, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Matsumoto, G.; Hanyu, Y. TTX resistivity of Na+ channel in newt retinal neuron. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 240, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T. TTX accumulation in pufferfish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2006, 1, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finefield, J.M.; Frisvad, J.C.; Sherman, D.H.; Williams, R.M. Fungal origins of the bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane ring system of prenylated indole alkaloids. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 812–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumura, K. Tetrodotoxin as a pheromone. Nature 1995, 378, 563–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Noguchi, T.; Hwang, D.F. Neurotoxin tetrodotoxin as attractant for toxic snails. Fish. Sci. 2004, 70, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.H.; Ho, P.H.; Hwang, C.C.; Hwang, P.A.; Cheng, C.A.; Hwang, D.F. Tetrodotoxin in several species of xanthid crabs in southern Taiwan. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.L. Behavioral and chemical ecology of marine organisms with respect to tetrodotoxin. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvitti, L.R.; Wood, S.A.; Winsor, L.; Cary, S.C. Intracellular immunohistochemical detection of tetrodotoxin in Pleurobranchaea maculata (Gastropoda) and Stylochoplana sp. (Turbellaria). Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrer, R.P.; Zimmer, R.K. Molecules of Keystone Significance: Crucial Agents in Ecology and Resource Management. Bioscience 2013, 63, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmer, R.K.; Ferrer, R.P. Neuroecology, chemical defense, and the keystone species concept. Biol. Bull. 2007, 213, 208–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNab, J.M.; Rodriguez, J.; Karuso, P.; Williamson, J.E. Natural Products in Polyclad Flatworms. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritson-Williams, R.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Paul, V.J. Ecological functions of tetrodotoxin in a deadly polyclad flatworm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3176–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Abe, Y.; Kudo, Y.; Ritson-Williams, R.; Paul, V.J.; Konoki, K.; Cho, Y.; Adachi, M.; Imazu, T.; Nishikawa, T.; et al. First identification of 5,11-dideoxytetrodotoxin in marine animals, and characterization of major fragment ions of tetrodotoxin and its analogs by high resolution ESI-MS/MS. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2799–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kashitani, M.; Okabe, T.; Oyama, H.; Noguchi, K.; Yamazaki, H.; Suo, R.; Mori, T.; Sugita, H.; Itoi, S. Taxonomic Distribution of Tetrodotoxin in Acotylean Flatworms (Polycladida: Platyhelminthes). Mar. Biotechnol. 2020, 22, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prudhoe, S. Some polyclad turbellarians new to the fauna of the Australian coasts. Rec. Aust. Mus. 1978, 31, 586–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, L.J.; Cannon, L.R.G. Biodiversity of tropical polyclad flatworms from the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mem. Queensl. Mus. 1994, 36, 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, L.J.; Cannon, L.R.G. Marine Flatworms: The world of Polyclads; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrguez, J.; Hutchings, P.A.; Williamson, J.E. Biodiversity of intertidal marine flatworms (Polycladida, Platyhelminthes) in southeastern Australia. Zootaxa 2021, 5024, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNabb, P.; Selwood, A.I.; Munday, R.; Wood, S.A.; Taylor, D.I.; Mackenzie, L.A.; van Ginkel, R.; Rhodes, L.L.; Cornelisen, C.; Heasman, K.; et al. Detection of tetrodotoxin from the grey side-gilled sea slug—Pleurobranchaea maculata, and associated dog neurotoxicosis on beaches adjacent to the Hauraki Gulf, Auckland, New Zealand. Toxicon 2010, 56, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Yasumoto, T. Tetrodotoxin derivatives in puffer fish. Toxicon 1985, 23, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, Y.; Okada, K.; Takatani, T.; Kawatsu, K.; Hamano, Y.; Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T. Intra-tissue distribution of tetrodotoxin in two marine puffers Takifugu vermicularis and Chelonodon patoca. Toxicon 2003, 41, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanu, M.B.; Mahmud, Y.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T.; Kajihara, H.; Kawatsu, K.; Hamano, Y.; Asakawa, M.; Miyazawa, K.; Noguchi, T. Immunoenzymatic visualization of tetrodotoxin (TTX) in Cephalothrix species (Nemertea: Anopla: Palaeonemertea: Cephalotrichidae) and Planocera reticulata (Platyhelminthes: Turbellaria: Polycladida: Planoceridae). Toxicon 2004, 44, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudd, D.; Ronci, M.; Johnston, M.R.; Guinan, T.; Voelcker, N.H.; Benkendorff, K. Mass spectrometry imaging reveals new biological roles for choline esters and Tyrian purple precursors in muricid molluscs. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspar, S.; Peukert, M.; Svatos, A.; Matros, A.; Mock, H.P. MALDI-imaging mass spectrometry–an emerging technique in plant biology. Proteomics 2011, 11, 1840–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellino, S.; Groseclose, M.R.; Wagner, D. MALDI imaging mass spectrometry: Bridging biology and chemistry in drug development. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 2427–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.-H.; Vetter, I.; Hamilton, B.; Sunagar, K.; Lavergne, V.; Dutertre, V.; Fry, B.G.; Antunes, A.; Venter, D.J. Evolution of separate predation-and defence-evoked venoms in carnivorous cone snails. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronci, M.; Rudd, D.; Guinan, T.; Benkendorff, K.; Voelcker, N.H. Mass spectrometry imaging on porous silicon: Investigating the distribution of bioactives in marine mollusc tissues. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8996–9001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bane, V.; Brosnan, B.; Barnes, P.; Lehane, M.; Furey, A. High-resolution mass spectrometry analysis of tetrodotoxin (TTX) and its analogues in puffer fish and shellfish. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2016, 33, 1468–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasenko, A.E.; Magarlamov, T.Y. Tetrodotoxin and its analogues in Cephalothrix cf. simula (Nemertea: Palaeonemertea) from the sea of Japan (Peter the Great Gulf): Intrabody distribution and secretions. Toxins 2020, 12, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Sugimoto, A.; Takai, A.; Yasumoto, T. Effects of Specific Modifications of Several Hydroxyls of Tetrodotoxin on Its Affinity to Rat Brain Membrane. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 1688. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.J.; Chai, T.J.; Jeng, S.S.; Hwang, D.F. Toxicity of the puffer Takifugu rubripes cultured in northern Taiwan. Fish. Sci. 1998, 64, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyman, L.H. The Invertebrates: Platyhelminthes and Rhynchocoela. The Acoelomate Bilateria; McGraw Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1951; Volume 2, p. 550. [Google Scholar]
- Galleni, L.; Tongiorgi, P.; Ferrero, E.; Salghetti, U. Stylochus mediterraneus (Turbellaria: Polycladida), predator on the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar. Biol. 1980, 55, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, L.J.; Cannon, L.R.G.; Govan, H. Stylochus-(Imogene)-Matatasi N-Sp (Platyhelminthes, Polycladida)—Pest of Cultured Giant Clams and Pearl Oysters from Solomon-Islands. Hydrobiologia 1993, 257, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Beal, M.A.; Johnston, E.L. A new predatory flatworm (Platyhelminthes, Polycladida) from Botany Bay, New South Wales, Australia. J. Nat. Hist. 2006, 39, 3987–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, W.A.; Newman, L.J. Halotolerance of the oyster predator, Imogine mcgrathi, a stylochid flatworm from Port Stephens, New South Wales, Australia. Hydrobiologia 2001, 459, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluys, R.; Faubel, A.; Rajagopal, S.; Van Der Velde, G. A new and alien species of “oyster leech”(Platyhelminthes, Polycladida, Stylochidae) from the brackish North Sea Canal, The Netherlands. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2005, 59, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bane, V.; Hutchinson, S.; Sheehan, A.; Brosnan, B.; Barnes, P.; Lehane, M.; Furey, A. LC-MS/MS method for the determination of tetrodotoxin (TTX) on a triple quadruple mass spectrometer. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2016, 33, 1728–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oya, Y.; Kajihara, H. Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis of Acotylea (Platyhelminthes: Polycladida). Zoolog. Sci. 2020, 37, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitelaw, B.L.; Cooke, I.R.; Finn, J.; Zenger, K.; Strugnell, J.M. The evolution and origin of tetrodotoxin acquisition in the blue-ringed octopus (genus Hapalochlaena). Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 206, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogure, K.; Do, H.K.; Thuesen, E.V.; Nanba, K.; Ohwada, K.; Simidu, U. Accumulation of Tetrodotoxin in Marine Sediment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 45, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, H.K.; Kogure, K.; Simidu, U. Identification of deep-sea-sediment bacteria which produce tetrodotoxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1162–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Do, H.K.; Kogure, K.; Imada, C.; Noguchi, T.; Ohwada, K.; Simidu, U. Tetrodotoxin production of actinomycetes isolated from marine sediment. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1991, 70, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Specimen | TTX (1) (Scan Channel m/z 320.1088) RT (min) | 11-Deoxy TTX (2) (Scan Channel m/z 304.1139) RT (min) | 11-norTTX-6(S)-ol (3) (Scan Channel m/z 290.0983) RT (min) | 6,11-Dideoxy TTX (4) (Scan Channel m/z 288.1190) RT (min) | Unknown Compound #1 (Scan Channel m/z 270.1085) RT (min) | 4,4a-Anhydro-5,6,11-trideoxy TTX (9) (Scan Channel m/z 254.1135) RT (min) | Unknown Compound #2 (Scan Channel m/z 334.0881) RT (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stylochus sp. 1 1 | 6.11 | 7.58 | 7.55 | ||||
| Stylochus sp. 1 1 | 6.15 | 7.58 | |||||
| Stylochus cf mcgrathi 2 | 18.01 | 6.06 | 7.61 | 4.91 | 8.59 | ||
| Stylochus cf mcgrathi 2 | 17.41 | 7.55 | 4.86 | 8.56 | |||
| Stylochus cf mcgrathi 2 | 18.29 | 6.02 | 7.61 | 4.75 | 8.47 | ||
| Stylochus cf mcgrathi 2 | 18.31 | 6.19 | 7.58 | 4.82 | 8.44 | 7.57 | |
| Stylochus cf mcgrathi 2 | 18.25 | 6.15 | 7.61 | 8.61 | |||
| Stylochus cf mcgrathi 3 | 17.55 | 7.55 | 4.78 | 8.54 | 7.54 | ||
| Stylochus cf mcgrathi 3 | 7.62 | 4.89 | 8.70 | ||||
| Stylochus cf mcgrathi 3 | 7.61 | 4.89 | 8.58 | 7.57 | |||
| Stylochus cf mcgrathi 3 | 7.59 | 4.89 | 8.60 | 8.01 | 7.59 | ||
| Stylochus sp. 3 4 | |||||||
| Stylochus sp. 4 1 | |||||||
| Echinoplana cf celerrima 5 | 7.56 | 4.80 | |||||
| Echinoplana cf celerrima 1 | 7.56 | 4.84 | |||||
| Echinoplana cf celerrima 1 | 7.58 | 4.84 | 7.54 | ||||
| Echinoplana cf celerrima 1 | 6.14 | 7.63 | 4.78 | 7.55 | |||
| Notoplana cf longiducta 5 | 7.56 | 4.78 | |||||
| Pseudoceros sp. 1 1 | 7.58 | 4.91 | 8.49 | ||||
| Pseudoceros sp. 2 1 | 6.20 | ||||||
| Pseudoceros sp. 3 1 | 7.55 | 8.48 | |||||
| Pseudoceros cf velutinus 4 | 7.62 | 4.84 | 8.60 | ||||
| Pseudoceros cf velutinus 4 | 6.17 | 7.53 | |||||
| Thysanozoon brocchii4 | 7.58 | 8.48 | |||||
| Thysanozoon brocchii4 | 7.61 | 8.58 | |||||
| Eurylepta sp. 1 | 8.03 | ||||||
| Cycloporus sp. 1 | 7.60 | 4.85 | |||||
| Cestoplana cf rubocincta 5 | 7.49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McNab, J.M.; Briggs, M.T.; Williamson, J.E.; Hoffmann, P.; Rodriguez, J.; Karuso, P. Structural Characterization and Spatial Mapping of Tetrodotoxins in Australian Polyclads. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120788
McNab JM, Briggs MT, Williamson JE, Hoffmann P, Rodriguez J, Karuso P. Structural Characterization and Spatial Mapping of Tetrodotoxins in Australian Polyclads. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(12):788. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120788
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcNab, Justin M., Matthew T. Briggs, Jane E. Williamson, Peter Hoffmann, Jorge Rodriguez, and Peter Karuso. 2022. "Structural Characterization and Spatial Mapping of Tetrodotoxins in Australian Polyclads" Marine Drugs 20, no. 12: 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120788
APA StyleMcNab, J. M., Briggs, M. T., Williamson, J. E., Hoffmann, P., Rodriguez, J., & Karuso, P. (2022). Structural Characterization and Spatial Mapping of Tetrodotoxins in Australian Polyclads. Marine Drugs, 20(12), 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120788