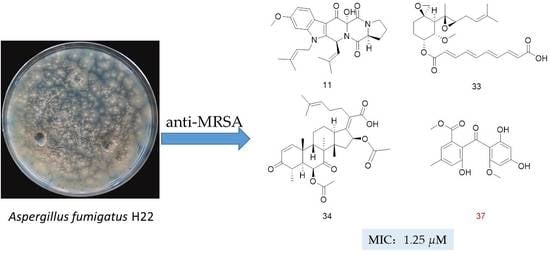
Discovery of Anti-MRSA Secondary Metabolites from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
Structure Elucidation of the Isolated Compounds
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General
4.2. Fungal Material
4.3. Fermentation and Extraction
4.4. Isolation and Characterization Data
4.5. Marfey’s Analysis of Compound 2
4.6. Computational Details for NMR and ECD
4.7. Antimicrobial Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuok, C.F.; Hoi, S.O.; Hoi, C.F.; Chan, C.H.; Fong, I.H.; Ngok, C.K.; Meng, L.R.; Fong, P. Synergistic antibacterial effects of herbal extracts and antibiotics on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A computational and experimental study. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asghar, M.A.; Yousuf, R.I.; Shoaib, M.H.; Asghar, M.A.; Ansar, S.; Zehravi, M.; Abdul Rehman, A. Synergistic nanocomposites of different antibiotics coupled with green synthesized chitosan-based silver nanoparticles: Characterization, antibacterial, in vivo toxicological and biodistribution studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 7841–7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezar, I.F.; Mashruwala, A.A.; Boyd, J.M.; Stock, A.M. Drug-like fragments inhibit agr-mediated virulence expression in Staphylococcus aureus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodvold, K.A.; McConeghy, K.W. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus therapy: Past, present, and future. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, S20–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Prioritization of Pathogens to Guide Discovery, Research and Development of New Antibiotics for Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections, Including Tuberculosis, 9789240026438 (electronic version); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Althagbi, H.I.; Alarif, W.M.; Al-Footy, K.O. Abdel-Lateff, A Marine-derived macrocyclic alkaloids (MDMAS): Chemical and Biological Diversity. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.; Aires-de-Sousa, J. Computational methodologies in the exploration of marine natural product leads. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagestad, O.C.; Andersen, J.H.; Altermark, B.; Hansen, E.; Rämä, T. Cultivable marine fungi from the arctic archipelago of svalbard and their antibacterial activity. Mycology 2020, 11, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, R.B.; Andrade, P.B.; Valentao, P. Chemical diversity and biological properties of secondary metabolites from sea hares of aplysia genus. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Li, D.; Tao, M.; Chen, Y.; Dan, F.; Zhang, W. Scopararanes C-G: New oxygenated pimarane diterpenes from the marine sediment-derived fungus Eutypella scoparia FS26. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhary, A.; Naughton, L.M.; Montanchez, I.; Dobson, A.D.W.; Rai, D.K. Current status and future prospects of marine natural products (MNPs) as antimicrobials. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 382–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 235–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanif, N.; Murni, A.; Tanaka, C.; Tanaka, J. Marine natural products from indonesian waters. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayer, A.M.; Rodriguez, A.D.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Fusetani, N. Marine pharmacology in 2016–2017: Marine compounds with antibacterial, antidiabetic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis and antiviral activities; affecting the immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, H.A.; Pham, N.B.; Muhammad, T.S.; Hooper, J.N.; Quinn, R.J. Merosesquiterpene congeners from the australian sponge Hyrtios digitatus as potential drug leads for atherosclerosis disease. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong Chin, J.M.; Puchooa, D.; Bahorun, T.; Jeewon, R. Antimicrobial properties of marine fungi from sponges and brown algae of Mauritius. Mycology 2021, 12, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Wiese, J.; Labes, A.; Kramer, A.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Lindgomycin, an unusual antibiotic polyketide from a marine fungus of the lindgomycetaceae. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4617–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, S.; Liu, D.; Hu, X.; Proksch, P.; Shao, Z.; Lin, W. Spiromastixones A-O, antibacterial chlorodepsidones from a deep-sea-derived Spiromastix sp. fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augner, D.; Krut, O.; Slavov, N.; Gerbino, D.C.; Sahl, H.G.; Benting, J.; Nising, C.F.; Hillebrand, S.; Kronke, M.; Schmalz, H.G. On the antibiotic and antifungal activity of pestalone, pestalachloride A, and structurally related compounds. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1519–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto, M.; Jensen, P.R.; Kauffman, C.; Fenical, W.; Lobkovsky, E.; Clardy, J. Pestalone, a new antibiotic produced by a marine fungus in response to bacterial challenge. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1444–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Wallwey, C.; Matuschek, M.; Steinbach, K.; Li, S.M. Formyl migration product of chanoclavine-I aldehyde in the presence of the old yellow enzyme FgaOx3 from Aspergillus fumigatus: A NMR structure elucidation. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Dai, H.Q.; Bao, L.; Ren, B.A.; Lu, J.C.; Luo, Y.M.; Guo, L.D.; Zhang, L.X.; Liu, H.W. Isolation and structural elucidation of proline-containing cyclopentapeptides from an endolichenic Xylaria sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.G.; Goodman, J.M. Assigning stereochemistry to single diastereoisomers by GIAO NMR calculation: The DP4 probability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12946–12959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, I.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Alfonso, C.; Calabro, K.; Alonso, E.; Sanchez, J.A.; Alfonso, A.; Thomas, O.P.; Botana, L.M. Gambierone, a ladder-shaped polyether from the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus belizeanus. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2392–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttachon, S.; Chandrapatya, A.; Manoch, L.; Silva, A.; Gales, L.; Bruyere, C.; Kiss, R.; Kijjoa, A. Sartorymensin, a new indole alkaloid, and new analogues of tryptoquivaline and fiscalins produced by Neosartorya siamensis (KUFC 6349). Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 3253–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Zhao, J.Y.; Fang, X.M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, D.W.; Liu, H.Y.; Su, J.; Cen, S.; Yu, L.Y. Metabolites from the plant endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. CPCC 400735 and their anti-hiv activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2595–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Li, X.B.; Zhou, J.C.; Xu, Q.Q.; Wang, X.N.; Yuan, H.Q.; Lou, H.X. Secondary metabolites from Aspergillus fumigatus, an endophytic fungus from the liverwort Heteroscyphus tener (Steph.) Schiffn. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, C.B.; Kakeya, H.; Osada, H. Novel mammalian cell cycle inhibitors, tryprostatins A, B and other diketopiperazines produced by Aspergillus fumigatus. II. Physico-chemical properties and structures. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abraham, W.R.; Arfmann, H.A. 12,13-Dihydroxy-Fumitremorgin C from Aspergillus fumigatus. Phytochemistry 1990, 29, 1025–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Song, H.; Song, F.; Guo, Y.; Wu, C.H.; Her, A.S.; Pu, Y.; Wang, S.; Naowarojna, N.; Weitz, A.; et al. Endoperoxide formation by an alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent mononuclear non-haem iron enzyme. Nature 2015, 527, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, F.; Zhang, H.C.; Liu, R.; Zhang, D.X. Isolation and biological evaluation of secondary metabolites of the endophytic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus from Astragalus membranaceus. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2013, 49, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, H.; Fujimaki, T.; Okuyama, E.; Yamazaki, M. Immunosuppressive constituents from an Ascomycete, Sordaria gondaensis. Mycotoxins 2000, 50, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, C.B.; Kakeya, H.; Osada, H. Novel mammalian cell cycle inhibitors, cyclotryprostatins A-D, produced by Aspergillus fumigatus, which inhibit mammalian cell cycle at G2/M phase. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Holte, D.; Zoller, J.; Umemiya, S.; Simke, L.R.; Baran, P.S. Total synthesis of verruculogen and fumitremorgin a enabled by ligand-controlled C–H borylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10160–10163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, W.L.; Fang, Y.C.; Zhu, T.J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhu, W.M. Cytotoxic alkaloids and antibiotic nordammarane triterpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowi. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.B.; Kakeya, H.; Osada, H. Novel mammalian cell cycle inhibitors, spirotryprostatins A and B, produced by Aspergillus fumigatus, which inhibit mammalian cell cycle at G2/M phase. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 12651–12666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Z.; Fang, Y.C.; Zhu, T.J.; Zhang, M.; Lin, A.Q.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhu, W.M. Seven new prenylated indole diketopiperazine alkaloids from holothurian-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 7986–7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, C.; Matsushita, T.; Doi, M.; Minoura, K.; Shingu, T.; Kumeda, Y.; Numata, A. Fumiquinazolines A-G, novel metabolites of a fungus separated from a Pseudolabrus marine fish. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1995, 18, 2345–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren-Yi, G.; Lei, X.; Yi, K.; Iii-Ming, C.; Jian-Chun, Q.; Li, L.; Sheng-Xiang, Y.; Li-Chun, Z. Chaetominine, (+)-alantrypinone, questin, isorhodoptilometrin, and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde produced by the endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. YL-6 inhibit wheat (Triticum aestivum) and radish (Raphanus sativus) germination. J. Plant. Interact. 2015, 10, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsen, T.O.; Frydenvang, K.; Frisvad, J.C.; Christophersen, C. UV-guided isolation of alantrypinone, a novel Penicillium alkaloid. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Lin, T.; Wang, W.; Xin, Z.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Antiviral alkaloids produced by the mangrove-derived fungus Cladosporium sp. PJX-41. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, R.H.; Xu, S.; Liu, J.Y.; Ge, H.M.; Ding, H.; Xu, C.; Zhu, H.L.; Tan, R.X. Chaetominine, a cytotoxic alkaloid produced by endophytic Chaetomium sp. IFB-E015. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 5709–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, M.G.; Yu, Z.G.; Jie, Z.; Wu, J.H.; Tan, R.X. Bioactive alkaloids from endophytic Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 753–755. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, R.J.; Kirksey, J.W.; Dorner, J.W.; Wilson, D.M.; Johnson, J.C., Jr.; Johnson, A.N.; Bedell, D.M.; Springer, J.P.; Chexal, K.K.; Clardy, J.C.; et al. Mycotoxins produced by Aspergillus fumigatus species isolated from molded silage. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 1977, 25, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Yoshida, K.; Uchida, I.; Nishikawa, M.; Kohsaka, M.; Aoki, H. Studies of platelet activating factor (PAF) antagonists from microbial products. I. Bisdethiobis(methylthio)gliotoxin and its derivatives. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, W.L.; Le, X.; Li, H.J.; Yang, X.L.; Chen, J.X.; Xu, J.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, K.T.; Hu, K.C.; et al. Exploring the chemodiversity and biological activities of the secondary metabolites from the marine fungus Neosartorya pseudofischeri. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5657–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joachim, W.; Susanne, G.; Manfred, G.; Ralf, T.; Reinhard, K. Pseurotin F1/F2, New Metabolites from Aspergillus fumigatus, Process for Their Preparation and Their Use as Apomorphine Antagonists. EP19920120724, 4 December 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Tsunematsu, Y.; Fukutomi, M.; Saruwatari, T.; Noguchi, H.; Hotta, K.; Tang, Y.; Watanabe, K. Elucidation of pseurotin biosynthetic pathway points to trans-acting C-methyltransferase: Generation of chemical diversity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 8475–8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boot, C.M.; Gassner, N.C.; Compton, J.E.; Tenney, K.; Tamble, C.M.; Lokey, R.S.; Holman, T.R.; Crews, P. Pinpointing pseurotins from a marine-derived Aspergillus as tools for chemical genetics using a synthetic lethality yeast screen. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1672–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Liu, R.; Chen, L.; Zhu, T.J.; Zhu, W.M.; Gu, Q.Q. Two new hetero-spirocyclic gamma-lactam derivatives from marine sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowi D2-6. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.X.; Blunt, J.W.; Cole, A.L.J.; Munro, M.H.G. Fumagiringillin, a new fumagillin derivative from a strain of the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Nat. Prod 2004, 67, 1434–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, M.; Mierzwa, R.; He, L.; Xu, L.; Patel, M.; Patel, D.; Chan, T.M. Structure of sch 528647: A new antitumor antibiotic related to fumagillin. J. Antibiot. 2001, 54, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, F.D.; Huang, X.L.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, P.W.; Zhou, L.M.; Yuan, J.Z.; Dai, H.F.; Luo, D.Q.; et al. Helvolic acid derivatives with antibacterial activities against Streptococcus agalactiae from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigatus HNMF0047. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Zhu, W.M.; Zhang, Y.P.; Zhu, T.J.; Liu, H.B.; Fang, Y.C.; Gu, Q.Q. A new diphenyl ether from marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp B-F-2. J. Antibiot 2006, 59, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujimoto, K.; Fujimaki, T.; Okuyama, E.; Yamazaki, M. Immunomodulatory constituents from an ascomycete, Microascus tardifaciens. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, W. Anti-H1N1-virus secondary metabolites from mangrove-derived aciduric fungus Penicillium sp. OUCMDZ-4736. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2016, 35, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.S.; Shi, X.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yu, J.Y.; Fu, X.M.; Li, X.; Chen, K.X.; Guo, Y.W.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, C.Y. Co-cultivation with 5-azacytidine induced new metabolites from the zoanthid-derived fungus Cochliobolus lunatus. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yong, K.; Kaleem, S.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Z.Z. New antiproliferative compounds against glioma cells from the marine-sourced fungus Penicillium sp. ZZ1750. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhijjleh, R.K.; Shabbir, S.; Al-Abd, A.M.; Jiaan, N.H.; Alshamil, S.; El-labbad, E.M.; Khalifa, S.I. Bioactive marine metabolites derived from the Persian Gulf compared to the Red Sea: Similar environments and wide gap in drug discovery. Peerj 2021, 9, 11778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Liao, Y.Y.; Chen, R.X.; Hou, Y.P.; Ke, W.Q.; Zhang, B.B.; Gao, M.L.; Shao, Z.Z.; Chen, J.M.; Li, F. Chlorinated azaphilone pigments with antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities isolated from the deep sea derived fungus Chaetomium sp. NA-S01-R1. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inostroza, A.; Lara, L.; Paz, C.; Perez, A.; Galleguillos, F.; Hernandez, V.; Becerra, J.; Gonzalez-Rocha, G.; Silva, M. Antibiotic activity of Emerimicin IV isolated from Emericellopsis minima from Talcahuano Bay, Chile. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Romani, L.; Netea, M.G.; Latgé, J.-P. Aspergillus fumigatus morphology and dynamic host interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, A.L.; Gao, J.M. Metabolites from Aspergillus fumigatus, an endophytic fungus associated with Melia azedarach, and their antifungal, antifeedant, and toxic activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3424–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, O.; Satake, H.; Nakajima, M.; Sato, A.; Nakamura, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Furuya, K.; Haneishi, T. Synerazol, a New Antifungal Antibiotic. J. Antibiot. 1991, 44, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinheiro, E.A.A.; Carvalho, J.M.; dos Santos, D.C.P.; Feitosa, A.D.O.; Marinho, P.S.B.; Guilhon, G.M.S.P.; de Souza, A.D.L.; da Silva, F.M.A.; Marinho, A.M.D.R. Antibacterial activity of alkaloids produced by endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. EJC08 isolated from medical plant Bauhinia guianensis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, K.; Bi, H.; Chai, W.; Lian, X.Y.; Zhang, Z. Antiglioma pseurotin A from marine Bacillus sp. FS8D regulating tumour metabolic enzymes. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komagata, D.; Fujita, S.; Yamashita, N.; Saito, S.; Morino, T. Novel neuritogenic activities of pseurotin A and penicillic acid. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 958–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asami, Y.; Kakeya, H.; Komi, Y.; Kojima, S.; Nishikawa, K.; Beebe, K.; Neckers, L.; Osada, H. Azaspirene, a fungal product, inhibits angiogenesis by blocking Raf-1 activation. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Igarashi, Y.; Yabuta, Y.; Sekine, A.; Fujii, K.; Harada, K.; Oikawa, T.; Sato, M.; Furumai, T.; Oki, T. Directed biosynthesis of fluorinated pseurotin A, synerazol and gliotoxin. J. Antibiot. 2004, 57, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asami, Y.; Kakeya, H.; Onose, R.; Yoshida, A.; Matsuzaki, H.; Osada, H. Azaspirene: A novel angiogenesis inhibitor containing a 1-oxa-7-azaspiro[4.4]non-2-ene-4,6-dione skeleton produced by the fungus Neosartotya sp. Organ. Lett. 2002, 4, 2845–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruceaga, X.; Perez-Cuesta, U.; de Cerio, A.A.D.; Gonzalez, O.; Alonso, R.M.; Hernando, F.L.; Ramirez-Garcia, A.; Rementeria, A. Fumagillin, a mycotoxin of Aspergillus fumigatus: Biosynthesis, biological activities, detection, and applications. Toxins 2020, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawadsitang, S.; Mongkolthanaruk, W.; Suwannasai, N.; Sodngam, S. Antimalarial and cytotoxic constituents of Xylaria cf. cubensis PK108. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 2033–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganaha, M.; Yoshii, K.; Otsuki, Y.; Iguchi, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Iseki, K.; Ban, S.; Ishiyama, A.; Hokari, R.; Iwatsuki, M.; et al. In Vitro antitrypanosomal activity of the secondary metabolites from the mutant strain IU-3 of the insect pathogenic fungus Ophiocordyceps coccidiicola NBRC 100683. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 988–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanmanoch, W.; Mongkolthanaruk, W.; Kanokmedhakul, S.; Aimi, T.; Boonlue, S. Helvolic acid, a secondary metabolite produced by Neosartorya spinosa KKU-1NK1 and its biological activities. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2016, 43, 484–494. [Google Scholar]
- Grimblat, N.; Zanardi, M.M.; Sarotti, A.M. Beyond DP4: An improved probability for the stereochemical assignment of isomeric compounds using quantum chemical calculations of NMR shifts. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12526–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.J.; Liu, C.C.; Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L.; Bao, L.; Chen, Q.; Song, F.H.; Zhang, L.X.; Li, E.W.; et al. Decalin-containing tetramic acids and 4-Hydroxy-2-pyridones with antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity from the fungus Coniochaeta cephalothecoides collected in Tibetan Plateau (Medog). J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 11474–11486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Positions | 1 | 2a | 2b | 3a | 3b | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH, Mult., (J in Hz) | δC | δH, Mult., (J in Hz) | δC | δH, Mult., (J in Hz) | δC | δH, Mult., (J in Hz) | δC | δH, Mult., (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 11.85 br. s | 11.83 br. s | 11.64 br. s | 11.92 br. s | 11.60 br. s | |||||
| 2 | 135.1 | 134.4 | 134.2 | 134.3 | 134.3 | |||||
| 3 | 142.4 | 142.5 | 141.9 | 143.4 | 141.4 | |||||
| 5 | 158.3 | 158.2 | 159.7 | 158.4 | 158.1 | |||||
| 6 | 111.1 | 8.59 s | 113.4 | 8.41 s | 113.3 | 8.37 s | 113.6 | 8.47 s | 113.5 | 8.45 s |
| 7 | 128.9 | 129.0 | 128.7 | 129.1 | 128.7 | |||||
| 8 | 115.0 | 114.8 | 114.9 | 114.8 | 114.9 | |||||
| 9 | 123.1 | 8.21 d (8.7) | 123.2 | 8.22 d (8.7) | 123.1 | 8.18 d (8.7) | 123.4 | 8.25 d (8.7) | 123.1 | 8.19 d (8.7) |
| 10 | 110.2 | 6.91 dd (8.7, 2.3) | 110.2 | 6.91 dd (8.7, 2.2) | 110.0 | 6.89 dd (8.7, 2.2) | 110.5 | 6.93 dd (8.7, 2.2) | 110.0 | 6.89 dd (8.7, 2.2) |
| 11 | 160.7 | 160.6 | 160.8 | 161.0 | 160.7 | |||||
| 12 | 94.8 | 7.05 d (2.3) | 94.7 | 7.05 d (2.2) | 94.7 | 7.04 d (2.2) | 94.7 | 7.06 d (2.2) | 94.8 | 7.04 d (2.2) |
| 13 | 142.8 | 142.9 | 142.8 | 143.2 | 142.8 | |||||
| 14 | 164.7 | 166.0 | 166.6 | 165.5 | 165.8 | |||||
| 15 | 8.42 br. s | |||||||||
| 16 | 38.3 | 3.39 q (7.4) | 49.6 | 3.96 m | 47.5 | 3.67 m | 49.6 | 3.98 m | 47.9 | 3.70 m |
| 3.88 m | 3.91 m | |||||||||
| 17 | 24.9 | 1.80 p (7.4) | 25.2 | 1.94 m | 21.9 | 1.92 m | 25.2 | 1.96 m | 21.8 | 1.92 m |
| 1.90 m | 1.82 m | 1.93 m | 1.83 m | |||||||
| 18 | 31.2 | 2.30 t (7.4) | 28.6 | 2.26 m | 31.2 | 2.29 m | 28.6 | 2.28 m | 31.3 | 2.29 m |
| 1.89 m | 2.02 m | 1.91 m | 1.98 m | |||||||
| 19 | 174.2 | 59.8 | 4.48 dd (8.8, 4.4) | 60.4 | 5.30 dd (8.5, 3.6) | 59.7 | 4.57 dd (8.6, 4.0) | 60.8 | 5.18 dd (8.6, 4.5) | |
| 20 | 118.5 | 6.79 s | 173.5 | 173.8 | 172.5 | 172.9 | ||||
| 21 | 138.7 | 118.5 | 6.76 s | 119.0 | 6.66 s | 118.0 | 6.75 s | 119.5 | 6.59 s | |
| 22 | 27.3 | 2.08 s | 138.1 | 138.0 | 138.1 | 138 | ||||
| 23 | 20.6 | 2.17 s | 27.1 | 2.07 s | 26.9 | 2.04 s | 27.0 | 2.07 s | 26.5 | 2.04 s |
| 24 | 55.4 | 3.89 s | 20.4 | 2.13 s | 20.2 | 2.01 s | 20.4 | 2.10 s | 20.1 | 1.90 s |
| 25 | 55.4 | 3.89 s | 55.4 | 3.88 s | 55.5 | 3.89 s | 55.4 | 3.88 s | ||
| 26 | 51.8 | 3.68 s | 51.6 | 3.45 s | ||||||
| Positions | δC | δH, Mult., (J in Hz) | Positions | δC | δH, Mult., (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 137.0 | 17 | 111.2 | 6.90 dd (8.6, 2.2) | |
| 3 | 43.3 | 6.37 dd (9.5, 1.2) | 18 | 157.7 | |
| 5 | 164.7 | 19 | 100.8 | 7.27 d (2.2) | |
| 6 | 59.8 | 4.32 dd (10.8, 6.0) | 20 | 136.1 | |
| 7 | 29.6 | 2.51 m | 21 | 39.5 | 2.29 dd (14.0, 9.5) |
| 1.95 m | 2.14 dd (14.0, 1.2) | ||||
| 8 | 22.0 | 2.08 m | 22 | 74.6 | |
| 1.98 m | 23 | 29.3 | 1.25 s | ||
| 9 | 45.7 | 3.76 m | 24 | 32.2 | 1.17 s |
| 3.65 m | 25 | 165.5 | |||
| 11 | 165.9 | 26 | 119.8 | 6.40 br. s | |
| 12 | 86.2 | 27 | 158.2 | ||
| 13 | 68.4 | 5.13 s | 28 | 27.4 | 2.11 s |
| 14 | 114.3 | 29 | 21.2 | 2.21 s | |
| 15 | 122.3 | 18-OCH3 | 55.9 | 3.85 s | |
| 16 | 119.4 | 7.45 d (8.6) |
| Positions | δC | δH, Mult., (J in Hz) | Positions | δC, Type | δH, Mult., (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 82.6 | 5.82 s | 14 | 172.4 | |
| 3 | 91.3 | 15 | 58.5 | 4.26 q (6.5) | |
| 4 | 134.4 | 18 | 161.0 | ||
| 5 | 124.4 | 7.31 d (7.5) | 19 | 121.9 | |
| 6 | 125.8 | 7.22 dd (8.0, 7.5) | 20 | 126.8 | 8.29 d (8.1) |
| 7 | 131.3 | 7.43 dd (8.0, 7.5) | 21 | 128.2 | 7.58 dd (8.1, 7.5) |
| 8 | 115.8 | 7.65 d (8.0) | 22 | 135.4 | 7.85 dd (8.1, 7.5) |
| 9 | 138.9 | 23 | 128.0 | 7.78 d (8.1) | |
| 11 | 170.9 | 24 | 148.1 | ||
| 12 | 58.3 | 5.03 dd (10.5, 4.3) | 26 | 145.6 | 8.11 s |
| 13 | 33.4 | 3.68 dd (13.4, 4.3) | 27 | 17.9 | 1.28 d (6.5) |
| 2.61 dd (13.4, 10.5) |
| Positions | δC | δH, Mult., (J in Hz) | Positions | δC | δH, Mult., (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 127.2 | 1′ | 105.9 | ||
| 2 | 153.1 | 2′ | 163.0 | ||
| 3 | 120.1 | 6.88 s | 3′ | 91.4 | 5.80 d (2.2) |
| 4 | 138.1 | 4′ | 165.2 | ||
| 5 | 120.2 | 7.19 s | 5′ | 95.5 | 5.90 d (2.2) |
| 6 | 130.3 | 6′ | 166.0 | ||
| 7 | 166.0 | 4-CH3 | 20.8 | 2.30 s | |
| 8 | 51.9 | 3.64 s | 2′-OCH3 | 55.7 | 3.26 s |
| 9 | 198.1 | 6′-OH | 13.55 s |
| MIC (μM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | MRSA a | Compound | MRSA a |
| 5 | 5.00 | 31 | 5.00 |
| 8 | 2.50 | 32 | 25.0 |
| 10 | 20.0 | 33 | 2.50 |
| 11 | 1.25 | 34 | 1.25 |
| 16 | 10.00 | 35 | 1.25 |
| 21 | 25.00 | 36 | 1.25 |
| 23 | 12.50 | 37 | 1.25 |
| 29 | 10.00 | 38 | 1.25 |
| 30 | 5.00 | 41 | 5.00 |
| Positive control | Vancomycin (1.00) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Wang, H.; Chen, B.; Dai, H.; Sun, J.; Han, J.; Liu, H. Discovery of Anti-MRSA Secondary Metabolites from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050302
Zhang R, Wang H, Chen B, Dai H, Sun J, Han J, Liu H. Discovery of Anti-MRSA Secondary Metabolites from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(5):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050302
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rui, Haifeng Wang, Baosong Chen, Huanqin Dai, Jingzu Sun, Junjie Han, and Hongwei Liu. 2022. "Discovery of Anti-MRSA Secondary Metabolites from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus" Marine Drugs 20, no. 5: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050302
APA StyleZhang, R., Wang, H., Chen, B., Dai, H., Sun, J., Han, J., & Liu, H. (2022). Discovery of Anti-MRSA Secondary Metabolites from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Marine Drugs, 20(5), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050302