Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Eicosapentaenoic Acid or Docosahexaenoic Acid Improved Ageing-Associated Cognitive Decline by Regulating Glial Polarization
Abstract
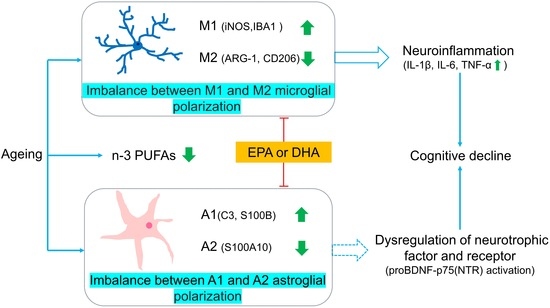
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Memory and Locomotor Impairment Occurred in Ageing Rats, Which Was Better Improved by DHA Than EPA
2.2. n-3 and n-6 PUFAs Imbalance Were Both Improved by DHA and EPA
2.3. Abnormal Microglial M1 and M2 Polarizations in the Hippocampus of Ageing Rats Was Better Ameliorated by DHA Than EPA through Upregulating CD206
2.4. Neuroinflammation in Ageing Rats Were Both Inhibited by DHA and EPA
2.5. Abnormal Astroglia A1/A2 Phenotypic Polarizations in the Hippocampus of Ageing Rats Were Both Attenuated by EPA and DHA
2.6. Activation of proBDNF-p75(NTR) in the Hippocampus of Ageing Rats Was Inhibited by EPA and DHA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Procedure
4.2. Morris Water Maze
4.3. Open Field Test
4.4. Brain n-3/n-6 PUFA Analysis by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
4.5. Cytokine Detections
4.6. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis
4.7. Western Blotting Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Y.; Dan, X.; Babbar, M.; Wei, Y.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettio, L.E.B.; Rajendran, L.; Gil-Mohapel, J. The effects of aging in the hippocampus and cognitive decline. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 79, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.S.; Koh, S.H. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.J.; Dexter, D.T.; Crichton, R.R. Ageing, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Front. Biosci. Sch. Ed. 2015, 7, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, J.; Salinas, S.; Huang, H.Y.; Zhou, M. Microglia regulation of synaptic plasticity and learning and memory. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 705–716. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, K.; Zu, H.B. Microglial polarization: Novel therapeutic mechanism against Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.E.; Liddelow, S.A.; Chakraborty, C.; Münch, A.E.; Heiman, M.; Barres, B.A. Normal aging induces A1-like astrocyte reactivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1896–E1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, D.; Block, R.; Mousa, S.A. Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA: Health benefits throughout life. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutuli, D. Functional and Structural Benefits Induced by Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids during Aging. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.C.; Frangou, S.; Chang, C.J.; Chiu, W.C.; Liu, H.C.; Sun, I.W.; Liu, S.I.; Lu, M.L.; Chen, C.H.; Huang, S.Y.; et al. Associations between n-3 PUFA concentrations and cognitive function after recovery from late-life depression. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Gu, M.Q.; Yang, Z.Y.; Xia, J.; Li, P.; Vasar, E.; Tian, L.; Song, C. Endogenous n-3 PUFAs attenuated olfactory bulbectomy-induced behavioral and metabolomic abnormalities in Fat-1 mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 96, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Brown, R.E.; Zhang, P.C.; Zhao, Y.T.; Ju, X.H.; Song, C. DHA, EPA and their combination at various ratios differently modulated Aβ-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2018, 136, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Shieh, C.H.; Wu, Y.S.; Kalueff, A.; Gaikwad, S.; Su, K.P. The role of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in the treatment of major depression and Alzheimer’s disease: Acting separately or synergistically? Prog. Lipid Res. 2016, 62, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffre, C.; Rey, C.; Layé, S. N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Resolution of Neuroinflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.P.; Zhang, Y.P.; Yang, Z.Y.; Liu, M.J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.T.; Song, C. ω-3 DPA Protected Neurons from Neuroinflammation by Balancing Microglia M1/M2 Polarizations through Inhibiting NF-κB/MAPK p38 Signaling and Activating Neuron-BDNF-PI3K/AKT Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Dong, L.J.; Luo, J.L.; Zeng, F.N.; Hong, Z.X.; Liu, Y.Z.; Zhao, Y.B.; Xia, Z.Y.; Zuo, D.M.; Xu, L.; et al. Supplemental N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Limit A1-Specific Astrocyte Polarization via Attenuating Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Ischemic Stroke in Mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5524705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Z.; Wang, J.; Sheridan, S.D.; Perlis, R.H.; Rasenick, M.M. N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids promote astrocyte differentiation and neurotrophin production independent of cAMP in patient-derived neural stem cells. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 4605–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczewska, A.; Stępień, T.; Bewicz-Binkowska, D.; Zgórzyńska, E. The role of docosahexaenoic acid in neuronal function. Postep. Hig. Med. Dosw. 2011, 65, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, R.; Tange, C.; Nishita, Y.; Kato, Y.; Imai, T.; Ando, F.; Shimokata, H. Serum docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acid and risk of cognitive decline over 10 years among elderly Japanese. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.M.; Chen, Y.J.; Bai, D.; Weng, J.X.; Du, Y.; Ma, F.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, H.; et al. Effect of folic acid combined with docosahexaenoic acid intervention on mild cognitive impairment in elderly: A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 1795–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Fan, J.T.; Li, M.Y.; Dong, C.X.; Gao, Y.M.; Fu, M.; Huang, G.W.; Liu, H. Effects of Folic Acid Combined with DHA Supplementation on Cognitive Function and Amyloid-β-Related Biomarkers in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment by a Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 81, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zussy, C.; John, R.; Urgin, T.; Otaegui, L.; Vigor, C.; Acar, N.; Canet, G.; Vitalis, M.; Morin, F.; Planel, E.; et al. Intranasal Administration of Nanovectorized Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Improves Cognitive Function in Two Complementary Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.M.; Yin, M.C. EPA or DHA enhanced oxidative stress and aging protein expression in brain of d-galactose treated mice. BioMedicine 2016, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.S.; Wen, M.; Zhao, Y.C.; Shi, H.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Xue, C.H.; Wei, Z.H.; Zhang, T.T. Short-term supplementation of EPA-enriched ethanolamine plasmalogen increases the level of DHA in the brain and liver of n-3 PUFA deficient mice in early life after weaning. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 1906–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalagala, P.C.R.; Sugasini, D.; Dasarathi, S.; Pahan, K.; Subbaiah, P.V. Dietary lysophosphatidylcholine-EPA enriches both EPA and DHA in the brain: Potential treatment for depression. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohman, R.A. Aging microglia: Relevance to cognition and neural plasticity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 934, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Zhao, Y.F. Aging modulates microglia phenotypes in neuroinflammation of MPTP-PD mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 111, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Yao, H.M.; Liu, W.Y.; Ya, B.L.; Cheng, H.J.; Xing, Z.K.; Wu, Y.L. Microglia Polarization in Alzheimer’s Disease: Mechanisms and a Potential Therapeutic Target. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 772717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’avila, J.C.; Siqueira, L.D.; Mazeraud, A.; Azevedo, E.P.; Foguel, D.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; Sharshar, T.; Chrétien, F.; Bozza, F.A. Age-related cognitive impairment is associated with long-term neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in a mouse model of episodic systemic inflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.R.; Wang, H.; Yin, Y.F. Microglia Polarization from M1 to M2 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 815347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.Q.; Li, Y.Y.; Tang, H.T.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.D.; Zhang, Y.P.; Li, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.T.; Song, C. Endogenous Omega (n)-3 Fatty Acids in Fat-1 Mice Attenuated Depression-Like Behavior, Imbalance between Microglial M1 and M2 Phenotypes, and Dysfunction of Neurotrophins Induced by Lipopolysaccharide Administration. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, E.; Zhu, M.; Toro, V.C.; Vedin, I.; Palmblad, J.; Cederholm, T.; Freund-Levi, Y.; Faxen-Irving, G.; Wahlund, L.O.; Basun, H.; et al. Omega-3 fatty acids enhance phagocytosis of Alzheimer’s disease-related amyloid-β42 by human microglia and decrease inflammatory markers. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 35, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Song, C. Potential treatment of Parkinson’s disease with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, A.; Ariyoshi, W.; Yoshioka, Y.; Hikiji, H.; Nishihara, T.; Okinaga, T. Docosahexaenoic acid enhances M2 macrophage polarization via the p38 signaling pathway and autophagy. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 12604–12617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, L.D.; Yin, Y.; Attarwala, I.Y.; Begum, G.; Deng, J.; Yan, H.Q.; Dixon, C.E.; Sun, D. Administration of DHA Reduces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Associated Inflammation and Alters Microglial or Macrophage Activation in Traumatic Brain Injury. ASN Neuro 2015, 7, 1759091415618969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.R.; Liu, J.C.; Bao, J.S.; Bai, Q.Q.; Wang, G.Q. Interaction of Microglia and Astrocytes in the Neurovascular Unit. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, N.R.; Day, J.R.; Laping, N.J.; Johnson, S.A.; Finch, C.E. GFAP mRNA increases with age in rat and human brain. Neurobiol. Aging 1993, 14, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wruck, W.; Adjaye, J. Meta-analysis of human prefrontal cortex reveals activation of GFAP and decline of synaptic transmission in the aging brain. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Pedrini, S.; Stoops, E.; Goozee, K.; Villemagne, V.L.; Asih, P.R.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Dave, P.; Taddei, K.; Sohrabi, H.R.; et al. Plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein is elevated in cognitively normal older adults at risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traub, J.; Otto, M.; Sell, R.; Homola, G.A.; Steinacker, P.; Oeckl, P.; Morbach, C.; Frantz, S.; Pham, M.; Störk, S.; et al. Serum glial fibrillary acidic protein indicates memory impairment in patients with chronic heart failure. Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 2626–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Guerrero, L.; García-delaTorre, P.; Sánchez-García, S.; Guzmán-Ramos, K. Serum Levels of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Association with Cognitive Impairment and Type 2 Diabetes. Arch. Med. Res. 2022, 53, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heras-Sandoval, D.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Pérez-Rojas, J.M. Role of docosahexaenoic acid in the modulation of glial cells in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, S.; Kushwaha, R.; Mishra, J.; Gupta, M.K.; Kumar, H.; Sanyal, S.; Singh, D.; Sanyal, S.; Sahasrabuddhe, A.A.; Kamthan, M.; et al. Docosahexaenoic acid up-regulates both PI3K/AKT-dependent FABP7–PPARγ interaction and MKP3 that enhance GFAP in developing rat brain astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2017, 140, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzhulo, I.V.; Ogurtsova, O.S.; Kipryushina, Y.O.; Latyshev, N.A.; Kasyanov, S.P.; Dyuizen, I.V.; Tyrtyshnaia, A.A. Neuron-astrocyte interactions in spinal cord dorsal horn in neuropathic pain development and docosahexaenoic acid therapy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 15, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Lewis, D.A.; Sibille, E. The Role of BDNF in Age-Dependent Changes of Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Markers in the Human Prefrontal Cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 3080–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Y.; Pan, B.S.; Tsai, S.F.; Chiang, Y.T.; Huang, B.M.; Mo, F.E.; Kuo, Y.M. BDNF reverses aging-related microglial activation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapchak, P.A.; Araujo, D.M.; Beck, K.D.; Finch, C.E.; Johnson, S.A.; Hefti, F. BDNF and trkB mRNA expression in the hippocampal formation of aging rats. Neurobiol. Aging 1993, 14, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhusi, M.; Etheredge, C.; Granholm, A.C.; Buhusi, C.V. Increased Hippocampal ProBDNF Contributes to Memory Impairments in Aged Mice. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minogue, A.M.; Lynch, A.M.; Loane, D.J.; Herron, C.E.; Lynch, M.A. Modulation of amyloid-beta-induced and age-associated changes in rat hippocampus by eicosapentaenoic acid. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 914–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimiuk, E.; Braszko, J.J. Long-term administration of cod liver oil ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by chronic stress in rats. Lipids 2011, 46, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chi, N.; Zou, P.; Chen, H.; Tang, G.; Zhao, W. Effect of docosahexaenoic acid on traumatic brain injury in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 4411–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.H.; Qi, C.X.; Liu, T.T.; Zheng, X.Y. Information transmission in mPFC-BLA network during exploratory behavior in the open field. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 414, 113483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Genes | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| BDNF | F:5′-CAAAAGGCCAACTGAAGC | R:5′-CGCCAGCCAATTCTCTTT |
| TrkB | F:5′-CACACACAGGGCTCCTTA | R:5′-AGTGGTGGTCTGAGGTTGG |
| p75 | F:5′-TGCTCCATTTCCATCTCAG | R:5′-GATAGGTCCGTAATCCTCTTC |
| iNOS | F:5′-TGGAGCGAGTTGTGGATTGT | R:5′-GTAGTGATGTCCAGGAAGTAGGT |
| CD206 | F:5′-GTTTCCATCGAGACTGCTGC | R:5′-GCCACTTTCCTTCAACATTTCG |
| ARG-1 | F:5′-GGTAGAGAAAGGTCCCGCAG | R:5′-CAGACCGTGGGTTCTTCACA |
| C3 | F:5′-TGTGGGTGGATGTGAAGGAC | R:5′-CTTGTCCACAGCCACTAGCC |
| IBA1 | F:5′-CAACAAGCACTTCCTCGATGATC | R:5′-TGAAGGCCTCCAGTTTGGACT |
| GFAP | F:5′-CCAAGATGAAACCAACCT | R:5′-CGCTGTGAGGTCTGGCTT |
| S100B | F:5′-CTCTGTCTACCCTCCTAGTCC | R:5′-GACATCAATGAGGGCAACCAT |
| S100A10 | F:5′-TATCACTAGTGGCGGGGCTC | R:5′-ATCAAGGTGTGGGTACCAGG |
| β-actin | F:5′-ACGGTCAGGTCATCACTATCG | R:5′-GTTTCATGGATGCCACAGGATT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, J.; Yang, L.; Huang, C.; Deng, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Song, C. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Eicosapentaenoic Acid or Docosahexaenoic Acid Improved Ageing-Associated Cognitive Decline by Regulating Glial Polarization. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21070398
Xia J, Yang L, Huang C, Deng S, Yang Z, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Song C. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Eicosapentaenoic Acid or Docosahexaenoic Acid Improved Ageing-Associated Cognitive Decline by Regulating Glial Polarization. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(7):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21070398
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Juan, Longen Yang, Chengyi Huang, Shuyi Deng, Zhiyou Yang, Yongping Zhang, Cai Zhang, and Cai Song. 2023. "Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Eicosapentaenoic Acid or Docosahexaenoic Acid Improved Ageing-Associated Cognitive Decline by Regulating Glial Polarization" Marine Drugs 21, no. 7: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21070398
APA StyleXia, J., Yang, L., Huang, C., Deng, S., Yang, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., & Song, C. (2023). Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Eicosapentaenoic Acid or Docosahexaenoic Acid Improved Ageing-Associated Cognitive Decline by Regulating Glial Polarization. Marine Drugs, 21(7), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21070398