Relationships between Meteorological Parameters and Particulate Matter in Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Data Measurement and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
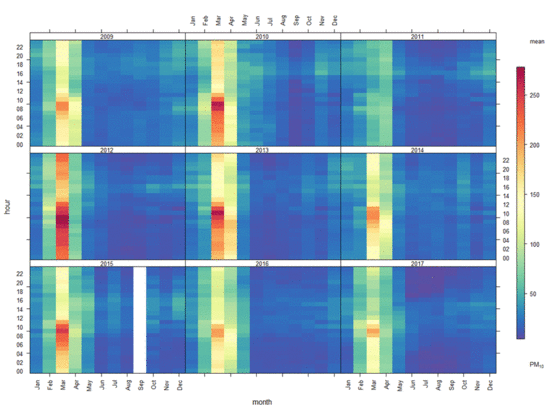
3.1. Onsite PM Measurement
3.2. Time Series
3.3. Correlation between PM10 and Other Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters
3.4. Seasonal Variation
3.5. Wind Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mannucci, P.M.; Franchini, M. Health effects of ambient air pollution in developing countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Air Pollution and Child Health: Prescribing Clean Air Summary; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- Chantara, S.; Sillapapiromsuk, S.; Wiriya, W. Atmospheric pollutants in Chiang Mai (Thailand) over a five-year period (2005–2009), their possible sources and relation to air mass movement. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Yuan, X.; Zeng, G.; Liang, J.; Li, X.; Xu, W.; Luo, Y.; Chen, G. Effects of human activities and climate change on the reduction of visibility in beijing over the past 36 years. Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Yuan, X.; Zeng, G.; León, T.; Liang, J.; Chen, G.; Yuan, X. Characteristics of particulate pollution (PM2.5 and PM10) and their spacescale-dependent relationships with meteorological elements in china. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.M.C.; Martins, E.S.; Pedrosa, D.M.A.S.; Evangelista, M.D.S.N. Relationship between climatic factors and air quality with tuberculosis in the federal district, brazil, 2003–2012. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 21, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominick, D.; Latif, M.T.; Juahir, H.; Aris, A.Z.; Zain, S.M. An assessment of influence of meteorological factors on pm and 10 and no2 at selectted stations in malasia. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2012, 22, 305–315. [Google Scholar]
- Vardoulakis, S.; Kassomenos, P. Sources and factors affecting PM10 levels in two european cities: Implications for local air quality management. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3949–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannidis, A.F.; Poupkou, A.; Giannaros, C.; Giannaros, T.; Dimopoulos, S.; Liora, N.; Melas, D.; Argiriou, A.A. Meteorological Parameters Affecting the Air Pollution of the City of Patras. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference of Meteorology, Climatology and Physics of the Atmosphere, Heraklion, Greece, 28–31 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, J.; Singh, G.; Pal, A.K. The Role of Meteorology on Predicting PM10 Concentrations around Dhanbad. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/230626032_The_Role_of_Meteorology_on_Predicting_PM10_Concentrations_around_Dhanbad (accessed on 2 December 2018).
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Ying, Q.; Hu, X.M. Relationships between meteorological parameters and criteria air pollutants in three megacities in china. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.; Qiao, Z.; Xu, X. Characteristics of particulate matter (PM10) and its relationship with meteorological factors during 2001–2012 in beijing. Environ. Pollut 2014, 192, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunrat, N.; Pumijumnong, N.; Sereenonchai, S. Air-pollutant emissions from agricultural burning in Mae Chaem Basin, Chiang Mai province, Thailand. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirimongkonlertkul, N.; Upayokhin, P.; Phonekeo, V. Multi-temporal analysis of haze problem in Northern Thailand: A case study in chiang rai province. Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 2013, 47, 768–780. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakreshnan, L.; Aghamohammadi, N.; Fong, C.S.; Bulgiba, A.; Zaki, R.A.; Wong, L.P.; Sulaiman, N.M. Haze and health impacts in asean countries: A systematic review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2096–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiyapairat, Y. Public sector responses to sustainable haze management in upper Northern Thailand. EnvironmentAsia 2012, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pardthaisong, L.; Sin-Ampol, P.; Suwanprasit, C.; Charoenpanyanet, A. Haze pollution in Chiang Mai, Thailand: A road to resilience. Procedia Eng. 2018, 212, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phairuang, W.; Hata, M.; Furuuchi, M. Influence of agricultural activities, forest fires and agro-industries on air quality in Thailand. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 52, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mae Hong Son, Thailand. Available online: https://www.google.com/maps/place/Mae+Hong+Son (accessed on 4 December 2018).
- The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org (accessed on 7 December 2018).
- Carslaw, D.C.; Ropkins, K. Openair—An R package for air quality data analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 27–28, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- READY (Real-time Environmental Applications and Display sYstem). Available online: https://www.ready.noaa.gov/index.php (accessed on 4 December 2018).
- National Thai Air Quality Standard. Available online: http://www.pcd.go.th/info_serv/reg_std_airsnd01.html (accessed on 4 December 2018).
- National Statistical. Available online: http://web.nso.go.th/index.htm (accessed on 4 December 2018).
- Jayamurugan, R.; Kumaravel, B.; Palanivelraja, S.; Chockalingam, M.P. Influence of temperature, relative humidity and seasonal variability on ambient air quality in a coastal urban area. Int. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of visibility and particulate matter (pm) in an urban area of northeast china. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2013, 4, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R. Atmospheric chemistry of vocs and nox. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2063–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ogawa, S. Effects of meteorological conditions on PM2.5 concentrations in Nagasaki, Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9089–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, B.A.; Biswas, S.K.; Pandit, G.G.; Saradhi, I.V.; Waheed, S.; Siddique, N.; Seneviratne, M.C.S.; Cohen, D.D.; Markwitz, A.; Hopke, P.K. Long–range transport of soil dust and smoke pollution in the south asian region. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2011, 2, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiriya, W.; Prapamontol, T.; Chantara, S. PM10-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Chiang Mai (Thailand): Seasonal variations, source identification, health risk assessment and their relationship to air-mass movement. Atmos. Res. 2013, 124, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameter | 1 h PM10 (ppm) | 24 h PM10 (ppm) | 1 h CO (ppm) | 1 h O3 (ppb) | Relative Humidity (%) | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (mbar) | Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Quartile | 13.0 | 15.0 | 0.40 | 6.0 | 57.0 | 23.0 | 976.0 | 0.0 |
| Median | 25.0 | 24.0 | 0.50 | 12.0 | 76.0 | 25.6 | 979.0 | 0.0 |
| Mean | 43.0 | 42.7 | 0.57 | 17.6 | 71.2 | 25.8 | 979.5 | 0.0 |
| 3rd Quartile | 48.0 | 47.5 | 0.70 | 23.0 | 88.0 | 29.6 | 982.0 | 0.1 |
| Maximum | 726.0 | 309.2 | 7.70 | 123.0 | 100.0 | 45.5 | 994.0 | 194.0 |
| Item | Year | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |
| Total rain (mm) | 841.5 | 1363.1 | 1686.1 | 1475.8 | 1250.6 | 1024.9 | 1064.9 |
| Number of rainy days (days) | 132 | 132 | 148 | 144 | 143 | 124 | 127 |
| Daily maximum (mm) | 35.6 | 128.0 | 99.9 | 74.8 | 69.0 | 55.9 | 54.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kliengchuay, W.; Cooper Meeyai, A.; Worakhunpiset, S.; Tantrakarnapa, K. Relationships between Meteorological Parameters and Particulate Matter in Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122801
Kliengchuay W, Cooper Meeyai A, Worakhunpiset S, Tantrakarnapa K. Relationships between Meteorological Parameters and Particulate Matter in Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(12):2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122801
Chicago/Turabian StyleKliengchuay, Wissanupong, Aronrag Cooper Meeyai, Suwalee Worakhunpiset, and Kraichat Tantrakarnapa. 2018. "Relationships between Meteorological Parameters and Particulate Matter in Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 12: 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122801
APA StyleKliengchuay, W., Cooper Meeyai, A., Worakhunpiset, S., & Tantrakarnapa, K. (2018). Relationships between Meteorological Parameters and Particulate Matter in Mae Hong Son Province, Thailand. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(12), 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122801