The Case for Visual Analytics of Arsenic Concentrations in Foods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Metabolism of Arsenic in the Human Body
3. Arsenic Concentrations in Various Foods
4. Factors Affecting Arsenic Uptake in Plants
5. Visual Analytics
5.1. Goal of Visual Analytics
5.2. “Insight” in Visual Analytics
5.3. Visual Analytics as an Integrated Approach
5.4. Challenges in Visual Analytics
6. Benefits of Visual Analytics for Comparative Assessment of Arsenic Concentration in Foods
Acknowledgments
References
- Al Rmalli, SW; Haris, PI; Harrington, CF; Ayub, M. A Survey of Arsenic in Foodstuffs on Sale in the United Kingdom and Imported From Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ 2005, 337, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E; Juhasz, AL; Weber, J. Arsenic Uptake and Speciation in Vegetables Grown Under Greenhouse Conditions. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Halim, MA; Majumder, RK; Nessa, SA; Hiroshiro, Y; Uddin, MJ; Shimada, J; Jinno, K. Hydrogeochemistry and Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater in the Ganges Delta Plain, Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater 2009, 164, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnaike, RN. Acute and Chronic Arsenic Toxicity. Postgrad. Med. J 2003, 79, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y; Marshall, G; Ferreccio, C; Steinmaus, C; Selvin, S; Liaw, J; Bates, MN; Smith, AH. Acute Myocardial Infarction Mortality in Comparison With Lung and Bladder Cancer Mortality in Arsenic-Exposed Region II of Chile from 1950 to 2000. Am. J. Epidemiol 2007, 166, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Keim, D; Mansmann, F; Schneidewind, J; Thomas, J; Ziegler, H. Visual Analytics: Scope and Challenges. In Visual Data Mining: Theory, Techniques and Tools for Visual Analytics; Simoff, SJ, Böhlen, MH, Mazeika, A, Eds.; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 76–90. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J; Cook, K. Illuminating the Path: The Research and Development Agenda for Visual Analytics; National Visualization and Analytics Ctr: Richmond, Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Borak, J; Hosgood, HD. Seafood Arsenic: Implications for Human Risk Assessment. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol 2007, 47, 204–212. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J; Zartarian, V; Wang, SW; Liu, SV; Georgopoulos, P. Probabilistic Modeling of Dietary Arsenic Exposure and Dose and Evaluation with 2003–2004 NHANES Data. Environ. Health Perspect 2009, 118, 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Uneyama, C; Toda, M; Yamamoto, M; Morikawa, K. Arsenic in Various Foods: Cumulative Data. Food Addit. Contam 2007, 24, 447–534. [Google Scholar]
- Drobna, Z; Walton, FS; Paul, DS; Xing, W; Thomas, DJ; Styblo, M. Metabolism of Arsenic in Human Liver: the Role of Membrane Transporters. Arch. Toxicol 2010, 84, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, DJ. Molecular Processes in Cellular Arsenic Metabolism. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 2007, 222, 365–373. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, DJ; Li, J; Waters, SB; Xing, W; Adair, BM; Drobna, Z; Devesa, V; Styblo, M. Arsenic (+3 Oxidation State) Methyltransferase and the Methylation of Arsenicals. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood.) 2007, 232, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, MF. Arsenic Methylation, Oxidative Stress and Cancer--Is There a Link? J. Natl. Cancer Inst 2009, 101, 1660–1661. [Google Scholar]
- Gamble, MV; Liu, X; Ahsan, H; Pilsner, JR; Ilievski, V; Slavkovich, V; Parvez, F; Chen, Y; Levy, D; Factor-Litvak, P; Graziano, JH. Folate and Arsenic Metabolism: a Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Folic Acid-Supplementation Trial in Bangladesh. Am. J. Clin. Nutr 2006, 84, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, MF. Biomarkers of Exposure: a Case Study With Inorganic Arsenic. Environ. Health Perspect 2006, 114, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Dopp, E; von Recklinghausen, U; Diaz-Bone, R; Hirner, AV; Rettenmeier, AW. Cellular Uptake, Subcellular Distribution and Toxicity of Arsenic Compounds in Methylating and Non-Methylating Cells. Environ Res 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, S; Kobayashi, Y; Cui, X; Kanno, S; Hayakawa, T; Shraim, A. The Accumulation and Toxicity of Methylated Arsenicals in Endothelial Cells: Important Roles of Thiol Compounds. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 2004, 198, 458–467. [Google Scholar]
- Benramdane, L; Accominotti, M; Fanton, L; Malicier, D; Vallon, JJ. Arsenic Speciation in Human Organs Following Fatal Arsenic Trioxide Poisoning—a Case Report. Clin. Chem 1999, 45, 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, NI; Bruce, D; Naidu, R; Owens, G. Implementation of Food Frequency Questionnaire for the Assessment of Total Dietary Arsenic Intake in Bangladesh: Part B, Preliminary Findings. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 221–238. [Google Scholar]
- Das, HK; Mitra, AK; Sengupta, PK; Hossain, A; Islam, F; Rabbani, GH. Arsenic Concentrations in Rice, Vegetables, and Fish in Bangladesh: a Preliminary Study. Environ. Int 2004, 30, 383–387. [Google Scholar]
- Jahiruddin, M; Harada, H; Tanaka, T; Islam, MR. Status of Trace Elements in Agricultural Soils of Bangladesh and Relationship With Soil Properties. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr 2000, 46, 963–968. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, MM; Owens, G; Naidu, R. Arsenic Levels in Rice Grain and Assessment of Daily Dietary Intake of Arsenic From Rice in Arsenic-Contaminated Regions of Bangladesh—Implications to Groundwater Irrigation. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Roychowdhury, T; Uchino, T; Tokunaga, H; Ando, M. Survey of Arsenic in Food Composites From an Arsenic-Affected Area of West Bengal, India. Food Chem. Toxicol 2002, 40, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar]
- Marin, A; Masscheleyn, P; Patrick, W. The Influence of Chemical Form and Concentration of Arsenic on Rice Growth and Tissue Arsenic Concentration. Plant Soil 1992, 139, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W-J; Zhu, Y-G; Smith, FA; Smith, SE. Do Phosphorus Nutrition and Iron Plaque Alter Arsenate (As) Uptake by Rice Seedlings in Hydroponic Culture? New Phytol 2004, 162, 481–488. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, GP; Sands, K; Waters, M; Wixson, BG; Dorward-Kind, E. Accumulation of Heavy Metals by Vegetables Grown in Mine Wastes. Environ. Toxicol. Chem 2000, 19, 600–607. [Google Scholar]
- Queirolo, F; Stegen, S; Restovic, M; Paz, M; Ostapczuk, P; Schwuger, MJ; Munoz, L. Total Arsenic, Lead, and Cadmium Levels in Vegetables Cultivated at the Andean Villages of Northern Chile. Sci. Total Environ 2000, 255, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Almela, C; Algora, S; Benito, V; Clemente, MJ; Devesa, V; Suner, MA; Velez, D; Montoro, R. Heavy Metal, Total Arsenic, and Inorganic Arsenic Contents of Algae Food Products. J. Agric. Food Chem 2002, 50, 918–923. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, J; Gochfeld, M. Heavy Metals in Commercial Fish in New Jersey. Environ. Res 2005, 99, 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Brammer, H; Ravenscroft, P. Arsenic in Groundwater: a Threat to Sustainable Agriculture in South and South-East Asia. Environ. Int 2009, 35, 647–654. [Google Scholar]
- Mahimairaja, S; Bolan, NS; Adriano, DC; Robinson, B. Arsenic Contamination and Its Risk Management in Complex Environmental Settings. Adv. Agron 2005, 86, 1–82. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, XY; McGrath, SP; Meharg, AA; Zhao, FJ. Growing Rice Aerobically Markedly Decreases Arsenic Accumulation. Environ. Sci. Technol 2008, 42, 5574–5579. [Google Scholar]
- Chabot, C. Demystifying Visual Analytics. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl 2009, 29, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Keim, DA; Mansmann, F; Schneidewind, J; Ziegler, H. Challenges in Visual Data Analysis. Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference Information Visualization, London, UK, July 2006; pp. 9–16.
- Robinson, AC; Chen, J; Lengerich, EJ; Meyer, HG; Maceachren, AM. Combining Usability Techniques to Design Geovisualization Tools for Epidemiology. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci 2005, 32, 243–255. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J; Roth, RE; Naito, AT; Lengerich, EJ; Maceachren, AM. Geovisual Analytics to Enhance Spatial Scan Statistic Interpretation: an Analysis of U.S. Cervical Cancer Mortality. Int. J. Health Geogr 2008, 7, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Bhowmick, T; Griffin, AL; Maceachren, AM; Kluhsman, BC; Lengerich, EJ. Informing Geospatial Toolset Design: Understanding the Process of Cancer Data Exploration and Analysis. Health Place 2008, 14, 576–607. [Google Scholar]
- Maciejewski, R; Tyner, B; Yun, J; Cheng, Z; Nehme, RRV; Ebert, DS; Cleveland, WS; Ouzzani, M; Grannis, SJ; Glickman, LT. LAHVA: Linked Animal-Human Health Visual Analytics. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Visual Analytics Science and Technology, Sacaramento, CA, USA, November 2007; pp. 27–34.
- Maciejewski, R; Rudolph, S; Hafen, R; Abusalah, A; Yakout, M; Ouzzani, M; Cleveland, WS; Grannis, SJ; Wade, M; Ebert, DS. Understanding syndromic hotspots—a visual analytics approach. Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Visual Analytics Science and Technology, Columbus, OH, USA; 2008; pp. 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Maciejewski, R; Hafen, R; Rudolph, S; Tebbetts, G; Cleveland, WS; Ebert, DS; Grannis, SJ. Generating Synthetic Syndromic-Surveillance Data for Evaluating Visual-Analytics Techniques. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl 2009, 29, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Plaisant, C; Grinstein, G; Scholtz, J; Whiting, M; O’Connell, T; Laskowski, S; Chien, L; Tat, A; Wright, W; Gorg, C; Zhicheng, L; Parekh, N; Singhal, K; Stasko, J. Evaluating Visual Analytics at the 2007 VAST Symposium Contest. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl 2008, 28, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Saraiya, P; North, C; Lam, V; Duca, KA. An Insight-Based Longitudinal Study of Visual Analytics. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph 2006, 12, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, J; Kang, Y; Satsko, J; Jacko, JA. Understanding and characterizing insights: how do people gain insights using information visualization? Proceedings of the 2008 conference on BEyond time and errors: novel evaLuation methods for Information Visualization, Florence, Italy; 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer, J. The Eureka Hunt: Why Do Good Ideas Come to Us When They Do? The New Yorker 2008, 2, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, XQ; Luo, J; Wu, JH; Luo, YJ. “Aha!” Effects in a Guessing Riddle Task: an Event-Related Potential Study. Hum. Brain Mapp 2004, 22, 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, EM; Jung-Beeman, M; Fleck, J; Kounios, J. New Approaches to Demystifying Insight. Trends Cogn. Sci 2005, 9, 322–328. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, R; Ziemkiewicz, C; Green, TM; Ribarsky, W. Defining Insight for Visual Analytics. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl 2009, 29, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, JJ; Cook, KAA. Visual Analytics Agenda. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl 2006, 26, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Eick, SG; Karr, AF. Visual Scalability. J. Comput. Graph. Stat 2002, 11, 22–43. [Google Scholar]
- Aragon, CR; Poon, SS; Aldering, GS; Thomas, RC; Quimby, R. Using visual analytics to maintain situation awareness in astrophysics. Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Visual Analytics Science and Technology, Columbus, OH, USA; 2008; pp. 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Savikhin, A; Maciejewski, R; Ebert, DS. Applied visual analytics for economic decision-making. Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Visual Analytics Science and Technology, Columbus, OH, USA; 2008; pp. 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Stasko, J. Visualization for information exploration and analysis. Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Visual Languages and Human-Centric Computing, Germany; 2008; pp. 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Egan, SK; Bolger, PM; Carrington, CD. Update of US FDA‘s Total Diet Study Food List and Diets. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol 2007, 17, 573–582. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, BM; Vannoort, RW; Haslemore, RM. Dietary Exposure and Trends of Exposure to Nutrient Elements Iodine, Iron, Selenium and Sodium From the 2003–4 New Zealand Total Diet Survey. Br. J. Nutr 2008, 99, 614–625. [Google Scholar]



| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Absorption | Gastrointestinal tract and lungs |
| Distribution | Liver, kidney, lung, spleen, aorta, and skin |
| Excretion | Urine at rates as high as 80% |
| Symptoms of Acute Inorganic Arsenic | Nausea, anorexia, vomiting, epigastric and abdominal pain, and diarrhea. |
| Poisoning in human | Dermatitis (exfoliative erythroderma), muscle cramps, cardiac abnormalities, hepatotoxicity, bone marrow suppression and hematologic abnormalities (anemia), vascular lesions, and peripheral neuropathy (motor dysfunction, paresthesia). |
| Effect of Severe Exposures | Acute encephalopathy, congestive heart failure, stupor, convulsions, paralysis, coma, and death. |
| General symptoms of chronic arsenic poisoning in human | Weakness, general debility and lassitude, loss of appetite and energy, loss of hair, hoarseness of voice, loss of weight, and mental disorders. |
| Primary target organs | Skin (hyperpigmentation and hyperkeratosis), nervous system (peripheral neuropathy), and vascular system. |
| Other symptoms of chronic arsenic poisoning in human | Anemia, cancer, leukopenia, hepatomegaly, and portal hypertension. |
| Focus Area | Function to Users |
|---|---|
| Analytical reasoning | Obtain deep insights into the data at hand that will directly support assessment, planning and decision making |
| Visual representations and interaction | See, explore, and understand large amounts of information at once |
| Data representations and transformations | Convert data which may previously have appeared in all types of conflicting and dynamic into ways that support its visualization and analysis |
| Support production, presentation and dissemination of results of analysis | Communicate the information in the appropriate context to a variety of audience |
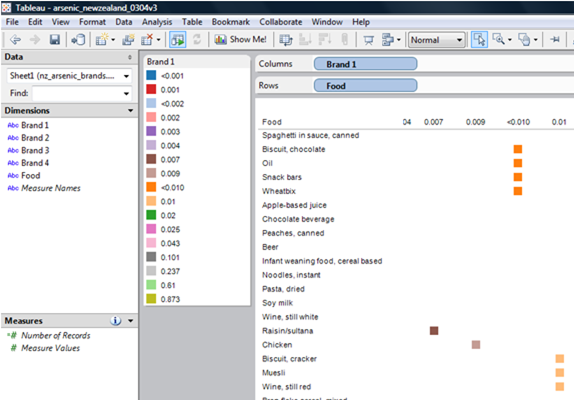
| Food | Brand 1 | Brand 2 | Brand 3 | Brand 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple-based juice | 0.001 | < 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.003 |
| Apricot, canned | < 0.002 | < 0.002 | < 0.002 | < 0.002 |
| Beer | 0.003 | < 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Biscuit, chocolate | < 0.010 | < 0.010 | < 0.010 | < 0.010 |
| Biscuit, cracker | 0.010 | 0.020 | 0.020 | < 0.010 |
| Bran flake cereal, mixed | 0.020 | < 0.010 | 0.020 | < 0.010 |
| Caffeinated beverage | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Chicken | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.010 |
| Chocolate beverage | 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Fish fingers | 0.873 | 0.727 | 0.485 | 0.790 |
| Fish, canned | 0.610 | 0.572 | 1.090 | 0.866 |
| Infant weaning food, cereal based | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.011 | 0.012 |
| Infant weaning food, custard/fruit dish | 0.043 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.011 |
| Infant weaning food, savoury | 0.025 | < 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.007 |
| Muesli | 0.010 | < 0.010 | 0.010 | < 0.010 |
| Noodles, instant | 0.003 | 0.005 | < 0.002 | < 0.002 |
| Oats, rolled | < 0.002 | 0.004 | < 0.002 | < 0.002 |
| Oil | < 0.010 | < 0.010 | 0.020 | < 0.010 |
| Pasta, dried | 0.003 | < 0.002 | < 0.002 | 0.003 |
| Peaches, canned | 0.002 | < 0.002 | < 0.002 | < 0.002 |
| Prunes | < 0.002 | < 0.002 | < 0.002 | 0.003 |
| Raisin/sultana | 0.007 | 0.017 | 0.008 | 0.021 |
| Rice, white | 0.101 | 0.039 | 0.031 | 0.050 |
| Snack bars | < 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.020 | < 0.010 |
| Soy milk | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.094 |
| Spaghetti in sauce, canned | < 0.002 | < 0.002 | 0.032 | < 0.002 |
| Wheatbix | < 0.010 | < 0.010 | 0.020 | < 0.010 |
| Wine, still red | 0.010 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.004 |
| Wine, still white | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.009 |
| Yeast extract | 0.237 | 0.148 |
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Johnson, M.O.; Cohly, H.H.P.; Isokpehi, R.D.; Awofolu, O.R. The Case for Visual Analytics of Arsenic Concentrations in Foods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1970-1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7051970
Johnson MO, Cohly HHP, Isokpehi RD, Awofolu OR. The Case for Visual Analytics of Arsenic Concentrations in Foods. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2010; 7(5):1970-1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7051970
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohnson, Matilda O., Hari H.P. Cohly, Raphael D. Isokpehi, and Omotayo R. Awofolu. 2010. "The Case for Visual Analytics of Arsenic Concentrations in Foods" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 7, no. 5: 1970-1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7051970
APA StyleJohnson, M. O., Cohly, H. H. P., Isokpehi, R. D., & Awofolu, O. R. (2010). The Case for Visual Analytics of Arsenic Concentrations in Foods. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(5), 1970-1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7051970