Influence of Two-Stage Combinations of Constructed Wetlands on the Removal of Antibiotics, Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Nutrients from Goose Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
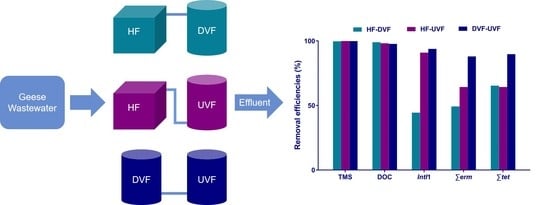
2.1. Design of Hybrid CWs
2.2. Analysis of TMS and DOC
2.3. Analysis of 16S rRNA, IntI1, and ARGs
2.4. Analysis of Nutrients
2.5. Calculation of Removal Efficiencies and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Removal Efficiencies of TMS and DOC in Hybrid CWs
3.2. Removal Efficiencies of 16S rRNA, IntI1, and ARGs in Hybrid CWs
3.3. Removal Efficiencies of Nutrients in Hybrid CWs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- All three hybrid CWs were efficient for removing high-concentration TMS and DOC from wastewater and the combined configuration of hybrid CWs has no significant effect on the removal of antibiotics;
- (2)
- DVF-UVF CWs possessed better ARG removal efficiencies from wastewater, probably due to the inhibition of bacterial growth;
- (3)
- DVF-UVF CWs might promote the establish of anammox and benefit for removing N from wastewater;
- (4)
- DVF-UVF CWs was the optimal choice for removing pollutants from goose wastewater.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, M.; Chu, L. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in soils from wastewater irrigation areas in the Pearl River Delta region, southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zheng, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H. Removal of antibiotics and resistance genes from swine wastewater using vertical flow constructed wetlands: Effect of hydraulic flow direction and substrate type. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic use in agriculture and its consequential resistance in environmental sources: Potential public health implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, X.-D.; Liu, Y.-S.; Ying, G.-G.; Liu, S.-S.; He, L.-Y.; Su, H.-C.; Hu, L.-X.; Chen, F.-R.; Yang, Y.-Q. Removal of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes from domestic sewage by constructed wetlands: Optimization of wetland substrates and hydraulic loading. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Ying, G.-G.; Singer, A.C.; Zhu, Y.-G. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment. Environ. Int. 2018, 110, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, R.; He, T.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, L.; Shang, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, R. Occurrence of seventeen veterinary antibiotics and resistant bacterias in manure-fertilized vegetable farm soil in four provinces of China. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Han, Q.; Jiang, L.; Ma, L.; Jin, L.; Zhang, D.; Lin, K.; Zhang, T. Occurrence, distribution, and seasonal variation of antibiotics in an artificial water source reservoir in the Yangtze River delta, East China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 19393–19402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Fu, C.; Tu, C.; Huang, Y.; Wu, L.; Tang, J.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Levels, distributions and sources of veterinary antibiotics in the sediments of the Bohai Sea in China and surrounding estuaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, H. Persistence and risk of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes in major mariculture sites in Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stange, C.; Yin, D.; Xu, T.; Guo, X.; Schäfer, C.; Tiehm, A. Distribution of clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in Lake Tai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Deng, W.-J.; Liu, Y.-S.; Hu, L.-X.; He, L.-Y.; Zhao, J.-L.; Wang, T.-T.; Ying, G.-G. Fate and removal of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hybrid constructed wetlands. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Plants used in constructed wetlands with horizontal subsurface flow: A review. Hydrobiologia 2011, 674, 133–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Murinda, S.E. Continuous flow-constructed wetlands for the treatment of swine waste water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. The use of hybrid constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment with special attention to nitrogen removal: A review of a recent development. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4795–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, D.Q.; Dong, J.W.; Tan, S.K. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in cold climate—A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 57, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Kröpfelová, L. Multistage hybrid constructed wetland for enhanced removal of nitrogen. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Ng, W.J.; Tan, S.K. A review on removing pharmaceutical contaminants from wastewater by constructed wetlands: Design, performance and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 908–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Liang, S.; Fan, J.; Lu, S.; Wu, H. Optimizations on supply and distribution of dissolved oxygen in constructed wetlands: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.-X.; Huang, X.; Zhu, G.-F. Behavior of tetracycline and sulfamethazine with corresponding resistance genes from swine wastewater in pilot-scale constructed wetlands. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 278, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glisson, J.R. Bacterial respiratory diseases of poultry. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijosa-Valsero, M.; Fink, G.; Schlüsener, M.P.; Sidrach-Cardona, R.; Martín-Villacorta, J.; Ternes, T.; Bécares, E. Removal of antibiotics from urban wastewater by constructed wetland optimization. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlicchi, P.; Galletti, A.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D.; Al Aukidy, M.; Zambello, E. Removal of selected pharmaceuticals from domestic wastewater in an activated sludge system followed by a horizontal subsurface flow bed—analysis of their respective contributions. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 454, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S. Present situation, future development trend and suggestions of waterfowl industry in 2018. Chin. J. Anim. Husb. 2019, 55, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Michel, F.C.; Sreevatsan, S.; Morrison, M.; Yu, Z. Occurrence and persistence of erythromycin resistance genes (erm) and tetracycline resistance genes (tet) in waste treatment systems on swine farms. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 60, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Chen, H.; Su, C.; Yan, S. Abundance and persistence of antibiotic resistance genes in livestock farms: A comprehensive investigation in eastern China. Environ. Int. 2013, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, C.; Li, K.; Su, J.; Zhu, G.; Liu, L. Performance of vertical up-flow constructed wetlands on swine wastewater containing tetracyclines and tet genes. Water Res. 2015, 70, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tong, J.; Chen, M.; Wei, Y. Seasonal variation and removal efficiency of antibiotic resistance genes during wastewater treatment of swine farms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9048–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation, W.E.; Association, A.P.H. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Conkle, J.L.; White, J.R.; Metcalfe, C.D. Reduction of pharmaceutically active compounds by a lagoon wetland wastewater treatment system in Southeast Louisiana. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, A.; Yang, Y.; Dai, Y.-N.; Chen, C.-X.; Wang, S.-Y.; Tao, R. Removal and factors influencing removal of sulfonamides and trimethoprim from domestic sewage in constructed wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, P.N.; Pirra, A.; Basto, M.C.P.; Almeida, C.M.R. Activated sludge systems removal efficiency of veterinary pharmaceuticals from slaughterhouse wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8790–8800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leston, S.; Freitas, A.; Rosa, J.; Barbosa, J.; Lemos, M.F.; Pardal, M.Â.; Ramos, F. A multiresidue approach for the simultaneous quantification of antibiotics in macroalgae by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1033, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Johnson, N.; Cizmas, L.; McDonald, T.J.; Kim, H. A review of the influence of treatment strategies on antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazel, D. Integrons: Agents of bacterial evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, C.; Luo, Y.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, J. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes in the urban rivers in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Zheng, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, G. Elimination of veterinary antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes from swine wastewater in the vertical flow constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, J.; Takala, S.; Barns, S.M.; Davis, J.A.; Kuske, C.R. Levels of bacterial community diversity in four arid soils compared by cultivation and 16S rRNA gene cloning. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, M.; He, F.; Xu, D.; Li, M.; Wu, Z. How Artificial Aeration Improved Sewage Treatment of an Integrated Vertical-Flow Constructed Wetland. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2010, 19, 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, N.; Qiao, M.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, W.-D.; Zhu, Y.-G. Abundance and diversity of tetracycline resistance genes in soils adjacent to representative swine feedlots in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6933–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, B.; Khan, G.A.; Weisner, S.E.; Ehde, P.M.; Fick, J.; Lindgren, P.-E. Efficient removal of antibiotics in surface-flow constructed wetlands, with no observed impact on antibiotic resistance genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, C.W.; Loftin, K.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Davis, J.G.; Pruden, A. Tet and sul antibiotic resistance genes in livestock lagoons of various operation type, configuration, and antibiotic occurrence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6102–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ávila, C.; Bayona, J.M.; Martín, I.; Salas, J.J.; García, J. Emerging organic contaminant removal in a full-scale hybrid constructed wetland system for wastewater treatment and reuse. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 80, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Xie, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Nitrous oxide emissions from surface flow and subsurface flow constructed wetland microcosms: Effect of feeding strategies. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, T. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation in constructed wetlands with bio-contact oxidation as pretreatment. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; He, F.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z. Microbial nitrogen removal pathways in integrated vertical-flow constructed wetland systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 207, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Items 2 | HF-DVF (%) | HF-UVF (%) | DVF-UVF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | |||
| TMS | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 |
| DOC | 99 ± 1 | 98 ± 2 | 98 ± 2 |
| ∑antibiotics | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 |
| Genes | |||
| 16S rRNA | −36 ± 38 b | 8 ± 34 ab | 45 ± 22 a |
| intI1 | 44 ± 33 b | 91 ± 7 a | 94 ± 6 a |
| ermB | 30 ± 39 b | 96 ± 4 a | 98 ± 2 a |
| ermF | 58 ± 29 | 42 ± 49 | 85 ± 19 |
| ermC | 64 ± 30 b | 92 ± 5a | 93 ± 4 a |
| ∑erm | 49 ± 13 b | 64 ± 25 ab | 88 ± 14 a |
| tetO | 93 ± 4 | 83 ± 13 | 76 ± 19 |
| tetQ | 50 ± 52 | 83 ± 20 | 93 ± 5 |
| tetW | 68 ± 18 b | 89 ± 7 a | 91 ± 8 a |
| tetA | 94 ± 8 | 96 ± 2 | 67 ± 51 |
| tetC | 73 ± 32 | 78 ± 14 | 91 ± 7 |
| tetG | 57 ± 29b | 79 ± 15 ab | 91 ± 12 a |
| tetX | 66 ± 33 | 10 ± 168 | 85 ± 13 |
| ∑tet | 65 ± 29 | 64 ± 42 | 90 ± 4 |
| Nutrients | |||
| TN | 54 ± 28 | 76 ± 19 | 68 ± 25 |
| NH4+-N | 68 ± 46 | 73 ± 44 | 95 ± 5 |
| NO3--N | 59 ± 40 | 75 ± 24 | 86 ± 20 |
| NO2--N | 47 ± 37 | 69 ± 31 | 90 ± 10 |
| TP | 83 ± 26 | 72 ± 23 | 82 ± 19 |
| COD | 74 ± 11 | 59 ± 25 | 61 ± 13 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, H.; Xue, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, C. Influence of Two-Stage Combinations of Constructed Wetlands on the Removal of Antibiotics, Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Nutrients from Goose Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16204030
Huang X, Luo Y, Liu Z, Zhang C, Zhong H, Xue J, Wang Q, Zhu Z, Wang C. Influence of Two-Stage Combinations of Constructed Wetlands on the Removal of Antibiotics, Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Nutrients from Goose Wastewater. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(20):4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16204030
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiaofeng, Yi Luo, Zuolan Liu, Changlian Zhang, Hang Zhong, Jiajia Xue, Qigui Wang, Zhiping Zhu, and Chao Wang. 2019. "Influence of Two-Stage Combinations of Constructed Wetlands on the Removal of Antibiotics, Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Nutrients from Goose Wastewater" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 20: 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16204030
APA StyleHuang, X., Luo, Y., Liu, Z., Zhang, C., Zhong, H., Xue, J., Wang, Q., Zhu, Z., & Wang, C. (2019). Influence of Two-Stage Combinations of Constructed Wetlands on the Removal of Antibiotics, Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Nutrients from Goose Wastewater. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(20), 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16204030