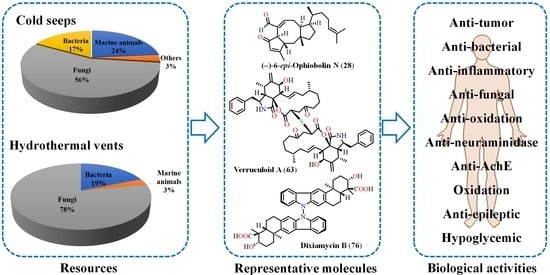
Deep-Sea Natural Products from Extreme Environments: Cold Seeps and Hydrothermal Vents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cold Seeps
2.1. Marine Animals
2.2. Marine Fungi
2.2.1. Aspergillus sp.
2.2.2. Penicillium sp.
2.2.3. Cladosporium sp.
2.2.4. Curvularia sp.
2.3. Marine Bacteria
2.3.1. Streptomyces sp.
2.3.2. Halomonas sp.
2.3.3. Vibrio sp.
2.3.4. Bacillus sp.
2.4. Others
3. Hydrothermal Vents
3.1. Marine Animal
3.2. Marine Fungi
3.2.1. Penicillium sp.
3.2.2. Aspergillus sp.
3.2.3. Graphostroma sp.
3.3. Marine Bacteria
3.3.1. Streptomyces sp.
3.3.2. Geobacillus sp.
3.3.3. Halomonas sp.
3.3.4. Vibrio sp.
3.3.5. Methanococcus sp.
3.3.6. Thermococcus sp.
3.3.7. Alteromonas sp.
4. Comprehensive Overview and Outlook
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rampelotto, P.H. Extremophiles and Extreme Environments. Life 2013, 3, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Lawrence, A.L. The Importance of Asking “How and Why?” In Natural Product Structure Elucidation. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chi, L.P.; Li, X.M.; Wan, Y.P.; Li, Y.H.; Li, X.; Wang, B.G. Two New Phenol Derivatives from the Cold Seep-Derived Fungus Aspergillus insuetus SD-512. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2100512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, E.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, F.; Li, W. Antibiotic Dixiamycins from a Cold-Seep-Derived Streptomyces olivaceus. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 2606–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, R.K. Culturability and Secondary Metabolite Diversity of Extreme Microbes: Expanding Contribution of Deep Sea and Deep-Sea Vent Microbes to Natural Product Discovery. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornburg, C.C.; Zabriskie, T.M.; McPhail, K.L. Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents: Potential Hot Spots for Natural Products Discovery? J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, E.D.; Gallegos, J.L.V.; Cruz, M.G.; Dehesa, A.Z. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Supplemented Diet and Its Preventive Effect on Tumor Growth in Nude Mice. Nutr. Clin. Diet. Hosp. 2018, 38, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Celik, M.; Diler, A.; Kucukgulmez, A. A Comparison of the Proximate Compositions and Fatty Acid Profiles of Zander (Sander lucioperca) from Two Different Regions and Climatic Conditions. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Seike, Y.; Ioka, H.; Osako, K.; Tanaka, M.; Takashima, A.; Keriko, J.M.; Kose, S.; Souza, J.C.R. High Docosahexaenoic Acid Levels in Both Neutral and Polar Lipids of a Highly Migratory Fish: Thunnus tonggol (Bleeker). Lipids 2005, 40, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delong, E.F.; Yayanos, A.A. Adaptation of the Membrane-Lipids of a Deep-Sea Bacterium to Changes in Hydrostatic-Pressure. Science 1985, 228, 1101–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H. Unusual Novel n-4 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Cold-Seep Mussels (Bathymodiolus japonicus and Bathymodiolus platifrons), Originating from Symbiotic Methanotrophic Bacteria. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1200, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H. Identification of Novel n-4 Series Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in a Deep-Sea Clam, Calyptogena phaseoliformis. J. Chromatogr. A. 2007, 1163, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, S.; Takada, Y.; Tsuchida, S.; Kado, R.; Kimura, J. Sterols from Bivalves Calyptogena soyoae and Bathymodiolus septemdierum Living in Deep Sea. Fish. Sci. 2007, 73, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.N.S.; Nair, R.V.R.; Nair, A.P.R.; Nair, A.S.; Thyagarajan, S.; Johnson, A.J.; Baby, S. Antidiabetes Constituents, Cycloartenol and 24-Methylenecycloartanol, from Ficus krishnae. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akihisa, T.; Yasukawa, K.; Yamaura, M.; Ukiya, M.; Kimura, Y.; Shimizu, N.; Arai, K. Triterpene Alcohol and Sterol Ferulates from Rice Bran and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2313–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulipati, S.; Babu, P.S.; Dommati, H. Phytochemical, in-Silico Analysis and Anticancer Activity of a Bioactive Principle Isolated from Amaranthus tricolor (L). Res. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 16, 122–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kongkathip, N.; Dhumma-upakorn, P.; Kongkathip, B.; Chawananoraset, K.; Sangchomkaeo, P.; Hatthakitpanichakul, S. Study on Cardiac Contractility of Cycloeucalenol and Cycloeucalenone Isolated from Tinospora crispa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 83, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekhuemelo, D.O.; Agbidye, F.S.; Anyam, J.V.; Ekhuemelo, C.; Igoli, J.O. Antifungal Activity of Compounds Obtained from Sawdust and Stem Bark of Sasswood Tree (Erythrophleum suaveolens) on Wood Rot Fungi. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2019, 23, 1685–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aghaei, M.; Yazdiniapour, Z.; Ghanadian, M.; Zolfaghari, B.; Lanzotti, V.; Mirsafaee, V. Obtusifoliol Related Steroids from Euphorbia sogdiana with Cell Growth Inhibitory Activity and Apoptotic Effects on Breast Cancer Cells (MCF-7 and MDA-MB231). Steroids 2016, 115, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Kim, M.J.; Li, H.; Zhang, P.; Bao, B.Q.; Lee, K.J.; Jung, J.H. Marine-Derived Aspergillus Species as a Source of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites. Mar. Biotechnol. 2013, 15, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.T. Chemistry and Biology of Secondary Metabolites from Aspergillus Genus. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 8, 275–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.P.; Li, X.M.; Wan, Y.P.; Li, X.; Wang, B.G. Ophiobolin Sesterterpenoids and Farnesylated Phthalide Derivatives from the Deep Sea Cold-Seep-Derived Fungus Aspergillus insuetus SD-512. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3652–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Miao, F.P.; Qiao, M.F.; Cichewicz, R.H.; Ji, N.Y. Terretonin, Ophiobolin, and Drimane Terpenes with Absolute Configurations from an Algicolous Aspergillus ustus. Rsc. Advances 2013, 3, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ebel, R.; Wang, Y.; Schulz, B.; Draeger, S.; Muller, W.E.G.; Wray, V.; Lin, W.H.; Proksch, P. Ophiobolin Sesterterpenoids and Pyrrolidine Alkaloids from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus ustus. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2011, 94, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Itoh, T.; Kinoshita, M.; Nakai, Y.; Kurotaki, M.; Kobayashi, M. Cytotoxic Sesterterpenes, 6-epi-ophiobolin G and 6-epi-ophiobolin N, from Marine Derived Fungus Emericella variecolor GF10. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 6015–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.K.; Trinh, P.T.H.; Lee, H.S.; Choi, B.W.; Kang, J.S.; Ngoc, N.T.D.; Van, T.T.T.; Shin, H.J. New Ophiobolin Derivatives from the Marine Fungus Aspergillus flocculosus and Their Cytotoxicities against Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brill, Z.G.; Grover, H.K.; Maimone, T.J. Enantioselective Synthesis of an Ophiobolin Sesterterpene Via a Programmed Radical Cascade. Science 2016, 352, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.X.; Bao, L.; Yang, X.L.; Liu, D.L.; Guo, H.; Dai, H.Q.; Song, F.H.; Zhang, L.X.; Guo, L.D.; Li, S.J.; et al. Ophiobolins P-T, Five New Cytotoxic and Antibacterial Sesterterpenes from the Endolichenic Fungus Ulocladium sp. Fitoterapia 2013, 90, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.L.; Zang, Y.; Zhu, Q.H.; Ouyang, S.; Luo, J.J.; Luo, N.H.; Zhu, H.C.; Zhang, Y.H. Two New Phenolic Glucosides from Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisuwan, K.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Sukpondma, Y.; Phongpaichit, S.; Preedanon, S.; Sakayaroj, J. Furo [3,2-H]Isochroman, Furo [3,2-H]Isoquinoline, Isochroman, Phenol, Pyranone, and Pyrone Derivatives from the Sea Fan-Derived Fungus Penicillium sp. PSU-F40. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 4484–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunbamrung, N.; Intaraudom, C.; Boonyuen, N.; Rachtawee, P.; Laksanacharoen, P.; Pittayakhajonwut, P. Penicisochromans from the Endophytic Fungus Penicillium sp. BCC18034. Phytochem. Lett. 2014, 10, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramochi, K.; Tsubaki, K. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of Natural Benzofuranoids. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.J.; Qin, X.D.; Dong, Z.J.; Zhang, H.B.; Liu, J.K. Induced Daldinin a, B, C with a New Skeleton from Cultures of the Ascomycete Daidinia concentrica. J. Antibiot. 2008, 61, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.D.; Dong, Z.J.; Liu, J.K.; Yang, L.M.; Wang, R.R.; Zheng, Y.T.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Y.S.; Zheng, Q.T. Concentricolide, an Anti-HIV Agent from the Ascomycete Daldinia concentrica. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2006, 89, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copmans, D.; Kildgaard, S.; Rasmussen, S.A.; Slezak, M.; Dirkx, N.; Partoens, M.; Esguerra, C.V.; Crawford, A.D.; Larsen, T.O.; de Witte, P.A.M. Zebrafish-Based Discovery of Antiseizure Compounds from the North Sea: Isoquinoline Alkaloids TMC-120A and TMC-120B. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haidar, A.K.; Kjeldsen, N.D.; Troelsen, N.S.; Previtali, V.; Lundquist, K.P.; Larsen, T.O.; Clausen, M.H. A Concise Total Synthesis of the Fungal Isoquinoline Alkaloid TMC-120B. Molecules 2022, 27, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, F.; Li, X.; Chi, L.; Meng, L.; Wang, B. A New Acyclic Peroxide from Aspergillus nidulans SD-531, a Fungus Obtained from Deep-Sea Sediment of Cold Spring in the South China Sea. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 38, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.N.; Lock, M.J.; Hutchison, J.M. Synthesis of 4-Benzyl-3-Phenylbutenolide Natural Products. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 5322–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, H.; Asai, T.; Kim, Y.P.; Ishibashi, M. Nine Constituents Including Six Xanthone-Related Compounds Isolated from Two Ascomycetes, Gelasinospora santi-florii and Emericella quadrilineata, Found in a Screening Study Focused on Immunomodulatory Activity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Yu, S.; Lin, W. Antioxidative Phenolic Compounds from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, H.E.; Kamel, R.A.; Ibrahim, R.R.; Abdel-Razek, A.S.; Shaaban, M.A.; Frese, M.; Sewald, N.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Moharram, F.A. Cytotoxicity, Antimicrobial, and in Silico Studies of Secondary Metabolites from Aspergillus sp. Isolated from Tecoma stans (L.) Juss. Ex Kunth Leaves. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 760083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Tian, W.J.; Liao, Z.J.; Wang, G.H.; Zeng, D.Q.; Liu, X.Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, H.F.; Lin, T. Chemical Constituents from Endophytic Fungus Annulohypoxylon cf. stygium in Leaves of Anoectochilus roxburghii. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.W.; Ouyang, Y.C.; Zou, K.; Wang, G.H.; Chen, M.J.; Sun, H.M.; Dai, S.K.; Li, X. Isolation and Difference in Anti-Staphylococcus aureus Bioactivity of Curvularin Derivates from Fungus Eupenicillium sp. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2009, 159, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, D.; Rahaman, H.; Pal, R.; Gurjar, M. Total Synthesis of (S)-(-)-Curvularin: A Ring-Closing-Metathesis-Based Construction of the Macrocyclic Framework. Synlett 2008, 2008, 1801–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wijeratne, E.M.K.; Bashyal, B.P.; Zhan, J.X.; Seliga, C.J.; Liu, M.P.X.; Pierson, E.E.; Pierson, L.S.; VanEtten, H.D.; Gunatilaka, A.A.L. Cytotoxic and Other Metabolites of Aspergillus Inhabiting the Rhizosphere of Sonoran Desert Plants. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1985–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of 3,3′-Diindolylmethane in Gastrointestinal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, K.W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sarkar, S.H.; Sarkar, F.H. Gene Expression Profiling Revealed Survivin as a Target of 3,3′-Diindolylmethane-Induced Cell Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4952–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Yue, Y.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.H. 3,3′-Diindolylmethane Suppresses Adipogenesis Using Ampkalpha-Dependent Mechanism in 3t3-L1 Adipocytes and Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Ahmad, A.; Bao, B.; Sarkar, F.H. Antioxidant Function of Isoflavone and 3,3′-Diindolylmethane: Are They Important for Cancer Prevention and Therapy? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, Y.H.; Cui, H.; Liu, X.L.; Xiao, Z.E.; Wen, S.T.; She, Z.G.; Huang, X.S. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Meroterpenoid from a Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus sp. 16-5c. Molecules 2017, 22, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orfali, R.; Perveen, S. New Bioactive Metabolites from the Thermophilic Fungus Penicillium sp. Isolated from Ghamiqa Hot Spring in Saudi Arabia. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 7162948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuda, Y.; Awakawa, T.; Wakimoto, T.; Abe, I. Spiro-Ring Formation Is Catalyzed by a Multifunctional Dioxygenase in Austinol Biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10962–10965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, S.; Yin, J.; Ye, Z.; Li, F.; Lin, S.; Zhang, S.; Yang, B.; Yao, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; et al. Asperanstinoids A–E: Undescribed 3,5-Dimethylorsellinic Acid-Based Meroterpenoids from Aspergillus calidoustus. Phytochemistry 2021, 190, 112892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, L.; Li, X.M.; Li, H.L.; Konuklugil, B.; Wang, B.G. Ustusaustin A: A New Neuraminidase Inhibitory Meroterpene from the Ascidian-Derived Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus ustus TK-5. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 4939–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, C.E.; Zetina-Serrano, C.; Tahtah, N.; El Khoury, A.; Atoui, A.; Oswald, I.P.; Puel, O.; Lorber, S. Regulation of Secondary Metabolism in the Penicillium Genus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Liu, J.P.; Mei, J.H.; Jiang, R.; Tu, S.Z.; Deng, H.F.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.M.; Li, J. Origins, Structures, and Bioactivities of Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Penicillium Fungi. Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 2000–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Fang, S.T.; Shi, Z.Z.; Wang, B.G.; Li, X.N.; Ji, N.Y. Phenylhydrazone and Quinazoline Derivatives from the Cold-Seep-Derived Fungus Penicillium oxalicum. Mar. Drugs 2020, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, M.M.; Andolfi, A.; Nicoletti, R. The Genus Cladosporium: A Rich Source of Diverse and Bioactive Natural Compounds. Molecules 2021, 26, 3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. Untapped Potential of Marine-Associated Cladosporium Species: An Overview on Secondary Metabolites, Biotechnological Relevance, and Biological Activities. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-P.; Song, Y.-P.; Wang, B.-G.; Ji, N.-Y. Sulfurated and Iodinated Metabolites from the Cold-Seep Fungus Cladosporium cladosporioides 8-1. Tetrahedron Lett. 2022, 93, 153689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiralla, A.; Spin, R.; Saliba, S.; Laurain-Mattar, D. Diversity of Natural Products of the Genera Curvularia and Bipolaris. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2019, 33, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, X.M.; Yang, S.Q.; Li, X.; Wang, B.G.; Si, S.Y.; Meng, L.H. Cytochalasin Derivatives from the Endozoic Curvularia verruculosa CS-129, a Fungus Isolated from the Deep-Sea Squat Lobster Shinkaia crosnieri Living in the Cold Seep Environment. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 3122–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretz, R.; Wendt, L.; Wongkanoun, S.; Luangsa-Ard, J.J.; Surup, F.; Helaly, S.E.; Noumeur, S.R.; Stadler, M.; Stradal, T.E.B. The Effect of Cytochalasans on the Actin Cytoskeleton of Eukaryotic Cells and Preliminary Structure(-)Activity Relationships. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.L.; Wang, H.; Park, J.H.; Hong, J.; Choi, J.S.; Im, D.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Jung, J.H. Cytochalasin Derivatives from a Jellyfish-Derived Fungus Phoma sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2096–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Goietsenoven, G.; Mathieu, V.; Andolfi, A.; Cimmino, A.; Lefranc, F.; Kiss, R.; Evidente, A. In Vitro Growth Inhibitory Effects of Cytochalasins and Derivatives in Cancer Cells. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Hwang, S.; Lee, Y.; Cho, S.; Palsson, B.; Cho, B.K. Synthetic Biology Tools for Novel Secondary Metabolite Discovery in Streptomyces. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 667–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, V.T.; Nguyen, C.T.; Dhakal, D.; Nguyen, H.T.; Kim, T.S.; Sohng, J.K. Recent Advances in the Heterologous Biosynthesis of Natural Products from Streptomyces. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Mándi, A.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Tian, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; et al. N-N-Coupled Indolo-Sesquiterpene Atropo-Diastereomers from a Marine-Derived Actinomycete. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5256–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, B.R.; Werner, E.W.; O’Brien, A.G.; Baran, P.S. Total Synthesis of Dixiamycin B by Electrochemical Oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5571–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baunach, M.; Ding, L.; Willing, K.; Hertweck, C. Bacterial Synthesis of Unusual Sulfonamide and Sulfone Antibiotics by Flavoenzyme-Mediated Sulfur Dioxide Capture. Angew. Chem. Inter. Ed. 2015, 54, 13279–13283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Garawani, I.M.; El-Sabbagh, S.M.; Abbas, N.H.; Ahmed, H.S.; Eissa, O.A.; Abo-Atya, D.M.; Khalifa, S.A.M.; El-Seedi, H.R. A Newly Isolated Strain of Halomonas sp. (Ha1) Exerts Anticancer Potential Via Induction of Apoptosis and G(2)/M Arrest in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HEPG2) Cell Line. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, M.; Zhang, J.; Yue, Y.; Wu, N.; Geng, L.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J. Structural Characteristics and Immune-Enhancing Activity of an Extracellular Polysaccharide Produced by Marine Halomonas sp. 2E1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredslund, F.; Borchert, M.S.; Poulsen, J.C.N.; Mortensen, S.B.; Perner, M.; Streit, W.R.; Lo Leggio, L. Structure of a Hyperthermostable Carbonic Anhydrase Identified from an Active Hydrothermal Vent Chimney. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2018, 114, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansson, M.; Gram, L.; Larsen, T.O. Production of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites by Marine Vibrionaceae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1440–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, R.; Wei, M.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C. EPS364, a Novel Deep-Sea Bacterial Exopolysaccharide, Inhibits Liver Cancer Cell Growth and Adhesion. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondol, M.A.M.; Shin, H.J.; Islam, M.T. Diversity of Secondary Metabolites from Marine Bacillus Species: Chemistry and Biological Activity. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2846–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Liu, G.; Zhou, S.; Sha, Z.; Sun, C. Characterization of Antifungal Lipopeptide Biosurfactants Produced by Marine Bacterium Bacillus sp. CS30. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pancost, R.D.; Bouloubassi, I.; Aloisi, G.; Damste, J.S.S.; The Medinaut Shipboard Scientific Party. Three Series of Non-Isoprenoidal Dialkyl Glycerol Diethers in Cold-Seep Carbonate Crusts. Org. Geochem. 2001, 32, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; He, X.; Yan, Z.; Li, X.; Ren, X.; Pan, L.; Qin, B. Allelochemicals from the Rhizosphere Soil of Cultivated Astragalus hoantchy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3345–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Fukamatsu, K.; Kido, M. Pheromone Synthesis, 152. Synthesis of Blattellastanoside-a and Blattellastanoside-B, Chlorinated Steroid Glucosides Isolated as the Aggregation Pheromone of the German-Cockroach, Blattella-germanica L. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1993, 1993, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Cai, J.; Zhong, W.; Xu, G.; Wang, F.; Tian, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1b (PTP1B) Inhibitorsfrom the Deep-Sea Fungus Penicillium chrysogenum SCSIO 07007. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 96, 103646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Feng, T.; Zhao, B.; Li, D.; Cai, S.; Zhu, T.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q. Alkaloids from a Deep Ocean Sediment-Derived Fungus Penicillium sp. and Their Antitumor Activities. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamed, A.; Abdel-Razek, A.S.; Araby, M.; Abu-Elghait, M.; El-Hosari, D.G.; Frese, M.; Soliman, H.S.M.; Stammler, H.G.; Sewald, N.; Shaaban, M. Meleagrin from Marine Fungus Emericella Dentata NQ45: Crystal Structure and Diverse Biological Activity Studies. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 3830–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Han, Z.; Peng, J.; Qian, P.Y.; Qi, S.H. Antifouling Indole Alkaloids from Two Marine Derived Fungi. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.; Dai, X.; Sun, J.; Bu, X.; Weng, C.; Li, H.; Zhu, H. A Diketopiperazine Factor from Rheinheimera aquimaris QSI02 Exhibits Anti-Quorum Sensing Activity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wattana-Amorn, P.; Charoenwongsa, W.; Williams, C.; Crump, M.P.; Apichaisataienchote, B. Antibacterial Activity of Cyclo(L-Pro-L-Tyr) and Cyclo(D-Pro-L-Tyr) from Streptomyces sp. Strain 22-4 against Phytopathogenic Bacteria. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1980–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wollenberg, R.D.; Saei, W.; Westphal, K.R.; Klitgaard, C.S.; Nielsen, K.L.; Lysoe, E.; Gardiner, D.M.; Wimmer, R.; Sondergaard, T.E.; Sorensen, J.L. Chrysogine Biosynthesis Is Mediated by a Two-Module Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2131–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, I.H.; Wong, O.T.; Reynolds, D.J.; Chang, J.J. The Hypolipidemic Effects of 2-Furoic Acid in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Arch. Pharm. 1993, 326, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.C.; du Toit, E.S.; Reinhardt, C.F.; Rimando, A.M.; van der Kooy, F.; Meyer, J.J.M. The Phenolic, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, Is an Endogenous Regulator of Rooting in Protea cynaroides. Plant Growth Regul. 2007, 52, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, C.Q.; Shi, Y.T.; Auckloo, B.N.; ul Hassan, S.S.; Akhter, N.; Wang, K.W.; Ye, Y.; Chen, C.T.A.; Tao, X.Y.; Wu, B. Isolation and Antibiotic Screening of Fungi from a Hydrothermal Vent Site and Characterization of Secondary Metabolites from a Penicillium Isolate. Mar. Biotechnol. 2017, 19, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geris, R.; Rodrigues-Fo, E.; da Silva, H.H.G.; da Silva, I.G. Larvicidal Effects of Fungal Meroterpenoids in the Control of Aedes aegypti L. the Main Vector of Dengue and Yellow Fever. Chem. Biodivers. 2008, 5, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wei, M.; Chen, G.; Lin, Y. Two New Dihydroisocoumarins from the Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus sp. Collected from the South China Sea. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2012, 48, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.S.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, Y.S.; Wang, H.C.; Chan, H.Y.; Hsieh, S.Y.; Wu, H.C.; Cheng, M.J.; Yuan, G.F.; Lin, S.Y.; et al. Secondary Metabolites of the Endophytic Fungus Lachnum abnorme from Ardisia cornudentata. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, C.; Shi, Y.; Auckloo, B.N.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, B. Four Verrucosidin Derivatives Isolated from the Hydrothermal Vent Sulfur-Derived Fungus Penicillium sp. Y-50-10. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2018, 54, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Shi, Y.; Auckloo, B.N.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.T.; Tao, X.; Wu, B. An Unusual Conformational Isomer of Verrucosidin Backbone from a Hydrothermal Vent Fungus, Penicillium sp. Y-50-10. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, C.; Wu, X.; Auckloo, B.N.; Chen, C.T.; Ye, Y.; Wang, K.; Wu, B. An Unusual Stress Metabolite from a Hydrothermal Vent Fungus Aspergillus sp. WU 243 Induced by Cobalt. Molecules 2016, 21, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, Y.; Tani, K.; Kojima, A.; Sotoma, G.; Okada, K.; Shimada, A. Cyclo-(L-Tryptophyl-L-Phenylalanyl), a Plant Growth Regulator Produced by the Fungus Penicillium sp. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunyapaiboonsri, T.; Yoiprommarat, S.; Intereya, K.; Kocharin, K. New Diphenyl Ethers from the Insect Pathogenic Fungus Cordyceps sp. BCC 1861. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pimjuk, P.; Mongkolthanaruk, W.; Suwannasai, N.; Senawong, T.; Tontapha, S.; Amornkitbumrung, V.; McCloskey, S. A New A-Pyrone Derivative from Annulohypoxylon stygium SWUF09-030. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 23, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riga, R.; Happyana, N.; Holisotan Hakim, E. Sesquiterpenes Produced by Pestalotiopsis microspora HF 12440 Isolated from Artocarpus heterophyllus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 2229–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myokei, R.; Sakurai, A.; Chang, C.F.; Kodaira, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Tamura, S. Aspochracin, a New Insecticidal Metabolite of Aspergillus ochraceus Part I. Isolation, Structure and Biological Activities. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1969, 33, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Finefield, J.M.; Kato, H.; Greshook, T.J.; Sherman, D.H.; Tsukamoto, S.; Williams, R.M. Biosynthetic Studies of the Notoamides: Isotopic Synthesis of Stephacidin a and Incorporation into Notoamide B and Sclerotiamide. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 3802–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.X.; Zheng, W.F.; Wang, X.Q.; Sun, D.Q.; Li, C.Z. Total Synthesis of Notoamides F, I, and R and Sclerotiamide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10435–10438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, E.M.O.A.; Shantier, S.W.; Mohammed, M.S.; Musa, H.H.; Osman, W.; Mothana, R.A.; Gupta, L. Quinoline and Quinazoline Alkaloids against COVID-19: An in Silico Multitarget Approach. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 3613268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Shen, L.; Jiang, W.; Ye, Y.; Chen, C.T.; Wu, X.; Wang, K.; Wu, B. Zn-Driven Discovery of a Hydrothermal Vent Fungal Metabolite Clavatustide C, and an Experimental Study of the Anti-Cancer Mechanism of Clavatustide B. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3203–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Ye, P.; Chen, C.T.; Wang, K.; Liu, P.; He, S.; Wu, X.; Gan, L.; Ye, Y.; Wu, B. Two Novel Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cycle Inhibitory Cyclodepsipeptides from a Hydrothermal Vent Crab-Associated Fungus Aspergillus clavatus C2WU. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4761–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettu, S.K.; Madhu, R.B.; Raolji, G.B.; Babu, K.R.; Rao, N.S.K.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Ismail, A.; Reddy, G.B.; Shafi, S. First Total Synthesis of Cyclodepsipeptides Clavatustide a and B and Their Enantiomers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 61555–61565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Ding, C.; Auckloo, B.N.; Wu, B. Bioactive Metabolites from a Hydrothermal Vent Fungus Aspergillus sp. YQ-13. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nordstrom, T.; Lindqvist, C.; Stahls, A.; Mustelin, T.; Andersson, L.C. Inhibition of CD3-Induced Ca2+ Signals in Jurkat T-Cells by Myristic Acid. Cell Calcium 1991, 12, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Deng, Y.; Bu, X.; Ye, H.; Guo, N. Antimicrobial Potential of Myristic Acid against Listeria monocytogenes in Milk. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takato, T.; Iwata, K.; Murakami, C.; Wada, Y.; Sakane, F. Chronic Administration of Myristic Acid Improves Hyperglycaemia in the Nagoya-Shibata-Yasuda Mouse Model of Congenital Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 2076–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, C.L.; Meng, Q.F.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.D.; Chen, X.; Fu, S.B. Investigation of Chemical Compounds and Dpph Radical Scavenging Activity of Oudemansiella raphanipes (Agaricomycetes) Based on Fermentation. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2020, 22, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, M.; Yao, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Absolute Configuration Determination of Two Diastereomeric Neovasifuranones a and B from Fusarium oxysporum R1 by a Combination of Mosher’s Method and Chiroptical Approach. J. Fungi 2021, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Lu, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Two New 5-Hydroxy-2-Pyrone Derivatives Isolated from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus flavus. J. Antibiot. 2008, 61, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagning, A.L.N.; Tamokou, J.-d.-D.; Khan, M.L.; Ali, M.I.; Hameed, A.; Ngnokam, D.; Tapondjou, L.A.; Kuiate, J.-R.; Ali, M.S. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibition Activities of Extracts and Isolated Compounds from Scadoxus pseudocaulus and Semi-Synthetic Farrerol Derivatives. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 102, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happi, G.M.; Kouam, S.F.; Talontsi, F.M.; Nkenfou, C.N.; Longo, F.; Zühlke, S.; Douanla-Meli, C.; Spiteller, M. A New Dimeric Naphtho-Γ-Pyrone from an Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus niger Akrn Associated with the Roots of Entandrophragma congoënse Collected in Cameroon. Z. Nat. B 2015, 70, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.Q.; Shi, Y.T.; Chen, X.G.; Chen, C.T.A.; Tao, X.Y.; Wu, B. New Compounds from a Hydrothermal Vent Crab-Associated Fungus Aspergillus versicolor XZ-4. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, W.; Huang, X.; Tian, X.; Liao, S.; Yang, B.; Wang, F.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y. Antifungal New Oxepine-Containing Alkaloids and Xanthones from the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus versicolor SCSIO 05879. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2910–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Xie, C.-L.; Zhong, T.; Xu, W.; Luo, Z.-H.; Shao, Z.; Yang, X.-W. Sesquiterpenes from a Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Graphostroma sp. MCCC 3a00421. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 7267–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, G.-D.; Hu, D.; Li, X.-X.; Sun, X.; Guo, L.-D.; Li, Y.; Yao, X.-S.; Gao, H. Xylariterpenoids a–D, Four New Sesquiterpenoids from the Xylariaceae Fungus. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 54144–54148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J. Microbe–Metal Interactions in Marine Hydrothermal Environments. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Pan, C.; Auckloo, B.N.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.A.; Wang, K.; Wu, X.; Ye, Y.; Wu, B. Stress-Driven Discovery of a Cryptic Antibiotic Produced by Streptomyces sp. WU20 from Kueishantao Hydrothermal Vent with an Integrated Metabolomics Strategy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1395–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurumurthy, D.M.; Neelagund, S.E. Molecular Characterization of Industrially Viable Extreme Thermostable Novel Alpha-Amylase of Geobacillus sp. ISO5 Isolated from Geothermal Spring. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 6, 1759–1773. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Sun, X.; Jin, M.; Zhang, X. A Novel Benzoquinone Compound Isolated from Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Triggers Apoptosis of Tumor Cells. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Homann, V.V.; Sandy, M.; Tincu, J.A.; Templeton, A.S.; Tebo, B.M.; Butler, A. Loihichelins A-F, a Suite of Amphiphilic Siderophores Produced by the Marine Bacterium Halomonas LOB-5. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rougeaux, H.; Kervarec, N.; Pichon, R.; Guezennec, J. Structure of the Exopolysaccharide of Vibrio diabolicus Isolated from a Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent. Carbohydr. Res. 1999, 322, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianasolo, E.H.; Haramaty, L.; Rosario-Passapera, R.; Bidle, K.; White, E.; Vetriani, C.; Falkowski, P.; Lutz, R. Ammonificins a and B, Hydroxyethylamine Chroman Derivatives from a Cultured Marine Hydrothermal Vent Bacterium, Thermovibrio ammonificans. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrianasolo, E.H.; Haramaty, L.; Rosario-Passapera, R.; Vetriani, C.; Falkowski, P.; White, E.; Lutz, R. Ammonificins C and D, Hydroxyethylamine Chromene Derivatives from a Cultured Marine Hydrothermal Vent Bacterium, Thermovibrio ammonificans. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2300–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comita, P.B.; Gagosian, R.B.; Pang, H.; Costello, C.E. Structural Elucidation of a Unique Macrocyclic Membrane Lipid from a New, Extremely Thermophilic, Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Archaebacterium, Methanococcus jannaschii. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 15234–15241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonthier, I.; Rager, M.N.; Metzger, P.; Guezennec, J.; Largeau, C. A Di-O-Dihydrogeranylgeranyl Glycerol from Thermococcus S 557, a Novel Ether Lipid, and Likely Intermediate in the Biosynthesis of Diethers in Archaea. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 2795–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubreucq, G.; Domon, B.; Fournet, B. Structure Determination of a Novel Uronic Acid Residue Isolated from the Exopolysaccharide Produced by a Bacterium Originating from Deep Sea Hydrothermal Vents. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 290, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Tian, X.; Zhang, S.; Ju, J.; Zhang, C. Identification and Characterization of Xiamycin a and Oxiamycin Gene Cluster Reveals an Oxidative Cyclization Strategy Tailoring Indolosesquiterpene Biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8996–9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]























Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cong, M.; Pang, X.; Zhao, K.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Deep-Sea Natural Products from Extreme Environments: Cold Seeps and Hydrothermal Vents. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060404
Cong M, Pang X, Zhao K, Song Y, Liu Y, Wang J. Deep-Sea Natural Products from Extreme Environments: Cold Seeps and Hydrothermal Vents. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(6):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060404
Chicago/Turabian StyleCong, Mengjing, Xiaoyan Pang, Kai Zhao, Yue Song, Yonghong Liu, and Junfeng Wang. 2022. "Deep-Sea Natural Products from Extreme Environments: Cold Seeps and Hydrothermal Vents" Marine Drugs 20, no. 6: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060404
APA StyleCong, M., Pang, X., Zhao, K., Song, Y., Liu, Y., & Wang, J. (2022). Deep-Sea Natural Products from Extreme Environments: Cold Seeps and Hydrothermal Vents. Marine Drugs, 20(6), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060404