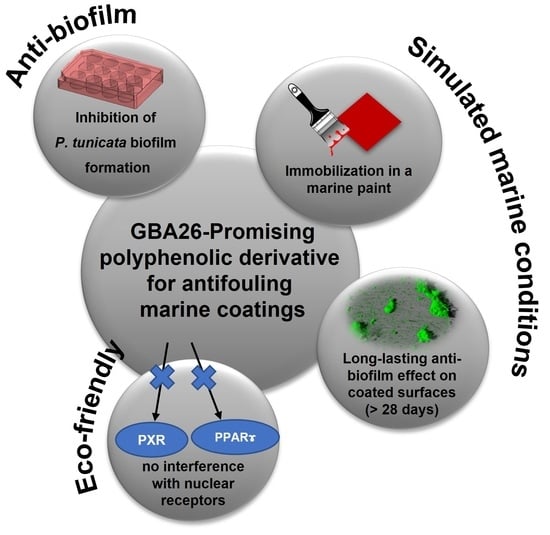
Antifouling Marine Coatings with a Potentially Safer and Sustainable Synthetic Polyphenolic Derivative
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Anti-Biofilm Performance of GBA26
2.2. PU-Based Coatings Containing GBA26
2.3. Pseudoalteromonas Tunicata Biofilm Formation under Defined Hydrodynamic Conditions
2.4. In Vitro Transcriptional Activation of HsPPARγ, DrPPARγ, and DrPXR
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Anti-Biofilm Assays
3.3. Immobilization of GBA26 in a Polyurethane-Based Marine Coating
3.4. Dynamic Biofilm Assay
3.5. In Vitro Transcriptional Activation of HsPPARγ, DrPPARγ and DrPXR
3.6. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Callow, M.; Callow, J.E. Marine biofouling: A sticky problem. Biologist 2002, 49, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bressy, C.; Lejars, M. Marine fouling: An overview. J. Ocean Technol. 2014, 9, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Amara, I.; Miled, W.; Slama, R.B.; Ladhari, N. Antifouling processes and toxicity effects of antifouling paints on marine environment. A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 57, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, V.W.; Leung, K.M.; Qiu, J.W.; Lam, M.H. Acute toxicities of five commonly used antifouling booster biocides to selected subtropical and cosmopolitan marine species. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Lovell, C.R. Microbial surface colonization and biofilm development in marine environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2016, 80, 91–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Resende, D.I.S.P.; Almeida, J.R.; Pereira, S.; Campos, A.; Lemos, A.; Plowman, J.E.; Thomas, A.; Clerens, S.; Vasconcelos, V.; Pinto, M.; et al. From natural xanthones to synthetic C-1 aminated 3,4-dioxygenated xanthones as optimized antifouling agents. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.; Gonçalves, C.; Martins, B.T.; Palmeira, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Pinto, M.; Almeida, J.R.; Correia-da-Silva, M.; Cidade, H. Flavonoid glycosides with a triazole moiety for marine antifouling applications: Synthesis and biological activity evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.R.; Palmeira, A.; Campos, A.; Cunha, I.; Freitas, M.; Felpeto, A.B.; Turkina, M.V.; Vasconcelos, V.; Pinto, M.; Correia-da-Silva, M.; et al. Structure-antifouling activity relationship and molecular targets of bio-inspired(thio)xanthones. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.R.; Almeida, J.R.; Carvalhal, F.; Câmara, A.; Pereira, S.; Antunes, J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Pinto, M.; Silva, E.R.; Sousa, E.; et al. Overcoming environmental problems of biocides: Synthetic bile acid derivatives as a sustainable alternative. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.R.; Moreira, J.; Pereira, D.; Pereira, S.; Antunes, J.; Palmeira, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Pinto, M.; Correia-da-Silva, M.; Cidade, H. Potential of synthetic chalcone derivatives to prevent marine biofouling. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.R.; Correia-da-Silva, M.; Sousa, E.; Antunes, J.; Pinto, M.; Vasconcelos, V.; Cunha, I. Antifouling potential of nature-inspired sulfated compounds. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rita Neves, A.; Vilas Boas, C.; Gonçalves, C.; Vasconcelos, V.; Pinto, M.; Silva, E.R.; Sousa, E.; Almeida, J.R.; Correia-da-Silva, M. Gallic acid derivatives as inhibitors of mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) larval settlement: Lead optimization, biological evaluation and use in antifouling coatings. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 126, 105911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, I.B.; Groh, K.J.; Stadnicka-Michalak, J.; Schönenberger, R.; Beiras, R.; Barroso, C.M.; Langford, K.H.; Thomas, K.V.; Suter, M.J.F. Tralopyril bioconcentration and effects on the gill proteome of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 177, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, P.-Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Fusetani, N. Mini-review: Marine natural products and their synthetic analogs as antifouling compounds: 2009–2014. Biofouling 2015, 31, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, D.; Webb, J.S.; Kjelleberg, S. Competitive interactions in mixed-species biofilms containing the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas tunicata. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abouelkheir, S.S.; Abdelghany, E.A.; Ghozlan, H.A.; Sabry, S.A. Characterization of biofilm forming marine Pseudoalteromonas spp. J. Mar. Sci. 2020, 2, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, S.I.; Teixeira-Santos, R.; Gomes, L.C.; Silva, E.R.; Morais, J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Mergulhão, F.J.M. Experimental assessment of the performance of two marine coatings to curb biofilm formation of microfoulers. Coatings 2020, 10, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, S.I.; Gomes, L.C.; Teixeira-Santos, R.; Morais, J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Mergulhão, F.J.M. Developing new marine antifouling surfaces: Learning from single-strain laboratory tests. Coatings 2021, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Boas, C.; Carvalhal, F.; Pereira, B.; Carvalho, S.; Sousa, E.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Calhorda, M.J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Almeida, J.R.; Silva, E.R.; et al. One step forward towards the development of eco-friendly antifouling coatings: Immobilization of a sulfated marine-inspired compound. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeu, M.J.; Alves, P.; Morais, J.; Miranda, J.M.; de Jong, E.D.; Sjollema, J.; Ramos, V.; Vasconcelos, V.; Mergulhão, F.J.M. Biofilm formation behaviour of marine filamentous cyanobacterial strains in controlled hydrodynamic conditions. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 4411–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiessen, P.; Gibbs, P.E. Critical appraisal of the evidence for tributyltin-mediated endocrine disruption in mollusks. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.M.; Ruivo, R.; Capitão, A.; Fonseca, E.; Castro, L.F.C. Identifying the gaps: Resources and perspectives on the use of nuclear receptor based-assays to improve hazard assessment of emerging contaminants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 358, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, D.; Reis-Henriques, M.A.; Silva, R.; Santos, A.I.; Castro, L.F.; Santos, M.M. Tributyltin-induced imposex in marine gastropods involves tissue-specific modulation of the retinoid X receptor. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Lam, J.C.W. SeaNine 211 as antifouling biocide: A coastal pollutant of emerging concern. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 61, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Li, P.; He, S.; Xing, S.; Cao, Z.; Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.-H. Effects of short-term exposure to tralopyril on physiological indexes and endocrine function in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 245, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson-Rechavi, M.; Garcia, H.E.; Laudet, V. The nuclear receptor superfamily. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 585–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.-C.; Wang, B.; Zeng, Y.-H.; Cai, Z.-H.; Zhou, J. The microbial mechanisms of a novel photosensitive material (treated rape pollen) in anti-biofilm process under marine environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, E.; Machado, A.M.; Vilas-Arrondo, N.; Gomes-dos-Santos, A.; Veríssimo, A.; Esteves, P.; Almeida, T.; Themudo, G.; Ruivo, R.; Pérez, M.; et al. Cartilaginous fishes offer unique insights into the evolution of the nuclear receptor gene repertoire in gnathostomes. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 295, 113527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, P.; Navarro-Herrera, D.; Zabala, M.; Miguéliz, I.; Romo-Hualde, A.; López-Yoldi, M.; Martínez, J.A.; Vizmanos, J.L.; Milagro, F.I.; González-Navarro, C.J. Phenolic compounds inhibit 3T3-L1 adipogenesis depending on the stage of differentiation and their binding affinity to PPARγ. Molecules 2019, 24, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kluth, D.; Banning, A.; Paur, I.; Blomhoff, R.; Brigelius-Flohé, R. Modulation of pregnane X receptor-and electrophile responsive element-mediated gene expression by dietary polyphenolic compounds. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goksøyr, A. Endocrine disruptors in the marine environment: Mechanisms of toxicity and their influence on reproductive processes in fish. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2006, 69, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitão, A.; Lopes-Marques, M.; Páscoa, I.; Ruivo, R.; Mendiratta, N.; Fonseca, E.; Castro, L.F.C.; Santos, M.M. The Echinodermata PPAR: Functional characterization and exploitation by the model lipid homeostasis regulator tributyltin. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitão, A.M.F.; Lopes-Marques, M.S.; Ishii, Y.; Ruivo, R.; Fonseca, E.S.S.; Páscoa, I.; Jorge, R.P.; Barbosa, M.A.G.; Hiromori, Y.; Miyagi, T.; et al. Evolutionary exploitation of vertebrate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ by organotins. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13951–13959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.M.; Barish, G.D.; Wang, Y.-X. PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, C.-H.; Beglov, D.; Rudnitskaya, A.N.; Kozakov, D.; Waxman, D.J.; Vajda, S. The structural basis of pregnane X receptor binding promiscuity. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 11572–11581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, E.R.; Tulcidas, A.V.; Ferreira, O.; Bayón, R.; Igartua, A.; Mendoza, G.; Mergulhão, F.J.M.; Faria, S.I.; Gomes, L.C.; Carvalho, S.; et al. Assessment of the environmental compatibility and antifouling performance of an innovative biocidal and foul-release multifunctional marine coating. Environ. Res. 2021, 198, 111219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Coating Formulation | Base/Curing Agent Ratio (wt.%) | GBA26 Content (wt.%) | CL 1 Content (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GBA26-PU 2 | 9/1 | 1.05 ± 0.01 | - |
| GBA26-PU | 1.98 ± 0.01 | - | |
| GBA26/PU/CL | 1.88 ± 0.01 | 1.08 ± 0.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neves, A.R.; Gomes, L.C.; Faria, S.I.; Sousa, J.; Ruivo, R.; Páscoa, I.; Pinto, M.; Sousa, E.; Santos, M.M.; Silva, E.R.; et al. Antifouling Marine Coatings with a Potentially Safer and Sustainable Synthetic Polyphenolic Derivative. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080507
Neves AR, Gomes LC, Faria SI, Sousa J, Ruivo R, Páscoa I, Pinto M, Sousa E, Santos MM, Silva ER, et al. Antifouling Marine Coatings with a Potentially Safer and Sustainable Synthetic Polyphenolic Derivative. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(8):507. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080507
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeves, Ana R., Luciana C. Gomes, Sara I. Faria, João Sousa, Raquel Ruivo, Inês Páscoa, Madalena Pinto, Emília Sousa, Miguel M. Santos, Elisabete R. Silva, and et al. 2022. "Antifouling Marine Coatings with a Potentially Safer and Sustainable Synthetic Polyphenolic Derivative" Marine Drugs 20, no. 8: 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080507
APA StyleNeves, A. R., Gomes, L. C., Faria, S. I., Sousa, J., Ruivo, R., Páscoa, I., Pinto, M., Sousa, E., Santos, M. M., Silva, E. R., Correia-da-Silva, M., & Mergulhão, F. (2022). Antifouling Marine Coatings with a Potentially Safer and Sustainable Synthetic Polyphenolic Derivative. Marine Drugs, 20(8), 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080507