Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Activity of Epi-Oxyzoanthamine Isolated from Zoanthid
Abstract
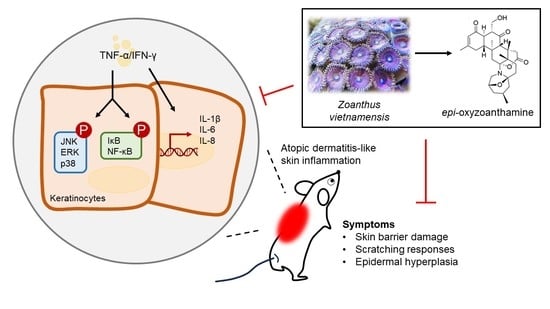
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Epi-Oxyzoanthamine on HaCaT Cell Viability
2.2. The Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Epi-Oxyzoanthamine in Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α)/Interferon-γ (IFN-γ)-Induced Inflammation in HaCaT Cells
2.3. Effects of Epi-Oxyzoanthamine on Phosphrylation of MAPK Pathway in HaCaT Cells
2.4. Epi-Oxyzoanthamine Reduced IκB and NF-κB Activation in TNF-α/IFN-γ-Stimulated Keratinocytes
2.5. The Effect of Epi-Oxyzoanthamine on the Skin Appearance in DNCB-Induced BALB/c Mouse
2.6. Change in Physiological Functions of DNCB-Induced BALB/c Mouse Skin after Treatment with Epi-Oxyzoanthamine
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of Epi-Oxyzoanthamine
4.2. Culture of Human Keratinocyte
4.3. Western Blotting
4.4. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.5. Animal Model of DNCB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Inflammation
4.6. Data and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salimian, J.; Salehi, Z.; Ahmadi, A.; Emamvirdizadeh, A.; Davoudi, S.M.; Karimi, M.; Korani, M.; Azimzadeh Jamalkandi, S. Atopic dermatitis: Molecular, cellular, and clinical aspects. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 3333–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiello, N.; Comberiati, P.; Giannetti, A.; Ricci, G.; Carello, R.; Galli, E. New Directions in Understanding Atopic March Starting from Atopic Dermatitis. Children 2022, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Man, X.Y. Immunotherapy in atopic dermatitis. Immunotherapy 2022, 14, 1149–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, S.; Novak, N. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2016, 387, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, N.A.; Pirozzi, G.; Graham, N.M.H. Commonality of the IL-4/IL-13 pathway in atopic diseases. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenfield, L.F.; Tom, W.L.; Berger, T.G.; Krol, A.; Paller, A.S.; Schwarzenberger, K.; Bergman, J.N.; Chamlin, S.L.; Cohen, D.E.; Cooper, K.D.; et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: Section 2. Management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J. Am. Acad. Derm. 2014, 71, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeki, H.; Ohya, Y.; Furuta, J.; Arakawa, H.; Ichiyama, S.; Katsunuma, T.; Katoh, N.; Tanaka, A.; Tsunemi, Y.; Nakahara, T.; et al. English Version of Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Atopic Dermatitis 2021. J. Derm. 2022, 49, e315–e375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovatiya, R.; Paller, A.S. JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbein, A.B.; Silverberg, J.I.; Wilson, E.J.; Ong, P.Y. Update on Atopic Dermatitis: Diagnosis, Severity Assessment, and Treatment Selection. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2020, 8, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, C.-G.; Chang, D.; Bensoussan, A. Current Status and Major Challenges to the Safety and Efficacy Presented by Chinese Herbal Medicine. Medicines 2019, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindequist, U. Marine-Derived Pharmaceuticals—Challenges and Opportunities. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haque, N.; Parveen, S.; Tang, T.; Wei, J.; Huang, Z. Marine Natural Products in Clinical Use. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.; Yee, K.W.L. Cytarabine and daunorubicin for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Opin. Pharm. 2017, 18, 1765–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammoun, I.; Ben Salah, H.; Ben Saad, H.; Cherif, B.; Droguet, M.; Magné, C.; Kallel, C.; Boudawara, O.; Hakim, A.; Gharsallah, N.; et al. Hypolipidemic and cardioprotective effects of Ulva lactuca ethanolic extract in hypercholesterolemic mice. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.; Herath, K.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Jayawardena, T.U. Recent Reports on Bioactive Compounds from Marine Cyanobacteria in Relation to Human Health Applications. Life 2023, 13, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone, A.; Mannino, D.; Capra, A.P.; Repici, A.; Filippone, A.; Esposito, E.; Campolo, M. New Insights into the Mechanism of Ulva pertusa on Colitis in Mice: Modulation of the Pain and Immune System. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijs, Y.; Bech, P.K.; Vazquez-Albacete, D.; Bentzon-Tilia, M.; Sonnenschein, E.C.; Gram, L.; Zhang, S.D. Marine Proteobacteria as a source of natural products: Advances in molecular tools and strategies. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 1333–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, P.O.; Jaramillo, K.B.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Thomas, O.P. Marine natural products from zoantharians: Bioactivity, biosynthesis, systematics, and ecological roles. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 515–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-M.; Chang, F.-R.; Lo, I.W.; Lai, K.-H.; El-Shazly, M.; Wu, T.-Y.; Du, Y.-C.; Hwang, T.-L.; Cheng, Y.-B.; Wu, Y.-C. Zoanthamine-Type Alkaloids from the Zoanthid Zoanthus kuroshio Collected in Taiwan and Their Effects on Inflammation. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2674–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-B.; Lo, I.W.; Shyur, L.-F.; Yang, C.-C.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Su, J.-H.; Lu, M.-C.; Chiou, S.-F.; Lan, C.-C.; Wu, Y.-C.; et al. New alkaloids from Formosan zoanthid Zoanthus kuroshio. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 8601–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-R.; Wang, S.-W.; Lin, Y.-C.; Yu, C.-L.; Yen, J.-Y.; Chen, Y.-F.; Cheng, Y.-B. Additional alkaloids from Zoanthus vietnamensis with neuroprotective and anti-angiogenic effects. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 109, 104700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Yada, M.; Tsuji, T.; Kuramoto, M.; Uemura, D. Suppressive effect of norzoanthamine hydrochloride on experimental osteoporosis in ovariectomized mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 22, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.-R.; Wang, S.-W.; Sheu, J.-H.; Chang, T.-H.; Cheng, Y.-B. Zoanthamine Alkaloid Derivatives from the Zoantharian Zoanthus vietnamensis with Antimetastatic Activity. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 12553–12560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Ko, H.-H.; Chang, D.-C.; Hung, C.-F. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Cycloheterophyllin on Dinitrochlorobenzene-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in HaCaT Cells and BALB/c Mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-C.; Chang, H.-H.; Chou, S.-C.; Chu, T.W.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Lo, Y.-H.; Wu, N.-L.; Chang, D.-C.; Hung, C.-F. Evaluation of the Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effects of α-Boswellic Acid on Tnf-α/Ifn-γ-Stimulated HaCat Cells and DNCB-Induced BALB/c Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.N.; Jana, M.; Pahan, K. MAPK p38 regulates transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB in primary human astrocytes via acetylation of p65. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7101–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garrigue, J.L.; Nicolas, J.F.; Fraginals, R.; Benezra, C.; Bour, H.; Schmitt, D. Optimization of the mouse ear swelling test for in vivo and in vitro studies of weak contact sensitizers. Contact Dermat. 1994, 30, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; He, R.; Oyoshi, M.; Geha, R.S. Animal models of atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Derm. 2009, 129, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 40, 275–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.; Jeong, S.; Lee, I.-K.; Yun, B.-S.; Lee, J.S.; Ro, S.; Park, J.K. Regulation of p53 Activity by (+)-Epiloliolide Isolated from Ulva lactuca. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, W.A.; Ezzat, S.M.; Zayed, A. Marine organisms as potential sources of natural products for the prevention and treatment of malaria. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 4436–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.; Lee, W.H.; Jeong, J.; Park, M.; Ko, J.Y.; Kwon, O.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.J. Pyropia yezoensis Extract Suppresses IFN-Gamma- and TNF-Alpha-Induced Proinflammatory Chemokine Production in HaCaT Cells via the Down-Regulation of NF-κB. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.; Lee, W.H.; Kim, J.K.; Jeon, H.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.J. Polyopes affinis Suppressed IFN-γ- and TNF-α-Induced Inflammation in Human Keratinocytes via Down-Regulation of the NF-κB and STAT1 Pathways. Molecules 2022, 27, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.C.; Lo, Y.H.; Huang, S.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Yao, Z.K.; Chang, C.I.; Wen, Z.H. The anti-inflammatory properties of ethyl acetate fraction in ethanol extract from Sarcodia suiae sp. alleviates atopic dermatitis-like lesion in mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2022, 86, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.K.; Kim, D.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, J.C.; Lim, S.S.; Kang, I.J.; Hong, S.; Choi, S.Y.; Won, M.H.; et al. Protective Effects of Topical Administration of Laminarin in Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, S.K.; Park, N.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, A.T.; Liu, X.; Kim, S.M.; Yang, M.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.N. Trifuhalol A Suppresses Allergic Inflammation through Dual Inhibition of TAK1 and MK2 Mediated by IgE and IL-33. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihindukulasooriya, S.P.; Dinh, D.T.T.; Herath, K.; Kim, H.J.; Han, E.J.; Cho, J.; Ko, M.O.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ahn, G.; Jee, Y. Sargassum horneri extract containing polyphenol alleviates DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice through restoring skin barrier function. Histol. Histopathol. 2022, 37, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.Q.; Liang, L.F.; Guo, Y.W. Cladiella Octocorals: Enormous Sources of Secondary Metabolites with Diverse Structural and Biological Properties. Chem. Amp; Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202201065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Lu, S.Q.; Han, G.Y.; Li, X.W.; Guo, Y.W. Sinuhirtone A, An Uncommon 17,19-Dinorxeniaphyllanoid, and Nine Related New Terpenoids from the Hainan Soft Coral Sinularia hirta. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 113088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xia, F.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, T.; Shi, Y.; Yan, X.; Yan, X.; He, S. Nardosinane-related antimicrobial terpenoids from Lemnalia sp. soft coral. Phytochemistry 2022, 196, 113088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, P.; Tang, X.; Luo, X.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, G. Lemnardosinanes A-I: New Bioactive Sesquiterpenoids from Soft Coral Lemnalia sp. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Li, T.; Wu, B.; Yan, X.; He, S. Antimicrobial Terpenoids from South China Sea Soft Coral Lemnalia sp. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matar, D.Y.; Ng, B.; Darwish, O.; Wu, M.; Orgill, D.P.; Panayi, A.C. Skin Inflammation with a Focus on Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2022, 12, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y. Understanding the mechanisms underlying obesity in remodeling the breast tumor immune microenvironment: From the perspective of inflammation. Cancer Biol. Med. 2023, 20, 268–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, C.J.; Su, J.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Huang, M.S.; Wen, Z.H.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the soft coral Cladiella krempfi. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Z.R.; Li, W.S.; Nay, B.; Hu, P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.W.; Guo, Y.W. Sinunanolobatone A, an Anti-inflammatory Diterpenoid with Bicyclo[13.1.0]pentadecane Carbon Scaffold, and Related Casbanes from the Sanya Soft Coral Sinularia nanolobata. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 7575–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Shi, X.; Li, K.; Li, F.; Tang, X.; Li, G.; Li, P. Sarcoeleganolides C-G, Five New Cembranes from the South China Sea Soft Coral Sarcophyton elegans. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.H.; Liu, C.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Chien, S.Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Fang, L.S.; Chen, J.J.; Wu, Y.C.; Su, J.H.; Sung, P.J. Briavioids E-G, Newly Isolated Briarane-Diterpenoids from a Cultured Octocoral Briareum violaceum. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behenna, D.C.; Stockdill, J.L.; Stoltz, B.M. The Biology and Chemistry of the Zoanthamine Alkaloids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2365–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-R.; Wang, S.-W.; Su, C.-J.; Hu, H.-C.; Yang, Y.-L.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Peng, C.-C.; Chang, F.-R.; Cheng, Y.-B. Anti-Lymphangiogenesis Components from Zoanthid Palythoa tuberculosa. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.-C.; Hung, Y.-L.; Ko, W.-C.; Tsai, Y.-J.; Chang, J.-F.; Liang, C.-W.; Chang, D.-C.; Hung, C.-F. Effect of Neferine on DNCB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in HaCaT Cells and BALB/c Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daranas, A.H.; Fernández, J.; Gavín, J.; Norte, M. Epioxyzoanthamine, a new zoanthamine-type alkaloid and the unusual deuterium exchange in this series. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 7891–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.R.; Wang, S.W.; Chang, F.R.; Cheng, Y.B. Anti-Lymphangiogenic Alkaloids from the Zoanthid Zoanthus vietnamensis Collected in Taiwan. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2790–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Name | Forward Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | CTC TCA CCT CTC CTA CTC ACT | ATC AGA ATG TGG GAG CGA AT |
| IL-6 | ATC AGA ATG TGG GAG CGA AT | GGA CCG AAG GCG CTT GTG GAG |
| IL-8 | ACT GAG AGT GAT TGA GAG TGG AC | AAC CCT CTG CAC CCA GTT TTC |
| GAPDH | CTG CTC CTG TTC GAC AGT | CCG TTG ACT CCG ACC TTC AC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.-C.; Lo, Y.-H.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Cheng, Y.-B.; Kung, C.-C.; Liang, C.-W.; Chang, D.-C.; Wang, K.-L.; Hung, C.-F. Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Activity of Epi-Oxyzoanthamine Isolated from Zoanthid. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21080447
Huang C-C, Lo Y-H, Hsu Y-J, Cheng Y-B, Kung C-C, Liang C-W, Chang D-C, Wang K-L, Hung C-F. Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Activity of Epi-Oxyzoanthamine Isolated from Zoanthid. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(8):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21080447
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chieh-Chen, Yuan-Hsin Lo, Yu-Jou Hsu, Yuan-Bin Cheng, Chia-Chi Kung, Cher-Wei Liang, Der-Chen Chang, Kang-Ling Wang, and Chi-Feng Hung. 2023. "Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Activity of Epi-Oxyzoanthamine Isolated from Zoanthid" Marine Drugs 21, no. 8: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21080447
APA StyleHuang, C. -C., Lo, Y. -H., Hsu, Y. -J., Cheng, Y. -B., Kung, C. -C., Liang, C. -W., Chang, D. -C., Wang, K. -L., & Hung, C. -F. (2023). Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Activity of Epi-Oxyzoanthamine Isolated from Zoanthid. Marine Drugs, 21(8), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21080447