The Loss of Structural Integrity of 3D Chitin Scaffolds from Aplysina aerophoba Marine Demosponge after Treatment with LiOH
Abstract
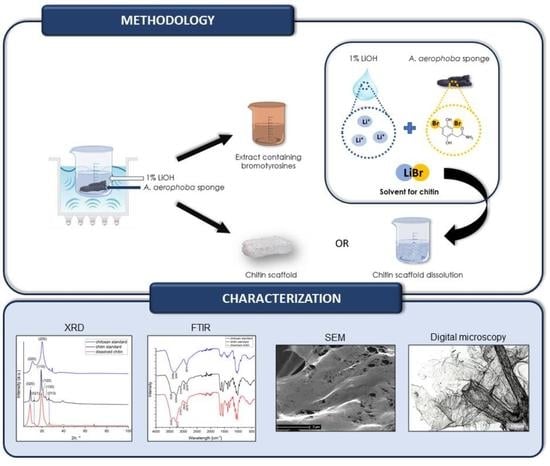
:1. Introduction
| Solvent | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-chloroethanol and mineral acid | Dissolving chitin rapidly at room or mildly elevated temperature | Hydrolytic degradation occurs | [45] |
| Carboxylic acids (formic, dichloroacetic, trichloroacetic) | Dissolving chitin rapidly, usually at room or mildly elevated temperature | Chitin is degrading slowly; solutions of chitin in formic acid are unstable | [43,44,46] |
| Concentrated phosphoric acid | Dissolving chitin rapidly at room temperature | Chitin is hydrolyzed after a long time in the acid at room temperature | [47] |
| Hexafluoroacetone sesquihydrate | The solutions formed may be wet or dry spun into filaments, or cast into films or solid articles | Toxicity | [48] |
| Hexafluoro-2-propanol | No chitin degradation occurs | Toxicity | [49] |
| CaCl2·2H2O-saturated methanol | Clear chitin solution easy to regenerate chitin into diverse forms | Chitin solubility depends on the degree of deacetylation and molecular weight | [50,51] |
| LiCl/N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) | Non-degrading solvent | Toxicity | [43,46,52,53] |
| LiCl/dimethylacetamide (DMA) | Non-degrading solvent | Not all species of chitin can be dissolved; toxicity | [43,46,52,53] |
| LiSCN | No hydrolysis | High temperatures required | [46,54] |
| LiI | No hydrolysis | High temperatures required | [54] |
| LiCl/DMF | Relatively short time (1 h) | Toxicity | [52,55] |
| NaOH/crushed ice or freezing | Chitin in alkali is stable with respect to degradation | Hydrolysis occurs | [52,56,57,58,59] |
| NaOH/urea | Little effect on the chitin structure; retaining the degree of deacetylation | Temperature not higher than −20 °C | [52,60] |
| KOH/urea | Good chitin solubility (~80%) | Deacetylation occurs (ca. 12.5%); Low temperatures required (−25 °C) | [41] |
| Deep eutectic solvents | No structural degradation | High temperatures required; depolymerization occurs | [61] |
| Ionic liquids | Dissolve chitin of all polymorphic forms; green solvents | Elevated temperatures required | [42,62] |
2. Results
2.1. Digital Microscopy
2.2. Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5. Control Test
2.6. CFW Staining and Fluorescence Microscopy for Chitin Identification
2.7. Bromotyrosines-Based Extracts
3. Discussion

4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Isolation of Chitin Scaffolds
4.3. Dissolution of A. aerophoba Chitin in LiOH
4.4. Chemicals
4.5. FTIR Spectroscopy
4.6. X-ray Diffraction
4.7. Digital Microscopy
4.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDX)
4.9. Calcofluor White (CFW) Staining
4.10. Fluorescent Microscopy
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ehrlich, H. Chitin of Poriferan Origin as a Unique Biological Material. In Blue Biotechnology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 821–854. ISBN 978-3-527-80171-8. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzarelli, R.; Boudrant, J.; Meyer, D.; Manno, N.; DeMarchis, M.; Paoletti, M. Current Views on Fungal Chitin/Chitosan, Human Chitinases, Food Preservation, Glucans, Pectins and Inulin: A Tribute to Henri Braconnot, Precursor of Thecarbohydrate Polymers Science, on the Chitin Bicentennial. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 995–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Góngora, E.; Ebert, F.; Willhoeft, U.; Said-Fernández, S.; Tannich, E. Characterization of Chitin Synthases from Entamoeba. Protist 2004, 155, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, E.; Richthammer, P.; Ehrlich, H.; Paasch, S.; Simon, P.; Ueberlein, S.; van Pée, K.-H. Chitin-Based Organic Networks: An Integral Part of Cell Wall Biosilica in the Diatom Thalassiosira Pseudonana. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 9724–9727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H. Chitin and Collagen as Universal and Alternative Templates in Biomineralization. Int. Geol. Rev. 2010, 52, 661–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Maldonado, M.; Spindler, K.-D.; Eckert, C.; Hanke, T.; Born, R.; Goebel, C.; Simon, P.; Heinemann, S.; Worch, H. First Evidence of Chitin as a Component of the Skeletal Fibers of Marine Sponges. Part I. Verongidae (Demospongia: Porifera). J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2007, 308, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinger, C.; Żółtowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Wysokowski, M.; Tsurkan, M.V.; Galli, R.; Petrenko, I.; Machałowski, T.; Ereskovsky, A.; Martinović, R.; Muzychka, L.; et al. Express Method for Isolation of Ready-to-Use 3D Chitin Scaffolds from Aplysina Archeri (Aplysineidae: Verongiida) Demosponge. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żółtowska, S.; Klinger, C.; Petrenko, I.; Wysokowski, M.; Joseph, Y.; Jesionowski, T.; Ehrlich, H. Methods of Isolating Chitin from Sponges (Porifera). In Chitin and Chitosan: Properties and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 35–59. ISBN 978-1-119-45046-7. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, W. Occurrence of Chitin in Mollusca. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1972, 41, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, I.M.; Schönitzer, V. The Distribution of Chitin in Larval Shells of the Bivalve Mollusk Mytilus Galloprovincialis. J. Struct. Biol. 2006, 153, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraud-Guille, M.-M.; Chanzy, H.; Vuong, R. Chitin Crystals in Arthropod Cuticles Revealed by Diffraction Contrast Transmission Electron Microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 1990, 103, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, F.; Younis, T.; Sidra, S.; Muneer, B.; Nasreen, Z.; Saleh, F.; Mumtaz, S.; Saeed, R.F.; Abbas, A.S. Extraction of Chitin from Edible Crab Shells of Callinectes Sapidus and Comparison with Market Purchased Chitin. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 83, e246520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percot, A.; Viton, C.; Domard, A. Optimization of Chitin Extraction from Shrimp Shells. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rødde, R.; Einbu, A.; Varum, K. A Seasonal Study of the Chemical Composition and Chitin Quality of Shrimp Shells Obtained from Northern Shrimp (Pandalus Borealis). Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xie, W.; Yu, J.; Xin, R.; Shi, Z.; Song, L.; Yang, X. Extraction of Chitin From Shrimp Shell by Successive Two-Step Fermentation of Exiguobacterium Profundum and Lactobacillus Acidophilus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 677126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, G.P.; Lo, J.; Laine, R.; Almeder, M. Chitin in the Epidermal Cuticle of a Vertebrate (Paralipophrys Trigloides, Blenniidae, Teleostei). Experientia 1993, 49, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and Chitosan: Properties and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurkan, M.V.; Voronkina, A.; Khrunyk, Y.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Ehrlich, H. Progress in Chitin Analytics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kertmen, A.; Petrenko, I.; Schimpf, C.; Rafaja, D.; Petrova, O.; Sivkov, V.; Nekipelov, S.; Fursov, A.; Stelling, A.L.; Heimler, K.; et al. Calcite Nanotuned Chitinous Skeletons of Giant Ianthella Basta Marine Demosponge. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machałowski, T.; Wysokowski, M.; Żółtowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Bechmann, N.; Binnewerg, B.; Schubert, M.; Guan, K.; Bornstein, S.R.; Czaczyk, K.; Pokrovsky, O.; et al. Spider Chitin. The Biomimetic Potential and Applications of Caribena Versicolor Tubular Chitin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 226, 115301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzychka, L.; Voronkina, A.; Kovalchuk, V.; Smolii, O.B.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Ehrlich, I.; Ehrlich, H. Marine Biomimetics: Bromotyrosines Loaded Chitinous Skeleton as Source of Antibacterial Agents. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertmen, A.; Ehrlich, H. Patentology of Chitinous Biomaterials. Part I: Chitin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 282, 119102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Sowmya, S.; Kumar, P.T.S.; Deepthi, S.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Ehrlich, H.; Tsurkan, M.; Jayakumar, R. Chitin and Chitosan in Selected Biomedical Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1644–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, V.; Voronkina, A.; Binnewerg, B.; Schubert, M.; Muzychka, L.; Wysokowski, M.; Tsurkan, M.V.; Bechmann, N.; Petrenko, I.; Fursov, A.; et al. Naturally Drug-Loaded Chitin: Isolation and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Song, S.; Li, H.; Gözaydın, G.; Yan, N. Expanding the Boundary of Biorefinery: Organonitrogen Chemicals from Biomass. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Li, F.; Fu, X. Towards Shell Biorefinery: Advances in Chemical-Catalytic Conversion of Chitin Biomass to Organonitrogen Chemicals. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 6498–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Gözaydın, G.; Yang, H.; Ning, W.; Han, X.; Poon, N.Y.; Liang, H.; Yan, N.; Zhou, K. Upcycling Chitin-Containing Waste into Organonitrogen Chemicals via an Integrated Process. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 7719–7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kertmen, A.; Dziedzic, I.; Ehrlich, H. Patentology of Chitinous Biomaterials. Part II: Chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 301, 120224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H. 2—Biomimetic Potential of Chitin-Based Composite Biomaterials of Poriferan Origin. In Biomimetic Biomaterials; Ruys, A.J., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 46–66. ISBN 978-0-85709-416-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, H.; Steck, E.; Ilan, M.; Maldonado, M.; Muricy, G.; Bavestrello, G.; Kljajic, Z.; Carballo, J.L.; Schiaparelli, S.; Ereskovsky, A.; et al. Three-Dimensional Chitin-Based Scaffolds from Verongida Sponges (Demospongiae: Porifera). Part II: Biomimetic Potential and Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutsenko, V.; Gryshkov, O.; Rogulska, O.; Lode, A.; Petrenko, A.Y.; Gelinsky, M.; Glasmacher, B.; Ehrlich, H. Chitinous Scaffolds from Marine Sponges for Tissue Engineering. In Marine-Derived Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications; Choi, A.H., Ben-Nissan, B., Eds.; Springer Series in Biomaterials Science and Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 285–307. ISBN 978-9-81-138855-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mutsenko, V.V.; Bazhenov, V.V.; Rogulska, O.; Tarusin, D.N.; Schütz, K.; Brüggemeier, S.; Gossla, E.; Akkineni, A.R.; Meißner, H.; Lode, A.; et al. 3D Chitinous Scaffolds Derived from Cultivated Marine Demosponge Aplysina Aerophoba for Tissue Engineering Approaches Based on Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1966–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsenko, V.V.; Gryshkov, O.; Lauterboeck, L.; Rogulska, O.; Tarusin, D.N.; Bazhenov, V.V.; Schütz, K.; Brüggemeier, S.; Gossla, E.; Akkineni, A.R.; et al. Novel Chitin Scaffolds Derived from Marine Sponge Ianthella Basta for Tissue Engineering Approaches Based on Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Biocompatibility and Cryopreservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1955–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Wysokowski, M.; Jesionowski, T. The Philosophy of Extreme Biomimetics. SMT 2022, 32, e00447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Galli, R.; Schimpf, C.; Rafaja, D.; Hubalkova, J.; Aneziris, C.G.; Dyshlovoy, S.; von Amsberg, G.; Meissner, H.; et al. Extreme Biomineralization: The Case of the Hypermineralized Ear Bone of Gray Whale (Eschrichtius Robustus). Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Simon, P.; Motylenko, M.; Wysokowski, M.; Bazhenov, V.V.; Galli, R.; Stelling, A.L.; Stawski, D.; Ilan, M.; Stöcker, H.; et al. Extreme Biomimetics: Formation of Zirconium Dioxide Nanophase Using Chitinous Scaffolds under Hydrothermal Conditions. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5092–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machałowski, T.; Czajka, M.; Petrenko, I.; Meissner, H.; Schimpf, C.; Rafaja, D.; Ziętek, J.; Dzięgiel, B.; Adaszek, Ł.; Voronkina, A.; et al. Functionalization of 3D Chitinous Skeletal Scaffolds of Sponge Origin Using Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Properties. Mar Drugs 2020, 18, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrenko, I.; Bazhenov, V.V.; Galli, R.; Wysokowski, M.; Fromont, J.; Schupp, P.J.; Stelling, A.L.; Niederschlag, E.; Stöker, H.; Kutsova, V.Z.; et al. Chitin of Poriferan Origin and the Bioelectrometallurgy of Copper/Copper Oxide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysokowski, M.; Motylenko, M.; Beyer, J.; Makarova, A.; Stöcker, H.; Walter, J.; Galli, R.; Kaiser, S.; Vyalikh, D.; Bazhenov, V.V.; et al. Extreme Biomimetic Approach for Developing Novel Chitin-GeO2 Nanocomposites with Photoluminescent Properties. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysokowski, M.; Behm, T.; Born, R.; Bazhenov, V.V.; Meißner, H.; Richter, G.; Szwarc-Rzepka, K.; Makarova, A.; Vyalikh, D.; Schupp, P.; et al. Preparation of Chitin–Silica Composites by In Vitro Silicification of Two-Dimensional Ianthella Basta Demosponge Chitinous Scaffolds under Modified Stöber Conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3935–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Ru, G.; Feng, J. Dissolution of Chitin in Aqueous KOH. Cellulose 2016, 23, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, M.M.; Kozlecki, T.; Gorak, A. Review of the Application of Ionic Liquids as Solvents for Chitin. J. Polym. Eng. 2012, 32, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.R. Chitin Solvents and Solubility Parameters. In Chitin, Chitosan, and Related Enzymes; Zikakis, J.P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1984; pp. 227–237. ISBN 978-0−12-780950-2. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, P.R. Solvents for and Purification of Chitin 1975. U.S. Patent US4062921A, 13 December 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, P.R. Purification of Chitin 1975. U.S. Patent 3879377, 22 April 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Gagnaire, D.; Saint-Germain, J.; Vincendon, M. NMR Studies of Chitin and Chitin Derivatives. Makromol. Chem. 1982, 183, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincendon, M. Regenerated Chitin from Phosphoric Acid Solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 1997, 32, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozza, R.C. Spinning and Shaping Poly-(N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine) 1975. U.S. Patent US3988411A, 26 October 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Rolandi, M.; Rolandi, R. Self-Assembled Chitin Nanofibers and Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 207, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokura, S.; Nishimura, S.-I.; Sakairi, N.; Nishi, N. Biological Activities of Biodegradable Polysaccharide. Macromol. Symp. 1996, 101, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Nagahama, H.; Tokura, S. Preparation of Chitin Hydrogel Under Mild Conditions. Cellulose 2006, 13, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Du, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Feng, T.; Yang, J.; Kennedy, J.F. Solubility and Property of Chitin in NaOH/Urea Aqueous Solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 70, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincendon, M. 1H NMR Study of the Chitin Dissolution Mechanism. Makromol. Chem. 1985, 186, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.L.; Smith, A.F. X-ray Diffraction Studies of Chitin, Chitosan, and Derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. 1936, 40, 863–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ling Chew, S.; Kerton, F.M.; Yan, N. Direct Conversion of Chitin into a N-Containing Furan Derivative. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2204–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannan, T.; Kurita, K.; Iwakura, Y. Studies on Chitin, 1. Solubility Change by Alkaline Treatment and Film Casting. Makromol. Chem. 1975, 176, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannan, T.; Kurita, K.; Iwakura, Y. Studies on Chitin, 2. Effect of Deacetylation on Solubility. Makromol. Chem. 1976, 177, 3589–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einbu, A.; Naess, S.N.; Elgsaeter, A.; Vårum, K.M. Solution Properties of Chitin in Alkali. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 2048–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Liu, Y.; Hu, K. Influence of Alkali-Freezing Treatment on the Solid State Structure of Chitin. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 2321–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L. Novel Hydrogels Prepared via Direct Dissolution of Chitin at Low Temperature: Structure and Biocompatibility. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3865–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Mukesh, C.; Mondal, D.; Prasad, K. Dissolution of α-Chitin in Deep Eutectic Solvents. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 18149–18155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L. Chitin in Ionic Liquids: Historical Insights into the Polymer’s Dissolution and Isolation. A Review. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 3974–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueberlein, S.; Machill, S.; Niemann, H.; Proksch, P.; Brunner, E. The Skeletal Amino Acid Composition of the Marine Demosponge Aplysina Cavernicola. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4417–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnewerg, B.; Schubert, M.; Voronkina, A.; Muzychka, L.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Djurović, M.; Kovalchuk, V.; Tsurkan, M.; Martinovic, R.; et al. Marine Biomaterials: Biomimetic and Pharmacological Potential of Cultivated Aplysina Aerophoba Marine Demosponge. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, E.; Ehrlich, H.; Schupp, P.; Hedrich, R.; Hunoldt, S.; Kammer, M.; Machill, S.; Paasch, S.; Bazhenov, V.V.; Kurek, D.V.; et al. Chitin-Based Scaffolds Are an Integral Part of the Skeleton of the Marine Demosponge Ianthella Basta. J. Struct. Biol. 2009, 168, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Ilan, M.; Maldonado, M.; Muricy, G.; Bavestrello, G.; Kljajic, Z.; Carballo, J.L.; Schiaparelli, S.; Ereskovsky, A.; Schupp, P.; et al. Three-Dimensional Chitin-Based Scaffolds from Verongida Sponges (Demospongiae: Porifera). Part I. Isolation and Identification of Chitin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziedzic, I.; Kertmen, A. Methods of Chitosan Identification: History and Trends. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2023, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Queiroz, M.; Melo, K.R.T.; Sabry, D.A.; Sassaki, G.L.; Rocha, H.A.O. Does the Use of Chitosan Contribute to Oxalate Kidney Stone Formation? Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Sun, Q.; She, X.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, D. Fabrication and Characterisation of α-Chitin Nanofibers and Highly Transparent Chitin Films by Pulsed Ultrasonication. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Saito, T.; Isogai, A. Preparation of Chitin Nanofibers from Squid Pen β-Chitin by Simple Mechanical Treatment under Acid Conditions. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1919–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Wang, X.; Wu, M.; Wu, S.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Dai, F. Insignificant Difference in Biocompatibility of Regenerated Silk Fibroin Prepared with Ternary Reagent Compared with Regenerated Silk Fibroin Prepared with Lithium Bromide. Polymers 2022, 14, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, D.; Li, M.; You, R.; Xu, W. Fabrication of Porous Silk Fibroin/Cellulose Nanofibril Sponges with Hierarchical Structure Using a Lithium Bromide Solvent System. Cellulose 2019, 26, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, J.; Shi, H.; Xia, Z.; Sahoo, J.K.; Yeo, J.; Kaplan, D.L. Fiber-Based Biopolymer Processing as a Route toward Sustainability. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2105196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, N.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Pan, X. Preparation and Characterization of Regenerated Cellulose Film from a Solution in Lithium Bromide Molten Salt Hydrate. Polymers 2018, 10, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowacki, K.; Galiński, M.; Fursov, A.; Voronkina, A.; Meissner, H.; Petrenko, I.; Stelling, A.L.; Ehrlich, H. Electrolysis as a Universal Approach for Isolation of Diverse Chitin Scaffolds from Selected Marine Demosponges. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, M.; Binnewerg, B.; Voronkina, A.; Muzychka, L.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Kovalchuk, V.; Tsurkan, M.; Martinovic, R.; Bechmann, N.; et al. Naturally Prefabricated Marine Biomaterials: Isolation and Applications of Flat Chitinous 3D Scaffolds from Ianthella Labyrinthus (Demospongiae: Verongiida). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, N.; Ehrlich, H.; Eisenhofer, G.; Ehrlich, A.; Meschke, S.; Ziegler, C.G.; Bornstein, S.R. Anti-Tumorigenic and Anti-Metastatic Activity of the Sponge-Derived Marine Drugs Aeroplysinin−1 and Isofistularin-3 against Pheochromocytoma In Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of Infrared Spectra, A Practical Approach. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-470-02731-8. [Google Scholar]
- Gopichand, Y.; Schmitz, F.J. Marine Natural Products: Fistularin−1, -2 and -3 from the Sponge Aplysina Fistularis Forma Fulva. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 3921–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, G.; De Rosa, S.; De Stefano, S.; Self, R.; Sodano, G. The Bromo-Compounds of the True Sponge Verongia Aerophoba. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24, 3029–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AYDOĞMUŞ, Z.; ERSOY, N.; İMRE, S. Chemical Investigation of the Sponge Verongia Aerophoba. Turk. J. Chem. 1999, 23, 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Machałowski, T.; Rusak, A.; Wiatrak, B.; Haczkiewicz-Leśniak, K.; Popiel, A.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Żak, A.; Podhorska-Okołów, M.; Jesionowski, T. Naturally Formed Chitinous Skeleton Isolated from the Marine Demosponge Aplysina Fistularis as a 3D Scaffold for Tissue Engineering. Materials 2021, 14, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welinder, B.S. Halogenated Tyrosines from the Cuticle of Limulus Polyphemus (L.). Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 1972, 279, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, S.; Breuer, S.W. Chlorinated and Brominated Tyrosine Residues in Molluscan Scleroprotein. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1973, 1, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Stelling, A.L.; Stawski, D.; Jesionowski, T.; Ehrlich, H. Poriferan Chitin as a Versatile Template for Extreme Biomimetics. Polymers 2015, 7, 235–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.-J.; Kim, D.; You, J.; Choi, J.W.; Kimura, S.; Wada, M. Preparation of Cellulose-Chitosan Foams Using an Aqueous Lithium Bromide Solution and Their Adsorption Ability for Congo Red. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2615–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gözaydın, G.; Song, S.; Yan, N. Chitin Hydrolysis in Acidified Molten Salt Hydrates. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5096–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gözaydın, G.; Sun, Q.; Oh, M.; Lee, S.; Choi, M.; Liu, Y.; Yan, N. Chitin Hydrolysis Using Zeolites in Lithium Bromide Molten Salt Hydrate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 2511–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnovali, M.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Mollo, E.; Roussis, V.; Banfi, G.; Carbone, M.; Mariotti, M. Aerophobin−1 from the Marine Sponge Aplysina Aerophoba Modulates Osteogenesis in Zebrafish Larvae. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Bazhenov, V.; Meschke, S.; Bürger, M.; Ehrlich, A.; Petovic, S.; Durovic, M. Marine Invertebrates of Boka Kotorska Bay Unique Sources for Bioinspired Materials Science. In The Boka Kotorska Bay Environment; Joksimović, A., Djurović, M., Semenov, A.V., Zonn, I.S., Kostianoy, A.G., Eds.; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 313–334. ISBN 978-3-319-51614-1. [Google Scholar]












| Chitosan Standard (cm−1) | Chitin Standard (cm−1) | Dissolved Chitin (cm−1) | Peak Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3359 | 3428 | 3430 | O–H stretching |
| 3295 | 3259 | 3272 | N–H stretching |
| - | 3103 | 3100 | N–H stretching |
| - | 2930 | 2933 | CHx stretching |
| 2874 | 2878 | 2876 | CHx stretching |
| 1648 | 1652 | - | Amide I |
| - | 1621 | 1627 | Amide I |
| 1591 | 1553 | 1557 | Amide II |
| 1418 | 1428 | 1429 | CH2 bending |
| 1376 | 1375 | 1375 | CH3 deformation |
| 1320 | 1308 | 1309 | Amide III |
| 1262 | 1260 | 1263 | Amide III |
| 1197 | 1204 | 1203 | Amide III |
| 1150 | 1154 | 1154 | C–O–C, C–O stretching |
| - | 1112 | 1112 | C–O–C, C–O stretching |
| 1062 | 1063 | 1067 | C–O–C, C–O stretching |
| 1026 | 1023 | 1028 | C–O–C, C–O stretching |
| - | 1008 | - | C–O stretch in phase ring |
| - | 952 | 951 | CH3 wagging |
| 895 | 896 | 899 | CH ring stretching |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dziedzic, I.; Voronkina, A.; Pajewska-Szmyt, M.; Kotula, M.; Kubiak, A.; Meissner, H.; Duminis, T.; Ehrlich, H. The Loss of Structural Integrity of 3D Chitin Scaffolds from Aplysina aerophoba Marine Demosponge after Treatment with LiOH. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060334
Dziedzic I, Voronkina A, Pajewska-Szmyt M, Kotula M, Kubiak A, Meissner H, Duminis T, Ehrlich H. The Loss of Structural Integrity of 3D Chitin Scaffolds from Aplysina aerophoba Marine Demosponge after Treatment with LiOH. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(6):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060334
Chicago/Turabian StyleDziedzic, Izabela, Alona Voronkina, Martyna Pajewska-Szmyt, Martyna Kotula, Anita Kubiak, Heike Meissner, Tomas Duminis, and Hermann Ehrlich. 2023. "The Loss of Structural Integrity of 3D Chitin Scaffolds from Aplysina aerophoba Marine Demosponge after Treatment with LiOH" Marine Drugs 21, no. 6: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060334
APA StyleDziedzic, I., Voronkina, A., Pajewska-Szmyt, M., Kotula, M., Kubiak, A., Meissner, H., Duminis, T., & Ehrlich, H. (2023). The Loss of Structural Integrity of 3D Chitin Scaffolds from Aplysina aerophoba Marine Demosponge after Treatment with LiOH. Marine Drugs, 21(6), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060334