Protection against Microglia Senescence by the Dietary Supplement Dekosilhue® in BV2 Cells: A New Perspective for Obesity and Related Complications
Abstract
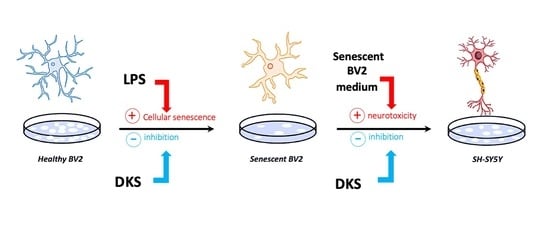
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Cultures
2.3. Senescent Microglia Model
2.4. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay
2.5. Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci Analysis (SAHF)
2.6. ß-Galactosidase Activity Assay
2.7. Neuroprotection Model
2.8. Western Blot (WB)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of DKS on Microglial Senescent Cells
3.2. Effect on ß-Galactosidase Activity and Expression
3.3. Reduction of SAHF Formation
3.4. DKS Reduced SASP Inflammatory Markers
3.5. Neuroprotective Activity of DKS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez, A.; Apovian, C.M. Updates on obesity pharmacotherapy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1411, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghar, A.; Sheikh, N. Role of immune cells in obesity induced low grade inflammation and insulin resistance. Cell. Immunol. 2017, 315, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindhu, S.; Thomas, R.; Kochumon, S.; Wilson, A.; Abu-Farha, M.; Bennakhi, A.; Al-Mulla, F.; Ahmad, R. Increased adipose tissue expression of interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-5 in obesity: Association with metabolic inflammation. Cells 2019, 8, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Saltiel, A.R. Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Foundations of Immunometabolism and Implications for Metabolic Health and Disease. Immunity 2017, 47, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, R. Neuroimmune interactions: From the brain to the immune system and vice versa. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 477–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivest, S. Regulation of innate immune responses in the brain. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.S.P.; Liu, C.S.; Rau, A.; Lanctôt, K.L.; Köhler, C.A.; Pakosh, M.; Carvalho, A.F.; Herrmann, N. Peripheral inflammatory markers in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 175 studies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemot-Legris, O.; Muccioli, G.G. Obesity-Induced Neuroinflammation: Beyond the Hypothalamus. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulton, S.; Décarie-Spain, L.; Fioramonti, X.; Guiard, B.; Nakajima, S. The menace of obesity to depression and anxiety prevalence. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 33, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Cho, M.H.; Shim, W.H.; Kim, J.K.; Jeon, E.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Yoon, S.-Y. Deficient autophagy in microglia impairs synaptic pruning and causes social behavioral defects. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexaki, V.I. The impact of obesity on microglial function: Immune, metabolic and endocrine perspectives. Cells 2021, 10, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhramanyam, C.S.; Wang, C.; Hu, Q.; Dheen, S.T. Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 94, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojiljkovic, M.R.; Ain, Q.; Bondeva, T.; Heller, R.; Schmeer, C.; Witte, O.W. Phenotypic and functional differences between senescent and aged murine microglia. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 74, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.K.; Tchkonia, T.; Kirkland, J.L.; Jensen, M.D. Senescence in obesity. In Cellular Senescence in Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 289–308. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, A.K.; Xu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Weivoda, M.M.; Hachfeld, C.M.; Prata, L.G.; Dijk, T.H.; Verkade, E.; Casaclang-Verzosa, G.; et al. Targeting senescent cells alleviates obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, A.; Flores, R.R.; Camell, C.D.; Bernlohr, D.A.; Robbins, P.D.; Niedernhofer, L.J. Cellular Senescence in Obesity and Associated Complications: A New Therapeutic Target. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2022, 22, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deursen, J.M. The role of senescent cells in ageing. Nature 2014, 509, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bano, D.; Ehninger, D. Cellular senescence in vivo: From cells to tissues to pathologies. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 190, 111308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagoumtzi, S.M.; Chondrogianni, N. Senolytics and senomorphics: Natural and synthetic therapeutics in the treatment of aging and chronic diseases. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 171, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, G.; Unnikrishnan, M.K. Multi-target drugs to address multiple checkpoints in complex inflammatory pathologies: Evolutionary cues for novel “first-in-class” anti-inflammatory drug candidates: A reviewer’s perspective. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, H.; Ulrich-Merzenich, G. Synergy research: Approaching a new generation of phytopharmaceuticals. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgonetti, V.; Cenci, L.; Galeotti, N. Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effect of the Anti-Obesity Dietary Supplement Dekosilhue® in an In Vitro Model of Neuroinflammation. Nutraceuticals 2022, 2, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgonetti, V.; Galeotti, N. Rosmarinic Acid Reduces Microglia Senescence: A Novel Therapeutic Approach for the Management of Neuropathic Pain Symptoms. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.Y.H.; Liao, W.C.; Chang, H.M. Comparison of antitumor activity of vitamins K1, K2 and K3 on human tumor cells by two (MTT and SRB) cell viability assays. Life Sci. 1993, 52, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgonetti, V.; Governa, P.; Biagi, M.; Pellati, F.; Galeotti, N. Zingiber officinale Roscoe rhizome extract alleviates neuropathic pain by inhibiting neuroinflammation in mice. Phytomedicine 2020, 78, 153307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.Y.; McNeely, T.L.; Baker, D.J. Untangling senescent and damage-associated microglia in the aging and diseased brain. FEBS J. 2021, 290, 1326–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, K.M.; Zhang, R. Detection of senescence-associated heterochromatin foci (SAHF). Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 965, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, D.G.A.; Stolzing, A. Cellular senescence: Immunosurveillance and future immunotherapy. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 43, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Segura, A.; de Jong, T.V.; Melov, S.; Guryev, V.; Campisi, J.; DeMaria, M. Unmasking Transcriptional Heterogeneity in Senescent Cells. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 2652–2660.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohanna, M.; Giuliano, S.; Bonet, C.; Imbert, V.; Hofman, V.; Zangari, J.; Bille, K.; Robert, C.; Paillerets, B.B.-D.; Hofman, P.; et al. Senescent cells develop a parp-1 and nuclear factor-κB-associated secretome (PNAS). Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Campisi, J. Chronic inflammation (Inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahima, R.S. Connecting obesity, aging and diabetes. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 996–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Palmer, A.K.; Ding, H.; Weivoda, M.M.; Pirtskhalava, T.; A White, T.; Sepe, A.; O Johnson, K.; Stout, M.B.; Giorgadze, N.; et al. Targeting senescent cells enhances adipogenesis and metabolic function in old age. Elife 2015, 4, e12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamino, T.; Orimo, M.; Shimizu, I.; Kunieda, T.; Yokoyama, M.; Ito, T.; Nojima, A.; Nabetani, A.; Oike, Y.; Matsubara, H.; et al. A crucial role for adipose tissue p53 in the regulation of insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, M.J.; Miller, J.D.; LeBrasseur, N.K. Cellular senescence: Implications for metabolic disease. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 455, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Chen, L.; Mo, H.; Shastri, A.; Su, R.; Bapat, P.; Kwun, I.; Shen, C.-L. Novel insights of dietary polyphenols and obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Segura, A.; Nehme, J.; Demaria, M. Hallmarks of Cellular Senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 436–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cáceres, C.; Balland, E.; Prevot, V.; Luquet, S.; Woods, S.C.; Koch, M.; Horvath, T.L.; Yi, C.-X.; Chowen, J.A.; Verkhratsky, A.; et al. Role of astrocytes, microglia, and tanycytes in brain control of systemic metabolism. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, S.N.; Miller, A.A.; Sominsky, L.; Spencer, S.J. Microglial regulation of satiety and cognition. J. Neuroendocr. 2020, 32, e12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, A.; Botta, A.; Shi, S.S.W.; Paus, T.; Pausova, Z. Obesity-Related Neuroinflammation: Magnetic Resonance and Microscopy Imaging of the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurz, D.J.; Decary, S.; Hong, Y.; Erusalimsky, J.D. Senescence-associated ß-galactosidase reflects an increase in lysosomal mass during replicative ageing of human endothelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 3613–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, M.; Nũnez, S.; Heard, E.; Narita, M.; Lin, A.W.; Hearn, S.A.; Spector, D.L.; Hannon, G.J.; Lowe, S.W. Rb-mediated heterochromatin formation and silencing of E2F target genes during cellular senescence. Cell 2003, 113, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, A.; Kauppinen, A.; Kaarniranta, K. Emerging role of NF-kB signaling in the induction of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). Cell Signal. 2012, 24, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pitcher, L.E.; Prahalad, V.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Robbins, P.D. Targeting cellular senescence with senotherapeutics: Senolytics and senomorphics. FEBS J. 2022, 290, 1362–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, J.; Gil, J. Senescence and the SASP: Many therapeutic avenues. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanigur Sultuybek, G.; Soydas, T.; Yenmis, G. NF-kB as the mediator of metformin’s effect on ageing and ageing-related diseases. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 46, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ren, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Yang, J. Microglia in depression: An overview of microglia in the pathogenesis and treatment of depression. J. Neuroinflammation 2022, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrodnik, M.; Zhu, Y.; Langhi, L.G.P.; Tchkonia, T.; Krüger, P.; Fielder, E.; Victorelli, S.; Ruswhandi, R.A.; Giorgadze, N.; Pirtskhalava, T.; et al. Obesity-Induced Cellular Senescence Drives Anxiety and Impairs Neurogenesis. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1061–1077.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.N.; Stein, L.M.; Fortin, S.M.; Hayes, M.R. The role of glia in the physiology and pharmacology of glucagon-like peptide-1: Implications for obesity, diabetes, neurodegeneration and glaucoma. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M.; Acosta, A. Combination Therapies for Obesity. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2018, 16, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| DKS Constituent | g/L |
|---|---|
| Cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume) bark | 90 |
| Orthosiphon (Orthosiphon stamineus Benth) leaf | 90 |
| Green tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze) leaf | 90 |
| Mate (Ilex paraguariensis A.St.Hill) leaf | 70 |
| Gymnema (Gymnema sylvestre R. Br.) leaf | 70 |
| Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) pod | 60 |
| Pineapple (Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.) stem | 40 |
| Common gromwell (Lithospermum officinale L.) seeds | 40 |
| Horsetail (Equisetum arvense L.) herb | 40 |
| Curly dock (Rumex crispus L.) root | 30 |
| Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.) root | 30 |
| Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Miller) fruit | 30 |
| Birch (Betuta pendolo Roth.) leaf | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borgonetti, V.; Sasia, C.; Morozzi, M.; Cenci, L.; Galeotti, N. Protection against Microglia Senescence by the Dietary Supplement Dekosilhue® in BV2 Cells: A New Perspective for Obesity and Related Complications. Nutraceuticals 2023, 3, 250-261. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals3020020
Borgonetti V, Sasia C, Morozzi M, Cenci L, Galeotti N. Protection against Microglia Senescence by the Dietary Supplement Dekosilhue® in BV2 Cells: A New Perspective for Obesity and Related Complications. Nutraceuticals. 2023; 3(2):250-261. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals3020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorgonetti, Vittoria, Chiara Sasia, Martina Morozzi, Lorenzo Cenci, and Nicoletta Galeotti. 2023. "Protection against Microglia Senescence by the Dietary Supplement Dekosilhue® in BV2 Cells: A New Perspective for Obesity and Related Complications" Nutraceuticals 3, no. 2: 250-261. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals3020020
APA StyleBorgonetti, V., Sasia, C., Morozzi, M., Cenci, L., & Galeotti, N. (2023). Protection against Microglia Senescence by the Dietary Supplement Dekosilhue® in BV2 Cells: A New Perspective for Obesity and Related Complications. Nutraceuticals, 3(2), 250-261. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals3020020