Fast and Sustained Axonal Growth by BDNF Released from Chitosan Microspheres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chitosan Microspheres-BDNF versus Chitosan Hydrochloride Microspheres-BDNF
2.2. Zeta Potential and Dynamic Light Scattering of Chitosan Microspheres
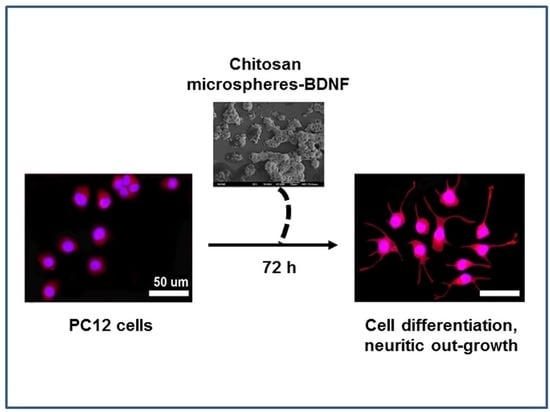
2.3. Effect of Chitosan Microspheres-BDNF on Neural Cell Differentiation and Neuritic Growth in PC12 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Line
4.2. Encapsulation of BDNF in Chitosan Microspheres
4.3. Analysis by Zeta Potential (ζ)
4.4. Analysis by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
4.5. Chitosan Microspheres-BDNF Treatment
4.6. Immunocytochemistry
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Zhen, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, B. Deconvoluting the Complexity of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neuroanat. 2022, 16, 910427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, M.P.; Roberts, C.; Waseem, M.; Tyagi, P. Drug Targets in Neurotrophin Signaling in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6939–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welling, P.G.; Balant, L.P.E. (Eds.) Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, R.G.; Frey, W.H. Delivery of Neurotrophic Factors to the Central Nervous System. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2001, 40, 907–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyileten, C.; Sharif, L.; Wicik, Z.; Jakubik, D.; Jarosz-Popek, J.; Soplinska, A.; Postula, M.; Czlonkowska, A.; Kaplon-Cieslicka, A.; Mirowska-Guzel, D. The Relation of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor with MicroRNAs in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Ischemic Stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xie, Y.; Qin, D. Proteolytic cleavage of proBDNF to mBDNF in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 166, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Míguez, M.J.; Vargas, M.; Perez, C.; Espinoza, L.; Chan, W. Exposure to Stress and Separation-induced BDNF impairments in adolescents. J. Neurol. Sci. Psychiatry 2016, 2, 113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hilițanu, L.N.; Mititelu-Tarțău, L.; Bogdan, M.; Buca, B.R.; Păuna, A.-M.R.; Pavel, L.L.; Pelin, A.-M.; Meca, A.-D.; Popa, G.E. The Use of Chitosan-Coated Nanovesicles in Repairing Alcohol-Induced Damage of Liver Cells in Mice. Medicina 2022, 58, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Sahoo, S.K. Long circulating chitosan/PEG blended PLGA nanoparticle for tumor drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.U.A.; Yaqoob, Z.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Razak, S.I.A.; Raza, M.A.; Sajjad, A.; Haider, S.; Busra, F.M. Chitosan/Poly Vinyl Alcohol/Graphene Oxide Based pH-Responsive Composite Hydrogel Films: Drug Release, Anti-Microbial and Cell Viability Studies. Polymers 2021, 13, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.U.A.; Haider, S.; Raza, M.A.; Shah, S.A.; Razak, S.I.A.; Kadir, M.R.A.; Subhan, F.; Haider, A. Smart and pH-sensitive rGO/Arabinoxylan/chitosan composite for wound dressing: In-vitro drug delivery, antibacterial activity, and biological activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, V.; Gaud, R.; Bajaj, A.; Wairkar, S. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of intranasally administered selegiline nanoparticles with improved brain delivery in Parkinson’s disease. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostolska, I.; Wiśniewska, M. Application of the zeta potential measurements to explanation of colloidal Cr2O3 stability mechanism in the presence of the ionic polyamino acids. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 2453–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panos, I.; Acosta, N.; Heras, A. New Drug Delivery Systems Based on Chitosan. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2008, 5, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mati-Baouche, N.; Delattre, C.; de Baynast, H.; Grédiac, M.; Mathias, J.-D.; Ursu, A.V.; Desbrières, J.; Michaud, P. Alkyl-Chitosan-Based Adhesive: Water Resistance Improvement. Molecules 2019, 24, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mang, C.S.; Campbell, K.L.; Ross, C.J.D.; Boyd, L.A. Promoting Neuroplasticity for Motor Rehabilitation After Stroke: Considering the Effects of Aerobic Exercise and Genetic Variation on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor. Phys. Ther. 2013, 93, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, L.; Li, C.; Du, X.; Shi, Q.; Huang, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q. Effect of aerobic exercise on BDNF/proBDNF expression in the ischemic hippocampus and depression recovery of rats after stroke. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 362, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Torres, V.; Gransee, H.M.; Mantilla, C.B.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, W.Z.; Sieck, G.C. BDNF effects on functional recovery across motor behaviors after cervical spinal cord injury. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 117, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geoffroy, C.G.; Zheng, B. Myelin-associated inhibitors in axonal growth after CNS injury. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2014, 27, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, L.F.; Costa, R.O.; Pedro, J.R.; Aguiar, P.; Serra, S.C.; Teixeira, F.G.; Sousa, N.; Salgado, A.J.; Almeida, R.D. Mesenchymal stem cells secretome-induced axonal outgrowth is mediated by BDNF. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, H.M.; Wu, H.C.; Sun, Z.G.; Lian, F.; Leung, P.C.K. Neurotrophins and glial cell linederived neurotrophic factor in the ovary: Physiological and pathophysiological implications. Hum. Reprod. Update 2019, 25, 224–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.V. Neurotrophins and their receptors: A convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Pang, K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Han, F.; Yao, H.; Liu, H.; Lopes-Rodrigues, V.; et al. TrkB agonistic antibodies superior to BDNF: Utility in treating motoneuron degeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 132, 104590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.M.; Zhou, C.F.; Gao, S.L.; Tian, Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, L.; Gu, H.F.; Tang, X.Q. BDNF-TrkB pathway mediates neuroprotection of hydrogen sulfide against formaldehyde-induced toxicity to PC12 cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Song, J.; Meng, D.; Chang, Q. TPPU, a sEH Inhibitor, Attenuates Corticosterone-Induced PC12 Cell Injury by Modulation of BDNF-TrkB Pathway. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 67, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Muroi, M.; Cao, S.; Bian, L.; Osada, H.; Xiang, L.; Qi, J. 3β,23,28-Trihydroxy-12-oleanene 3β-Caffeate from Desmodium sambuense-Induced Neurogenesis in PC12 Cells Mediated by ER Stress and BDNF-TrkB Signaling Pathways. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Hu, J.; Park, H.; Lee, M. Chitosan-based nanoparticles as a sustained protein release carrier for tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100A, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Q.; Weng, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, W.; Yang, Q.; Guo, F.; Wu, D.; Song, Y.; Chen, F.; Yang, G. Characteristics, Cryoprotection Evaluation and In Vitro Release of BSA-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Cohen, A.; Maysinger, D. In vitro effects of brain derived neurotrophic factor released from microspheres. Neuroreport 1994, 5, 2577–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Alvarez, I.; Garrido, L.; Doncel-Pérez, E.; Nieto-Sampedro, M.; Fernández-Mayoralas, A. Detection of metabolite changes in C6 glioma cells cultured with antimitotic oleyl glycoside by 1H MAS NMR. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Sample | ζ 1 (mV) | Size by DLS 2 (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Chitosan Microspheres-BDNF | −9.7 ± 10 | 6091 |
| Chitosan Hydrochloride Microspheres-BDNF | −70.7 ± 8.7 | 508 |
| Salt Powder (Control) | 17.5 ± 3.2 | 5800 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aranaz, I.; Acosta, N.; Revuelta, J.; Bastida, A.; Gómez-Casado, V.; Civera, C.; Garrido, L.; García-Junceda, E.; Heras, Á.; Alcántara, A.R.; et al. Fast and Sustained Axonal Growth by BDNF Released from Chitosan Microspheres. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020091
Aranaz I, Acosta N, Revuelta J, Bastida A, Gómez-Casado V, Civera C, Garrido L, García-Junceda E, Heras Á, Alcántara AR, et al. Fast and Sustained Axonal Growth by BDNF Released from Chitosan Microspheres. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(2):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020091
Chicago/Turabian StyleAranaz, Inmaculada, Niuris Acosta, Julia Revuelta, Agatha Bastida, Víctor Gómez-Casado, Concepción Civera, Leoncio Garrido, Eduardo García-Junceda, Ángeles Heras, Andrés R. Alcántara, and et al. 2023. "Fast and Sustained Axonal Growth by BDNF Released from Chitosan Microspheres" Marine Drugs 21, no. 2: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020091
APA StyleAranaz, I., Acosta, N., Revuelta, J., Bastida, A., Gómez-Casado, V., Civera, C., Garrido, L., García-Junceda, E., Heras, Á., Alcántara, A. R., Fernández-Mayoralas, A., & Doncel-Pérez, E. (2023). Fast and Sustained Axonal Growth by BDNF Released from Chitosan Microspheres. Marine Drugs, 21(2), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020091