Application of a Fuzzy Logic Based Methodology to Validate the Hydrochemical Characterization and Determining Seasonal Influence of a Watershed Affected by Acid Mine Drainage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
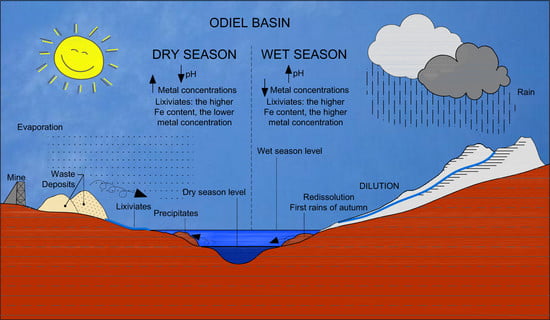
2. Site Description
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling Points
3.2. Analytical Procedure
3.3. Data Mining and Fuzzy Logic
3.3.1. Fuzzy Clustering
3.3.2. PreFuRGe Methodology (Predictive Fuzzy Rules Generator)
- The fuzzy set assigned to each parameter is represented by a trapezium,
- The parameters values are represented on the x-axis of each fuzzy set,
- The parameters membership grade to a cluster is represented on the y-axis.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Hydrochemistry of the Odiel River Basin
4.2. Application of the Proposed Fuzzy Methodology to the Seasonal Variations in the Odiel River Hydrochemistry
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galhardi, J.A.; Bonotto, D.M. Hydrogeochemical features of surface water and groundwater contaminated with acid mine drainage (AMD) in coal mining areas: A case study in southern Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 18911–18927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, P.; Sun, X.; Xiao, E.; Xu, Z.; Li, B.; Sun, W. Characterization of iron-metabolizing communities in soils contaminated by acid mine drainage from an abandoned coal mine in Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 9585–9598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.J.; Luís, A.T.; Grande, J.A.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Dávila, J.M.; Fortes, J.C.; Córdoba, F.; Diaz-Curiel, J.; Santisteban, M. Physico-Chemical Influence of Surface Water Contaminated by Acid Mine Drainage on the Populations of Diatoms in Dams (Iberian Pyrite Belt, SW Spain). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2019, 16, 4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nordstrom, D.K.; Alpers, C.N. Geochemistry of acid mine waters. In The Environmental Geo-chemistry of Mineral Deposits, Part A: Processes, Techniques, and Health Issues: Society of Economic Geologists; Plumlee, G.S., Logsdon, M.J., Eds.; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 1999; Volume 6, pp. 133–160. [Google Scholar]
- Grande, J.A.; Andújar, J.M.; Aroba, J.; De La Torre, M.L.; Beltrán, R. Precipitation, pH and metal load in AMD river basins: An application of fuzzy clustering algorithms to the process characterization. J. Environ. Monit. 2005, 7, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, P.C.; Stumm, W. Acidic Mine Drainage: The Rate-Determining Step. Science 1970, 167, 1121–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis Jr, R.A.; Welty, A.T.; Borrego, J.; Morales, J.A.; Pendon, J.G.; Ryan, J.G. Rio Tinto estuary (Spain): 5000 years of pollution. Environ. Earth Sci. 2000, 39, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, M.; Morales, J.A.; Borrego, J.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F. 4,500-Year-Old Mining Pollution in Southwestern Spain: Long-Term Implications for Modern Mining Pollution. Econ. Geol. 2000, 95, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, A.M.; Nieto, J.M.; Olías, M.; Cánovas, C.R. Hydrochemical characteristics and seasonal influence on the pollution by acid mine drainage in the Odiel river Basin (SW Spain). Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 697–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dold, B. Evolution of Acid Mine Drainage Formation in Sulphidic Mine Tailings. Minerals 2014, 4, 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-M.; Choi, Y. SIMPL: A Simplified Model-Based Program for the Analysis and Visualization of Groundwater Rebound in Abandoned Mines to Prevent Contamination of Water and Soils by Acid Mine Drainage. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebepe, J.; Oberholster, P.J.; Ncube, I.; Smit, W.; Luus-Powell, W.J. Metal levels in two fish species from a waterbody impacted by metallurgic industries and acid mine drainage from coal mining in South Africa. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2020, 55, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaie, B.; Anderson, A. Sustainable resolutions for environmental threat of the acid mine drainage. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, A.; Sheoran, V. Heavy metal removal mechanism of acid mine drainage in wetlands: A critical review. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen, J.; Zipper, C.E.; Rose, A.; Ziemkiewicz, P.F.; Nairn, R.; McDonald, L.M.; Kleinmann, R.L. Review of Passive Systems for Acid Mine Drainage Treatment. Mine Water Environ. 2017, 36, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cánovas, C.; Olías, M.; Nieto, J.; Sarmiento, A.; Cerón, J. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of the Tinto and Odiel Rivers (SW Spain). Factors controlling metal contents. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 373, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáinz, A.; Grande, J.; de la Torre, M.; Rodasc, D. Characterisation of sequential leachate discharges of mining waste rock dumps in the Tinto and Odiel rivers. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 64, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olı́as, M.; Nieto, J.; Sarmiento, A.; Cerón, J.; Cánovas, C. Seasonal water quality variations in a river affected by acid mine drainage: The Odiel River (South West Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 333, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- España, J.S.; Pamo, E.L.; Santofimia, E.; Aduvire, O.; Reyes, J.; Barettino, D. Acid mine drainage in the Iberian Pyrite Belt (Odiel river watershed, Huelva, SW Spain): Geochemistry, mineralogy and environmental implications. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1320–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego, J.M.J.; Morales, J.; De La Torre, M.L.; Grande, J. Geochemical characteristics of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of the Tinto and Odiel river estuary (southwestern Spain). Environ. Earth Sci. 2002, 41, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Dupuy, C. Behaviour of rare earth elements at the freshwater–seawater interface of two acid mine rivers: The Tinto and Odiel (Andalucia, Spain). Appl. Geochem. 1999, 14, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, J.A.; Borrego, J.; Morales, J.A. A study of heavy metal pollution in the Tinto-Odiel estuary in southwestern Spain using factor analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2000, 39, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, J.M.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Olías, M.; Canovas, C.R.; Riba, I.; Kalman, J.; Delvalls, T.A. Acid mine drainage pollution in the Tinto and Odiel rivers (Iberian Pyrite Belt, SW Spain) and bioavailability of the transported metals to the Huelva Estuary. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, A.; Nieto, J.; Olías, M. The contaminant load transported by the river Odiel to the Gulf of Cádiz (SW Spain). Appl. Earth Sci. 2004, 113, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz, A.; Grande, J.; de la Torre, M. Characterisation of heavy metal discharge into the Ria of Huelva. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila, J.M.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Santisteban, M.; Luís, A.T.; Fortes, J.C.; Diaz-Curiel, J.; Valbuena, C.; Grande, J.A. The UNESCO national biosphere reserve (Marismas del Odiel, SW Spain): An area of 18,875 ha affected by mining waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 33594–33606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, J.; De La Torre, M.; Valente, T.; Fernández, J.; Borrego, J.; Santisteban, M.; Ceron, J.C.; Sánchez-Rodas, D. Stratification of Metal and Sulphate Loads in Acid Mine Drainage Receiving Water Dams—Variables Regionalization by Cluster Analysis. Water Environ. Res. 2015, 87, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luís, A.T.; Grande, J.A.; Durães, N.; Dávila, J.M.; Santisteban, M.; Almeida, S.F.P.; Sarmiento, A.M.; De La Torre, M.L.; Fortes, J.C.; Da Silva, E.F. Biogeochemical characterization of surface waters in the Aljustrel mining area (South Portugal). Environ. Geochem. Heal. 2019, 41, 1909–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, J.A.; Andújar, J.M.; Aroba, J.; Beltrán, R.; De La Torre, M.L.; Cerón, J.C.; Gomez, T.; Andújar-Márquez, J.M. Fuzzy Modeling of the Spatial Evolution of the Chemistry in the Tinto River (SW Spain). Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 3219–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroba, J.; Grande, J.A.; Andújar, J.M.; de la Torre, M.L.; Riquelme, J.C. Application of fuzzy logic and data mining techniques as tools for qualitative interpretation of acid mine drainage processes. Environ. Earth Sci. 2007, 53, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroba, J. Advances in the Decision Making in Software Development Projects. Ph.D.Thesis, University of Seville, Sevilla, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Maiti, S.; Naidu, S.; Gupta, G. Estimation of spatial variability of aquifer parameters from geophysical methods: A case study of Sindhudurg district, Maharashtra, India. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2017, 31, 1709–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadiati, M.; Asghari-Moghaddam, A.; Nakhaei, M.; Adamowski, J.; Akbarzadeh, A. A fuzzy-logic based decision-making approach for identification of groundwater quality based on groundwater quality indices. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 184, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güler, C.; Thyne, G.D. Delineation of hydrochemical facies distribution in a regional groundwater system by means of fuzzyc-means clustering. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jalalifar, H.; Mojedifar, S.; Sahebi, A.; Nezamabadi-Pour, H. Application of the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for prediction of a rock engineering classification system. Comput. Geotech. 2011, 38, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez, R.; Pascual, E.; Toscano, M.; Almodóvar, G.R. The Iberian type of volcano-sedimentary massive sulphide deposits. Miner. Deposita 1999, 34, 549–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, A.M.; Nieto, J.M. Preliminary study of the pollutants load of the Odiel River. Geogaceta 2003, 34, 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, J.M.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Canovas, C.R.; Olias, M.; Ayora, C. Acid mine drainage in the Iberian Pyrite Belt: 1. Hydrochemical characteristics and pollutant load of the Tinto and Odiel rivers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7509–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodier, J.; Bazin, C.; Broutin, J.P.; Chambon, P.; Champsaur, H.; Rodi, L. L’Analyse de l’Eau: Eauxnaturelles, Eauxrésiduaires, Eau de Mer, 8th ed.; Dunod: Paris, France, 1996; p. 1383. [Google Scholar]
- Glymour, C.; Madigan, D.; Pregibon, D.; Smyth, P. Statistical inference and data mining. Commun. ACM 1996, 39, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, D.J. Data Mining: Statistics and More? Am. Stat. 1998, 52, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, T.; Suzuki, T. On interpretability of fuzzy models based on conciseness measure. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (Cat. No.01CH37297), Melbourne, Australia, 2–5 December 2001; pp. 284–287. [Google Scholar]
- Guillaume, S. Designing fuzzy inference systems from data: An interpretability-oriented review. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2001, 9, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakajima, H. Fuzzy logic and data mining. In Proceedings of the Soft Computing in Intelligent Systems and Information Processing. Proceedings of the 1996 Asian Fuzzy Systems Symposium, Kenting, Taiwan, 11–14 December 1996; pp. 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control. 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamed, A.K.; Dan, L.; Kai, S.; Mohamed, M.A.A.; Aldaw, E.; Elubid, B.A.; Liu, D.; Song, K. Hydrochemical Analysis and Fuzzy Logic Method for Evaluation of Groundwater Quality in the North Chengdu Plain, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agah, A.; Soleimanpourmoghadam, N. Design and implementation of heavy metal prediction in acid mine drainage using mul-ti-output adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems (ANFIS)—A case study. Int. J. Min. Geo. Ing. 2020, 54, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, L.; Rousseeuw, P.J. Finding Groups in Data: An Introduction to Cluster Analysis; Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 0-471-73578-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway, R.; Bezdek, J. Switching regression models and fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1993, 1, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Sun, S. A new method based on Fuzzy C-Means algorithm for search results clustering. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2013, 320, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höppner, F.; Klawonn, F. A contribution to convergence theory of Fuzzy C-Means and derivatives. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2003, 11, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugeno, M.; Yasukawa, T. A fuzzy-logic-based approach to qualitative modeling. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1993, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bezdek, J.C. Pattern Recognition with Fuzzy Objective Function Algorithms; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981; ISBN 978-1-4757-0452-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S. Seasonal factors controlling mineral precipitation in the acid mine drainage at Donghae coal mine, Korea. Sci. Total. Environ. 2004, 325, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, M.; Islam, N.; Rabha, S.; Narzary, B.; Bordoloi, M.; Saikia, D.; Silva, L.F.; Saikia, B.K. Acid mine drainage in an Indian high-sulfur coal mining area: Cytotoxicity assay and remediation study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Nordstrom, D.K.; Dold, B.; Kirschbaum, A. Seasonal fluctuations and geochemical modeling of acid mine drainage in the semi-arid Puna region: The Pan de Azúcar Pb–Ag–Zn mine, Argentina. J. South Am. Earth Sci. 2021, 109, 103197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Wei, P.; Pei, L.; Du, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Dong, H. Significant seasonal variations of microbial community in an acid mine drainage lake in Anhui Province, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, R.; Banda, J.F.; Hao, C.; Dong, H.; Pei, L.; Guo, D.; Wei, P.; Du, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, H. Contrasting seasonal variations of geochemistry and microbial community in two adjacent acid mine drainage lakes in Anhui Province, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.J.; Santisteban, M.; Aroba, J.; Grande, J.A.; Dávila, J.M.; Sarmiento, A.; Fortes, J.C.; Curiel, J.; Luís, A.T. Application of Fuzzy Logic Techniques for Biogeochemical Characterization of Dams Affected by Acid Mine Drainage (AMD) Processes in the Iberian Pyrite Belt (IPB), Spain. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Torre, M.L.; Grande, J.A.; Valente, T.; Santisteban, M.; Cerón, J.C. Hydrochemical changes in a reservoir that receives water contaminated by acid mine drainage. Hydrol. Res. 2014, 46, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerón, J.; Grande, J.; De La Torre, M.L.; Borrego, J.; Santisteban, M.; Valente, T. Hydrochemical characterization of an acid mine drainage-affected reservoir: The Sancho Reservoir, Huelva, southwest Spain. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cánovas, C.; Olías, M.; Nieto, J.; Galván, L. Wash-out processes of evaporitic sulfate salts in the Tinto river: Hydrogeochemical evolution and environmental impact. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, A.; Nieto, J.; Casiot, C.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Egal, M. Inorganic arsenic speciation at river basin scales: The Tinto and Odiel Rivers in the Iberian Pyrite Belt, SW Spain. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneel, O.; Personne, J.-C.; Casiot, C.; Leblanc, M.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Mahler, B.; Le Fleche, A.; Grimont, P. Mediation of arsenic oxidation by Thiomonas sp. in acid-mine drainage (Carnoules, France). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, A.M.; Oliveira, V.; Gómez-Ariza, J.L.; Nieto, J.M.; Sánchez-Rodas, D. Diel cycles of arsenic speciation due to photooxidation in acid mine drainage from the Iberian Pyrite Belt (Sw Spain). Chemosphere 2007, 66, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigham, J.M.; Nordstrom, D.K. Iron and Aluminum Hydroxysulfates from Acid Sulfate Waters. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2000, 40, 351–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigham, J.; Schwertmann, U.; Traina, S.; Winland, R.; Wolf, M. Schwertmannite and the chemical modeling of iron in acid sulfate waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | Annual Range | Wet Season (n = 111) | Dry Season (n = 121) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | ||
| pH | 2.12–8.77 | 2.49 | 8.59 | 4.14 | 1.48 | 2.12 | 8.77 | 3.79 | 1.62 |
| Eh (mV) | 211–813 | 211 | 781 | 594 | 130 | 259 | 813 | 621 | 129 |
| EC (mS/cm) | 0.1–18.5 | 0.1 | 13.7 | 2.0 | 2.79 | 0.2 | 18.5 | 3.5 | 4.05 |
| DO (%) | 26–122 | 28 | 122 | 90 | 13.9 | 26 | 122 | 87 | 17.8 |
| Al (mg/L) | bdl–2045 | bdl | 1139 | 82 | 197 | bdl | 2045 | 186 | 347 |
| As (µg/L) | bdl–7466 | bdl | 7466 | 245 | 889 | bdl | 3817 | 162 | 555 |
| Cd (µg/L) | bdl–2249 | bdl | 1446 | 107 | 255 | bdl | 2249 | 207 | 383 |
| Co (µg/L) | bdl–30,869 | bdl | 15,761 | 782 | 2210 | bdl | 30,869 | 1646 | 3800 |
| Cr (µg/L) | bdl–926 | bdl | 477 | 27 | 78 | bdl | 926 | 41 | 103 |
| Cu (mg/L) | bdl–321 | bdl | 192 | 12 | 30 | bdl | 321 | 22 | 43 |
| Fe (mg/L) | bdl–4282 | bdl | 2003 | 133 | 326 | bdl | 4282 | 317 | 690 |
| Fe(II) (mg/L) | bdl–4000 | bdl | 1756 | 107 | 287 | bdl | 4000 | 213 | 567 |
| Mn (mg/L) | bdl–374 | bdl | 220 | 16.8 | 37.6 | bdl | 374 | 38.4 | 65.5 |
| Mo (µg/L) | bdl–467 | bdl | 240 | 14 | 35 | bdl | 467 | 44 | 81 |
| Ni (µg/L) | bdl–14,429 | bdl | 6839 | 413 | 1104 | bdl | 14,429 | 937 | 2080 |
| Pb (µg/L) | bdl–5930 | bdl | 5930 | 275 | 732 | bdl | 1501 | 178 | 257 |
| Sb (µg/L) | bdl–1041 | bdl | 623 | 30 | 93 | bdl | 1041 | 82 | 154 |
| Sn (µg/L) | bdl–496 | bdl | 46 | 3 | 6.2 | bdl | 496 | 45 | 81.8 |
| Zn (mg/L) | bdl–860 | bdl | 402 | 31 | 74 | bdl | 860 | 70 | 134 |
| SO4 (mg/L) | 10–36,397 | 11 | 19,332 | 1629 | 3600 | 10 | 36,397 | 3729 | 6227 |
| Parameters | Wet Season | Dry Season | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 2.5–8.6 | 2.1–8.8 | 2.1–8.8 |
| Eh (mV) | 211–781 | 259–813 | 211–813 |
| EC (µS/cm) | 115–18,480 | ||
| DO (%) | 28–122 | 40–122 | 26–122 |
| Al (mg/L) | 0.1–1139 | 0.1–1614 | 0.1–1045 |
| As (µg/L) | 2–3487 | 2–2006 | 2–7466 |
| Cd (µg/L) | 2–1446 | 2–1605 | 2–2249 |
| Co (µg/L) | 2–15,761 | 2–14,478 | 2–30,869 |
| Cr (µg/L) | 2–477 | 2–446 | 2–926 |
| Cu (mg/L) | 0.1–192 | 0.1–164 | 0.1–321 |
| Fe (mg/L) | 0.1–1528 | 0.1–2085 | |
| Fe (II) (mg/L) | 0.1–1300 | 0.1–1787 | 0.1–4000 |
| Fe (III) (mg/L) | 0.1–1757 | ||
| Pb (µg/L) | 2–5930 | 2–1501 | 2–5930 |
| Zn (mg/L) | 0.1–402 | 0.1–584 | 0.1–860 |
| SO4 (mg/L) | 11.1–19,332 | 9.9–24,155 | 9.9–36,397 |
| pp30 (mm) * | 0–203 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davila, J.M.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Aroba, J.; Fortes, J.C.; Grande, J.A.; Santisteban, M.; Cordoba, F.; Leiva, M.; Luís, A.T. Application of a Fuzzy Logic Based Methodology to Validate the Hydrochemical Characterization and Determining Seasonal Influence of a Watershed Affected by Acid Mine Drainage. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094693
Davila JM, Sarmiento AM, Aroba J, Fortes JC, Grande JA, Santisteban M, Cordoba F, Leiva M, Luís AT. Application of a Fuzzy Logic Based Methodology to Validate the Hydrochemical Characterization and Determining Seasonal Influence of a Watershed Affected by Acid Mine Drainage. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(9):4693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094693
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavila, Jose M., Aguasanta M. Sarmiento, Javier Aroba, Juan C. Fortes, Jose A. Grande, Maria Santisteban, Francisco Cordoba, Mercedes Leiva, and Ana T. Luís. 2021. "Application of a Fuzzy Logic Based Methodology to Validate the Hydrochemical Characterization and Determining Seasonal Influence of a Watershed Affected by Acid Mine Drainage" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 9: 4693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094693
APA StyleDavila, J. M., Sarmiento, A. M., Aroba, J., Fortes, J. C., Grande, J. A., Santisteban, M., Cordoba, F., Leiva, M., & Luís, A. T. (2021). Application of a Fuzzy Logic Based Methodology to Validate the Hydrochemical Characterization and Determining Seasonal Influence of a Watershed Affected by Acid Mine Drainage. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(9), 4693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094693