Contributing Factors to the Burden on Primary Family Caregivers of Stroke Survivors in South Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Sampling
2.2. Grouping by the Level of Caregiver Burden
2.2.1. Patient-Related Factors and the Burden of Care
2.2.2. Caregiver-Related Factors and the Burden of Care
2.3. Statistical Analysis
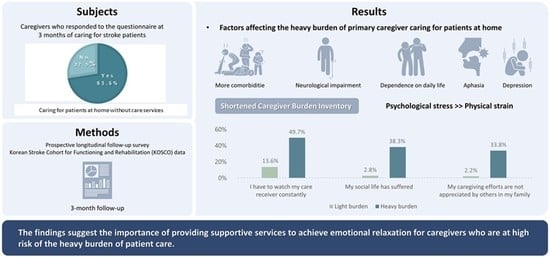
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Patients and Caregivers
3.2. Patient- and Caregiver-Related Factors Associated with the Heavier Burden of Family Caregivers Who Care for the Patients at Home without Care Services
3.3. Difference in Responses Rate for the Shortened CBI Items between the Heavier and Lighter Caregiver Burden Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, K.S.; Bang, O.Y.; Kang, D.W.; Yu, K.H.; Bae, H.J.; Lee, J.S.; Heo, J.H.; Kwon, S.U.; Oh, C.W.; Lee, B.C.; et al. Stroke statistics in Korea: Part I. Epidemiology and risk factors: A report from the korean stroke society and clinical research center for stroke. J. Stroke 2013, 15, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.L.; Roth, G.A.; Naghavi, M.; Parmar, P.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Chugh, S.; Mensah, G.A.; Norrving, B.; Shiue, I.; Ng, M.; et al. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.Y.; Jung, K.H.; Mo, H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, T.J.; Park, J.M.; Oh, M.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, J.T.; et al. Characteristics and management of stroke in Korea: 2014-2018 data from Korean Stroke Registry. Int. J. Stroke 2020, 15, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.H. Changes in Epidemiological Trends and Rehabilitation Usage in Neurological Diseases in Korea: Stroke. Brain Neurorehabil. 2021, 14, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Haley, W.E. Family caregiving for patients with stroke. Review and analysis. Stroke 1999, 30, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, H.; Gubitz, G.; Phillips, S. A systematic review of caregiver burden following stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2009, 4, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Carstensen, K.; Jorgensen, C.R.; Nielsen, C.P. Stroke patients’ and informal carers’ experiences with life after stroke: An overview of qualitative systematic reviews. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Jiang, Y. A Meta-analytic Study of Predictors for Informal Caregiver Burden in Patients with Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 3636–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooth, L.; McKenna, K.; Barnett, A.; Prescott, C.; Murphy, S. Caregiver burden, time spent caring and health status in the first 12 months following stroke. Brain Inj. 2005, 19, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi-Kwon, S.; Kim, H.S.; Kwon, S.U.; Kim, J.S. Factors affecting the burden on caregivers of stroke survivors in South Korea. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Tam, W.; Mao, J.; Lopez, V. Chinese family caregivers of stroke survivors: Determinants of caregiving burden within the first six months. J. Clin. Nurs. 2017, 26, 4558–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.S.; Bartolucci, A.A.; Elliot, T.R.; Giger, J.N. Sociodemographic, physical, and psychosocial characteristics of depressed and non-depressed family caregivers of stroke survivors. Brain Inj. 2000, 14, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugge, C.; Alexander, H.; Hagen, S. Stroke patients’ informal caregivers—Patient, caregiver, and service factors that affect caregiver strain. Stroke 1999, 30, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, M.; Vairale, J.; Gawali, K.; Dalal, P.M. Factors affecting burden on caregivers of stroke survivors: Population-based study in Mumbai (India). Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2012, 15, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.N.; Lee, Y.K.; Lim, J.M.; Ju, B.H.; Bae, H.W. Long-Term Care Survey; Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs: Yeongi-gun, Republic of Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.H.; Sohn, M.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, S.G.; Shin, Y.I.; Oh, G.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Joo, M.C.; Han, E.Y.; et al. Korean Stroke Cohort for functioning and rehabilitation (KOSCO): Study rationale and protocol of a multi-centre prospective cohort study. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valer, D.B.; Aires, M.; Fengler, F.L.; Paskulin, L.M.G. Adaptation and validation of the Caregiver Burden Inventory for use with caregivers of elderly individuals. Rev. Lat.-Am. Enferm. 2015, 23, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.S.; Yu, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, S.; Ko, I.S.; Shin, J.H.; Cho, S.J.; Choi, H.C.; Kim, H.H.; Lee, B.C. Validity and reliability of a korean version of the national institutes of health stroke scale. J. Clin. Neurol. 2012, 8, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fugl-Meyer, A.R.; Jaasko, L.; Leyman, I.; Olsson, S.; Steglind, S. The post-stroke hemiplegic patient. 1. A method for evaluation of physical performance. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1975, 7, 13–31. [Google Scholar]
- Burn, J.P. Reliability of the modified Rankin Scale. Stroke 1992, 23, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesling, M.; Brady, S.; Jensen, M.; Nickell, M.; Statkus, D.; Escobar, N. Dysphagia outcomes in patients with brain tumors undergoing inpatient rehabilitation. Dysphagia 2003, 18, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.-W.; Ho, S.-B.P.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, Y.-m.; Nam, K. Reliability and Validity Analyses of the Korean version of Frenchay Aphasia Screening Test in Brain-Damaged Patients. Korean J. Commun. Disord. 2009, 14, 46–57. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Na, D.L.; Hahn, S. A validity study on the Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J. Korean Neurol. Assoc. 1997, 15, 300–308. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh, J.I.; Yesavage, J.A. Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS): Recent evidence and development of a shorter version. Clin. Gerontol. 1986, 5, 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- McCullagh, E.; Brigstocke, G.; Donaldson, N.; Kalra, L. Determinants of caregiving burden and quality of life in caregivers of stroke patients. Stroke 2005, 36, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blake, H.; Lincoln, N.B.; Clarke, D.D. Caregiver strain in spouses of stroke patients. Clin. Rehabil. 2003, 17, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruithof, W.J.; Post, M.W.M.; van Mierlo, M.L.; van den Bos, G.A.M.; de Man-van Ginkel, J.M.; Visser-Meily, J.M.A. Caregiver burden and emotional problems in partners of stroke patients at two months and one year post-stroke: Determinants and prediction. Patient Educ. Couns. 2016, 99, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W. A Study on Factors of Care Resources Use among the Korean Elderly. Korea Inst. Health Soc. Aff. 2022, 42, 333–350. [Google Scholar]
- Sacco, R.L.; Wolf, P.A.; Kannel, W.B.; McNamara, P.M. Survival and recurrence following stroke. The Framingham study. Stroke 1982, 13, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Davis, P.H.; Leira, E.C.; Chang, K.C.; Bendixen, B.H.; Clarke, W.R.; Woolson, R.F.; Hansen, M.D. Baseline NIH Stroke Scale score strongly predicts outcome after stroke: A report of the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST). Neurology 1999, 53, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneebone, R.M.I.I. The problems faced by informal carers to people with aphasia after stroke: A literature review. Aphasiology 2013, 27, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, M.; Kim, K.; Kim, I.; Cho, N.; Choi, H.; Noh, S. Caregiver’s burden, depression and support as predictors of post-stroke depression: A cross-sectional survey. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2005, 42, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.; Morris, R.G. Psychological Adjustment of the Spouses of Aphasic Stroke Patients. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 1988, 11, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tielemans, N.S.; Visser-Meily, J.M.A.; Schepers, V.P.M.; Passier, P.E.; van de Port, I.G.L.; Vloothuis, J.D.M.; Struyf, P.A.A.; van Heugten, C.M. Effectiveness of the Restore4stroke Self-Management Intervention "Plan Ahead!": A Randomized Controlled Trial in Stroke Patients and Partners. J. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 47, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostwald, S.K.; Godwin, K.M.; Cron, S.G.; Kelley, C.P.; Hersch, G.; Davis, S. Home-based psychoeducational and mailed information programs for stroke-caregiving dyads post-discharge: A randomized trial. Disabil. Rehabil. 2014, 36, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minshall, C.; Castle, D.J.; Thompson, D.R.; Pascoe, M.; Cameron, J.; McCabe, M.; Apputhurai, P.; Knowles, S.R.; Jenkins, Z.; Ski, C.F. A psychosocial intervention for stroke survivors and carers: 12-month outcomes of a randomized controlled trial. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2020, 27, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, H.; Wong, M.S.; Chien, W.T.P. Effectiveness of dyadic psychoeducational intervention for stroke survivors and family caregivers on functional and psychosocial health: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2021, 120, 103969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Variables | Total (n = 1133) |
|---|---|
| Patients | |
| Age (years) [range] | 67.1 ± 11.6 [20–95] |
| Sex [n] | |
| Male | 675 (59.6%) |
| Female | 458 (40.4%) |
| WIC [n] | |
| 1–4 | 1080 (95.3%) |
| ≥5 | 53 (4.7%) |
| Initial NIHSS (score) [range] | 4.4 ± 4.6 [0–34] |
| mRS [n] | |
| 0–1 | 672 (59.3%) |
| 2 | 199 (17.6%) |
| 3–5 | 262 (23.1%) |
| FMA (affected side) [range] | 89.1 ± 21.6 [0–100] |
| Cognitive impairment [n] | |
| Yes | 337 (29.7%) |
| no | 796 (70.3%) |
| Aphasia [n] | |
| yes | 373 (32.9%) |
| no | 760 (67.1%) |
| Types of feeding [n] | |
| No restriction | 937 (82.7%) |
| Tube feeding or oral feeding with restriction | 196 (17.3%) |
| Depression [n] | |
| yes | 253 (22.3%) |
| no | 880 (77.7%) |
| Caregivers | |
| Age (years) [range] | 54.9 ± 13.7 [19–92] |
| Sex [n] | |
| Male | 391 (34.5%) |
| Female | 742 (65.5%) |
| CBI total score [range] | 15.5 ± 13.5 [0–60] |
| Living with the patient [n] | |
| Yes | 821 (72.5%) |
| No | 312 (27.5%) |
| Level of intimacy [n] | |
| good | 927 (81.8%) |
| medium or bad | 206 (18.2%) |
| Receiving long-term care services [n] | |
| Yes | 235 (20.7%) |
| No | 898 (79.3%) |
| Level of education [n] | |
| Low | 374 (33.0%) |
| High | 759 (67.0%) |
| Types of health insurance [n] | |
| health insurance payer | 1049 (92.6%) |
| benefit recipient | 35 (3.1%) |
| other | 49 (4.3%) |
| Availaibility of ancillary caregiver [n] | |
| Yes | 402 (35.5%) |
| no | 731 (64.5%) |
| Variables | Total (n = 719) | Lighter Caregiver Burden Group (n =361) | Heavier Caregiver Burden Group (n = 358) | Unadjusted OR | Adjusted OR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | ||||
| Patients | |||||||
| Age (years) | 65.6 ± 11.5 | 65.2 ± 11.8 | 66.1 ± 11.2 | 1.007 | 0.315 | NA | NA |
| [20–95] | [20–94] | [26–95] | (0.994–1.020) | ||||
| Sex [n] | |||||||
| Male | 469 (65.2%) | 248 (68.7%) | 221 (61.7%) | 1.000 | |||
| Female | 250 (34.8%) | 113 (31.3%) | 137 (38.3%) | 1.361 | 0.050 | NA | NA |
| (1.000–1.853) | |||||||
| WIC [n] | |||||||
| 1–4 | 685 (95.3%) | 354 (98.1%) | 331 (92.5%) | 1.000 | |||
| ≥5 | 34 (4.7%) | 7 (1.9 %) | 27 (7.5 %) | 4.125 | 0.001 | 4.027 | 0.002 |
| (1.870–10.401) | (1.731–0.529) | ||||||
| Initial NIHSS (score) [range] | 3.9 ± 4.1 [0–27] | 3.0 ± 3.2 | 4.8 ± 4.6 | 1.128 | <0.001 | 1.079 | <0.001 |
| [0–27] | (1.082–1.180) | (1.034–1.129) | |||||
| mRS [n] | |||||||
| 0–1 | 492 (68.4%) | 429 (75.3%) | 260 (43.8%) | 1.000 | NA | ||
| 2 | 123 (17.1%) | 86 (15.1%) | 116 (19.6%) | 2.463 | <0.001 | 3.217 | NA < 0.001 |
| 3–5 | 104 (14.5%) | 55 (9.6%) | 217 (36.6%) | (1.647–3.716) | <0.001 | (1.680–6.395) | |
| 7.795 | |||||||
| (4.606–13.832) | |||||||
| FMA (affected side) (score) [range] | 94.3 ± 13.5 | 97.4 ± 7.4 | 91.3 ± 17.1 | 0.955 | <0.001 | NA | NA |
| [8–100] | [39–100] | [8–100] | (0.937–0.970) | ||||
| Cognitive impairment (yes) [n] | 177 (24.6%) | 58 (16.1 %) | 119 (33.2 %) | 2.601 | <0.001 | NA | NA |
| (1.828–3.735) | |||||||
| Aphasia (yes) [n] | 193 (26.8%) | 67 (18.6%) | 126 (35.2%) | 2.383 | <0.001 | 1.562 | 0.024 |
| (1.697–3.370) | (1.059–2.305) | ||||||
| Types of feeding [n] | 1.000 | ||||||
| No restriction | 613 (85.3%) | 313 (86.7%) | 300 (83.8%) | 1.261 | |||
| Tube feeding or oral Feeding with restriction | 106 (14.7%) | 48 (13.3%) | 58 (16.2%) | (0.834–1.913) | 0.273 | NA | NA |
| Depression (yes) [n] | 142 (19.7%) | 34 (9.4%) | 108 (30.2%) | 4.155 | <0.001 | 2.543 | <0.001 |
| (2.760–6.395) | (1.616–4.059) | ||||||
| Caregivers | |||||||
| CBI total score | 14.8 ± 12.8 | 4.47 ± 4.61 | 25.16 ± 9.64 | ||||
| [0–59] | [0–14] | [15–59] | |||||
| Age (years) | 58.5 ± 13.6 | 58.0 ± 14.2 [19–92] | 58.9 ± 13.0 | 1.005 | 0.347 | NA | NA |
| [19–92] | [23–85] | (0.994–1.016) | |||||
| Sex [n] | 1.000 | ||||||
| Male | 245 (34.1%) | 126 (34.9%) | 119 (33.2%) | 1.077 | |||
| Female | 474 (65.9%) | 235 (65.1%) | 239 (66.8%) | (0.791–1.467) | 0.638 | NA | NA |
| Level of intimacy [n] | |||||||
| Good | 575 (80.0%) | 301 (83.4%) | 274 (76.5%) | 1.000 | |||
| Medium or bad | 144 (20.0%) | 60 (16.6%) | 84 (23.5%) | 1.538 (1.065–2.232) | 0.022 | NA | |
| Level of education [n] | |||||||
| Low | 292 (40.6%) | 145 (40.2%) | 147 (41.1%) | 1.000 | |||
| High | 427 (59.4%) | 216 (59.8%) | 211 (58.9%) | 0.964 | 0.807 | NA | NA |
| (0.715–1.298) | |||||||
| Types of health insurance [n] | 338 (93.6%) | ||||||
| Health insurance payer | 662 (92.1%) | 324 (90.5%) | 1.000 | ||||
| Benefit recipient | 22 (3.1%) | 6 (1.7%) | 2.782 | 0.035 | NA | NA | |
| Other | 35 (4.9%) | 17 (4.7%) | 16 (4.5%) | (1.129–7.833) | 0.774 | NA | NA |
| 18 (5.0%) | 1.105(0.557–2.197) | ||||||
| Availability of ancillary caregiver (yes) [n] | >192 (26.7%) | >91(25.2%) | >101 (28.2%) | >1.166 (0.838–1.625) | >0.363 | >NA | >NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, B.M.; Lee, H.H.; Sohn, M.K.; Kim, D.Y.; Shin, Y.-I.; Oh, G.-J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Joo, M.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Song, M.-K.; et al. Contributing Factors to the Burden on Primary Family Caregivers of Stroke Survivors in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032760
Kwon BM, Lee HH, Sohn MK, Kim DY, Shin Y-I, Oh G-J, Lee Y-S, Joo MC, Lee SY, Song M-K, et al. Contributing Factors to the Burden on Primary Family Caregivers of Stroke Survivors in South Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(3):2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032760
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Bo Mi, Hyun Haeng Lee, Min Kyun Sohn, Deog Young Kim, Yong-Il Shin, Gyung-Jae Oh, Yang-Soo Lee, Min Cheol Joo, So Young Lee, Min-Keun Song, and et al. 2023. "Contributing Factors to the Burden on Primary Family Caregivers of Stroke Survivors in South Korea" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 3: 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032760
APA StyleKwon, B. M., Lee, H. H., Sohn, M. K., Kim, D. Y., Shin, Y. -I., Oh, G. -J., Lee, Y. -S., Joo, M. C., Lee, S. Y., Song, M. -K., Han, J., Ahn, J., Chang, W. H., Lee, J., & Kim, Y. -H. (2023). Contributing Factors to the Burden on Primary Family Caregivers of Stroke Survivors in South Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(3), 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032760