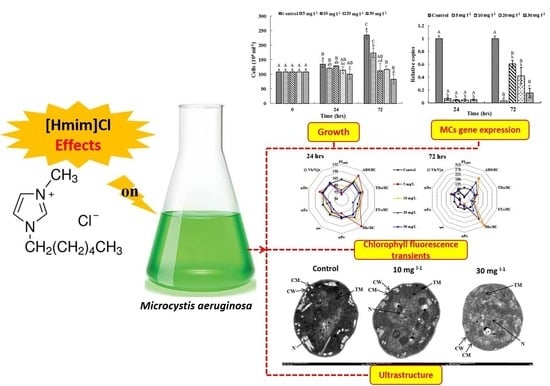
Inhibition Effect of Ionic Liquid [Hmim]Cl on Microcystis Growth and Toxin Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurement of Cell Growth and Photosynthetic Pigments Content
2.2. Measurement of Chlorophyll Fluorescence Transients
2.3. Observation of Cell Ultrastructure
2.4. Transcription of mcyB Gene
2.4.1. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
2.4.2. Determination of mcyB Gene Transcription
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Inhibition of [Hmim]Cl on M. aeruginosa PCC 7806 Growth
3.2. Effects of [Hmim]Cl on the Pigment Contents
3.3. Characteristics of Chlorophyll Fluorescence Transients
3.4. Effect of [Hmim]Cl on the Cell Ultrastructure
3.5. Transcription of mcyB Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- i.
- The EC50 of [Hmim]Cl on M. aeruginosa PCC 7806 was 10.624 ± 0.221 mg L−1 after 72 h of exposure.
- ii.
- [Hmim]Cl could destruct the electron-accepting side of the photosystem II of M. aeruginosa PCC 7806.
- iii.
- Cellular ultrastructure examination indicated that the distortion of the thylakoid membrane and the loss of the integrity of the cell membrane were associated with [Hmim]Cl treatment and concentration.
- iv.
- The transcriptional profiles of mcyB were depressed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mei, X.; Yue, Z.; Ma, Q.; Dunya, H.; Mandal, B.K. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of new dicationic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 1001–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gathergood, N.; Garcia, M.T.; Scammells, P.J. Biodegradable ionic liquids: Part I. Concept, preliminary targets and evaluation. Green Chem. 2004, 6, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Radošević, K.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Halambek, J.; Gaurina Srček, V. A brief overview of the potential environ-mental hazards of ionic liquids. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaise, C.R. Practical Laboratory Applications with Microalgae for Hazard Assessment of Aquatic Contaminants; Richardson, M.L., Ed.; Ecotoxicology Monitoring VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1993; pp. 83–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, M.A. Algae and Vascular Plant Tests. In Fundamentals of Aquatic Toxicology: Effects, Environment Fate, and Risk Assessment; Rand, G.M., Ed.; Taylor and Francis: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 135–170. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Du, S.; Dong, Y. Effects of imidazolium chloride ionic liquids and their toxicity to Scenedesmus obliquus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Flieger, M. Ionic Liquids Toxicity—Benefits and Threats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretti, C.; Chiappe, C.; Baldetti, I.; Brunini, S.; Monni, G.; Intorre, L. Acute toxicity of ionic liquids for three freshwater organisms: Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata, Daphnia magna and Danio rerio. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarpali, V.; Belavgeni, A.; Dailianis, S. Investigation of toxic effects of imidazolium ionic liquids, [bmim][BF4] and [omim][BF4], on marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis with or without the presence of conventional solvents, such as acetone. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 164, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.P.F.; Azevedo, A.M.O.; Pinto, P.C.A.G.; Saraiva, M.L.M.F.S. Environmental Impact of Ionic Liquids: Recent Advances in (Eco)toxicology and (Bio)degradability. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 2321–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.P.T.; Cho, C.-W.; Yun, Y.-S. Environmental fate and toxicity of ionic liquids: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmaso, N.; Boscaini, A.; Capelli, C.; Cerasino, L. Ongoing ecological shifts in a large lake are driven by climate change and eutrophication: Evidences from a three-decade study in Lake Garda. Hydrobiologia 2017, 824, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H.; Cheng, Y.; Geng, R.Z.; Cheng, X.L.; Xiao, P.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Z.L. Taxonomic separation and combination of cyanobacterial genera Cylindrospermopsis and Raphidiopsis. J. Henan Norm. Univ. 2022, 50, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Rahman, G.N.; Sultan, Y.Y.; Hassoub, M.A.; Marrez, D. Cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of the blue green alga Microcystis aeruginosa extracts against human cancer cell lines and foodborne bacteria. Egypt. J. Chem. 2020, 63, 4095–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fang, H.; Lu, H.; Wu, X.; Yu, G.; Nakano, S.-I.; Li, R. Relationship between morphospecies and microcystin-producing genotypes of Microcystis species in Chinese freshwaters. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 1926–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmayer, R.; Kutzenberger, T. Application of Real-Time PCR for Quantification of Microcystin Genotypes in a Population of the Toxic Cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 6723–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, W.; Shangguan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Sultan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, X. Negative impacts of microcystin-LR and glyphosate on zebrafish intestine: Linked with gut microbiota and microRNAs? Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, J.; Gong, H.; Wen, X.; Ren, H.; Lu, C. Effects of heat stress on PSII photochemistry in a cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. Plant Sci. 2008, 175, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, G.H.; Weis, E. Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Photosynthesis: The Basics. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1991, 42, 313–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, B.J.; Strasser, R.J. Measuring Fast Fluorescence Transients to Address Environmental Questions: The JIP-Test. In Photosynthesis: From Light to Biosphere; Mathis, P., Ed.; KAP Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 977–980. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Vonshak, A. Characterization of PSII photochemistry in salt-adapted cells of cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. New Phytol. 1999, 141, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bueno, M.; Fillat, M.F.; Strasser, R.J.; Maldonado-Rodriguez, R.; Marina, N.; Smienk, H.; Gómez-Moreno, C.; Barja, F. Effects of lindane on the photosynthetic apparatus of the cyanobacterium Anabaena. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2004, 11, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilgili, S.; Atac, A.; Bardak, F. Theoretical and experimental investigation of the spectroscopic features of and interionic interactions in 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride, 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate and 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippka, R.; Deruelles, J.; Waterbury, J.B.; Herdman, M.; Stanier, R.Y. Generic Assignments, Strain Histories and Properties of Pure Cultures of Cyanobacteria. Microbiology 1979, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, F.A.; Thompson, T.G. The estimation and characterization of plankton populations by pigment analyses. II. A spectrophotometric method for the estimation of plankton pigments. J. Mar. Res. 1952, 11, 156–172. [Google Scholar]
- Appenroth, K.-J.; Stöckel, J.; Srivastava, A.; Strasser, R. Multiple effects of chromate on the photosynthetic apparatus of Spi-rodela polyrhiza as probed by OJIP chlorophyll a fluorescence measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 115, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, D.; Schönmann, S.; Jermini, M.; Strasser, R.J.; Défago, G. Characterization and early detection of grapevine (Vitis vinifera) stress responses to esca disease by in situ chlorophyll fluorescence and comparison with drought stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 60, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Wu, Z.; Yu, G.; Peng, X.; Li, R. Allelopathic mechanism of pyrogallol to Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 (Cyanobacteria): From views of gene expression and antioxidant system. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; He, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, A.; Luo, S.; Gu, J.-D. Growth inhibition and possible mechanism of oleamide against the toxin-producing cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa NIES-843. Ecotoxicology 2015, 25, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.P.T.; Cho, C.-W.; Min, J.; Yun, Y.-S. Alkyl-chain length effects of imidazolium and pyridinium ionic liquids on photosynthetic response of Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2008, 105, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amde, M.; Liu, J.-F.; Pang, L. Environmental Application, Fate, Effects, and Concerns of Ionic Liquids: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12611–12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Pillai, V.V.; Benedetto, A. Mechanisms of action of ionic liquids on living cells: The state of the art. Biophys. Rev. 2020, 12, 1187–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, M.; Rodrigues, T.; Silva, L.; Pacheco, A.; Ferrão-Filho, A.; Azevedo, S. Ecophysiological Aspects and sxt Genes Expression Underlying Induced Chemical Defense in STX-Producing Raphidiopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) against the Zooplankter Daphnia gessneri. Toxins 2021, 13, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulacki, K.J.; Lamberti, G.A. Toxicity of imidazolium ionic liquids to freshwater algae. Green Chem. 2007, 10, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, K.M.; Joyce, M.V.; Kulacki, K.J.; Kulpa, C.F. Microbial biodegradation and metabolite toxicity of three pyridinium-based cation ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Malhotra, S.V.; Dodge, C.J.; Francis, A.J. Biodegradation of pyridinium-based ionic liquids by an axenic culture of soil Corynebacteria. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Du, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Acute Toxicity of Imidazole Nitrate Ionic Liquids with Varying Chain Lengths to Earthworms (Eisenia foetida). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, M.; Peng, X.J.; Ning, D.; Chen, J. Toxicity of [C8mim]PF6 to aquatic organisms. China Environ. Sci. 2009, 29, 1196–1201, (In Chinese, English Summary). [Google Scholar]
- Sena, D.W.; Kulacki, K.J.; Chaloner, D.T.; Lamberti, G.A. The role of the cell wall in the toxicity of ionic liquids to the alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-W.; Pham, T.P.T.; Jeon, Y.-C.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Choe, W.-S.; Yun, Y.-S. Toxicity of imidazolium salt with anion bromide to a phytoplankton Selenastrum capricornutum: Effect of alkyl-chain length. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, S.; Yamada, S.; Hosomi, M. Anti-cyanobacterial fatty acids released from Myriophyllum spicatum. Hydrobiologia 2005, 543, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Wang, J. Effects of 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide on the antioxidant system of Lemna minor. Protoplasma 2012, 250, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Jing, C.-Q.; Zang, X.-Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.-J. Toxic cytological alteration and mitochondrial dysfunction in PC12 cells induced by 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.-M.; Lee, S.J.; Jang, M.-H.; Yoon, B.-D. Microcystin Production by Microcystis aeruginosa in a Phosphorus-Limited Chemostat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sultan, Y.; Xiao, P.; Yang, L.; Lu, H.; Zhang, B. Inhibition Effect of Ionic Liquid [Hmim]Cl on Microcystis Growth and Toxin Production. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148719
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Sultan Y, Xiao P, Yang L, Lu H, Zhang B. Inhibition Effect of Ionic Liquid [Hmim]Cl on Microcystis Growth and Toxin Production. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(14):8719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148719
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yang, Yijie Zhang, Yousef Sultan, Peng Xiao, Li Yang, Hanyang Lu, and Bangjun Zhang. 2022. "Inhibition Effect of Ionic Liquid [Hmim]Cl on Microcystis Growth and Toxin Production" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 14: 8719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148719
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhang, Y., Sultan, Y., Xiao, P., Yang, L., Lu, H., & Zhang, B. (2022). Inhibition Effect of Ionic Liquid [Hmim]Cl on Microcystis Growth and Toxin Production. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(14), 8719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148719