Human Amebiasis: Breaking the Paradigm?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Patients and Analyzed Samples
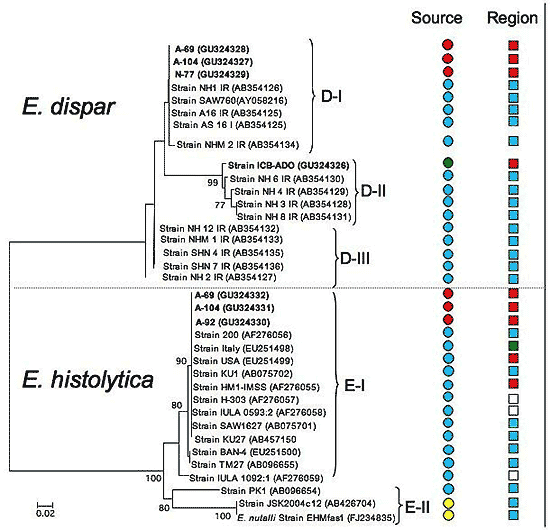
2.2. Species Description and Phylogenetic Reconstructions
2.3. Genetic Diversity
2.4. Hypothetical Considerations to Explain the Presence of E. dispar in Amebic Abscess of the Liver
3. Experimental Section
3.1. DNA Extraction and Molecular Markers (Targets)
3.2. Phylogenetic Reconstruction for Different Molecular Markers
3.3. Population Genetics Analysis
3.4. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Espinosa-Cantellano, M; Martínez-Palomo, A. Pathogenesis of intestinal amebiasis: from molecules to disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev 2000, 13, 318–331. [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt, PG; Jackson, TFHG; Wiffen, SR; Bhojnani, R. Bological evidence of genetic exchange in Entamoeba histolytica. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg 1988, 82, 862–867. [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt, PG. Zymodemes expressing possible genetic exchange in Entamoeba histolytica. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg 1985, 79, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Amoebiasis. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec 1997, 72, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, JA. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of the morbidity and mortality. Rev. Infect. Dis 1986, 8, 228–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, IK; Clark, CG; Petri, WA, Jr. Molecular epidemiology of amebiasis. Infect. Genet. Evol 2008, 8, 698–707. [Google Scholar]
- Ximenéz, C; Morán, P; Rojas, L; Valadez, A; Gómez, A. Reassessment of the epidemiology of amebiasis: state of the art. Infect. Genet. Evol 2009, 9, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Gosh, S; Frisardi, M; Ramírez-Avila, L; Descoteaux, S; Sturm-Ramírez, K; Newton-Sanchez, OA; Santos-Preciado, JI; Ganguly, C; Lohia, A; Reed, S; Samuelson, J. Molecular epidemiology of Entamoeba spp. Evidence of a bottleneck (demographic sweep) and transcontinental spread of diploid parasites. J. Clin. Microbiol 2000, 38, 3815–3821. [Google Scholar]
- Fotedar, R; Stark, D; Beebe, N; Marriott, D; Ellis, J; Harkness, J. Laboratory diagnostic techniques for Entamoeba species. Clin. Microbiol. Rev 2007, 20, 511–532. [Google Scholar]
- Tawari, B; Ali, IKM; Scott, C; Quail, MA; Berriman, M; Hall, N; Clark, CG. Patterns of evolution in the unique tRNA gene arrays of the genus Entamoeba. Mol. Biol. Evol 2008, 25, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki, T; Kobayashi, S; Takeuchi, T; Haghighi, A. Diversity of clinical isolates of Entamoeba histolytica in Japan. Arch. Med. Res 2006, 37, 277–279. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, F; García, G; Valadez, A; Morán, P; González, E; Gómez, A; Melendro, EI; Valenzuela, O; Ximénez, C. E. dispar strain: Analysis of polimorphism as a tool for study of geographic distribution. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol 2005, 141, 175–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, KI; Solaymani-Mohammady, S; Akhter, J; Roy, S; Gorrini, A; Parker, S; Haque, R; Petri, WA, Jr; Clark, G. Tissue invasion by Entamoeba histolytica: evidence of genetic selection and/or DNA reorganization events in organ tropism. PloS. Negl. Trop. Dis 2008, 2, e219. [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela, O; Morán, P; Ramos, F; Cardoza, JI; García, G; Valadez, A; Rojas, L; Garibay, A; González, E; Ximénez, C. Short report: Two different chitinase genotypes in a patient with an amebic liver abscess: a case report. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg 2009, 80, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jetter, AB; Walderich, B; Britten, D; Mete, O; Goral, V; Burchard, GD; Ackers, J. An epidemiological study of Entamoeba histolytica and E. dispar infection in eastern Turkey using a colorimetric polymerase chain reaction. Arch. Med. Res 1997, 28, 319–321. [Google Scholar]
- Parija, SC; Khainar, K. Entamoeba moshkovskii and Entamoeba dispar-associated infections in Pondicherry, India. J. Health Pop. Nutr 2005, 23, 292–295. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, OA; Gomes, AM; Rocha, AO; Silva, FE. Pathogenicity of Entamoeba dispar under xenic and monoxigenic cultivation compared to a virulent E. histolytica. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. S. Paulo 2006, 48, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Chadee, KJ; Smith, M; Meerovitch, E. Entamoeba histolytica: electrophoretic isoenzyme patterns of strains and their virulence in the cecum of gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus). Am. J. Top. Med. Hyg 1985, 34, 870–878. [Google Scholar]
- Vohra, H; Bhatti, HS; Ganguly, NK; Mahajan, RC. Virulence of pathogenic and non pathogenic zymodemes of Entamoeba histolytica (Indian strains) in guinea pigs. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg 1989, 83, 648–650. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza-Cantellano, M; Castañón-Gutiérrez, G; Martínez-Palomo, A. In vivo pathogenesis of Entamoeba dispar. Arch. Med. Res 1997, 28, 204–206. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa-Cantellano, M; Gonzáles-Robles, A; Chávez, B; Castañón, G; Argüello, C; Lázaro-Haller, A; Martínez-Palomo. Entamoeba dispar: ultrastructure, surface properties, and cythopatic effect. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol 1998, 45, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Olivos-García, A; Saavedra, E; Ramos-Martínez, E; Nequiz, M; Pérez-Tamayo, R. Molecular nature of virulence in Entamoeba histolytica. Infect. Genet. Evo 2009, 9, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Morán, P; Gómez, A; Valadez, A; Ramos, F; González, E; García, G; Limón, A; Valenzuela, O; Ramiro, M; Hidalgo, H; Melendro, E; Ximénez, C. Amebic and pyogenic liver abscess: importance of differential diagnosis in endemic areas of amebiasis. International Proceedings, 5th European Congress on Tropical Medicine and Internatinal Health Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands; 2007; pp. 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, J; Kobayashi, S; Murata, R; Tajima, H; Hashizaki, F; Yanagawa, Y; Takeuchi, T. A survey of amoebic infections and differentiation of an Entamoeba histolytica-like variant (JSK2004) in nonhuman primates by a multiplex polymerase chain reaction. J. Zoo Wildl. Med 2008, 39, 370–379. [Google Scholar]
- Mojarad, EN; Haghighi, A; Kazemi, B; Nejad, MR; Abadi, A; Zali, MR. High genetic diversity among Iranian Entamoeba dispar isolates based on the noncoding short tandem repeat locus D-A. Acta Trop 2009, 111, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zaki, M; Clark, CG. Isolation and characterization of polymorphic DNA from Entamoeba histolytica. J. Clin. Microbiol 2001, 39, 897–905. [Google Scholar]
- Shibayama, M; Dolabella, SS; Silva, EF; Tsutsumi, V. A Brazilian species of Entamoeba dispar (ADO) produces ameobic liver abscess in hamsters. Ann. Hepatol 2007, 6, 117–118. [Google Scholar]
- Bracha, R; Kobiler, D; Mirelman, D. Attachment and ingestion of bacteria by trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica. Infect. Immun 1982, 36, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman, D. Amoeba-bacterium relationship in amoebiasis. Microbiol. Rev 1987, 51, 272–784. [Google Scholar]
- Seydel, KE; Li, E; Zwanson, PE; Stanley, SL, Jr. Human intestinal epithelial cells-produce pro-inflammatory cytokines in response to infection in SCID mouse-human intestinal xenograph model of amoebiasis. Infect. Immun 1997, 65, 1631–1939. [Google Scholar]
- Hacker, J; Kaper, JB. Pathogenicity island and the evolution of microbes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol 2000, 54, 641–679. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrindt, U; Hochhut, B; Hentschel, U; Hacker, J. Genomic islands in pathogenic and environmental microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2004, 2, 414–424. [Google Scholar]
- Seydel, KB; Li, E; Zhang, Z; Stanley, SL. Epithelial cell-initiated inflammation plays a crucial ole in early tissue damage in ameobic infection of human intestine. Gastroenterology 1998, 115, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar]
- van der Giezen, M; Cox, S; Tovar, J. The iron-sulfur cluster assembly gene iscS amd iscU of Entamoeba histolytica were acquired by horizontal gene transfer. BMC Evol. Biol 2004, 4, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, SL, Jr. The Entamoeba histolytica genome: something old, something new, something borrowed and sex too? Trends Parasitol 2005, 21, 451–453. [Google Scholar]
- Loftus, B; Anderson, I; Davies, R; Alsmark, UC; Samuelson, J; Amadeo, P; Roncaglia, P; Berriman, M; Hirt, RP; Mann, BJ; Nozaki, T; Suh, B; Pop, M; Duchene, M; Ackers, J; Tannich, E; Leippe, M; Hofer, M; Bruchhaus, I; Willhoeft, U; Bhattacharya, A; Chillingworth, T; Churcher, C; Hance, Z; Harris, B; Harris, D; Jagels, K; Moule, S; Mungall, K; Ormond, D; Squares, R; Whitehead, S; Quail, MA; Rabbinowitsch, E; Norbertczak, H; Price, C; Wang, Z; Guillén, N; Gilchrist, C; Stroup, SE; Bhattacharya, S; Lohia, A; Foster, PG; Sicheritz-Ponten, T; Weber, C; Singh, U; Mukherjee, C; El-Sayed, NM; Petri, WA, Jr; Clark, CG; Embley, TM; Barrell, B; Fraser, CM; Hall, N. The genome of the protist parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Nature 2005, 433, 865–868. [Google Scholar]
- Galván-Moroyoqui, JM; Domínguez-Robles, MC; Franco, E; Meza, I. The interplay between Entamoeba and enteropathogenic bacteria modulates epithelial cell damage. PLoS. Negl. Trop. Dis 2008, 23, e266. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D; Kabir, M; Mondal, D; Ali, IK; Petri, WA, Jr; Haque, R. Real-time-PCR assay for diagnosis of Entamoeba histolytica infection. J. Clin. Microbiol 2005, 43, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, TA. BioEdit: user-friendly biological sequence aligment editos and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleotic Acids Symp Ser 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, JD; Gibson, TJ; Plewniak, F; Jeanmougin, F; Higgins, DG. The ClustalX Windows interface: flexile strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quantity analysis tools. Nucleic Acid Res 1997, 24, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K; Dudley, J; Nei, M; Kumar, S. MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Rozas, J; Sanchez-DelBarrio, JC; Messenguer, X; Rozas, R. DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analysis by the coalescent and method. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2496–2497. [Google Scholar]



| Sample Code | CD1 | Gender | Age | ELISA2 | PCR-MD3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-69 | MLA | F | 57 | 0.63 | E.h, E.d |
| A-92 | ALA | F | 39 | 1.1 | E.h, E.d |
| A-104 | ALA | M | 40 | 1.1 | E.h, E.d |
| N-49 | PLA | F | 52 | 0.14 | E.d |
| N-61 | PLA | F | 38 | 0.47 | E.d |
| N-77 | PLA | M | 55 | 0.27 | E.d |
| Group1 | No. Sequences | No. Haplotypes | Ss2 | π | θ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. dispar ALA | 4 | 3 | 33 | 0.065 | 0.071 |
| E. dispar total | 19 | 15 | 53 | 0.081 | 0.064 |
| E. histolytica ALA | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| E. histolytica total | 17 | 7 | 49 | 0.034 | 0.069 |
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ximénez, C.; Cerritos, R.; Rojas, L.; Dolabella, S.; Morán, P.; Shibayama, M.; González, E.; Valadez, A.; Hernández, E.; Valenzuela, O.; et al. Human Amebiasis: Breaking the Paradigm? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1105-1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7031105
Ximénez C, Cerritos R, Rojas L, Dolabella S, Morán P, Shibayama M, González E, Valadez A, Hernández E, Valenzuela O, et al. Human Amebiasis: Breaking the Paradigm? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2010; 7(3):1105-1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7031105
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiménez, Cecilia, Rene Cerritos, Liliana Rojas, Silvio Dolabella, Patricia Morán, Mineko Shibayama, Enrique González, Alicia Valadez, Eric Hernández, Olivia Valenzuela, and et al. 2010. "Human Amebiasis: Breaking the Paradigm?" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 7, no. 3: 1105-1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7031105
APA StyleXiménez, C., Cerritos, R., Rojas, L., Dolabella, S., Morán, P., Shibayama, M., González, E., Valadez, A., Hernández, E., Valenzuela, O., Limón, A., Partida, O., & Silva, E. F. (2010). Human Amebiasis: Breaking the Paradigm? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(3), 1105-1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7031105