Mitigative Effects of PFF-A Isolated from Ecklonia cava on Pigmentation in a Zebrafish Model and Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
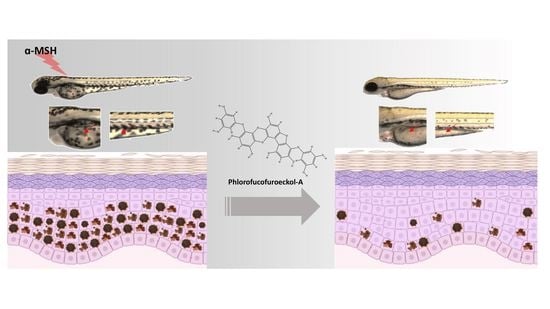
2.1. Melanin Synthesis Mitigative Activity of Low Doses of PFF-A in Zebrafish Larvae
2.2. Effects of Low Doses of PFF-A on Melanin Synthesis in B16F10 Cells and Tyrosinase Activity and Melanin Synthesis in α-MSH-treated B16F10 Cells
2.3. Low Doses of PFF-A Inhibit Melanogenesis by Regulating MITF Levels and Tyrosinase Activity via the PI3K/Akt Signaling in α-MSH-Exposed B16F10 Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Preparation and Isolation of PFF-A
3.3. Determination of Tyrosinase Activity
3.4. In Vivo Assays
3.4.1. Origin and Maintenance of Parental Zebrafish
3.4.2. Zebrafish Pigmentation Measurement
3.5. Cell Assay
3.5.1. Determination of Melanin Content
3.5.2. Cellular Tyrosinase Mitigative Activity
3.5.3. Western Blotting Analysis
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Han, E.; Chang, B.; Kim, D.; Cho, H.; Kim, S. Melanogenesis inhibitory effect of aerial part of Pueraria thunbergiana in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2015, 307, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.M.; Su, W.C.; Li, C.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Q.X.; Zheng, J.; Tang, D.L.; Chen, S.M.; Wang, Q. Anti-melanogenesis of novel kojic acid derivatives in B16F10 cells and zebrafish. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Song, H.; Seok, J.K.; Hong, S.S.; Boo, Y.C. Luteolin 7-Sulfate Attenuates Melanin Synthesis through Inhibition of CREB- and MITF-Mediated Tyrosinase Expression. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, Y.J.; Lee, E.H.; Kang, T.H.; Ha, S.K.; Oh, M.S.; Kim, S.M.; Yoon, T.J.; Kang, C.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.Y. Inhibitory effects of arbutin on melanin biosynthesis of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone-induced hyperpigmentation in cultured brownish guinea pig skin tissues. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 367–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, M.S.; Kwon, M.; Choi, J.; Kim, H.R. Sargaquinoic acid ameliorates hyperpigmentation through cAMP and ERK-mediated downregulation of MITF in alpha-MSH-stimulated B16F10 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, T.; Takahashi, M.; Ito, M.; Hamatani, K.; Ohbayashi, M.; Wajjwalku, W.; Isobe, K.; Nakashima, I. Aberrant melanogenesis and melanocytic tumour development in transgenic mice that carry a metallothionein/ret fusion gene. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 3167–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.H.; Hwang, K.-S.; Shin, D.-S.; Kim, S.S.; Yang, J.Y.; Lee, B.H.; Bae, E.J.; Choi, B.W.; Bae, M.A.; Ahn, J.H. Identification of new arylsulfide derivatives as anti-melanogenic agents in a zebrafish model. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Paus, R.; Costantino, R. Differential expression and activity of melanogenesis-related proteins during induced hair growth in mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strähle, U.; Scholz, S.; Geisler, R.; Greiner, P.; Hollert, H.; Rastegar, S.; Schumacher, A.; Selderslaghs, I.; Weiss, C.; Witters, H. Zebrafish embryos as an alternative to animal experiments—a commentary on the definition of the onset of protected life stages in animal welfare regulations. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Ko, D.H.; Kim, C.H.; Hwang, J.S.; Ahn, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, C.D.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, T.J. Zebrafish as a new model for phenotype-based screening of melanogenic regulatory compounds. Pigment Cell Res. 2007, 20, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, H.-W.; Jiang, Y.; Oh, J.-Y.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Ryu, B. Ishophloroglucin A Isolated from Ishige okamurae Suppresses Melanogenesis Induced by α-MSH: In Vitro and In Vivo. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, S.-H.; Baek, M.-W.; Lee, H.-Y.; Kim, D.-J.; Na, Y.-R.; Noh, K.-J.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, H.-K.; Lee, B.-H.; Park, J.-H. In vivo alternative testing with zebrafish in ecotoxicology. J. Vet. Sci. 2008, 9, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailone, R.L.; Fukushima, H.C.S.; Ventura Fernandes, B.H.; De Aguiar, L.K.; Corrêa, T.; Janke, H.; Grejo Setti, P.; Roça, R.D.O.; Borra, R.C. Zebrafish as an alternative animal model in human and animal vaccination research. Lab. Anim. Res. 2020, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, M.; Larribere, L.; Bille, K.; Ortonne, J.-P.; Ballotti, R.; Bertolotto, C. Microphthalmia Associated Transcription Factor Is a Target of the Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase Pathway. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.M.; Heo, S.J.; Kim, K.N.; Lee, S.H.; Yang, H.M.; Kim, A.D.; Jeon, Y.J. Molecular docking studies of a phlorotannin, dieckol isolated from Ecklonia cava with tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012, 20, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, G.-Y.; Ha, Y.; Park, A.-H.; Kwon, O.W.; Kim, Y.-J. Leathesia difformis Extract Inhibits α-MSH-Induced Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells via Down-Regulation of CREB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oka, M.; Nagai, H.; Ando, H.; Fukunaga, M.; Matsumura, M.; Araki, K.; Ogawa, W.; Miki, T.; Sakaue, M.; Tsukamoto, K.; et al. Regulation of Melanogenesis through Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase-Akt Pathway in Human G361 Melanoma Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, J.Y.; Kim, H.N.; Kim, Y.R.; Choi, W.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Shin, H.K.; Choi, B.T. Partially purified components of Nardostachys chinensis suppress melanin synthesis through ERK and Akt signaling pathway with cAMP down-regulation in B16F10 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.; Park, S.; Park, J.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Yang, S.Y. Slow-Binding Inhibition of Tyrosinase by Ecklonia cava Phlorotannins. Mar. Drugs. 2019, 17, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-H.; Ko, J.-Y.; Oh, J.-Y.; Kim, E.-A.; Kim, C.-Y.; Jeon, Y.-J. Evaluation of phlorofucofuroeckol-A isolated from Ecklonia cava (Phaeophyta) on anti-lipid peroxidation in vitro and in vivo. Algae 2015, 30, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seong, S.H.; Paudel, P.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Identifying phlorofucofuroeckol-A as a dual inhibitor of amyloid-β25-35 self-aggregation and insulin glycation: Elucidation of the molecular mechanism of action. Mar. Drugs. 2019, 17, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.; Chang, S. Screening of inhibitory effect of edible mushrooms on tyrosinase and isolation of active component. J. Food Hyg. Saf. 1997, 12, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Manandhar, B.; Wagle, A.; Seong, S.H.; Paudel, P.; Kim, H.-R.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Phlorotannins with Potential Anti-Tyrosinase and Antioxidant Activity Isolated from the Marine Seaweed Ecklonia stolonifera. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, D.R.; Pichler, F.B.; Dodd, A.; Copp, B.R.; Greenwood, D.R. Technology for high-throughput screens: The present and future using zebrafish. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2004, 15, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajis, A.F.B. A Zebrafish Embryo as an Animal Model for the Treatment of Hyperpigmentation in Cosmetic Dermatology Medicine. Medicina 2018, 54, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.Y.; Wang, H.M.; Wen, Y.S.; Liu, W.; Li, P.H.; Chiu, C.C.; Chen, P.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Sheu, J.H.; Wen, Z.H. 4-(Phenylsulfanyl) butan-2-one suppresses melanin synthesis and melanosome maturation in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 20240–20257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibert, Y.; Trengove, M.; Ward, A. Zebrafish as a genetic model in pre-clinical drug testing and screening. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2458–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Lin, C.-S.; Chakraborty, C. The zebrafish model: Use in studying cellular mechanisms for a spectrum of clinical disease entities. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2007, 4, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, M.; Henderson, R.E.; Garraway, L.A.; Zon, L.I. Long-term drug administration in the adult zebrafish using oral gavage for cancer preclinical studies. Dis. Model. Mech. 2016, 9, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tokiwa, Y.; Kitagawa, M.; Raku, T. Enzymatic synthesis of arbutin undecylenic acid ester and its inhibitory effect on mushroom tyrosinase. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.-N.; Li, W.; Mehmood, S.; Pan, W.-J.; Wu, Q.-X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.-M. Effect of polysaccharide FMP-1 from Morchella esculenta on melanogenesis in B16F10 cells and zebrafish. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5007–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.-H.; Yao, C.; Oh, J.-H.; Park, C.-H.; Tian, Y.-D.; Han, M.; Kim, J.E.; Chung, J.H.; Jin, Z.-H.; Lee, D.H. Vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulates melanogenesis in B16F10 mouse melanoma cells via CREB/MITF/tyrosinase signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, E.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, W.J.; Shim, W.S.; Yeo, E.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.Y. A novel synthetic Piper amide derivative NED-180 inhibits hyperpigmentation by activating the PI 3K and ERK pathways and by regulating Ca2+ influx via TRPM 1 channels. Pigm. Cell Melanoma R. 2016, 29, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachtenheim, J.; Borovanský, J. “Transcription physiology” of pigment formation in melanocytes: Central role of MITF. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.-J.; Ko, S.-C.; Cha, S.-H.; Kang, D.-H.; Park, H.-S.; Choi, Y.-U.; Kim, D.; Jung, W.-K.; Jeon, Y.-J. Effect of phlorotannins isolated from Ecklonia cava on melanogenesis and their protective effect against photo-oxidative stress induced by UV-B radiation. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, X.B.; Luo, H.Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.H.; Ma, X.; Lu, C.L. Folic acid protects against arsenic-mediated embryo toxicity by up-regulating the expression of Dvr1. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Kim, H.S.; Oh, J.Y.; Je, J.G.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Ryu, B. Protective effect of diphlorethohydroxycarmalol isolated from Ishige okamurae against UVB-induced damage in vitro in human dermal fibroblasts and in vivo in zebrafish. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 110963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Yang, H.M.; Kang, S.M.; Ahn, G.N.; Roh, S.W.; Lee, W.; Kim, D.K.; Jeon, Y.J. Whitening Effect of Octaphlorethol A Isolated from Ishige foliacea in an In Vivo Zebrafish Model. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.-N.; Ahn, G.; Heo, S.-J.; Kang, S.-M.; Kang, M.-C.; Yang, H.-M.; Kim, D.; Roh, S.W.; Kim, S.-K.; Jeon, B.-T. Inhibition of tumor growth in vitro and in vivo by fucoxanthin against melanoma B16F10 cells. Environ. Toxicol. Phar. 2013, 35, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoi, J.; Abe, E.; Suda, T.; Kuroki, T. Regulation of Melanin Synthesis of B16 Mouse Melanoma Cells by 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and Retinoic Acid. Cancer Res. 1985, 45, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.-H.; Liu, S.; Xu, S.-Y.; Chen, L.; Shan, Y.-H.; Wei, W.; Liang, W.-Q.; Gao, J.-Q. Inhibitory effects of salidroside and paeonol on tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis in mouse B16F10 melanoma cells and ultraviolet B-induced pigmentation in guinea pig skin. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Je, J.-G.; Jiang, Y.; Heo, J.-H.; Li, X.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Ryu, B.-M. Mitigative Effects of PFF-A Isolated from Ecklonia cava on Pigmentation in a Zebrafish Model and Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020123
Je J-G, Jiang Y, Heo J-H, Li X, Jeon Y-J, Ryu B-M. Mitigative Effects of PFF-A Isolated from Ecklonia cava on Pigmentation in a Zebrafish Model and Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(2):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020123
Chicago/Turabian StyleJe, Jun-Geon, Yunfei Jiang, Jun-Ho Heo, Xining Li, You-Jin Jeon, and Bo-Mi Ryu. 2022. "Mitigative Effects of PFF-A Isolated from Ecklonia cava on Pigmentation in a Zebrafish Model and Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells" Marine Drugs 20, no. 2: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020123
APA StyleJe, J. -G., Jiang, Y., Heo, J. -H., Li, X., Jeon, Y. -J., & Ryu, B. -M. (2022). Mitigative Effects of PFF-A Isolated from Ecklonia cava on Pigmentation in a Zebrafish Model and Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells. Marine Drugs, 20(2), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020123