The Implication of Land-Use/Land-Cover Change for the Declining Soil Erosion Risk in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Materials and methods
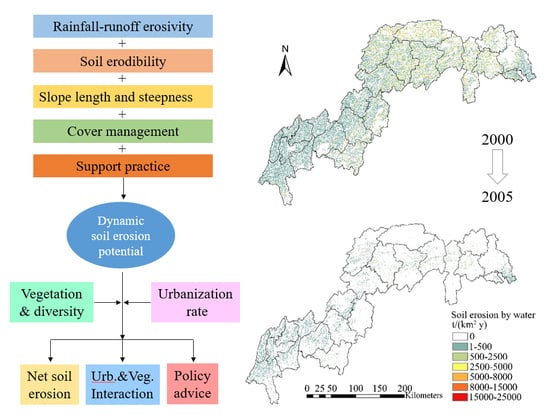
3.1. Soil Erosion Risk Estimation
3.1.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R)
3.1.2. Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
3.1.3. Slope Length and Steepness Factor (LS)
3.1.4. Cover Management (C) and Control Practice (P) Factors
3.2. Changes in Land Cover Related to Soil Erosion
3.3. Interactions between Urbanisation and Natural Resource Management and Their Impacts on Soil Erosion
4. Results
4.1. Estimated Rate of Soil Erosion by Water
4.2. Land Cover Determinants of Soil Erosion in the TGRR
4.3. Effects of NDVI and Vegetation Diversity Varied at Different Urbanisation Rates
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, Y. Dynamics of soil erosion at upper reaches of Minjiang river based on GIS. Chin. J. App. Ecol. 2005, 16, 2271–2278. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Bai, K.Z.; Wang, M.J.; Karthikeyan, R. Basin-scale spatial soil erosion variability: Pingshuo opencast mine site in Shanxi province, Loess Plateau of China. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 1213–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Deriving rusle cover factor from time-series fractional vegetation cover for hillslope erosion modelling in New South Wales. Soil Res. 2014, 52, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Chen, L. Effects of terracing practices on water erosion control in China: A meta-analysis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; He, D. Soil erosion evaluation of small watershed in Wuling Mountain based on GIS and RUSLE. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2011, 20, 468–474. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Gao, Z.; Ning, J.; Bi, X.; Wang, Q. Impact of progressive urbanization and changing cropping systems on soil erosion and net primary production. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zheng, H.; Rao, E.; Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Li, C. Evaluating indirect and direct effects of eco-restoration policy on soil conservation service in Yangtze River basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendse, F.; van Ruijven, J.; Jongejans, E.; Keesstra, S. Loss of plant species diversity reduces soil erosion resistance. Ecosystems 2015, 18, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Han, X.; Gao, X. The three gorges dam: An ecological perspective. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 2, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Yuan, X. Spatiotemporal features of soil and water loss in three gorges reservoir area of Chongqing. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundson, R.; Berhe, A.A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Olson, C.; Sztein, A.E.; Sparks, D.L. Soil science. Soil and human security in the 21st century. Science 2015, 348, 1261071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, J.; Evans, R.; Ford, J. Muddy floods on the south downs, southern England: Problem and responses. Environ. Sci. Policy 2003, 6, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Milliman, J.D. Seasonal variations of sediment discharge from the Yangtze River before and after impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam. Geomorphology 2009, 104, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, J.; Poesen, J. Soil Erosion in Europe; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Wen, A.; Shi, Z.; Ju, L.; He, X. Critical slope length of rill occurred in purple soil slope cultivated land in Three Gorges Reservoir area. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2010, 27, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, A.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xun, J.; Bai, L.; Huo, T.; Wang, J. Study on soil erosion rates using 137cs technique in upper Yangtze River. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 16, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, T.G.; Degener, J.; Kappas, M. Integrated universal soil loss equation (USLE) and geographical information system (GIS) for soil erosion estimation in a sap basin: Central Vietnam. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Li, B.; Zhang, P.; Xu, W.; Hui, B. GIS-based evaluation on potential hazard degree of soil erosion in hubei section of Three Gorges Reservoir area. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2017, 48, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, Z.; Wen, A.; Yan, D.; Shi, Z. Estimation of soil erosion in small watershed of the Three Gorges Reservoir Region based on GIS and RUSLE. Earth Environ. 2015, 43, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Reddy, K.C.; Yoder, D.C.; McCool, D.K. RUSLE revisited: Status, questions, answers, and the future. Soil Water Conserv. 1994, 49, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, H.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Shi, Z.; Behrens, T.; Chappell, A.; Bui, E. Assimilating satellite imagery and visible-near infrared spectroscopy to model and map soil loss by water erosion in Australia. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2016, 77, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Liu, P.; Li, D.; Wu, K. Temporal-spatial characteristics of coordinative development between the ecological and economic systems in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Ecol. Environ. Monitor. Three Gorges 2019, 4, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, T.; Xu, G.; Xia, D. Trend of geological hazards and countermeasure of disaster reduction in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. J. MT. Sci. 2004, 22, 719–724. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, X. Changing landscape in the three gorges reservoir area of Yangtze River from 1977 to 2005: Land use/land cover, vegetation cover changes estimated using multi-source satellite data. Int. J. App. Earth Obs. 2009, 11, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lufafa, A.; Tenywa, M.M.; Isabirye, M.; Majaliwa, M.J.G.; Woomer, P.L. Prediction of soil erosion in a lake Victoria basin catchment using a GIS-based universal soil loss model. Agric. Syst. 2003, 76, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Meusburger, K.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Alewell, C. Soil erodibility in Europe: A high-resolution dataset based on LUCAS. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479–480, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, H. The spatiotemporal patterns of rainfall erosivity in Yunnan province, southwest China: An analysis of empirical orthogonal functions. Global Planet. Change 2016, 144, 82–93. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, H.; Ma, Z.; Chappell, A.; Shi, Z.; Liang, Z.; Yu, W. Improving rainfall erosivity estimates using merged TRMM and gauge data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; van Noordwijk, M.; Lu, X. Spatial and temporal variation in rainfall erosivity in a Himalayan watershed. Catena 2014, 121, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Williams, J.R. Epic. Erosion/Productivity Impact Calculator: 1. Model Documentation. 2. User Manual; United States Department of Agriculture: Beltsville, MD, USA, 1990.
- Teng, H.; Liang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Chappell, A.; Yu, W.; Shi, Z. Current and future assessments of soil erosion by water on the Tibetan Plateau based on rusle and CMIP5 climate models. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renard, K.; Yoder, D.; Lightle, D.; Dabney, S. Universal Soil Loss Equation and Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.; McCool, D.; Yoder, D. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Rosewell, C. Potential Sources of Sediments and Nutrients: Sheet and Rill Erosion and Phosphorus Sources; Environment Australia: Canberra, Australia, 1997.
- Xue, J.; Lyu, D.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yin, D.; Zhao, Z.; Mu, Z. Assessment of soil erosion dynamics using the GIS-Based RUSLE Model: A Case Study of Wangjiagou Watershed from the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, Southwestern China. Water 2018, 10, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, P.; Govers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE ls factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Mhangara, P.; Kakembo, V.; Lim, K.J. Soil erosion risk assessment of the Keiskamma catchment, South Africa using GIS and remote sensing. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 65, 2087–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; United States Department of Agriculture: Beltsville, MD, USA, 1978.
- Lu, Q.; Xu, B.; Liang, F.; Gao, Z.; Ning, J. Influences of the Grain-for-Green Project on grain security in southern China. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, X.; Meng, X. Risk assessment of soil erosion in different rainfall scenarios by RUSLE model coupled with information diffusion model: A case study of Bohai Rim, China. Catena 2013, 100, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H. The case for being automatic: Introducing the automatic linear modeling (linear) procedure in spss statistics. Mult. Linear Regres. Viewp. 2013, 39, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Keylock, C. Simpson diversity and the Shannon–Wiener index as special cases of a generalized entropy. Oikos 2005, 109, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Park, T.; Wang, X.; Piao, S.; Xu, B.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Fuchs, R.; Brovkin, V.; Ciais, P.; Fensholt, R.; et al. China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management. Nature Sus. 2019, 2, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; Beguería, S.; Nadal-Romero, E.; González-Hidalgo, J.C.; Lana-Renault, N.; Sanjuán, Y. A meta-analysis of soil erosion rates across the world. Geomorphology 2015, 239, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X. China Three Gorges construction yearbook. In China Three Gorges Construction Yearbook; Three Gorges Media Corporation: Hubei, China, 2013; p. 120. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.L.; Wei, J.; Chen, G.J.; Li, Y.B. Review of soil erosion on purple-soil sloping croplands in Three Gorges Reservoir area. J. Chongqing Normal Univ. 2014, 31, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wen, A.; Shi, Z. Erosion rate of purple soil on a cultivated slope in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region using 137cs technique. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, A.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Fu, J.; Zhang, X. Study on erosion and sedimentation in Yangtze Three Gorge region. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 19, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Peng, W.; Yang, H. Soil erodibility and its estimation for agricultural soil in China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2007, 44, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Type | Environmental Variables | Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terrain | DEM | 30 m | SRTM digital evaluation (NASA) |
| Slope | 30 m | SRTM digital evaluation (NASA) | |
| Climate | Daily rainfall from 2000 to 2015 | - | Local meteorological stations |
| Vegetation | NDVI from 2000 to 2015 | 250 m | MODIS images |
| Land | Land use/cover type (LUCC) at 2000, 2005, 2010 and 2015 | 30 m | Resources and Environment Data Cloud Platform, Chinese Academy of Science |
| Soil property | Soil type | 1 km | HWSD soil database v1.2 (FAO) |
| Sand | 1 km | HWSD soil database v1.2 (FAO) | |
| Silt | 1 km | HWSD soil database v1.2 (FAO) | |
| Clay | 1 km | HWSD soil database v1.2 (FAO) | |
| TOC | 1 km | HWSD soil database v1.2 (FAO) |
| Land Use Type | p Value | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Paddy fields | 0.01 | [39] |
| Dry cropland | 0.4 | [40] |
| Dense forest | 1 | [40] |
| Shrub | 1 | [40] |
| Sparse forest | 1 | [40] |
| Other woodland | 0.7 | [2] |
| Dense grassland | 1 | [2] |
| Moderate dense grassland | 1 | [2] |
| Sparse grassland | 1 | [2] |
| River | 0 | [2] |
| Lake | 0 | [2] |
| Reservoir | 0 | [2] |
| Mudflat | 0 | [2] |
| Urban fabric | 0 | [40] |
| Rural fabric | 0 | [39] |
| Construction and transportation units | 0 | [2] |
| Soil Erosion Rate (t·km−2·y−1) | Erosion Grade | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extent (km2) | Proportion (%) | Extent (km2) | Proportion (%) | Extent (km2) | Proportion (%) | Extent (km2) | Proportion (%) | ||
| <500 | Grade 1 (slight) | 45,507 | 77.54 | 50,057 | 85.25 | 54,064 | 92.08 | 58,051 | 98.871 |
| 500–2500 | Grade 2 (light) | 2985 | 5.09 | 3045 | 5.19 | 1588 | 2.7 | 632 | 1.076 |
| 2500–5000 | Grade 3 (moderate) | 2798 | 4.77 | 1622 | 2.76 | 1039 | 1.77 | 28 | 0.048 |
| 5000–8000 | Grade 4 (intense) | 2715 | 4.63 | 1509 | 2.57 | 710 | 1.21 | 3 | 0.005 |
| 8000–15,000 | Grade 5 (extremely intense) | 2478 | 4.22 | 1327 | 2.26 | 694 | 1.18 | 0 | 0 |
| >15,000 | Grade 6 (severe) | 2203 | 3.75 | 1156 | 1.97 | 619 | 1.06 | 0 | 0 |
| Land Cover Type | Coefficient | Standard Deviation | T | p-Value | 95% Confidence Interval | Importance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Limit | Upper Limit | ||||||
| River | −6.199 | 1.482 | −4.181 | 0.001 | −9.378 | −3.019 | 0.308 |
| Sparse grassland | 17.201 | 4.595 | 3.743 | 0.002 | 7.346 | 27.057 | 0.247 |
| Other woodland | 6.860 | 2.512 | 2.730 | 0.016 | 1.471 | 12.248 | 0.131 |
| Shrub | 1.977 | 0.756 | 2.614 | 0.020 | 0.355 | 3.598 | 0.120 |
| Variables | B | Standard Deviation | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Limit | Upper LIMIT | ||||
| Intercept | 167.232 | 53.2636 | 62.837 | 271.627 | 0.002 |
| NDVI | –4817.538 | 552.0762 | –5899.588 | –3735.489 | 0.000 |
| NDVI × Urban rate | 39,743.093 | 11,681.8554 | 16,847.077 | 62,639.109 | 0.001 |
| Urban rate × Vegetation diversity | –5113.203 | 1804.2045 | –8649.379 | –1577.027 | 0.005 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiu, J.; Wu, H.; Li, S. The Implication of Land-Use/Land-Cover Change for the Declining Soil Erosion Risk in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101856
Jiu J, Wu H, Li S. The Implication of Land-Use/Land-Cover Change for the Declining Soil Erosion Risk in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(10):1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101856
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiu, Jinzhu, Hongjuan Wu, and Sen Li. 2019. "The Implication of Land-Use/Land-Cover Change for the Declining Soil Erosion Risk in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 10: 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101856
APA StyleJiu, J., Wu, H., & Li, S. (2019). The Implication of Land-Use/Land-Cover Change for the Declining Soil Erosion Risk in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(10), 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101856