Design of a Fuzzy Logic Evaluation to Determine the Ergonomic Risk Level of Manual Material Handling Tasks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Ergonomics design (ED) using FL;
- Ergonomic intervention (EI) and fuzzy approaches (FA);
- Ergonomic risk evaluation (ERE) and FL.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Context of Manual Material Handling Accordingly with ISO11228-1[17]
2.2. Step (1) Determination of Risk Levels (Fuzzy Choices)
- Low risk (long term): Conditions present in carrying and lifting tasks that do not generate work-related illness over a long time;
- Medium risk (medium-term): Conditions present in carrying and lifting tasks that generate work-related illness, in a medium amount of time;
- High risk (short term): Conditions present in carrying and lifting tasks which generate work-related illness in a short time.
2.3. Step (2) Definition of Ergonomic Parameters for Fuzzy Sets
2.3.1. Ergonomic Parameters and Risk Level for the Time of Exposition
2.3.2. Ergonomic Parameters and Risk Level for the Mass of the Object
2.3.3. Ergonomic Parameters and Risk Level for Frequency of Handling
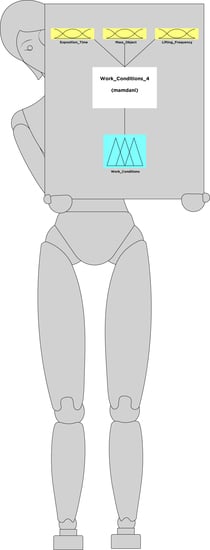
2.4. Step (3) Define Fuzzy Element for the FzEA in MATLAB Fuzzy Logic Designer
2.4.1. The MATLAB Fuzzy Logic Designer
- The fuzzy logic designer editor, where the input and output variables are defined;
- The membership function editor, where input variable values are implemented to their membership function to determine the degree of truth of each premise;
- The rule editor, where experts’ experience is processed as fuzzy rules. The membership functions and variables of input and output are defined by the expert according to his experience.
- The rule viewer is a mapping of a fuzzy subset for each output variable of the rule. Its process of decision-making comprises evaluating a set of alternatives to relevant objectives and restrictions. The fuzzy sets consisted of objectives and restrictions defined in a linguistic form. The decision-making will be determined considering their joint or aggregate consideration, and it is similar to human analysis. Decisions are inferred and based on the calculation of the degree of truth in their premise.
- The surface viewer is a graphical interface that shows the linear relationship between variables.
2.4.2. Fuzzy Sets
2.4.3. Rules for the Fuzzy Ergonomic Assessment (FzEA)
2.5. Step (4) Built the FzEA in MATLAB Fuzzy Logic Designer
2.5.1. Fuzzification
Exposition_Time
Mass_Object
Lifting_Frequency
Work_Conditions
2.5.2. Rules Definition
2.5.3. Defuzzification
3. Results
- The total time duration of the manual material handling in one shift, with 3 h maximal exposition time;
- The mass of the object to be manipulated, considered as maximal mass reference, which should never exceed 25 kg;
- The repetitiveness of the manual material handling task throughout the shift, considering that the maximal frequency of four lifts per min (1800 in 450 min of one shift) should never be exceeded.
- Low risk; does not generate work-related illness over a long period of time.
- Medium risk; generates work-related illness over a medium period of time.
- High risk; generates work-related illness over a short period of time.
- The testing stage comprised of feeding random data and verifying if the results obtained were according to the expected results.
- The validation stage consisted of comparing the results from the fuzzy interface concerning results obtained from ergonomic assessments directly using the ISO 11228-1, referred to in the testing as “expected results”.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GRE | General risk estimation. |
| DRE | Detailed risk estimation. |
| FL | Fuzzy logic. |
| ED | Ergonomic design. |
| EI | Ergonomic intervention. |
| FzEA | Fuzzy Ergonomic Assessment. |
| DDS | Decision support system. |
| FLD | Fuzzy logic designer. |
| FIS | Fuzzy interface system. |
Appendix A
| Test No. | Exposition_Time | Mass_Object | Lifting_Frequency | Expected Results | Work_Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 180 | 25 | 2700 | HIGH | 8.47 |
| 2 | 179 | 13 | 2500 | HIGH | 8.47 |
| 3 | 178 | 14 | 2300 | HIGH | 8.26 |
| 4 | 177 | 15 | 2100 | HIGH | 8.16 |
| 5 | 176 | 16 | 1900 | HIGH | 8.22 |
| 6 | 175 | 17 | 2160 | HIGH | 8.29 |
| 7 | 174 | 18 | 1900 | HIGH | 8.35 |
| 8 | 173 | 19 | 1750 | HIGH | 8.41 |
| 9 | 172 | 18 | 1140 | HIGH | 8.35 |
| 10 | 171 | 17 | 900 | HIGH | 8.29 |
| 11 | 170 | 16 | 535 | HIGH | 8.22 |
| 12 | 169 | 15 | 325 | HIGH | 8.16 |
| 13 | 168 | 14 | 497 | HIGH | 8.26 |
| 14 | 167 | 25 | 224 | HIGH | 8.47 |
| 15 | 166 | 14 | 67 | HIGH | 8.26 |
| 16 | 165 | 14 | 2400 | HIGH | 8.26 |
| 17 | 164 | 10 | 2100 | HIGH | 8.47 |
| 18 | 163 | 14 | 1800 | HIGH | 8.26 |
| 19 | 162 | 15 | 1600 | HIGH | 8.16 |
| 20 | 161 | 7 | 1300 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 21 | 160 | 15 | 1518 | HIGH | 8.16 |
| 22 | 159 | 8 | 800 | MEDIUM | 6.35 |
| 23 | 158 | 14 | 2094 | HIGH | 8.26 |
| 24 | 157 | 13 | 950 | HIGH | 8.47 |
| 25 | 156 | 8 | 1647 | MEDIUM | 6.35 |
| 26 | 155 | 7 | 520 | MEDIUM | 2.48 |
| 27 | 154 | 15 | 895 | HIGH | 8.16 |
| 28 | 153 | 14 | 537 | HIGH | 8.17 |
| 29 | 152 | 14 | 685 | HIGH | 8.26 |
| 30 | 151 | 8 | 722 | MEDIUM | 6.35 |
| 31 | 150 | 2 | 2300 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 32 | 149 | 5 | 2000 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 33 | 148 | 1 | 1700 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 34 | 147 | 4 | 1500 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 35 | 146 | 3 | 1200 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 36 | 145 | 2 | 1150 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 37 | 144 | 7 | 1761 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 38 | 143 | 7 | 1600 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 39 | 142 | 6 | 800 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 40 | 141 | 1 | 900 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 41 | 140 | 5 | 550 | LOW | 3.25 |
| 42 | 139 | 4 | 400 | LOW | 1.13 |
| 43 | 138 | 2 | 385 | LOW | 1.14 |
| 44 | 137 | 3 | 220 | LOW | 1.14 |
| 45 | 136 | 7 | 300 | LOW | 1.27 |
| 46 | 119 | 25 | 2200 | HIGH | 8.20 |
| 47 | 118 | 13 | 1900 | HIGH | 7.26 |
| 48 | 117 | 14 | 1600 | HIGH | 8.16 |
| 49 | 116 | 15 | 1400 | HIGH | 8.16 |
| 50 | 115 | 16 | 1100 | HIGH | 8.17 |
| 51 | 114 | 17 | 1770 | HIGH | 8.17 |
| 52 | 113 | 18 | 1740 | HIGH | 8.19 |
| 53 | 112 | 19 | 1710 | HIGH | 8.21 |
| 54 | 111 | 18 | 1680 | HIGH | 8.20 |
| 55 | 110 | 17 | 1650 | HIGH | 8.19 |
| 56 | 109 | 16 | 575 | MEDIUM | 6.94 |
| 57 | 108 | 15 | 400 | MEDIUM | 5.68 |
| 58 | 107 | 14 | 555 | MEDIUM | 6.23 |
| 59 | 106 | 25 | 545 | MEDIUM | 5.94 |
| 60 | 105 | 14 | 535 | MEDIUM | 5.68 |
| 61 | 104 | 13 | 2400 | MEDIUM | 4.88 |
| 62 | 103 | 10 | 2100 | MEDIUM | 4.78 |
| 63 | 102 | 9 | 1800 | MEDIUM | 5.26 |
| 64 | 101 | 15 | 1500 | HIGH | 8.16 |
| 65 | 100 | 7 | 1200 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 66 | 99 | 10 | 1620 | MEDIUM | 7.44 |
| 67 | 98 | 8 | 1590 | MEDIUM | 6.35 |
| 68 | 97 | 14 | 1560 | MEDIUM | 8.26 |
| 69 | 96 | 9 | 1530 | MEDIUM | 7.50 |
| 70 | 95 | 8 | 1500 | MEDIUM | 6.35 |
| 71 | 94 | 7 | 530 | LOW | 2.74 |
| 72 | 93 | 15 | 515 | MEDIUM | 5.45 |
| 73 | 92 | 14 | 500 | MEDIUM | 4.95 |
| 74 | 91 | 14 | 485 | MEDIUM | 4.69 |
| 75 | 90 | 8 | 470 | MEDIUM | 3.40 |
| 76 | 89 | 2 | 2300 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 77 | 88 | 5 | 2000 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 78 | 87 | 1 | 1700 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 79 | 86 | 4 | 1400 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 80 | 85 | 3 | 1100 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 81 | 84 | 2 | 1470 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 82 | 83 | 7 | 1600 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 83 | 82 | 4 | 1500 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 84 | 81 | 6 | 1470 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 85 | 80 | 1 | 1440 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 86 | 79 | 5 | 450 | LOW | 1.15 |
| 87 | 78 | 4 | 430 | LOW | 1.10 |
| 88 | 77 | 2 | 410 | LOW | 1.10 |
| 89 | 76 | 3 | 390 | LOW | 1.12 |
| 90 | 75 | 8 | 370 | LOW | 3.40 |
| 91 | 74 | 25 | 2700 | HIGH | 7.64 |
| 92 | 73 | 13 | 2500 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 93 | 72 | 14 | 2300 | MEDIUM | 5.26 |
| 94 | 71 | 15 | 2100 | HIGH | 6.57 |
| 95 | 70 | 16 | 1900 | HIGH | 6.87 |
| 96 | 69 | 17 | 1390 | HIGH | 8.24 |
| 97 | 68 | 18 | 1340 | HIGH | 8.21 |
| 98 | 67 | 19 | 1290 | HIGH | 8.19 |
| 99 | 66 | 18 | 1240 | HIGH | 8.17 |
| 100 | 65 | 17 | 1190 | HIGH | 8.17 |
| 101 | 64 | 16 | 350 | LOW | 2.96 |
| 102 | 63 | 15 | 330 | LOW | 2.85 |
| 103 | 62 | 14 | 310 | LOW | 2.34 |
| 104 | 61 | 25 | 290 | LOW | 1.89 |
| 105 | 60 | 14 | 270 | LOW | 1.28 |
| 106 | 59 | 14 | 2600 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 107 | 58 | 10 | 2400 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 108 | 57 | 14 | 2200 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 109 | 56 | 15 | 2000 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 110 | 55 | 9 | 2300 | MEDIUM | 4.00 |
| 111 | 54 | 15 | 1140 | HIGH | 8.16 |
| 112 | 53 | 8 | 1090 | MEDIUM | 3.40 |
| 113 | 52 | 14 | 1040 | MEDIUM | 5.26 |
| 114 | 51 | 13 | 990 | MEDIUM | 4.50 |
| 115 | 50 | 8 | 940 | MEDIUM | 3.40 |
| 116 | 49 | 7 | 250 | LOW | 1.27 |
| 117 | 48 | 15 | 230 | LOW | 1.34 |
| 118 | 47 | 14 | 210 | LOW | 1.24 |
| 119 | 46 | 14 | 190 | LOW | 1.24 |
| 120 | 45 | 8 | 170 | LOW | 1.31 |
| 121 | 44 | 2 | 2700 | LOW | 1.15 |
| 122 | 43 | 5 | 2500 | LOW | 1.15 |
| 123 | 42 | 1 | 2300 | LOW | 1.14 |
| 124 | 41 | 4 | 2100 | LOW | 1.13 |
| 125 | 40 | 3 | 1900 | LOW | 1.12 |
| 126 | 39 | 2 | 890 | LOW | 1.11 |
| 127 | 38 | 7 | 840 | LOW | 1.27 |
| 128 | 37 | 7 | 790 | LOW | 1.27 |
| 129 | 36 | 6 | 740 | LOW | 1.21 |
| 130 | 35 | 1 | 690 | LOW | 1.18 |
| 131 | 34 | 5 | 150 | LOW | 1.15 |
| 132 | 33 | 4 | 130 | LOW | 1.10 |
| 133 | 32 | 2 | 110 | LOW | 1.07 |
| 134 | 31 | 3 | 90 | LOW | 1.06 |
| 135 | 30 | 8 | 70 | LOW | 1.31 |
Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Obregón-Sánchez, M.G. Fundamentos de Ergonomía, 1st ed.; Grupo Editorial Patria: Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- IEA. What Is Ergonomics? International Ergonomic Association. Available online: https://iea.cc/what-is-ergonomics/ (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- ISO 6385:2016; Ergonomic Principles in the Design of Work Systems. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/63785.html (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Panjaitan, N.; Ali, A.Y.B. Classification of ergonomics levels for research. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering, Sumatra, Indonesia, 16–17 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Grooten, W.J.A.; Johanssons, E. Observational Methods for Assessing Ergonomic Risks for Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders. A Scoping Review. Rev. Cienc. Salud. 2018, 16, 8–38. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/jatsRepo/562/56255615002/56255615002.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2021). [CrossRef]
- STPS. NOM 036-1-STPS:2018; Norma Oficial Mexicana, Factores de riesgo ergonómico en el Trabajo-Identificación, Análisis, Prevención y Control. Parte 1: Manejo manual de Cargas. Secretaria del Trabajo y Previsión Solical: Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico, 2018. Available online: https://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5544579&fecha=23/11/2018 (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- ISO 11228-3:2007; Ergonomics—Manual handling—Part 3: Handling of Low Loads at High Frequency. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:11228:-3:ed-1:v2:en (accessed on 3 November 2021).
- McAtamney, L.; Nigel Corlett, E. RULA: A Survey Method for the Investigation of Work-Related Upper Limb Disorders). Appl. Ergon. 1993, 24, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hignett, S.; McAtamney, L. Rapid Entire Body Assessment (REBA). Appl. Ergon. 2000, 31, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhu, O.; Kansi, P.; Kuorinka, I. Correcting working postures in industry: A practical method for analysis. Appl. Ergon. 1977, 8, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guélaud, F.; Beauchesne, N.; Gautrat, J.; Roustang, G. Pour une Analyse des Conditions du Travail Ouvrier dans L’entreprise. Laboratoire d’Économie et de Sociologie du Travail, 4th ed.; Librairie Armand Colin: Paris, France, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- More, J.S.; Grag, A. The Strain Index: A proposed method to analyse jobs for risk of distal upper extremity disorders. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1995, 56, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HSE. Manual Handling Assessment Charts (the MAC Tool) Leaflet INDG383(rev2); HSE Books: London, UK, 2014. Available online: www.hse.gov.uk/pubns/indg383.htm (accessed on 3 November 2021).
- HSE. The Risk Assessment of Pushing and Pulling Tool—RAPP Tool Leaflet INDG478; HSE Books: London, UK, 2016. Available online: www.hse.gov.uk/msd/toolkit.htm (accessed on 3 November 2021).
- Colombini, D.; Occhipinti, E.; Álvarez-Casado, E. The Reised OCRA Checklist Method; Editorial Factors Humans: Barcelona, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- UNE EN 1005-5:2007; Safety of Machinery—Human Physical Performance—Part 5: Risk Assessment for Repetitive Handling at High Frequency. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Switzerland, 2007. Available online: https://www.en-standard.eu/une-en-1005-5-2007-safety-of-machinery-human-physical-performance-part-5-risk-assessment-for-repetitive-handling-at-high-frequency/ (accessed on 4 November 2021).
- ISO 11228-1:2003; Ergonomics—Manual Handling—Part 1: Lifting, Lowering and Carrying. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/76820.html (accessed on 3 November 2021).
- Seuret-Jiménez, D.; Nieto-Jalil, J.M.; Tecpoyotl-Torres, M.; Ayala-Mató, F.; Roman-B, J.E. Fuzzy Logic for Evaluation of Renewable Energy Projects. Int. J. Mod. Eng. Res. IJMER 2016, 6, 4–13. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Walker, C.L.; Walker, E.A. A First Course in Fuzzy Logic, 4th ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pacholski, L.M. Fuzzy logic application in ergonomic renewal of multiagent manufacturing systems. Cybern. Syst. Int. J. 1998, 29, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluclu, A.; Dalgic, A.; Toprak, Z. A fuzzy logic-based model for noise control at industrial workplaces. Appl. Ergon. 2008, 39, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancardo, P.; Hernández-Nolasco, J.A.; Acosta-Escalante, F. A Fuzzy Logic-Based Personalized Method to Classify Perceived Exertion in Workplaces Using a Wearable Heart Rate Sensor. Hindawi 2018, 2018, 4216172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ani, M.F.; Kamat, S.R.; Fukumi, M. Development of Decision Support System via Ergonomics Approach for Driving Fatigue Detection. J. Soc. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2020, 1, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Hamadi, M.; Zakerian, S.A.; Salmanzadeh, H.; Mortezapour, A. Identification of the Ergonomic Interventions Goals from the Viewpoint of Ergonomics Experts of Iran using Fuzzy Delphi Method. Int. J. Occup. Hyg. 2016, 8, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Abarqhouei, N.S.; Nasab, H.H.; Fakhrza, M.B. Design of the evaluation model for total ergonomics interventions with fuzzy approach. Contemp. Educ. Res. J. 2013, 3, 34–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bockelman-Morrow, P. A site-based ergonomic assessment of acoustics in school settings and the proposal of a fuzzy-logic metric. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society 55th Annual Meeting, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 1 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Galabaci, A.; Han, S.; Robinson Fayek, A. A Fuzzy Logic Approach to Posture-based Ergonomic Analysis for Field Observation and Assessment of Construction Manual Operations. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 43, 294–303. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kasasbeth, R.; Korenevskiy, N.; Alshamasin, M.; Maksim, I. Hybrid fuzzy logic modelling and software for ergonomics assessment of biotechnical systems. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 2019, 60, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.L.; García, R.R.; Pérez, M.D.R.; Mar, C.; Juárez, Z. Fuzzy logic and RULA method for assessing the risk of working. Porc. Manuf. 2015, 3, 4816–4822. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, I.L. Fast Ergo X–A tool for ergonomic auditing and work-related musculoskeletal disorders prevention. Work 2009, 34, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, I.L.; Simões-Marques, M. Chapter 2. Applications of Fuzzy Logic in Risk Assessment—The RA_X Case. Fuzzy Inference Syst. Theory Appl. 2012, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colella, Y.; Valente, A.S.; Rossano, L.; Trunfio, T.A.; Fiorillo, A.; Improta, G. A Fuzzy Inference System for the Assessment of Indoor Air Quality in an Operating Room to Prevent Surgical Site Infection. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MathWorks Inc. Fuzzy Logic Toolbox; United States. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/products/fuzzy-logic.html (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Esquivel, R.; Felix, G.; Bello, R. Impact assessment of training with fuzzy logic. Ingeniare Rev. Chil. Ing. 2014, 22, 41–52. [Google Scholar]









| Time of Exposition min | |
|---|---|
| Low | 0–80 |
| Medium | 60–120 |
| High | 100–180 or more |
| Risk Level | Mass of the Object kg |
|---|---|
| Low | 0–10 |
| Medium | 7–15 |
| High | 13–25 or more |
| Risk Level | Frequency of Carrying and Lifting Movements |
|---|---|
| Low | 0–700 |
| Medium | 600–1100 |
| High | 900–1800 or more |
| IF Time of Exposition | AND | IF Mass of the Object | AND | IF Frequency of Carrying and Lifting | THEN | The Risk Level of the Work Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | High | High | High risk | |||
| High | High | Medium | High risk | |||
| High | High | Low | High risk | |||
| High | Medium | High | High risk | |||
| High | Medium | Medium | High risk | |||
| High | Medium | Low | High risk | |||
| High | Low | High | High risk | |||
| High | Low | Medium | Medium risk | |||
| High | Low | Low | Low risk | |||
| Medium | High | High | High risk | |||
| Medium | High | Medium | High risk | |||
| Medium | High | Low | Medium risk | |||
| Medium | Medium | High | Medium risk | |||
| Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium risk | |||
| Medium | Medium | Low | Medium risk | |||
| Medium | Low | High | Medium risk | |||
| Medium | Low | Medium | Medium risk | |||
| Medium | Low | Low | Low risk | |||
| Low | High | High | Medium risk | |||
| Low | High | Medium | Medium risk | |||
| Low | High | Low | Low risk | |||
| Low | Medium | High | Medium risk | |||
| Low | Medium | Medium | Medium risk | |||
| Low | Medium | Low | Low risk | |||
| Low | Low | High | Low risk | |||
| Low | Low | Medium | Low risk | |||
| Low | Low | Low | Low risk |
| Variable | Fuzzy Set | Min |
|---|---|---|
| Exposition_Time | Low | 0–40 |
| Low/Medium | 60–80 | |
| Medium | 80–100 | |
| Medium/High | 100–120 | |
| High | 150 or more |
| Variable | Fuzzy Set | kg |
|---|---|---|
| Mass_Object | Low | 0–3 |
| Low/Medium | 7–10 | |
| Medium | 8–13 | |
| Medium/High | 13–15 | |
| High | 20 or more |
| Variable | Fuzzy Set | Movements |
|---|---|---|
| Lifting_Frequency | Low | 0–400 |
| Low/Medium | 400–600 | |
| Medium | 600–1400 | |
| Medium/High | 1400–1800 | |
| High | 1800 or more |
| Variable | Fuzzy Set | Movements | Severity of the Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work_Conditions | Low | 0–1 | No symptoms |
| Low/Medium | 1–3 | Occasional pain in muscles and joints | |
| Medium | 2–4.5 | Frequent pain in muscles and joints | |
| Medium/High | 4.5–7 | The pain is present for long periods | |
| High | 8 or more |
| Test No. | Exposition_Time | Mass_Object | Lifting_Frequency | Expected Results | Work_Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 180 | 25 | 1800 | HIGH | 8.47 |
| 2 | 170 | 20 | 800 | HIGH | 8.21 |
| 3 | 121 | 17 | 400 | HIGH | 8.22 |
| 4 | 80 | 13 | 1000 | MEDIUM | 4.5 |
| 5 | 175 | 11 | 950 | MEDIUM | 8.36 |
| 6 | 165 | 8 | 625 | MEDIUM | 5.54 |
| 7 | 150 | 6 | 1700 | MEDIUM | 4.5 |
| 8 | 177 | 4 | 750 | MEDIUM | 4.5 |
| 9 | 110 | 2 | 500 | LOW | 1.24 |
| 10 | 115 | 23 | 1600 | HIGH | 8.17 |
| 11 | 90 | 21 | 700 | HIGH | 8.46 |
| 12 | 70 | 16 | 400 | MEDIUM | 3.77 |
| 13 | 119 | 9 | 1500 | HIGH | 7.04 |
| 14 | 95 | 12 | 850 | MEDIUM | 8.47 |
| 15 | 73 | 8 | 600 | MEDIUM | 5.3 |
| 16 | 65 | 7 | 1400 | MEDIUM | 3.17 |
| 17 | 80 | 5 | 650 | LOW | 4.50 |
| 18 | 115 | 3 | 300 | LOW | 1.33 |
| 19 | 80 | 22 | 1300 | HIGH | 8.47 |
| 20 | 75 | 19 | 900 | HIGH | 8.37 |
| 21 | 60 | 15 | 200 | LOW | 1.34 |
| 22 | 53 | 10 | 1200 | MEDIUM | 4.5 |
| 23 | 50 | 8 | 800 | MEDIUM | 3.34 |
| 24 | 45 | 14 | 200 | LOW | 1.24 |
| 25 | 35 | 1 | 1800 | LOW | 1.09 |
| 26 | 20 | 3 | 1000 | LOW | 1.22 |
| 27 | 15 | 5 | 500 | LOW | 1.24 |
| Exposition Time | kg | Lifts | Risk Level | Severity of the Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34 | 5 | 150 | Low | 1.15 |
| 79 | 5 | 450 | Low | 1.5 |
| 88 | 5 | 2000 | Medium | 4.5 |
| 140 | 5 | 550 | Medium | 3.25 |
| 149 | 5 | 2000 | Medium | 4.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Contreras-Valenzuela, M.R.; Seuret-Jiménez, D.; Hdz-Jasso, A.M.; León Hernández, V.A.; Abundes-Recilla, A.N.; Trutié-Carrero, E. Design of a Fuzzy Logic Evaluation to Determine the Ergonomic Risk Level of Manual Material Handling Tasks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116511
Contreras-Valenzuela MR, Seuret-Jiménez D, Hdz-Jasso AM, León Hernández VA, Abundes-Recilla AN, Trutié-Carrero E. Design of a Fuzzy Logic Evaluation to Determine the Ergonomic Risk Level of Manual Material Handling Tasks. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(11):6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116511
Chicago/Turabian StyleContreras-Valenzuela, Martha Roselia, Diego Seuret-Jiménez, Ana María Hdz-Jasso, Viridiana Aydeé León Hernández, Alma Nataly Abundes-Recilla, and Eduardo Trutié-Carrero. 2022. "Design of a Fuzzy Logic Evaluation to Determine the Ergonomic Risk Level of Manual Material Handling Tasks" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 11: 6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116511
APA StyleContreras-Valenzuela, M. R., Seuret-Jiménez, D., Hdz-Jasso, A. M., León Hernández, V. A., Abundes-Recilla, A. N., & Trutié-Carrero, E. (2022). Design of a Fuzzy Logic Evaluation to Determine the Ergonomic Risk Level of Manual Material Handling Tasks. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(11), 6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116511