3.1. Baseline Convention Results
The first main set of results are presented in
Table 5. Here we can see the impacts of conventions on the five variables of interest: average daily rate (ADR), revenue (in thousands of US dollars), demand, occupancy, and revenue per available room (RevPar) in US dollars. The main independent variable of interest is the convention sub-group, and we control for all events mentioned before alongside day of the week, month, and year fixed effects.
The results showed that on convention days, ADR increased by around $19.93. This represented an increase of 20.7% of the mean average daily rate for the full sample. These effects occurred in the day preceding the convention, as ADR increased by around $11.36, or around 11.84% of the full sample mean. These were both statistically and economically significant. What is also interesting is that there seemed to be little persistence, as there was no statistically significant evidence for ADR being higher or lower after the event.
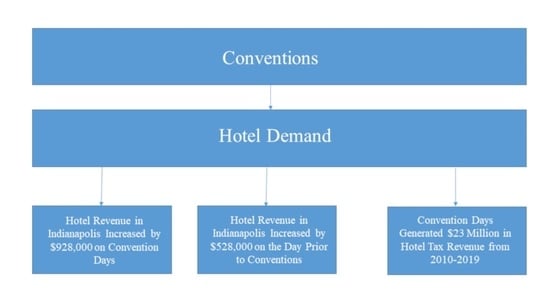
The revenue increases were also present and significant on convention day and the day preceding the conventions start. Revenue increased by approximately $928,000 per convention day and there was a boost in revenue of around $528,000 the day before the convention started. So for a convention day revenue increased by around 48% as compared to the full sample mean, which is impressive. This was reflected by the similar changes in revenue per available room. The gains on convention days might have been offset by dips in revenue directly after the convention, but there was no significant drop in revenue after the convention ended.
The demand data suggested the surge in demand from conventions was non-negligible and significant; thus, it was not shocking to see that occupancy increased during and immediately before a convention. Occupancy went up around 13.1 percentage points, and occupancy rate increased by approximately 21% on convention days. The day before occupancy increased 8.13 percentage points, or a 13% increase. In general, the results seemed to confirm that for most of the sup-group in question, the effects were positive on the major variables of interest for convention events. This suggests that it might not be necessary to look much beyond the two days before the start and end of a convention.
3.2. Specific Convention Results
The previous regression treated all conventions as the same. In this section we re-run our analysis with different conventions identified by their own binary variables. Each specification controls for day, month, and year fixed effects as well as all the major events listed in
Table 1. The coefficients for the other events are not reported here in order to focus on the convention results. However,
Table 6,
Table 7,
Table 8,
Table 9,
Table 10,
Table 11,
Table 12 and
Table 13 present the estimated coefficients for these other events (This is why the R-squared is the same in
Table 6,
Table 7,
Table 8,
Table 9,
Table 10,
Table 11,
Table 12 and
Table 13).
Table 6 breaks down the large convention group by individual convention results. There were not statistically significant leads and lags beyond one day. The Indy PopCon was insignificant in effect for all variables of interest. Since Pop-Con is a relatively new convention (it began in 2014) the lackluster and imprecise estimates may be due to a small attendance figure, or large but very local attendance. This convention was more of an exception but might be emblematic of a set of conventions that had decent attendance and support, but did not have much of an impact on local hotel demand.
For Gen Con, Fire Department Instructors Conference (FDIC) International, and the National Future Farmers of America (FFA) convention the stories are very similar. The NRA convention is significant, but the magnitude is less pronounced than for estimates of the group. For example, the revenue impact for the NRA National convention is approximately $596,000 compared to the $1,025,000 of FDIC International convention and the $1,044,000 for FFA. Gen Con generated approximately $1,189,000 in additional revenue per night, or an increase of around 61% over the full sample mean and the highest for conventions tested. ADR (in US dollars) increased by 25.86, 23.37, and 20.26 for Gen Con, FDIC, and FFA respectively. This was compared to NRA national which only had an ADR increase of 12.44. All these were significant, but the disparities between the top three conventions the NRA still raises an eye. Demand for rooms seems to be similar among Gen Con, FDIC, and FFA, the numbers for the conventions were 5157, 4436, and 4779 respectively and were significant at the 0.1% level. Gen Con and FFA sew increased demand the day before, while FDIC saw a jump two days before but nothing the day before. The NRA saw a statistically significant rise of 3136 the day of the event, but a marginally significant 3377 the day before.
These conventions seemed to generate a lot of revenue and led to noticeably higher rates. The occupancy story was also present. Occupancy jumped by 16 percentage points during the event, and considering the mean of 62% occupancy, this could push overall metro hotel occupancy to nearly 89%. Though from the sample we know that Gen Con conventions had days where metro occupancy was recorded at 97%, which occurred during Gen Con 2013.
Interestingly, for Gen Con, FDIC, and the FFA events, there was little to no evidence of reduced revenue or demand following the shock of the convention event. ADR and Revenue did not plummet past the trend, and for all five conventions, there was no statistical or economic significant changes to note. This is a startling lack of evidence of crowding out for these multi-day events (in hotel demand at the least). There do appear to be negative effects for the NRA convention; however, the estimates were imprecise and insignificant. The increases in the occupancy rate could raise concern of crowding out along a spatial dimension as Indianapolis has a large network of hotels connected to the convention center. So if occupancy is nearing the 90% range, there might be some crowding out in certain downtown locations.
3.3. Comparison with Sporting Events
Sporting events vary drastically as local sporting events seem to have very low impact when compared to the conventions and larger less-local events, but this is to be expected. In this subsection we focus on specific sporting events to compare to conventions. Due to the number of events simultaneously estimated we report the results in groupings, although they all come from the same regression.
The results for Indianapolis Colts games appear in
Table 7 and show that these games generated approximately 1934 additional room nights and
$284,000 dollars in revenue, with a slight increase of
$6.5 in the nightly room rate. This was in line with the rather anemic estimates found in
Depken and Stephenson (
2018) for Carolina Panthers home games, suggesting that NFL Games were not major drivers of hotel demand. This was also similar to the impact of West Virginia University home football games
Bonneau and Hall (
2020). So, hotel taxes were likely going to be generated from convention traffic.
Pacers games had no statistically significant results for the day of or for leads or lags and thus were not reported. This was true for regular season games as well as postseason games. This lack of a result mirrors the lack of result in
Depken and Stephenson (
2018) for Charlotte Bobcat games. It is for these reasons, that while we excluded several other local sports, there was little reason to believe that there would be a result for Minor League Baseball if the NBA drew such meagre impact. Likely the only impact that NBA teams generate from visitors outside the area is for the traveling teams, beat reporters, and the occasional crew for an NBA prime time game. Much the same could be said for the Women’s National Basketball Association, Minor League Baseball, and Major League Soccer.
The bigger and one-off events seemed to be an interesting comparison group for conventions, as the local sports teams would be lucky to equal an amount of impact over one season as just one day of Gen Con. The Big Ten college football championship results are presented in
Table 8, which Indianapolis has hosted since its inception, generated an additional
$2,000,000 in hotel revenue, and 10,000 hotel stays. This was only a one-day event, but it generated around
$1,047,000 in revenue the night before,
$437,000 the day after the game, and
$587,000 the second day after the game.
This effect was similar in scale to the impacts seen for the Indy 500, shown in
Table 9. The Indy 500 effects started to become significant 2 days before the race, with rates in the Indianapolis Area going up by 52.56 two days before and was approximately
$64 dollars more the day before race day and race day. This led to a drop in ADR for up to 4 days afterwards. The revenue story showed
$1.4 million two days before,
$2.5 million the day before, and roughly
$2.3 million the day of.
This did appear to have an offset as revenues were lower up to 4 days after the Indy 500. This is not consistent with the Big 10 Football game effects at all. Though the scope of the 500 was massive, it had noticeable local effects. The Brickyard 400 was more consistent with the conventions but had a lead in that was significant 2 days before the event, though no negative shocks to revenue or ADR occurred.
NCAA Tournament Games (excluding the Final Four) generated around
$325,000 per day of the Tournament and had no significant effects the day before or after, but the day of event effects were mildly significant. These results are presented in
Table 10. The Big Ten basketball tournament was almost identical in coefficients to the NCCA normal tournament games.
The NCAA and Indianapolis have a cozy connection and as a result the NCAA Final Four has rotated twice through the city, and two more are scheduled in 2021 and 2026. The ADR increased by $23.62 two days before the first Final Four Game, and the day before the first game the ADR was $70.51 more than it would be otherwise. During the Final Four, the ADR was $84.98 more (so room-rates were almost double the sample mean). This was reflected in the revenue, as revenue went from an imprecise $478,000 2 days before tipoff. The day before, revenue went up $2,357,000 and peaked during the tournament at $3,087,000. The Final Four hads no impact after the event though for any lag length. ADR returned to normal, and revenue was slightly negative, but hardly precise and not significant.
An event which has some elements of events that occur in the convention center, but utilize Lucas Oil Stadium, was included. Bands of America (BOA) Grand Nationals, which is a multi-day National High School Marching Band competition, was estimated to have brought in
$751,000 per day, and a little over
$440,000 for the day before and two days before. These results appear in
Table 11. This event occurred annually and was not on the same weekend every year.
Another event we included was an International Champions Cup Association Football match between Inter Milan and Chelsea. These are games played in exhibition and could conceivably be a draw for audiences that might be willing to travel to see their favorite teams in Europe. However, in the case of the one game in our sample, there was no significant effects and ADR was unchanged implying that there was little fanfare, though this only one event from 2013. These results are not reported for space.
We present the NFL Combine results in
Table 12. The NFL Combine though does register an uptick of ADR by
$6.4 the day before anything occurs, and over the course of the multi-day scouting event ADR is
$11.68 higher and stays up by
$9.50 the day after the combine. Revenues are up over
$359,000 during the event and the day after as well. Occupancy is up 11 percentage points the during the event and 12.46 percentage points the day after the event.
Finally, we present Super Bowl XLVI in
Table 13. Super Bowl XLVI saw ADR rise by around
$30 5 days before the game, but as the game approached ADR increased by almost
$180 and peaked at
$235 on Super Bowl Sunday. Revenue rose
$988,000 5 days before, going to around
$5,779,000 more 3 days out, and Super Bowl Sunday hotel revenue increased by approximately
$8,230,000. Occupancy during the 3 days leading to and including Super Bowl XLVI and Final Four Game Days were very similar and pushed hotel occupancy by around 34 percentage points putting occupancy around 95%. These mega events saw no noticeable decrease in ADR or Revenue after the event which is interesting considering the changes after the Indy 500. Demand was down but there was no real significance to the estimates for either event as soon as one day after.
The larger events that Indianapolis hosts seemed to increase revenue with few events having decreased revenue following the event. The Indy 500 had a large impact but seemed to involve some crowding out and shifting that dampens the value that the event brings. The Big Ten Football championship was a massive draw, with regularity for a one-day event. The constant stream of tidy revenue streams from College basketball were interesting, although the more interesting story was the revenue from conventions. Gen Con running for its usual 4 days would generate over $4,000,000 in additional hotel revenue during the event.